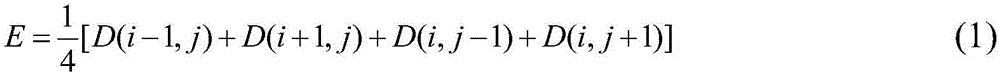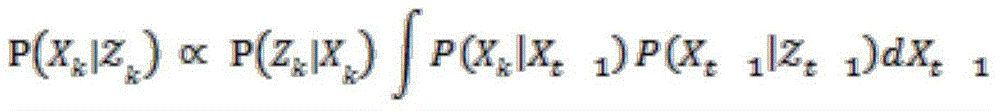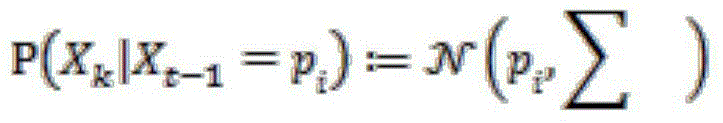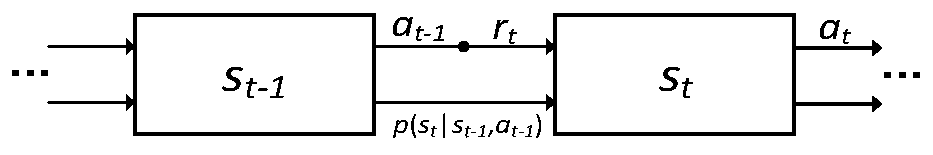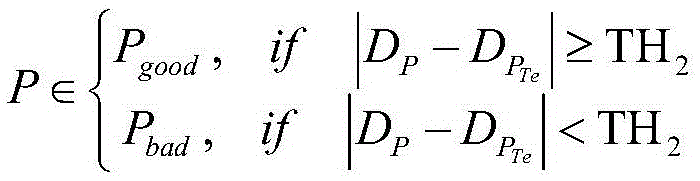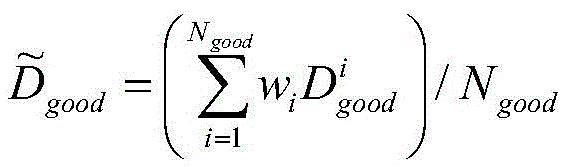Patents
Literature
35 results about "Depth enhancement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
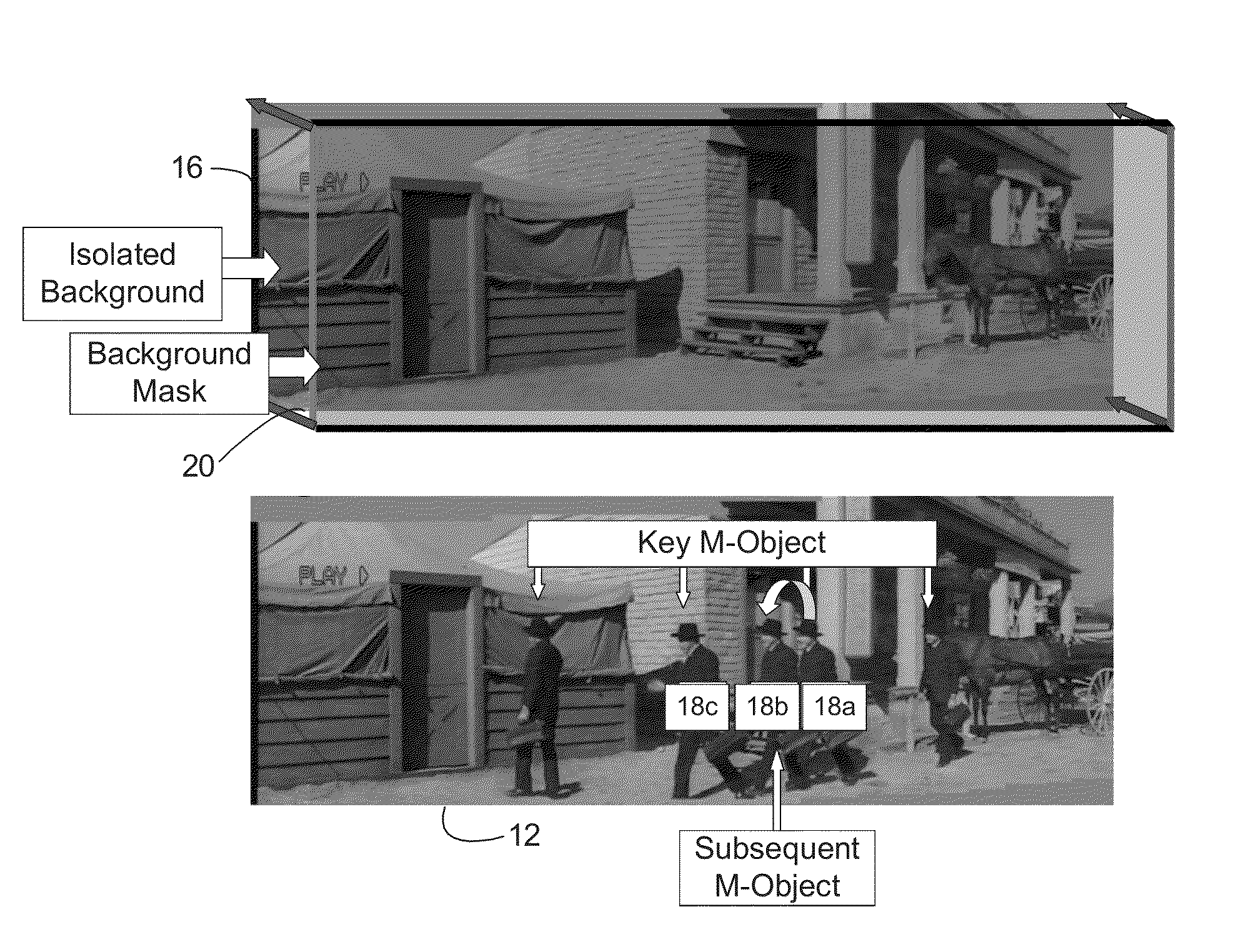
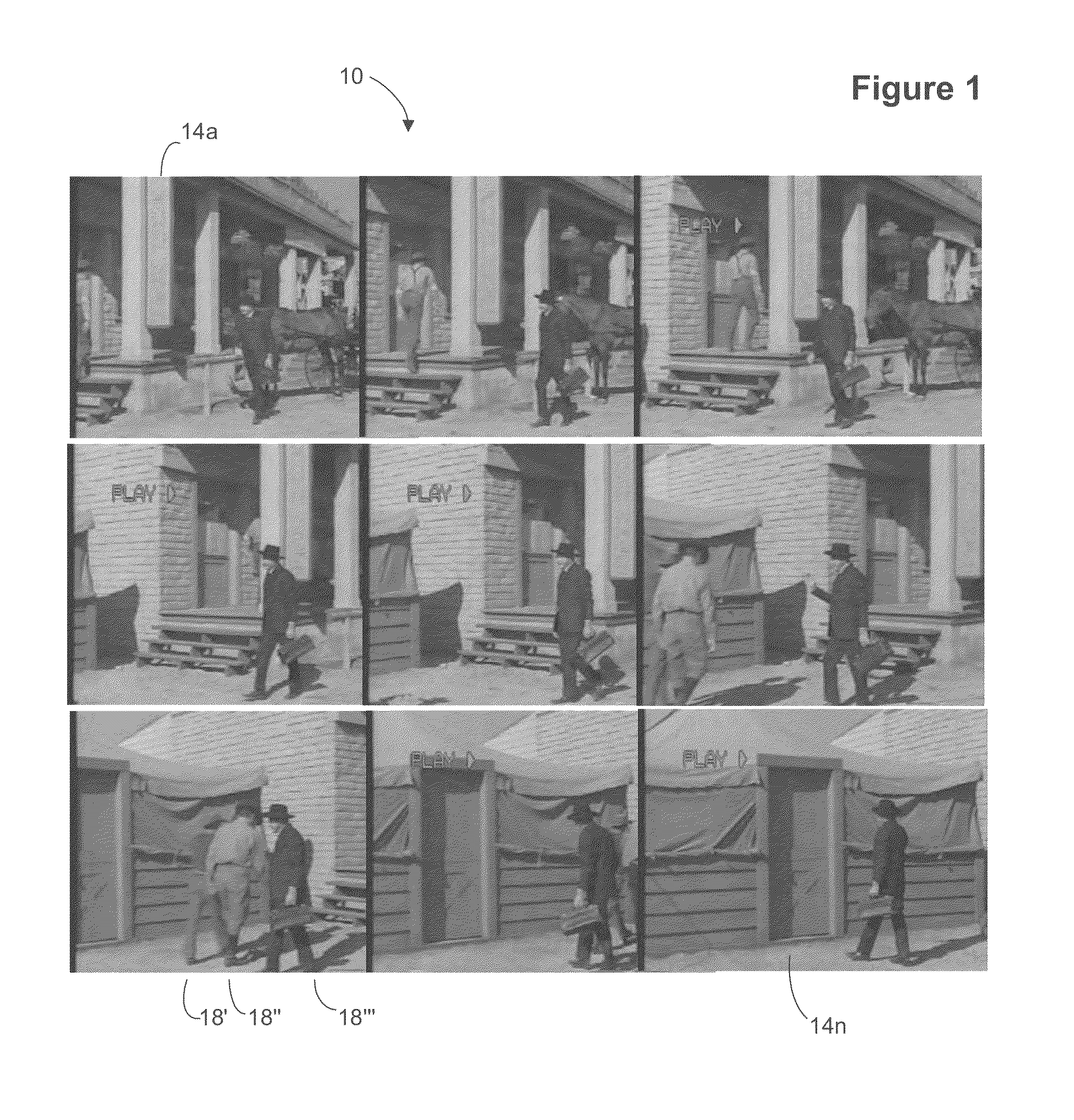
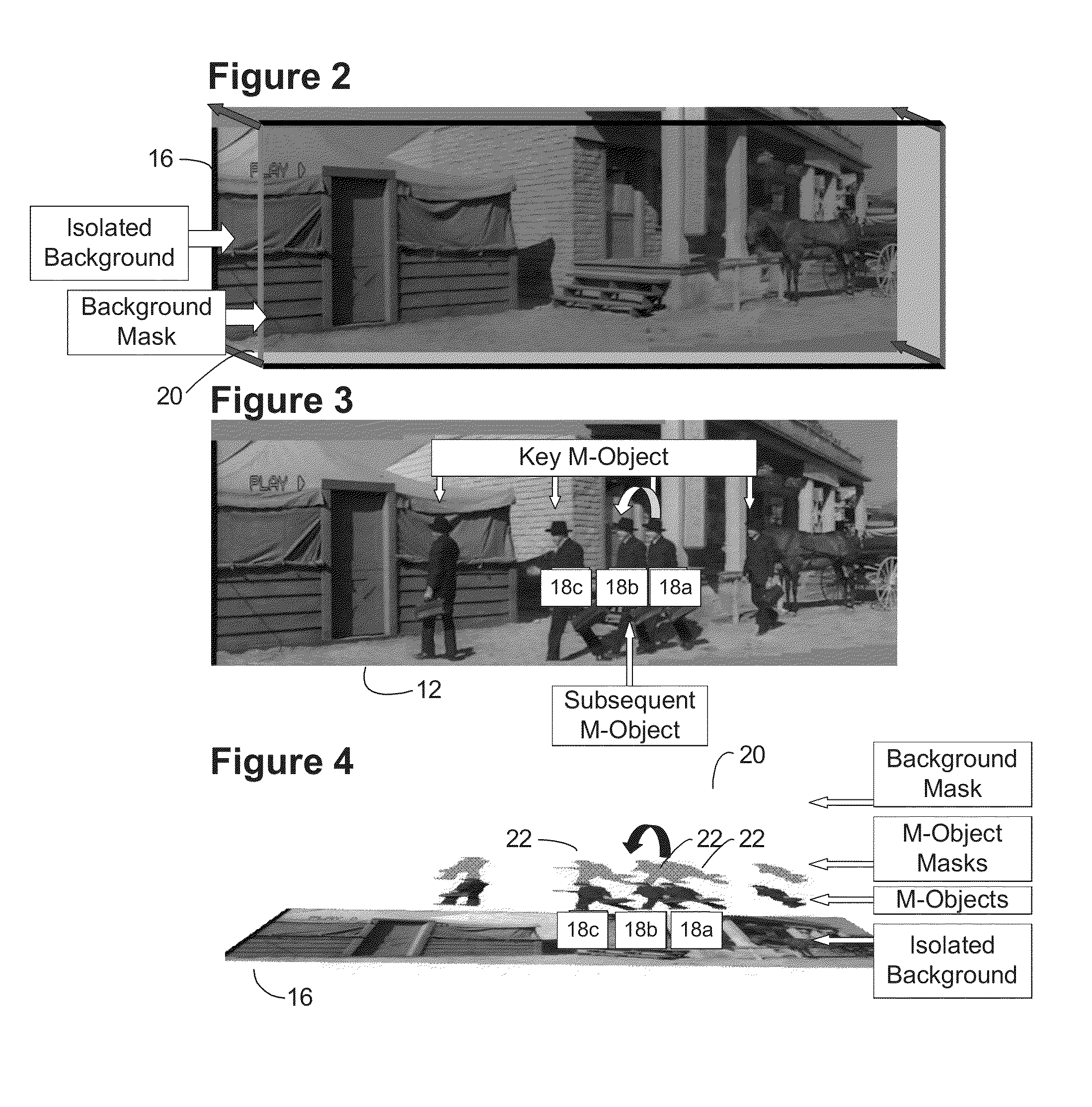
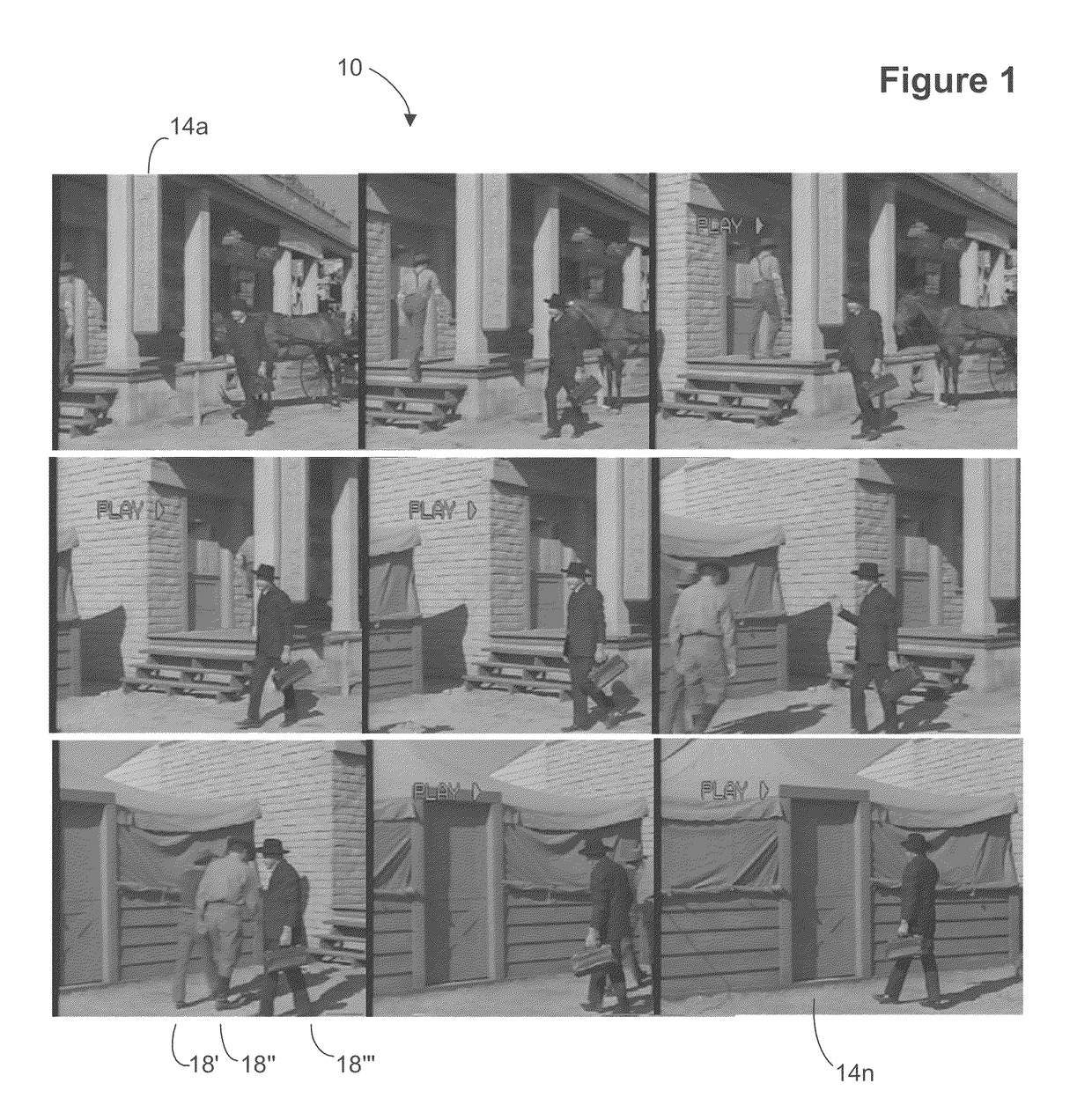
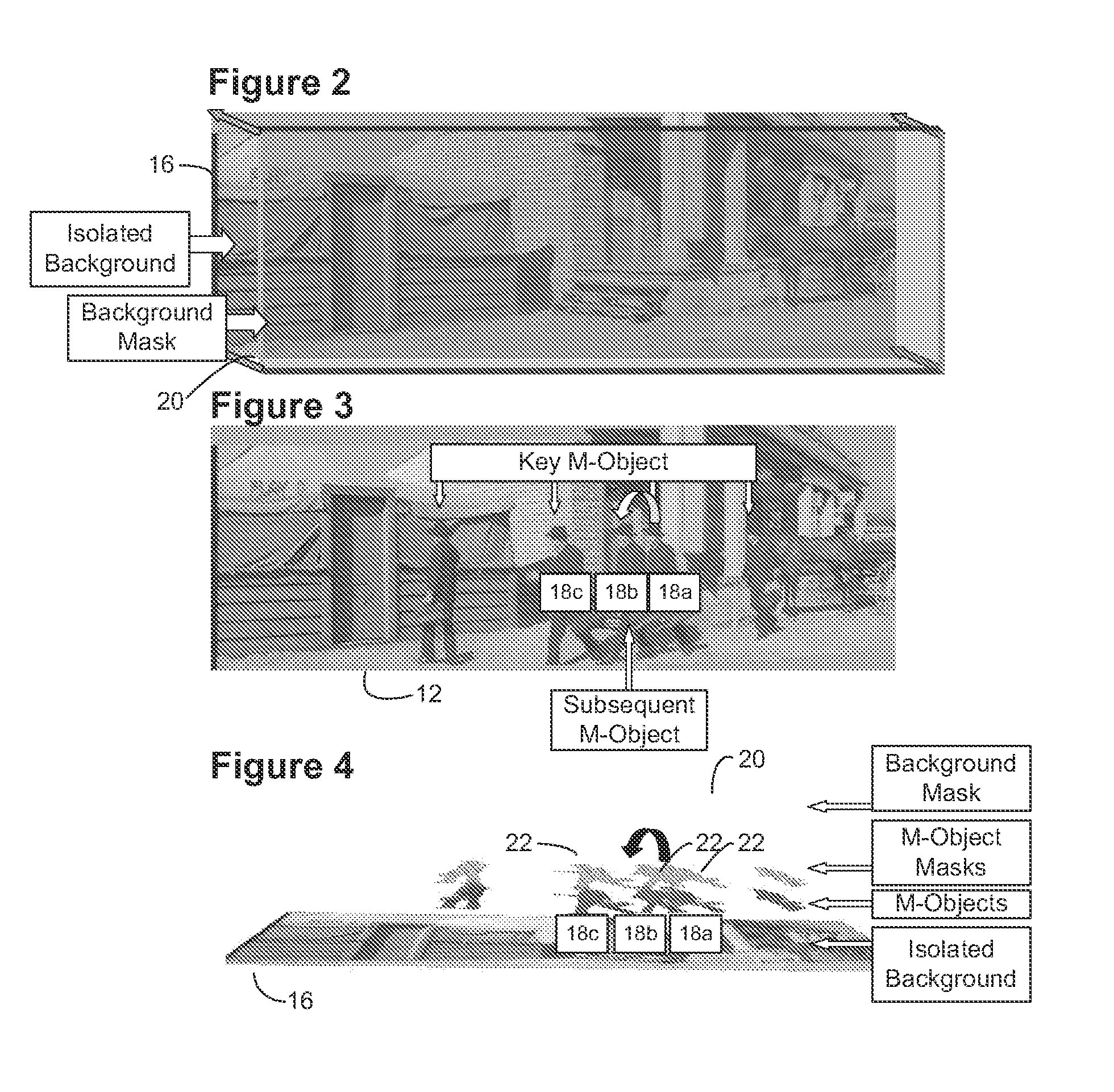
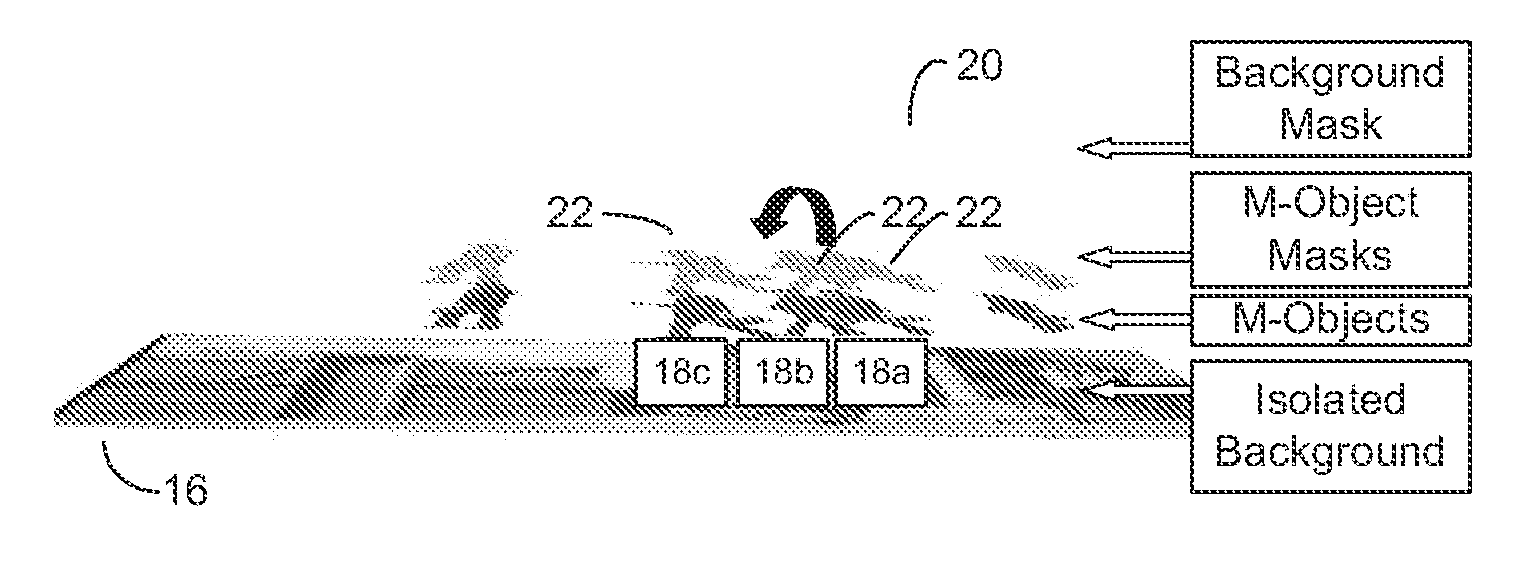
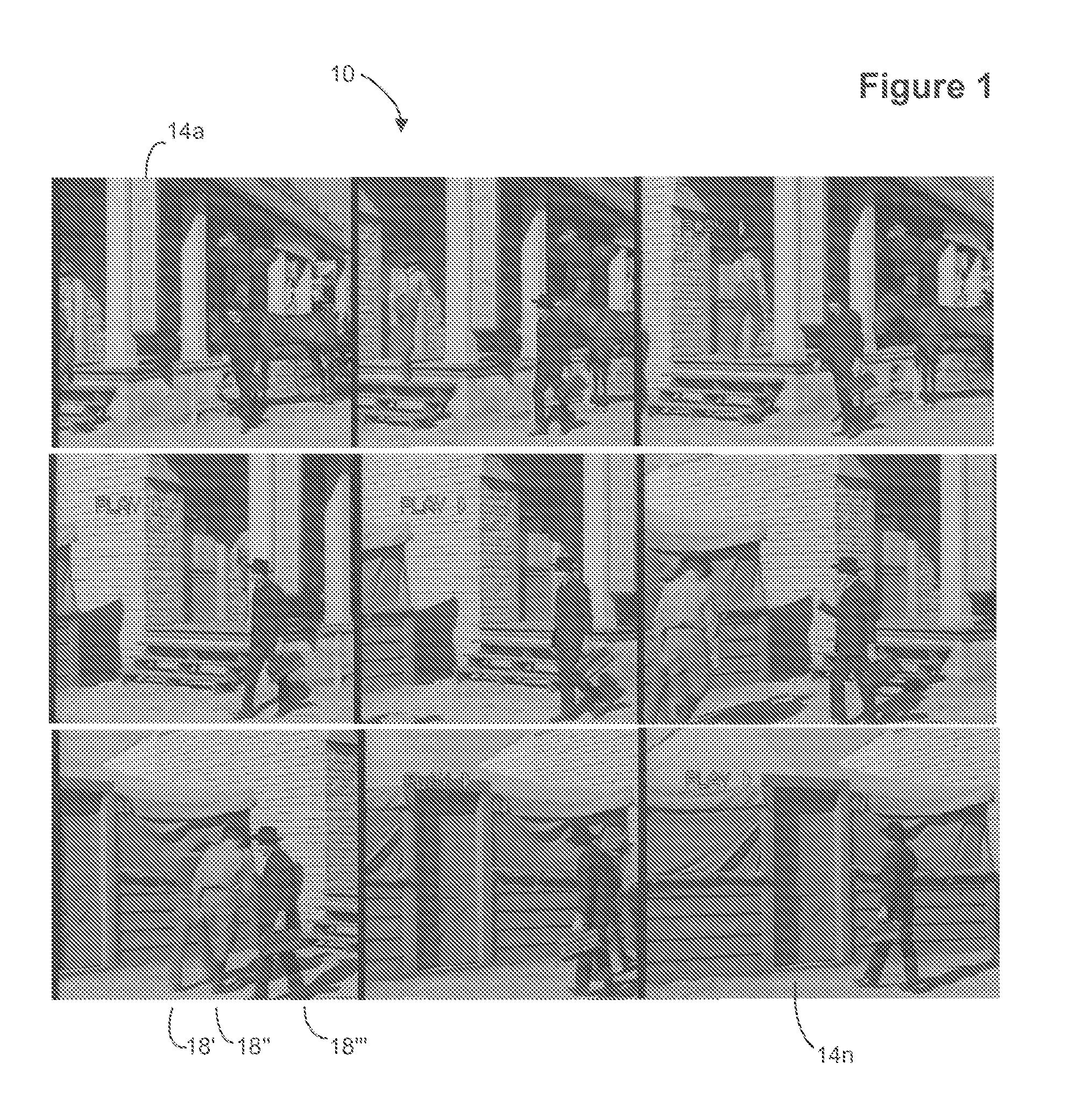
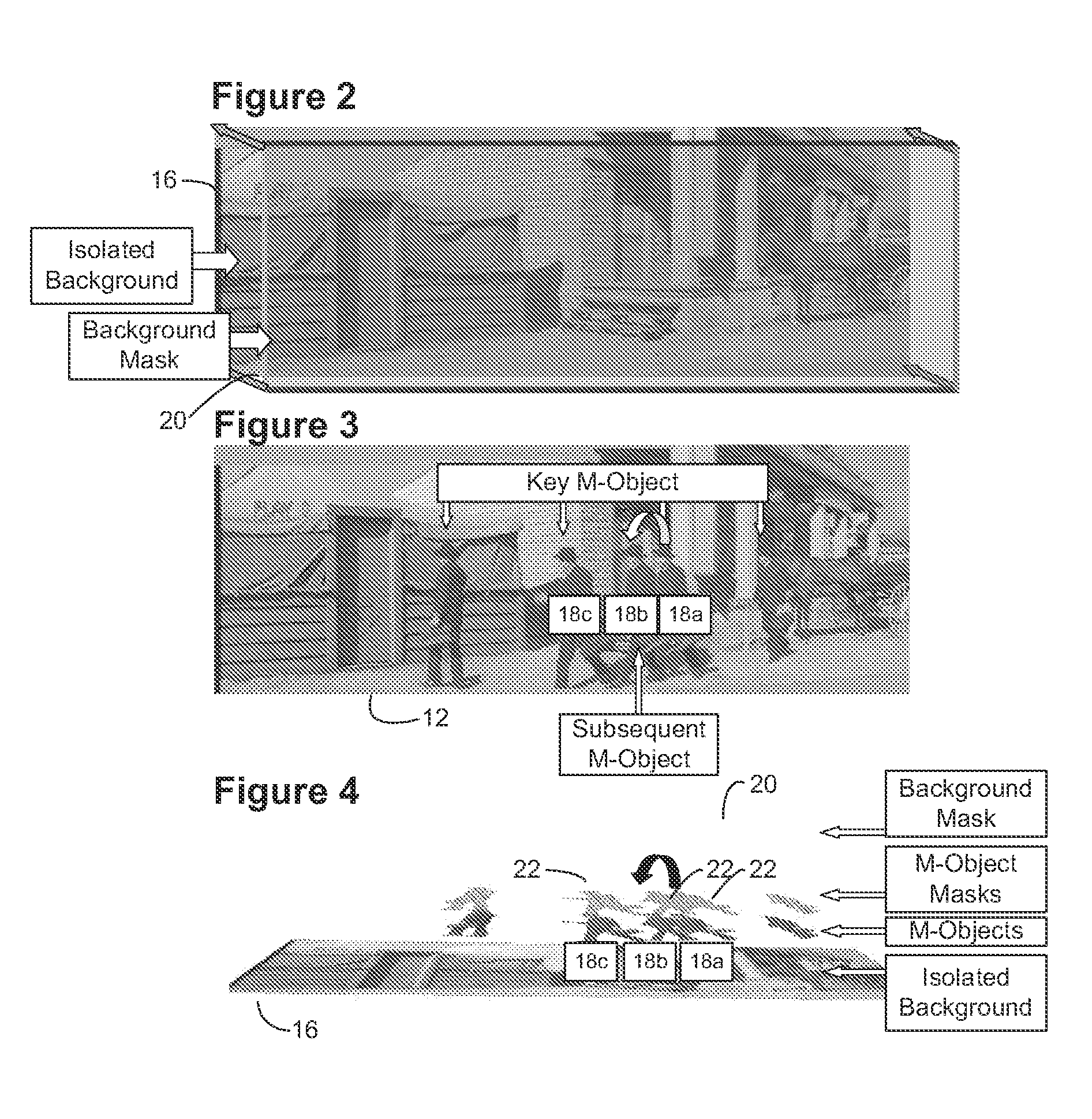
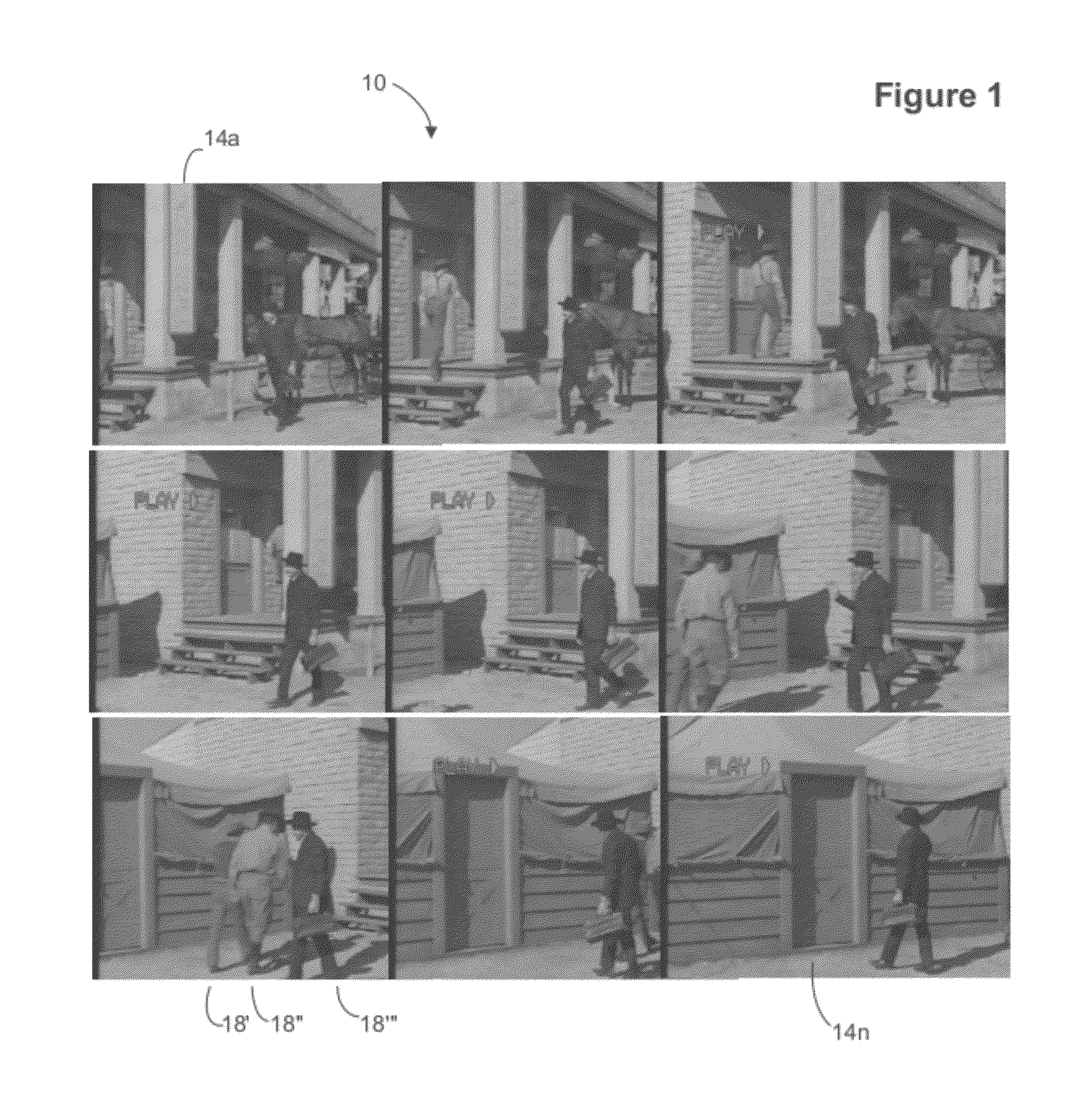
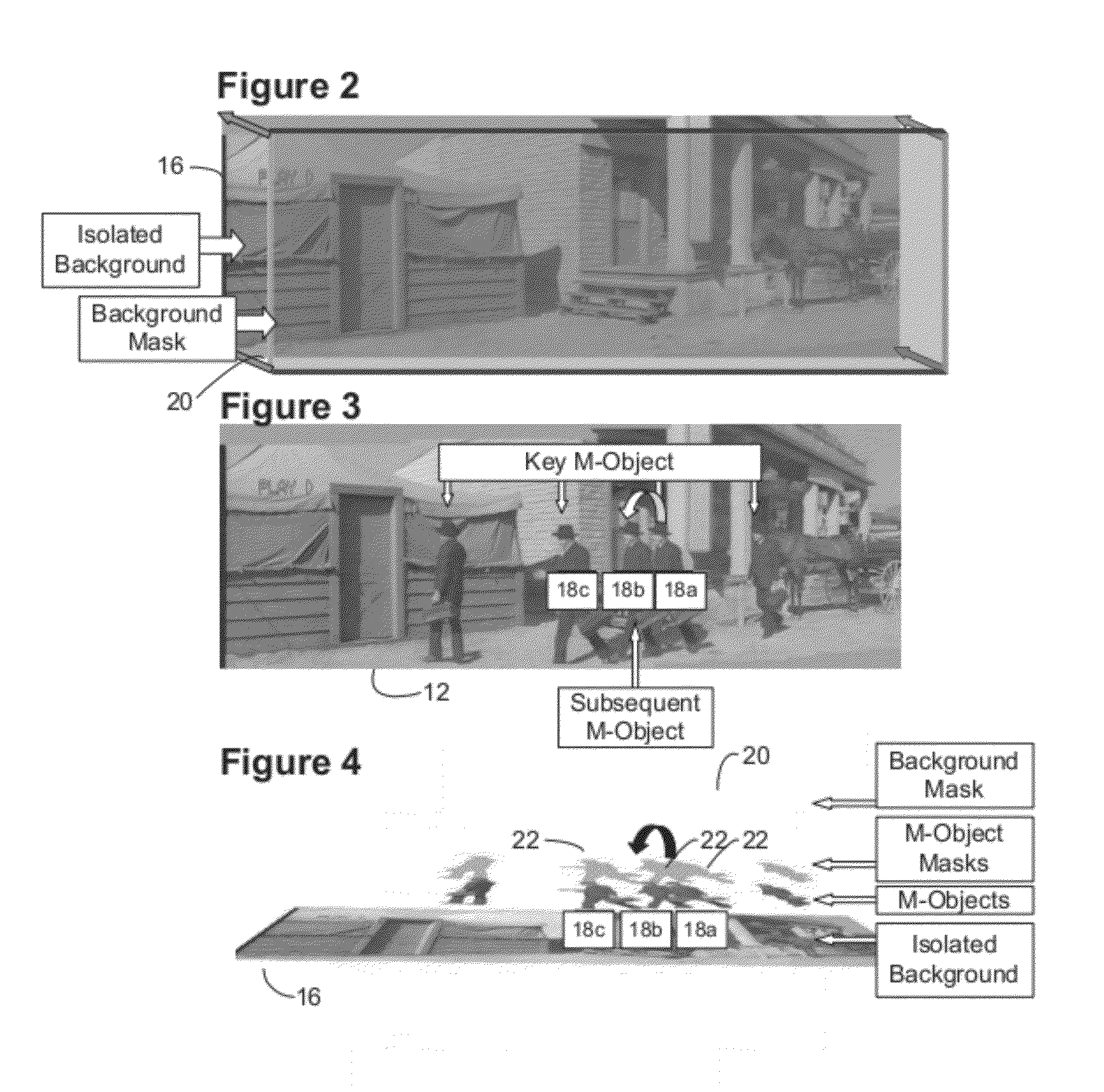
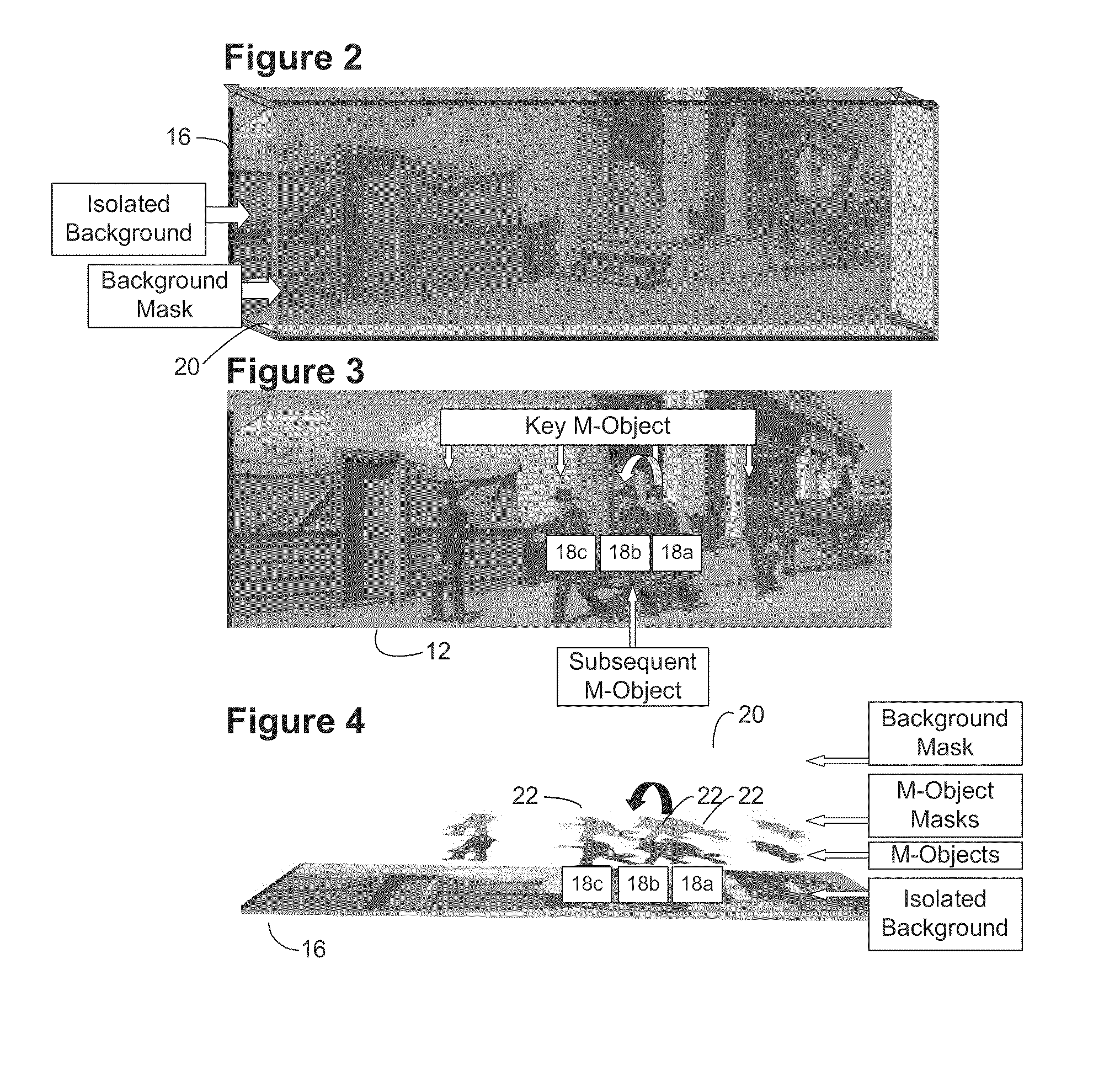
System and method for rapid image sequence depth enhancement with translucent elements
InactiveUS8897596B1Image enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionReference databaseImaging processing
