Method and system for adaptive bit depth enhancement for displays
a display and bit depth technology, applied in the field of visual displays, can solve the problems of exacerbated problem of inadequate bit resolution, often possessing inadequate bit depth resolution for high-resolution displays, and achieving the effects of reducing false contours, smoothing out background splotches, and improving quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
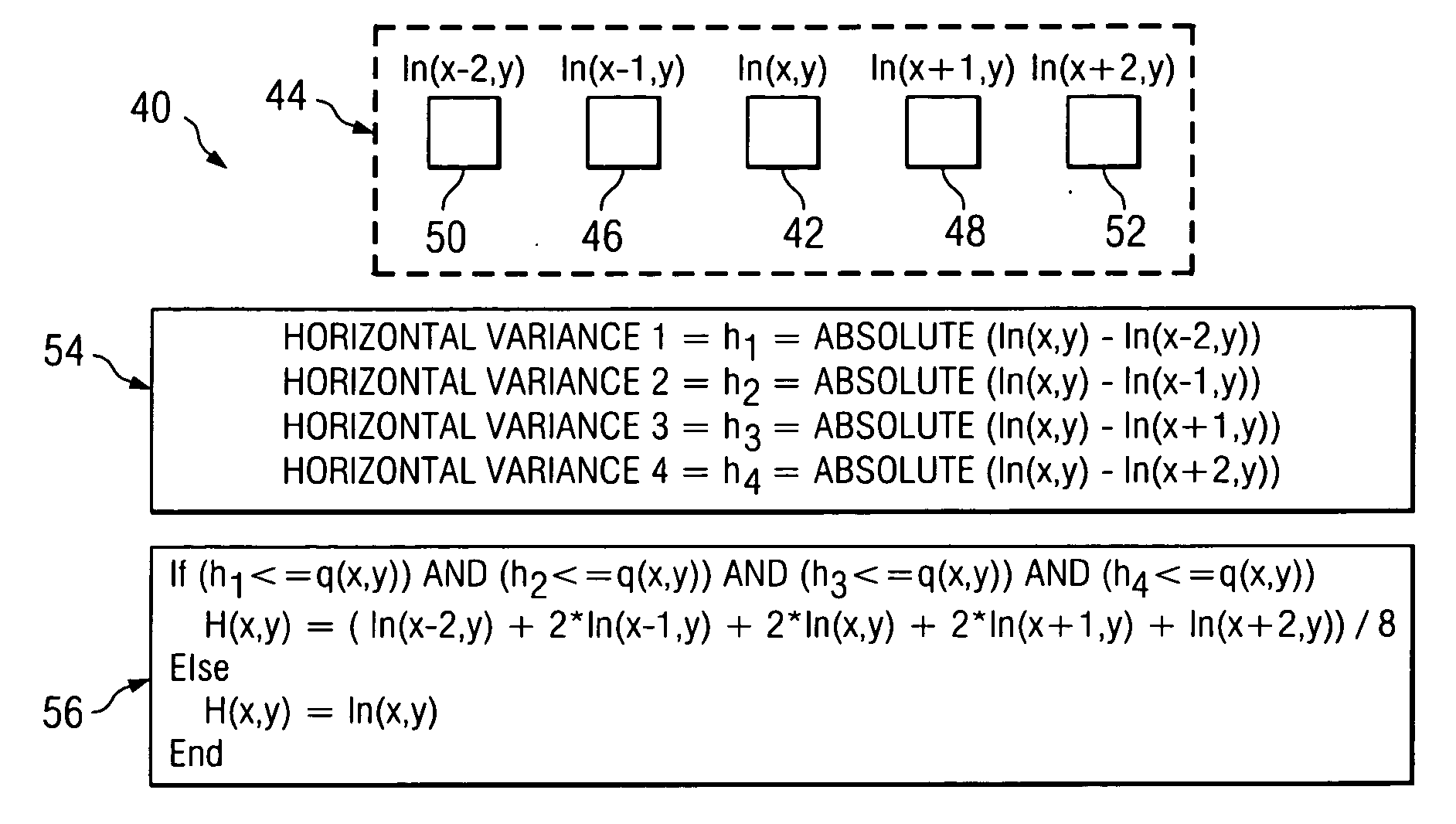
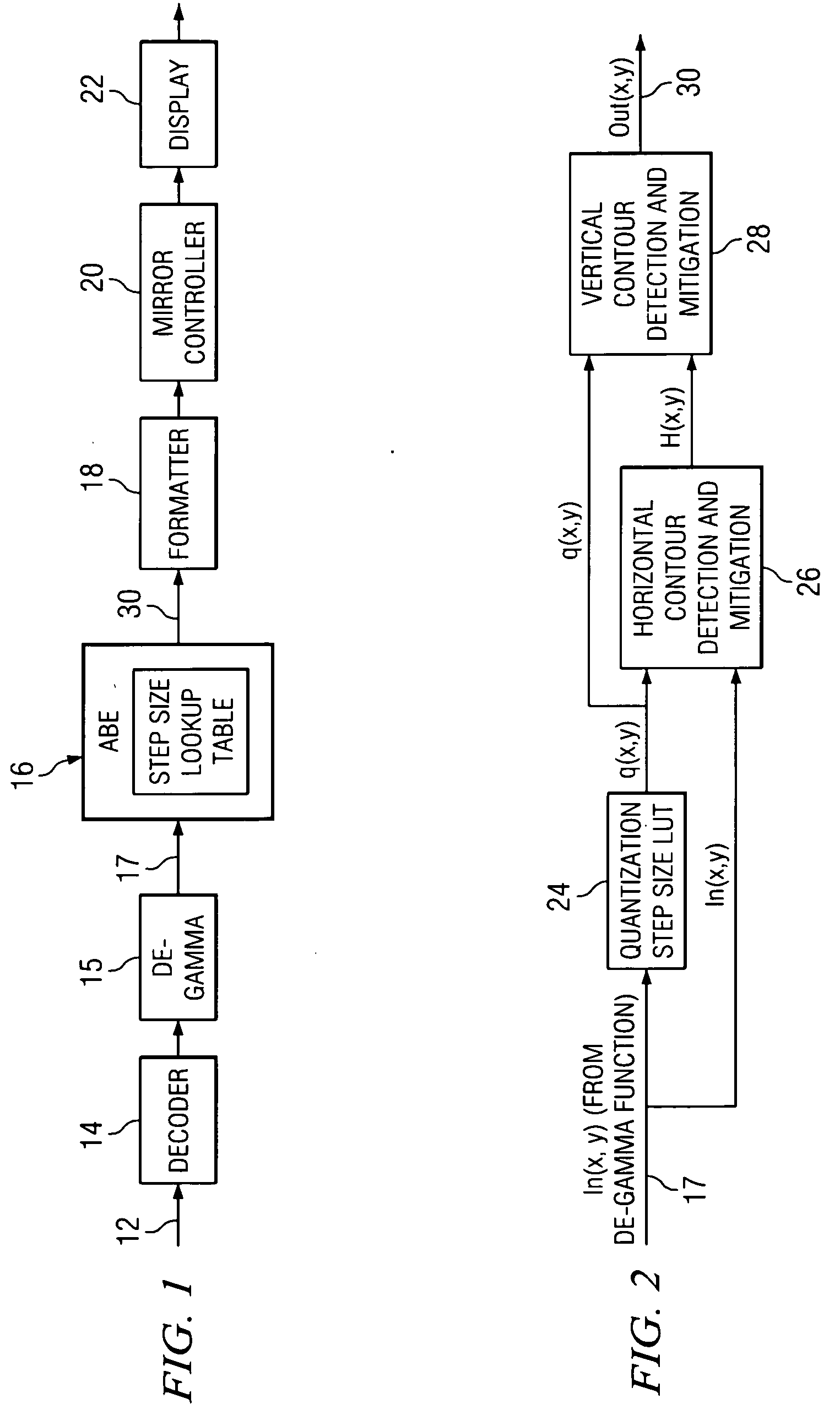