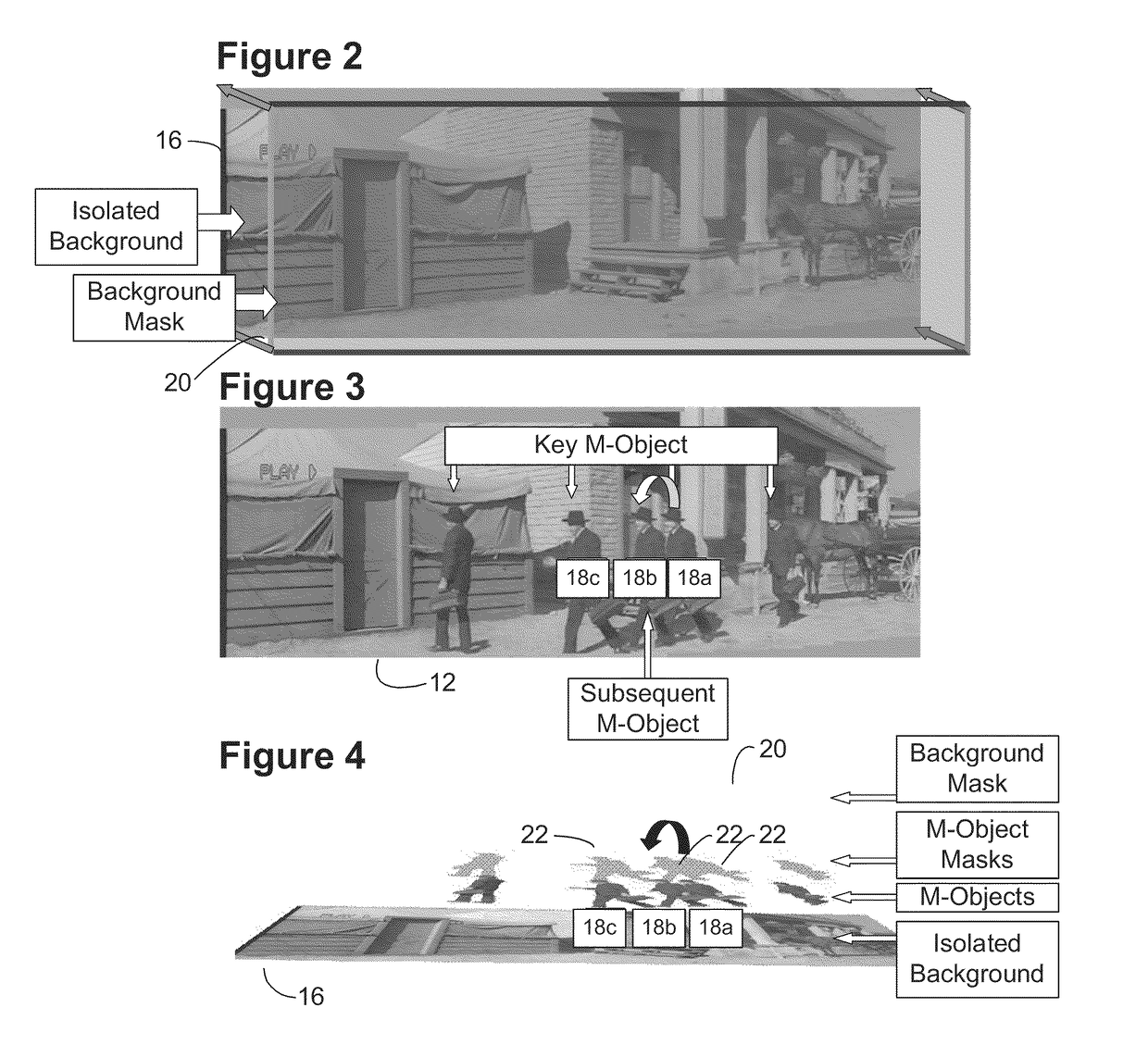
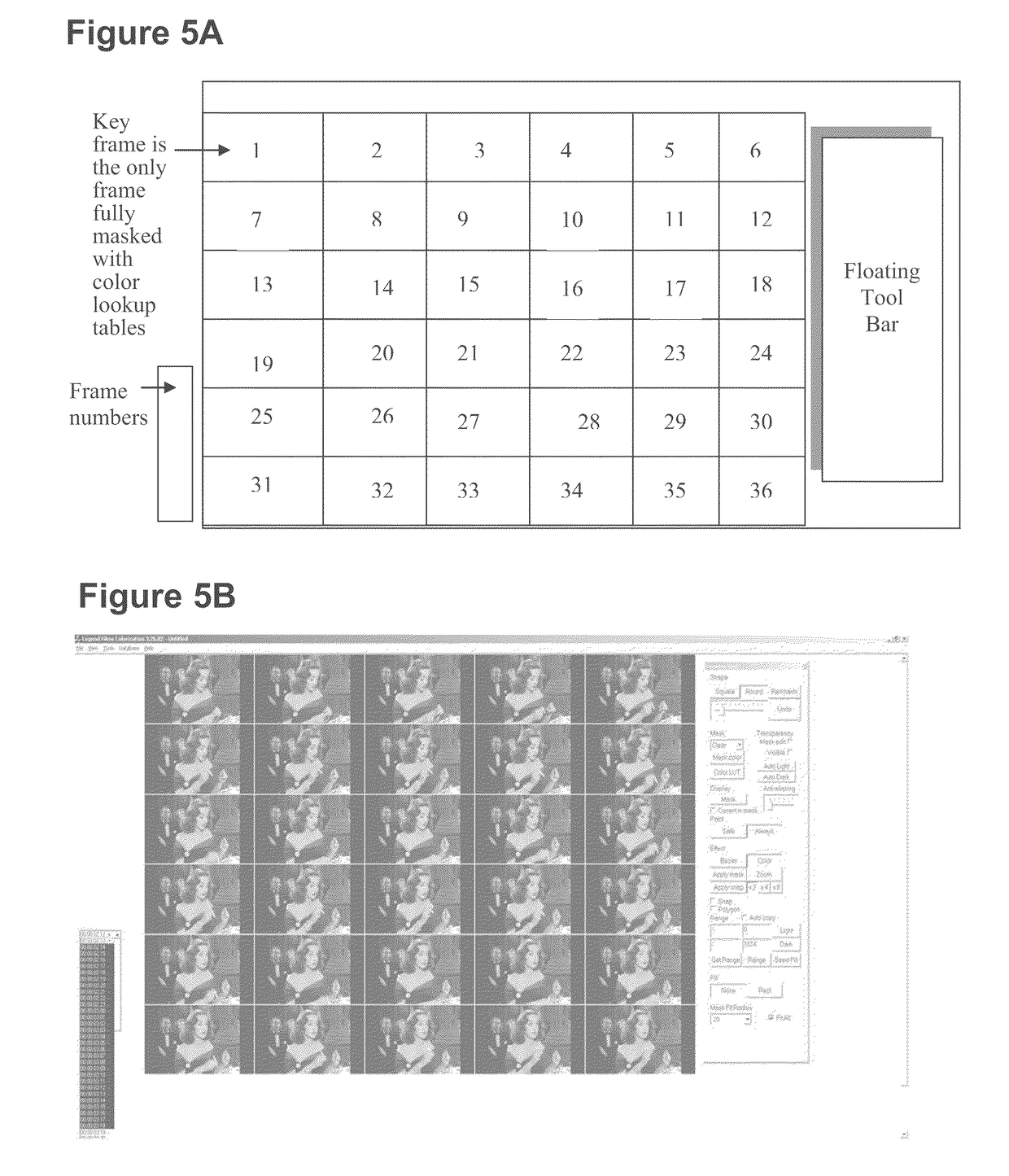
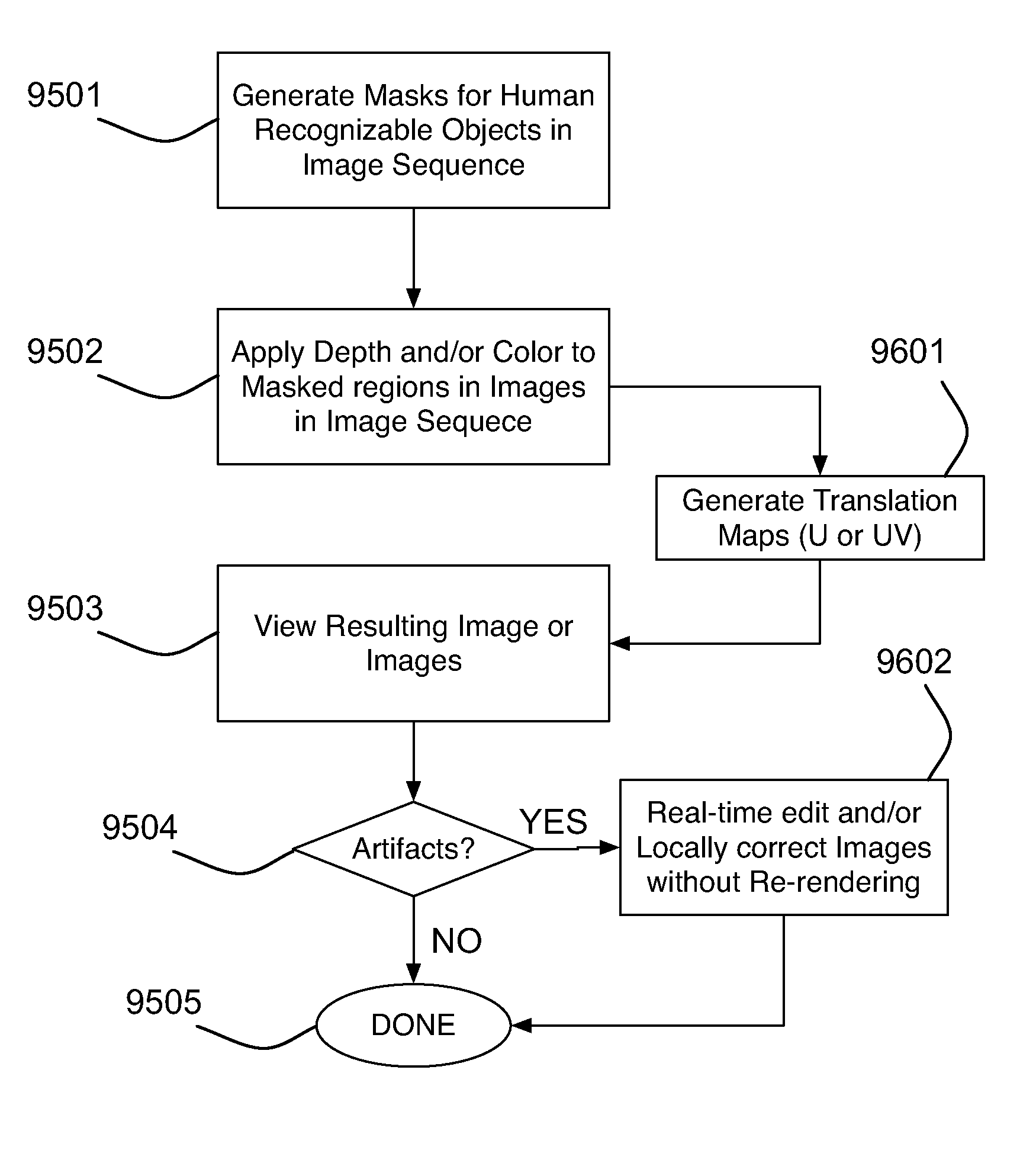
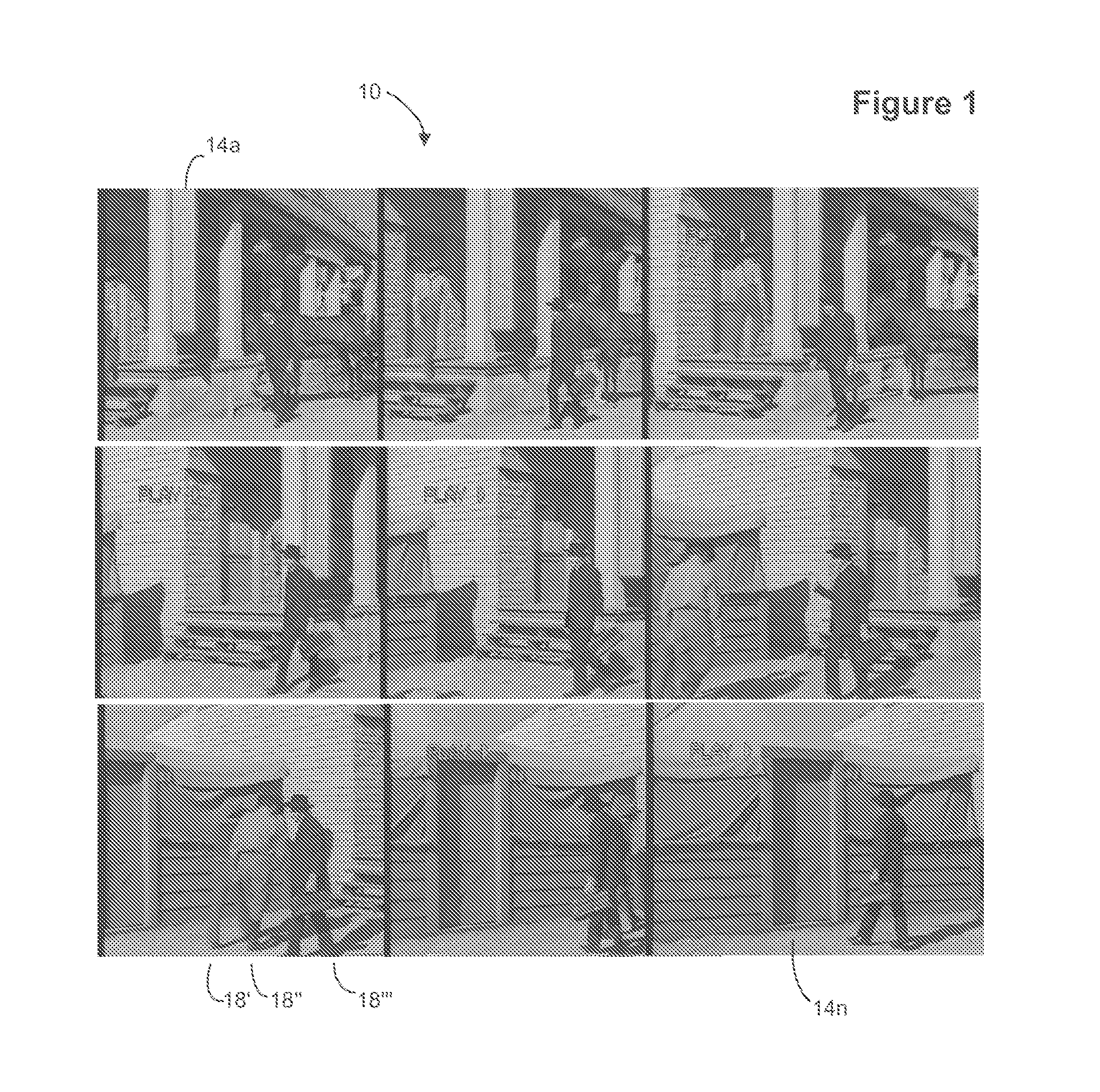
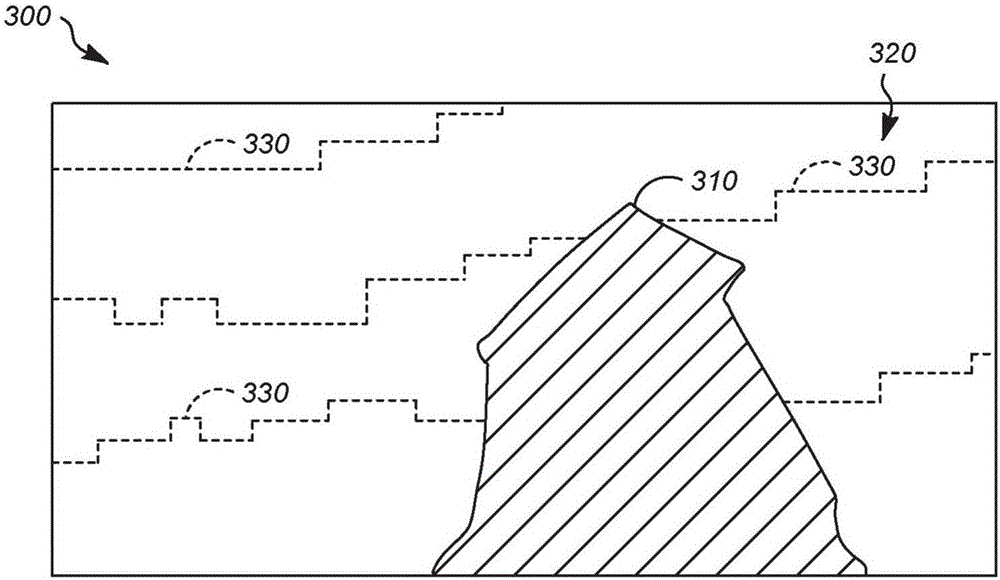
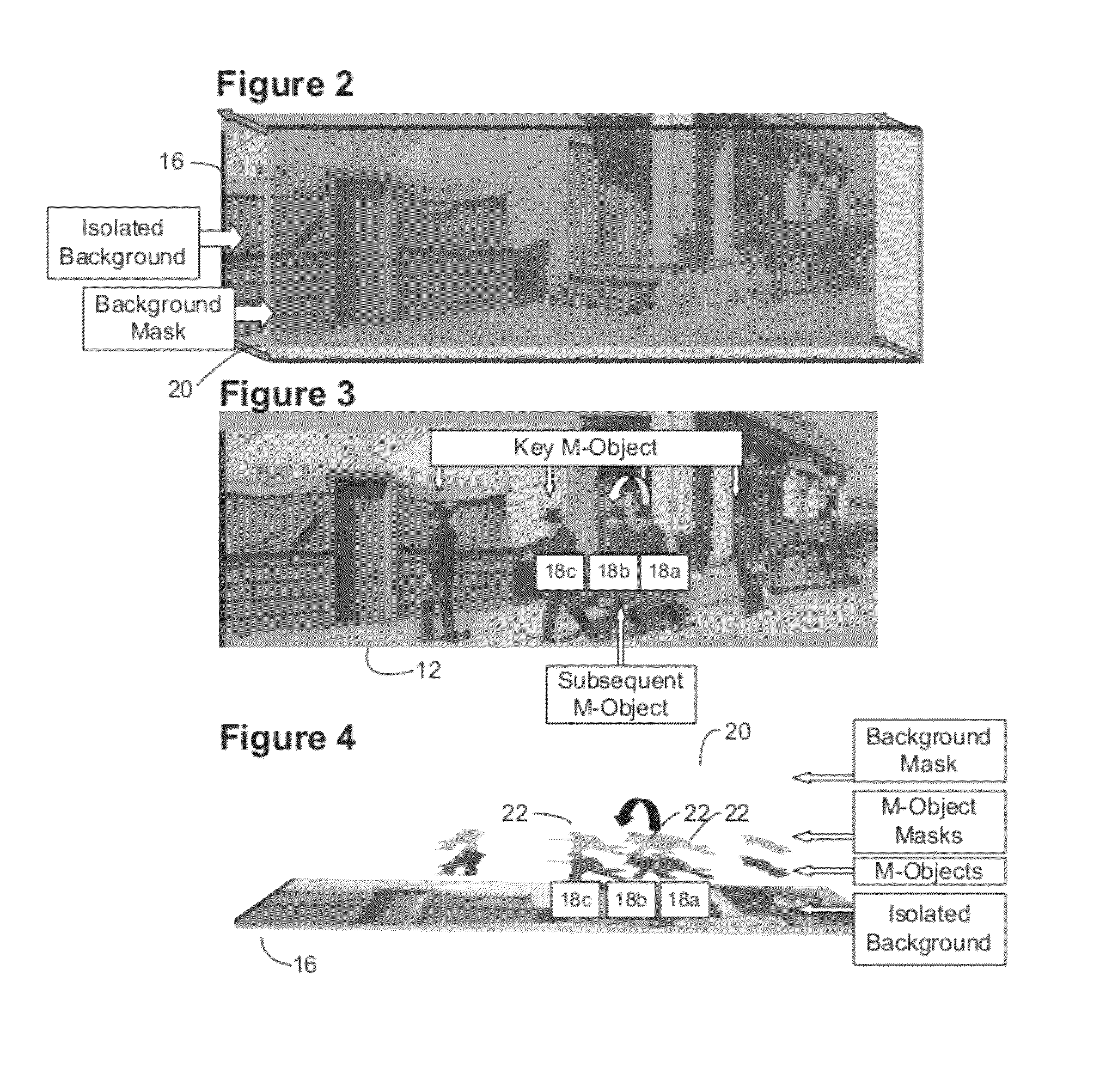
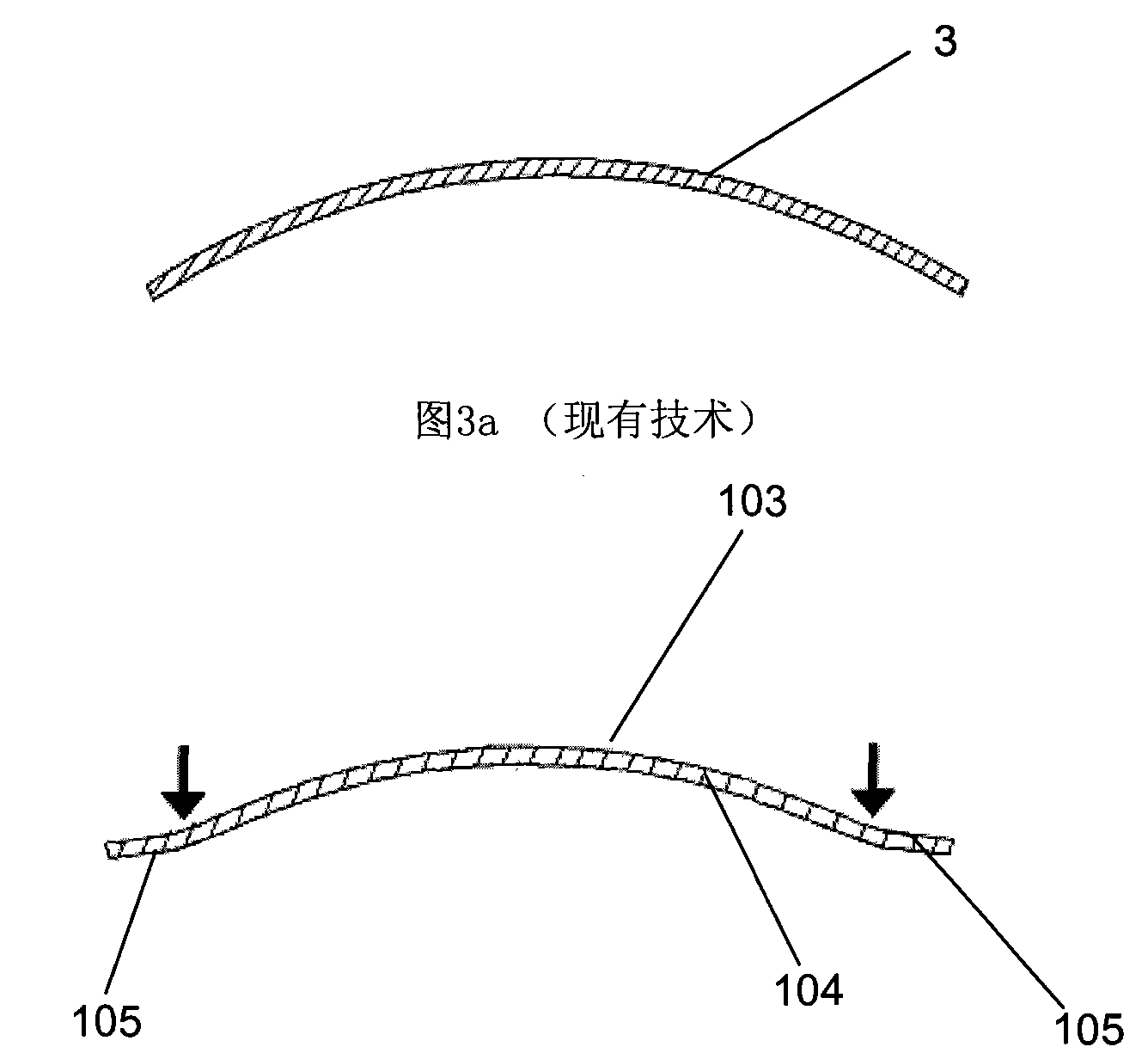
Motion picture scenes to be colorized / depth enhanced (2D→3D) are broken into separate elements, backgrounds / sets or motion / onscreen-action. Background and motion elements are combined into composite frame which becomes a visual reference database that includes data for all frame offsets used later for the computer controlled application of masks within a sequence of frames. Masks are applied to subsequent frames of motion objects based on various differentiating image processing methods, including automated mask fitting / reshaping. Colors and / or depths are automatically applied to masks throughout a scene from the composite background, translucent, motion objects. Areas never exposed by motion or foreground objects in a series of images