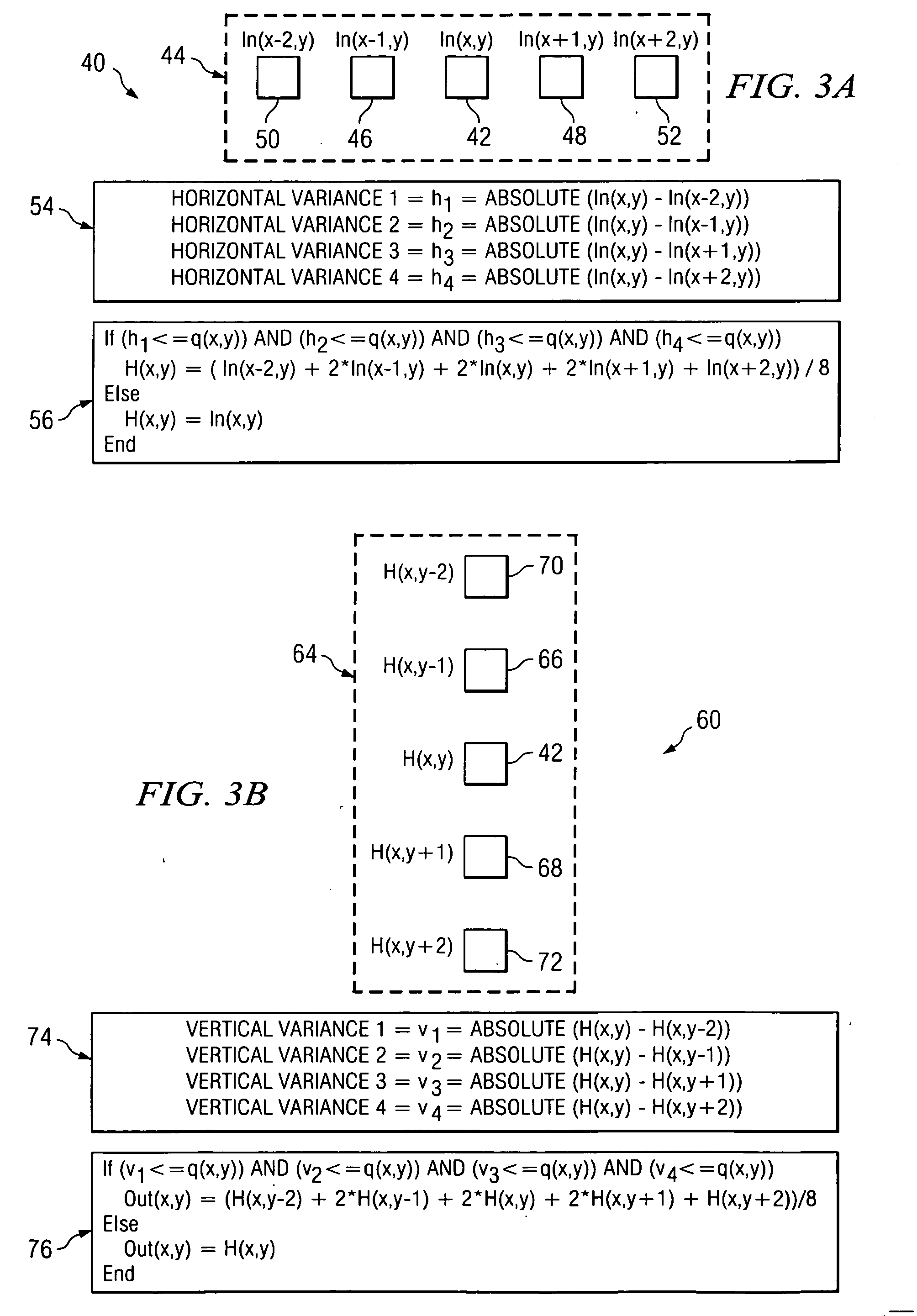
[0019] Embodiments of the invention and its advantages are best understood by referring to FIGS. 1 through 5C of the drawings, like numerals being used for like and corresponding parts of the various drawings.
[0020]FIG. 1 is a block diagram of a light processing system 10 according to the teachings of the invention. System 10 receives a data source 12, such as a television feed. Source 12 may be received by a decoder 14, which decodes the analog source signal and generates a plurality of digital bits. Conventionally a plurality of bits are utilized to represent a value corresponding to an intensity level for a particular pixel to be displayed. As described above, decoders 14 may be of insufficient precision for high resolution displays, particularly in Digital Light Processing (DLP) systems, which utilize a linear display as opposed to the non-linear display of conventional CRTs. Because of the linear display in DLP systems, a de-gamma function is applied to the decoded data receiv...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com