may be partially or fully realistically drawn or rendered and applied to the occluded areas of the background and then automatically applied throughout the images to generate of minimal artifact or artifact-free secondary viewpoints when translating foreground objects horizontally during 2D→3D conversion.
Owner:LEGEND FILMS INC
Image sequence depth enhancement system and method
InactiveUS7907793B1Maximum expressionTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsObject basedDepth enhancement
Motion picture scenes to be colorized / depth enhanced (2D→3D) are broken into separate elements, backgrounds / sets or motion / onscreen-action. Background and motion elements are combined separately into single frame representations of multiple frames which becomes a visual reference database that includes data for all frame offsets used later for the computer controlled application of masks within a sequence of frames. Each pixel address within the database corresponds to a mask / lookup table address within the digital frame and X, Y, Z location of subsequent frames. Masks are applied to subsequent frames of motion objects based on various differentiating image processing methods, including automated mask fitting of all masks or single masks in an entire frame, bezier and polygon tracing of selected regions with edge detected shaping and operator directed detection of subsequent regions. Colors and / or depths are automatically applied to masks throughout a scene from the composite background and to motion objects.
Owner:LEGEND FILMS INC
System and method for minimal iteration workflow for image sequence depth enhancement
InactiveUS20120120054A1Save a lotIncrease workforceCharacter and pattern recognitionSteroscopic systemsViewpointsObject based
Owner:LEGEND FILMS INC
System and method for rapid image sequence depth enhancement with augmented computer-generated elements
InactiveUS20110164109A1Character and pattern recognitionSteroscopic systemsDepth enhancementReference database
Motion picture scenes to be colorized / depth enhanced (2D->3D) are broken into separate elements, backgrounds / sets or motion / onscreen-action. Background and motion elements are combined into composite frame which becomes a visual reference database that includes data for all frame offsets used later for the computer controlled application of masks within a sequence of frames. Masks are applied to subsequent frames of motion objects based on various differentiating image processing methods, including automated mask fitting / reshaping. Colors and / or depths are automatically applied to masks throughout a scene from the composite background and to motion objects. Areas never exposed by motion or foreground objects in a series of images may be partially or fully realistically drawn or rendered and applied to the occluded areas of the background and then automatically applied throughout the images to generate of minimal artifact or artifact-free secondary viewpoints when translating foreground objects horizontally during 2D->3D conversion.
Owner:LEGEND FILMS INC
Depth map enhancement method blending high-resolution color image
ActiveCN106651938AReduce complexityIntegrity guaranteedImage analysisGeometric image transformationColor imageDepth enhancement
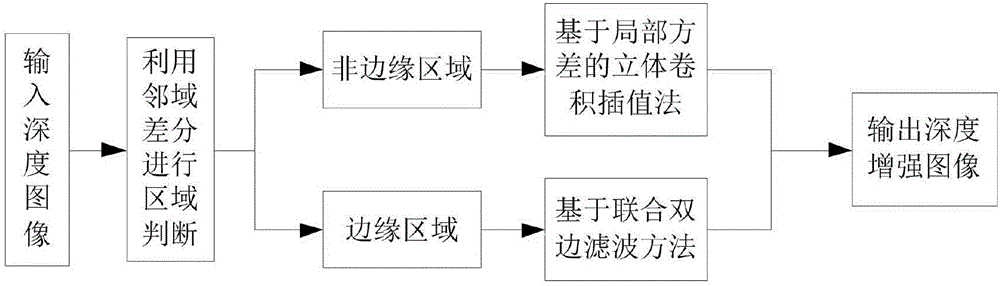
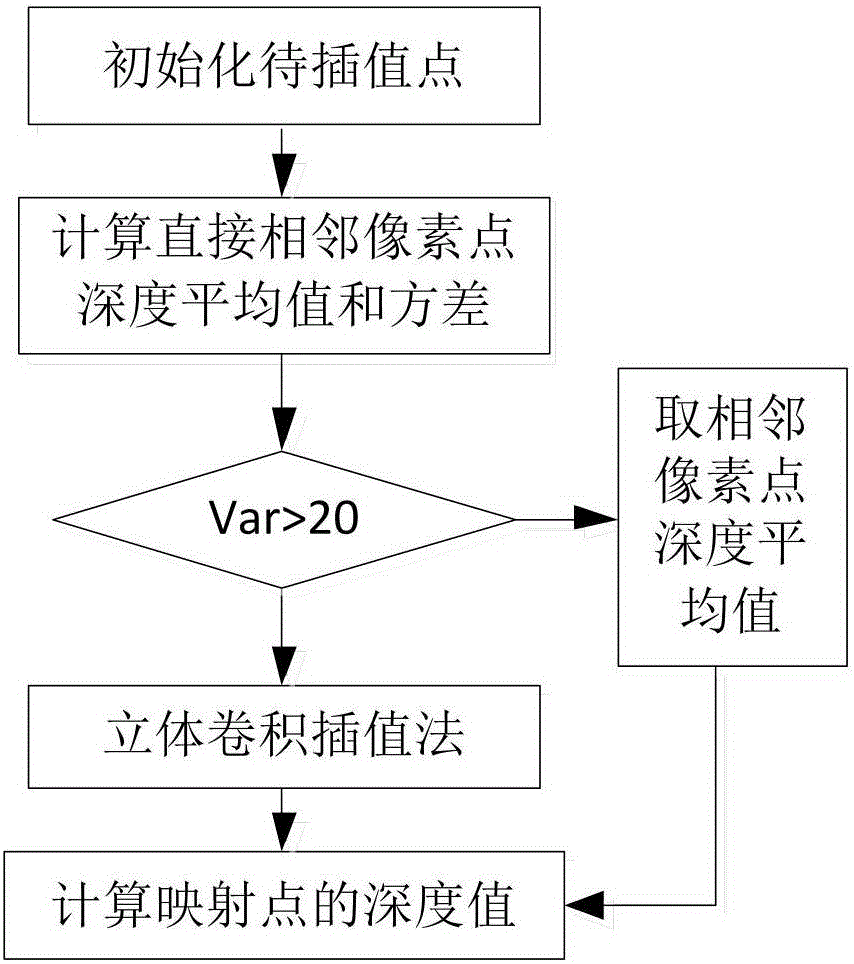
The invention provides a depth map enhancement method blending a high-resolution color image. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, calculating the maximum depth difference of pixel points in a neighborhood according to a neighborhood difference method; dividing a low-resolution depth image into an edge region and an non-edge region; conducting secondary dividing on the non-edge region by utilizing local neighborhood variance; obtaining depth values, corresponding to a mapping point, of a point to be interpolated by utilizing a mean interpolation method and a three-dimensional convolution interpolation method respectively; sampling a high-resolution image on the low-resolution depth image based on the principle of bilateral filtering by taking the high-resolution color image as a reference image; obtain the depth values, corresponding to the mapping point, of each pixel; and finally outputting a depth enhancement image subjected to interpolation processing. The method can not only effectively remove noise interference, reduce the complexity of a depth enhancement algorithm, but also maintain the integrity of image edge information.
Owner:湖南优象科技有限公司
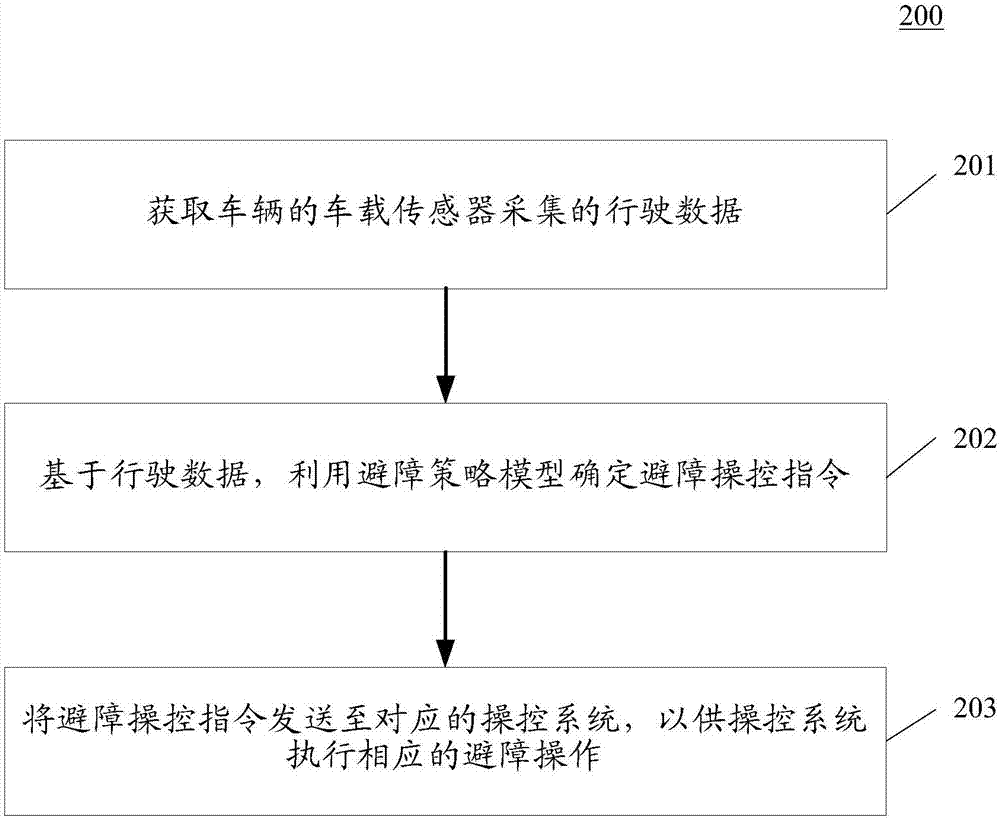
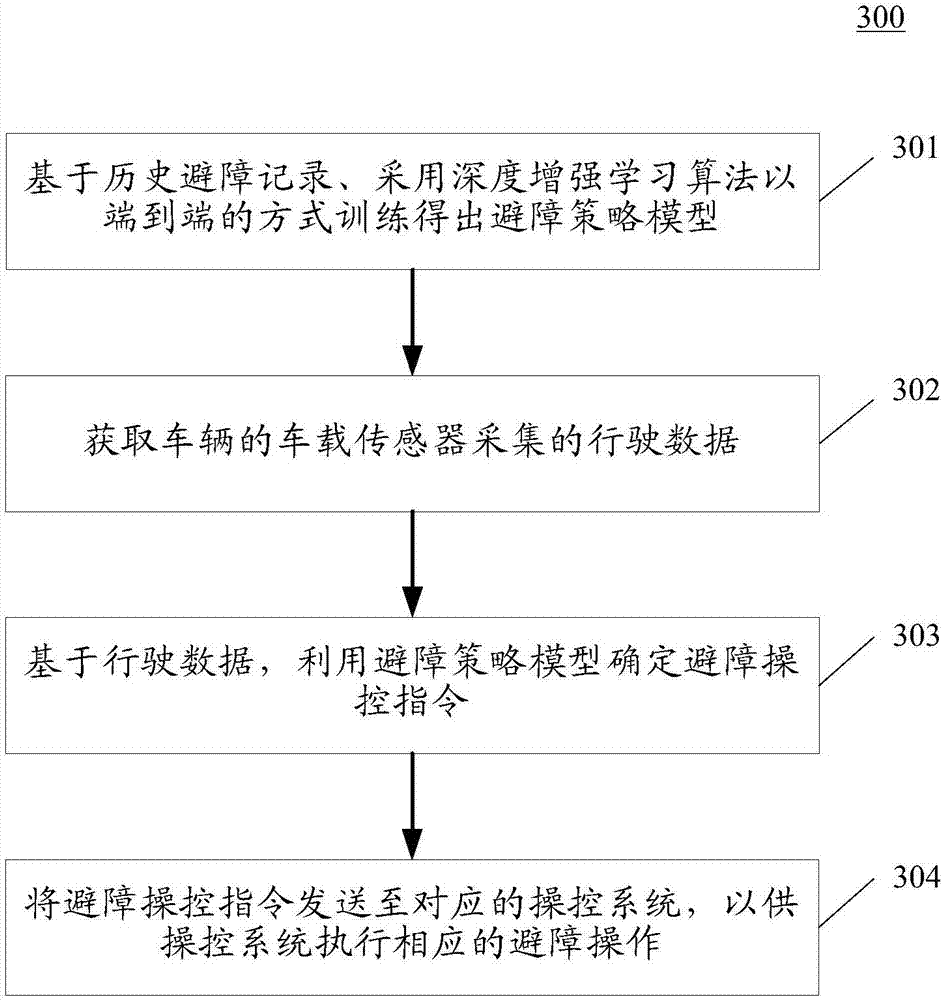
Vehicle obstacle avoidance method and device
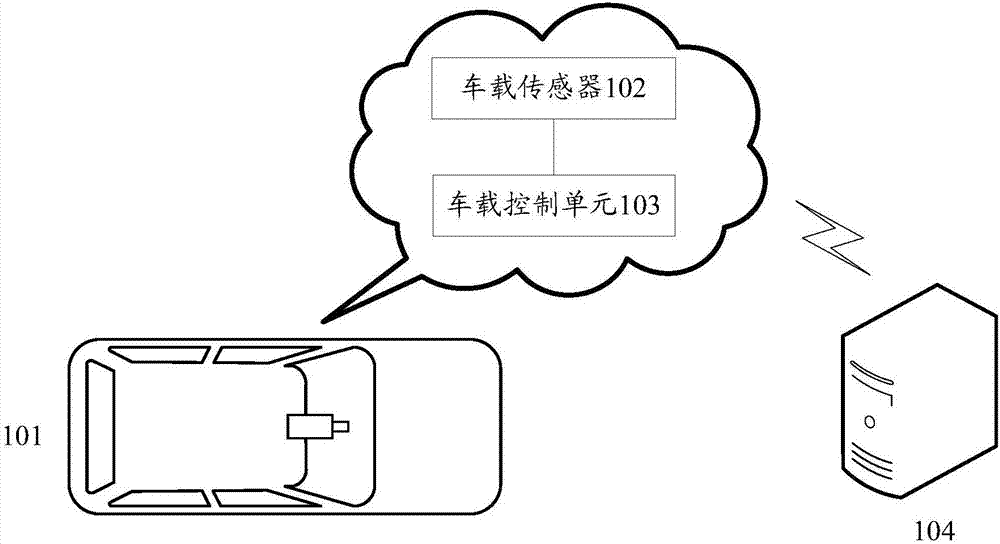
ActiveCN107491072ARealize automatic obstacle avoidanceSafe drivingPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesDepth enhancementControl system
The invention discloses a vehicle obstacle avoidance method and device. The method comprises steps that driving data acquired by a vehicle sensor of a vehicle is acquired, and the driving data comprises the obstacle information of the driving path and sensor data of the vehicle; based on the driving data, an obstacle avoidance strategy model is utilized to determine an obstacle avoidance control instruction, and the obstacle avoidance strategy model is acquired through training by employing a depth enhancement learning algorithm in an end to end mode on the basis of historical obstacle avoidance records; the obstacle avoidance control instruction is sent to a corresponding control system to make the control system perform corresponding obstacle avoidance operation. The method is advantaged in that the obstacle avoidance success rate of the vehicle can be enhanced.
Owner:BAIDU ONLINE NETWORK TECH (BEIJIBG) CO LTD
Minimal artifact image sequence depth enhancement system and method
Motion picture scenes to be colorized / depth enhanced (2D->3D) are broken into separate elements, backgrounds / sets or motion / onscreen-action. Background and motion elements are combined into composite frame which becomes a visual reference database that includes data for all frame offsets used later for the computer controlled application of masks within a sequence of frames. Masks are applied to subsequent frames of motion objects based on various differentiating image processing methods, including automated mask fitting / reshaping. Colors and / or depths are automatically applied to masks throughout a scene from the composite background and to motion objects. Areas never exposed by motion or foreground objects in a series of images may be partially or fully realistically drawn or rendered and applied to the occluded areas of the background and then automatically applied throughout the images to generate of minimal artifact or artifact-free secondary viewpoints when translating foreground objects horizontally during 2D->3D conversion.
Owner:LEGEND FILMS INC
Distribution type laser spot alloying method
InactiveCN1831195AImprove wear performanceOvercoming temper softening problemsMetallic material coating processesLaser beam welding apparatusDepth enhancementAlloy
The invention relates to a distributed laser point-shaped alloying method that uses the small-hole effect caused by high power density laser effect to form mixing liquid bath by metal base and high performance alloy power sent by powder sending machine, the alloying point would be formed in the following rapid concreting. Controlling the laser beam processing point to point to form alloying points on the surface of the material, the distributed laser depth enhancement would be realized. The invention optimizes the alloying points and the distributing state to improve abrasion resistance of the surface, and the useful life of the component would be improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Depth image enhancement method based on anisotropic diffusion
ActiveCN103198486AOvercoming blurry edgesEasy to fillImage enhancementImage analysisDiffusionColor image
The invention discloses a depth image enhancement method based on anisotropic diffusion. The similarity among pixel points of a color image corresponding to a depth image is used as a basis of depth diffusion, and based on the known depth of the depth image, filling of a depth missing region of the depth image is finished. Through the depth image enhancement method based on the anisotropic diffusion, the defect that in a traditional depth enhancement method based on interpolation, edges of an object are blurry is overcome, meanwhile, the limit of the size of a wave filtering window in a depth enhancement method based on wave filtering is broken through, and the depth image enhancement method based on the anisotropic diffusion has the advantages of being high in universality, high in robustness and the like. The depth image enhancement method based on the anisotropic diffusion can be widely used for a variety of depth images which have missing depth regions, and in a practical application process, based on the color image and the depth image which are in correspondence to each other, a good depth image missing region filling effect can be achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
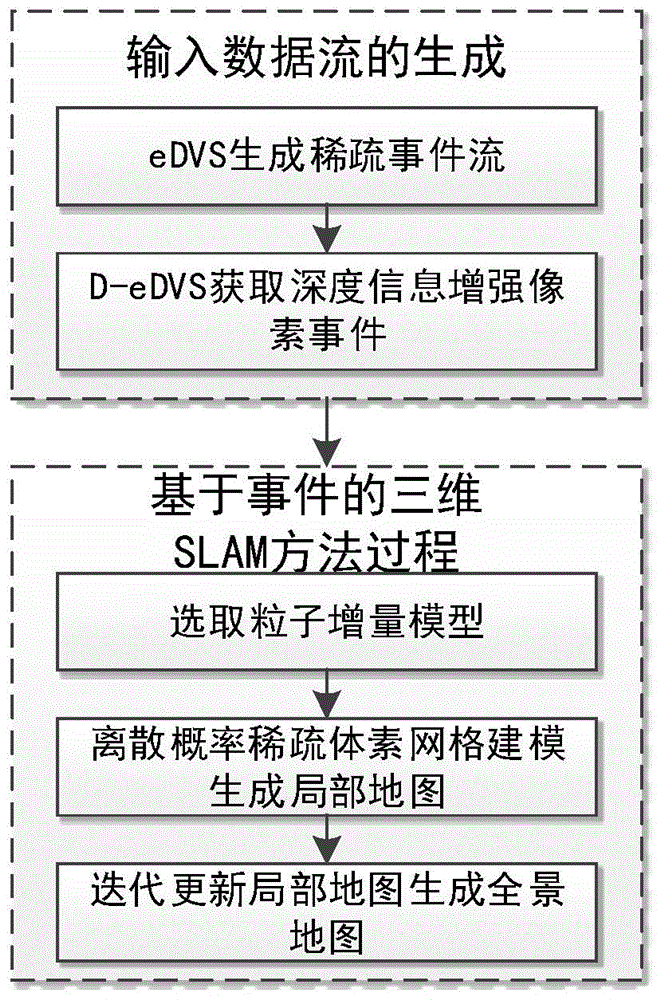
Three dimensional SLAM method based on events with depth enhanced vision sensor
ActiveCN105865462ALower latencyGood effectInstruments for road network navigationSimultaneous localization and mappingVoxel
The invention provides a three dimensional SLAM (simultaneous localization and mapping) method based on events with a depth enhanced vision sensor. The method comprises the following components: the embedded dynamic vision sensor and an individually movable depth induction sensor are combined in order to obtain an enhanced pixel event with depth information; the pixel event is used as an only input of the three dimensional SLAM method based on events, and a panoramic map is generated by selecting a particle increment model, generating a local map from discrete probability sparse voxel grid modeling, and updating the local map by iteration. Specific hardware is not needed, the processing speed is 20 times faster than the real time speed, and position update is carried out at hundred Hertz frequency; the method has the advantages of good effects, low memory demand, low power consumption, high efficiency calculating rate, etc.
Owner:上海趣立信息科技有限公司
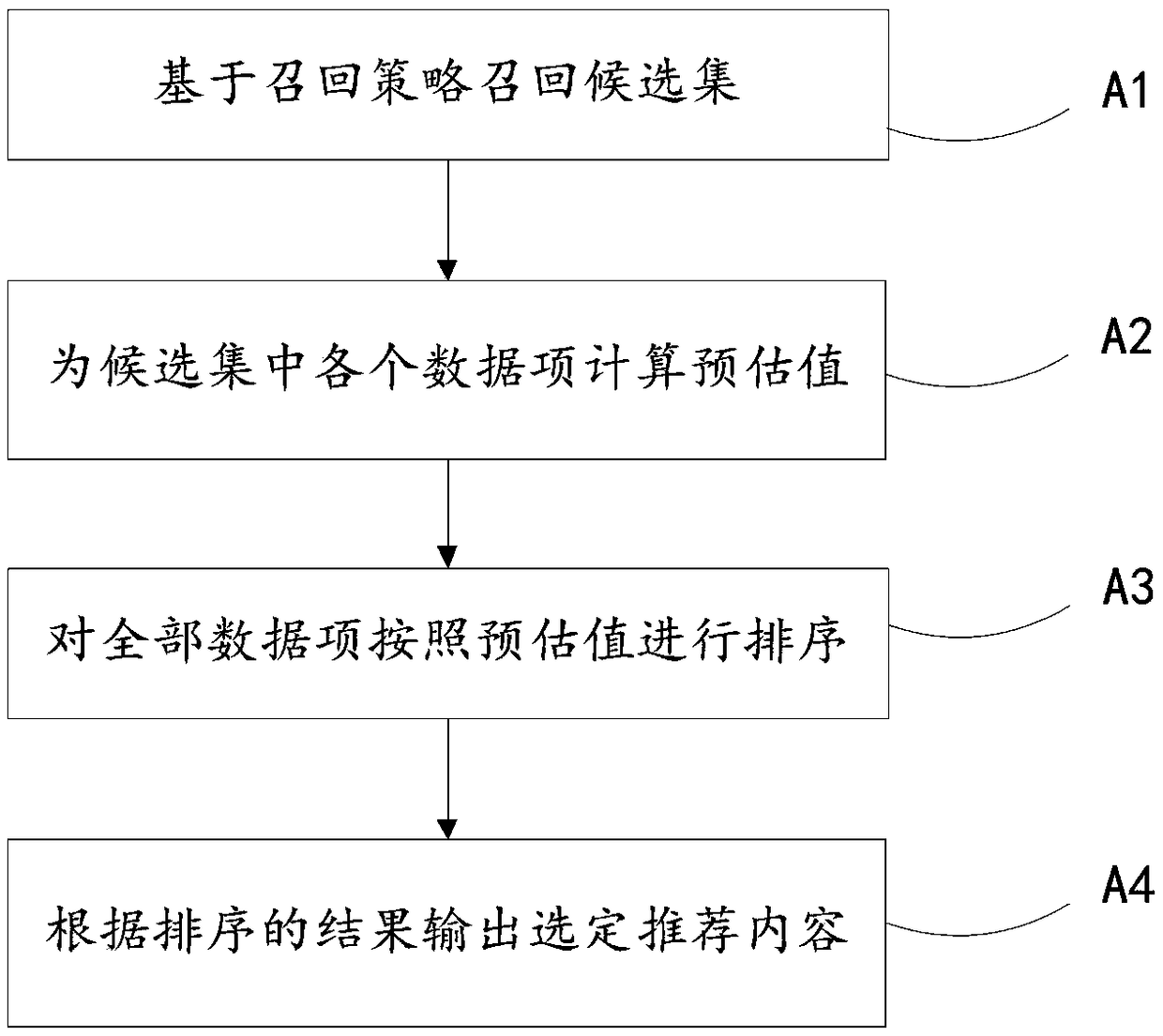
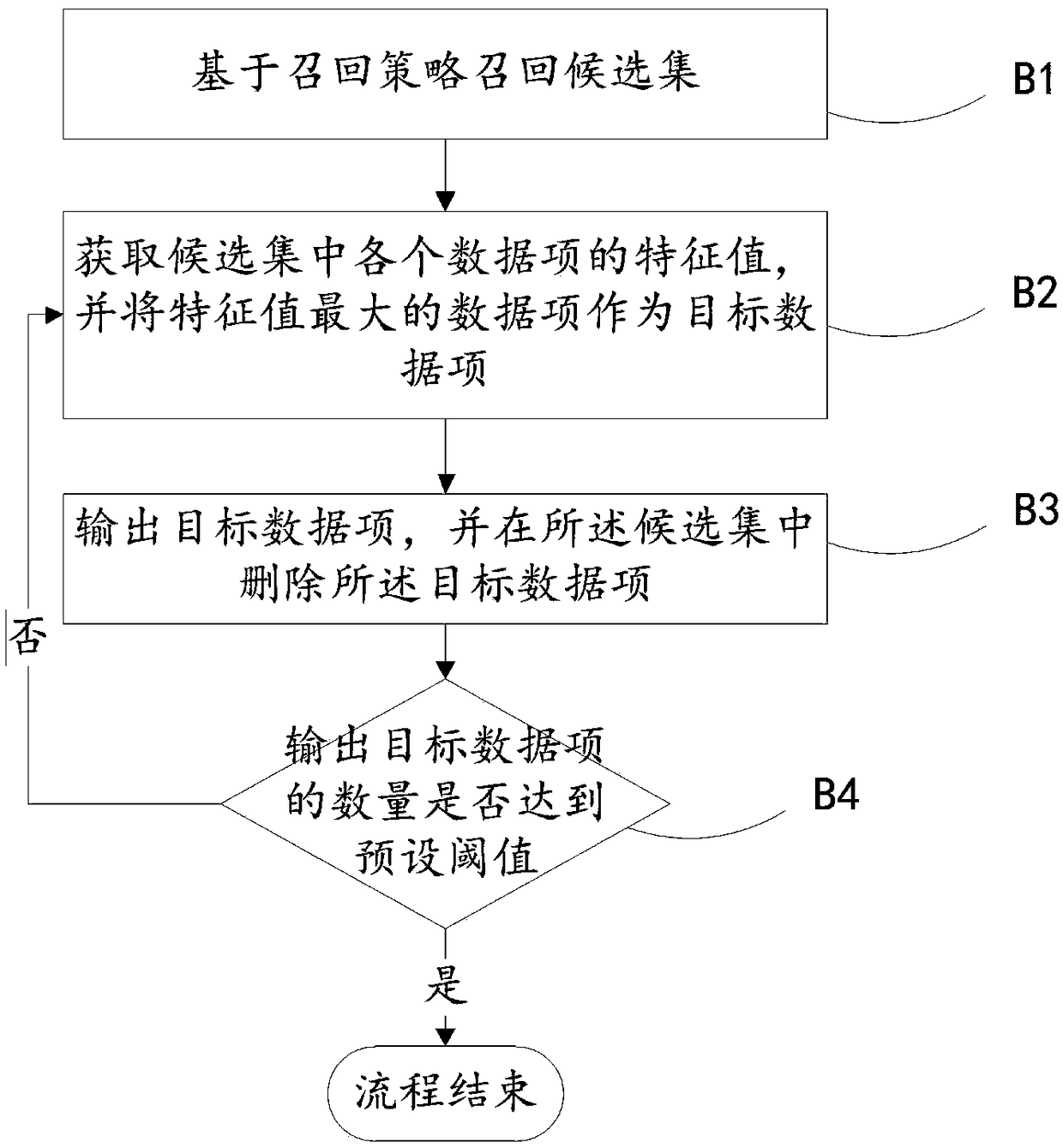
Content recommendation method and apparatus based on depth reinforcement learning
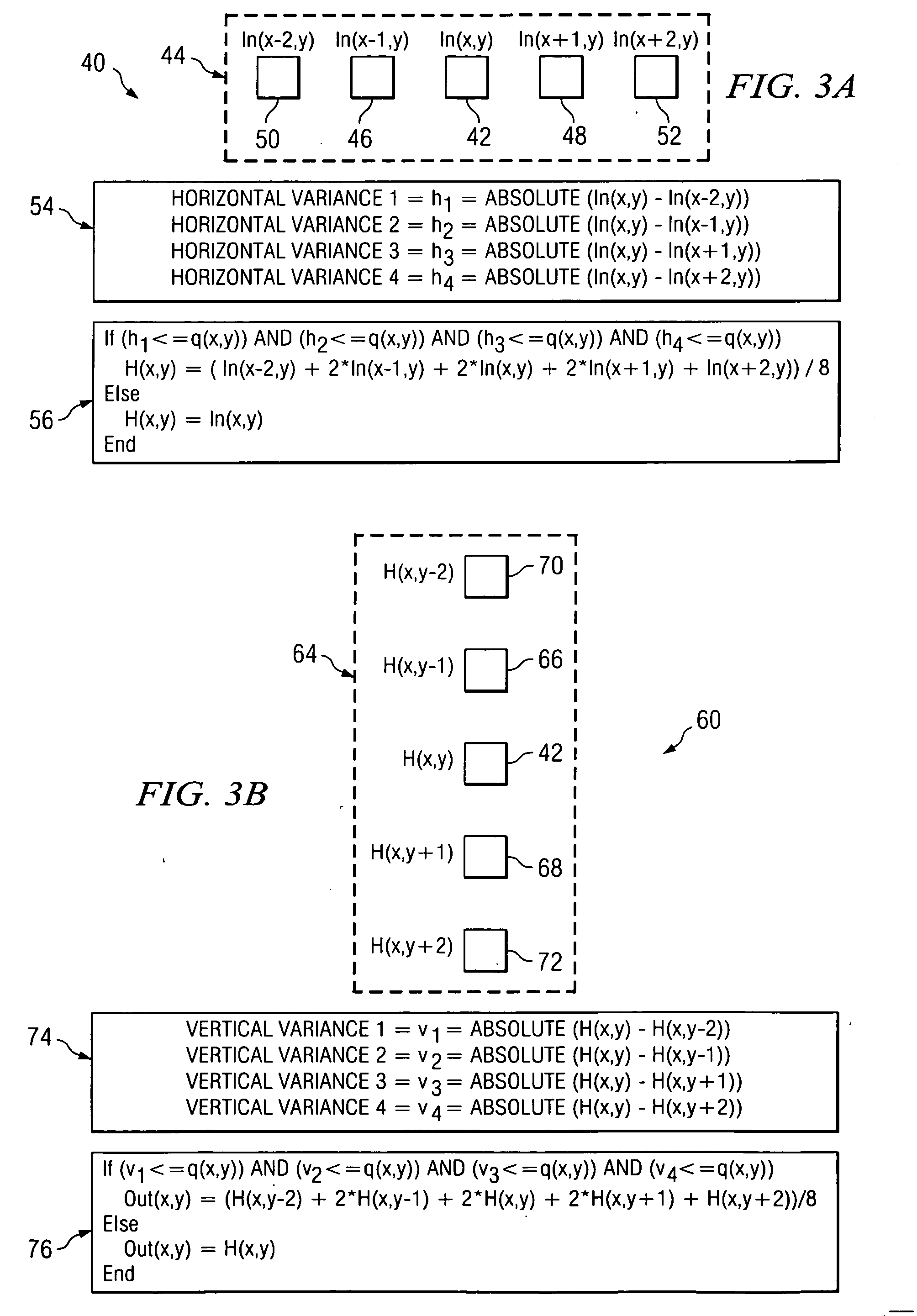
ActiveCN109062919AExcellent recommendation resultInspire browsing intentComputing modelsSpecial data processing applicationsDepth enhancementRanking
The invention provides a content recommendation method and a device based on depth reinforcement learning. The method comprises the following steps: training a depth reinforcement function to obtain atraining result for a parameter set in the depth reinforcement function; obtaining an ordered candidate set of recommended contents and a number of pieces of selected recommended contents; based on the training results of the parameter set, the comprehensive reward value of each recommended content in the candidate set being calculated by using the depth enhancement function; a comprehensive award value for each recommendation content being associated with the recommendation content and other recommendations ranked after the recommendation content; according to the result of calculation, selecting the recommended contents as the selected contents and outputting them in order. The invention synthetically considers the recommended content and the ranking of the recommended content by usingthe method of depth reinforcement learning, thereby obtaining a better recommended result.
Owner:云南腾云信息产业有限公司
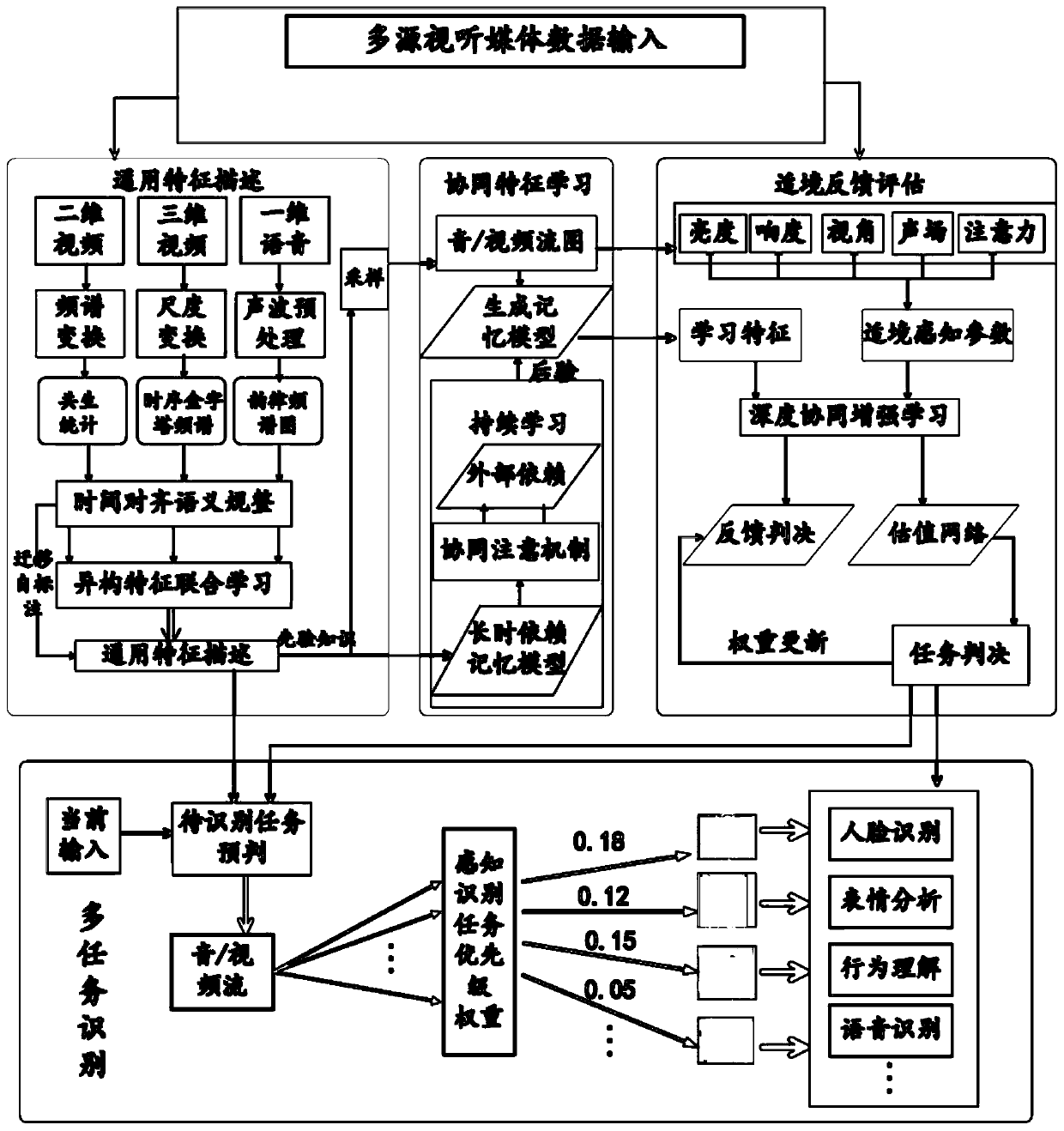
A multi-task collaborative identification method and system
ActiveCN109947954AImprove effectivenessImprove efficiencyMultimedia data indexingSpecial data processing applicationsDepth enhancementFeature learning
The invention provides a multi-task cooperative identification method and system, and belongs to the technical field of artificial intelligence task identification, and the system comprises a generalfeature extraction module, a cooperative feature learning module, and an adaptive feedback evaluation identification module. The method comprises steps of based on a time synchronization matching mechanism, extracting universal features of the multi-source heterogeneous data, and realizing universal feature description of the multi-source heterogeneous data; Training the general features as prioriknowledge by combining a collaborative attention mechanism based on external dependence, and generating an association memory relationship among the general features; and extracting environmental perception parameters of the multi-source heterogeneous data, and realizing multi-task identification in combination with the associated memory relationship. According to the method, the weight of the to-be-identified task is judged through depth enhancement feedback in combination with an environmental perception adaptive calculation theory, the priority of the to-be-identified task is adaptively adjusted according to environmental changes, and the effect of simultaneously outputting a plurality of visual and auditory perception identification results is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method and system for adaptive bit depth enhancement for displays
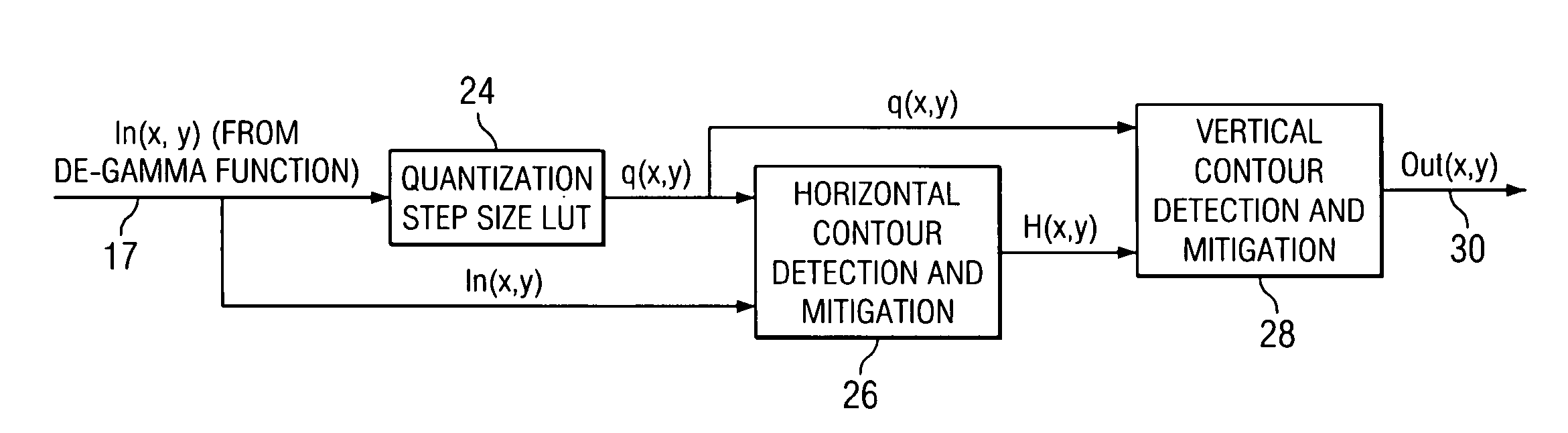
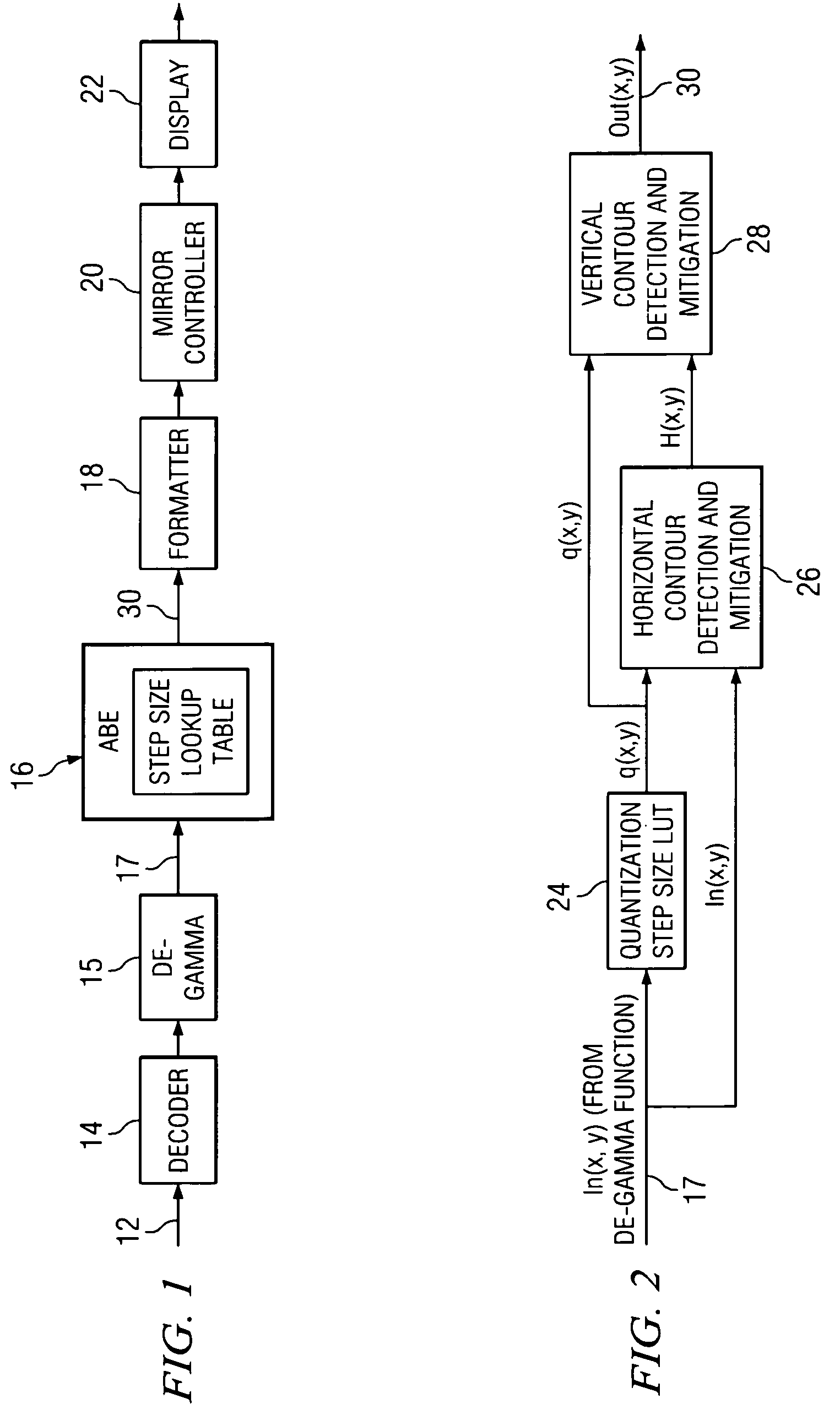
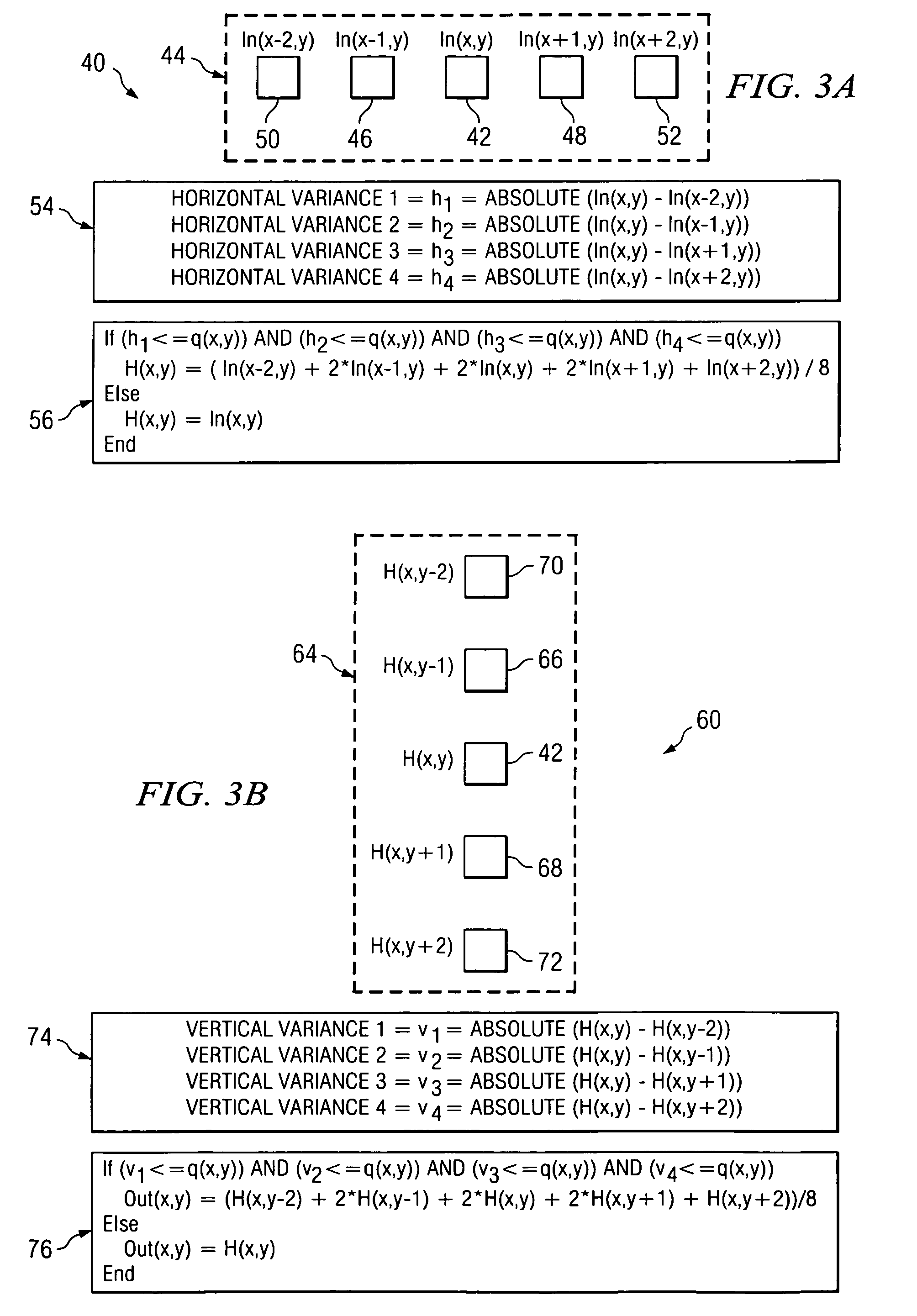
ActiveUS20050134612A1Quality improvementIncreased input resolutionCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsDepth enhancementDisplay device
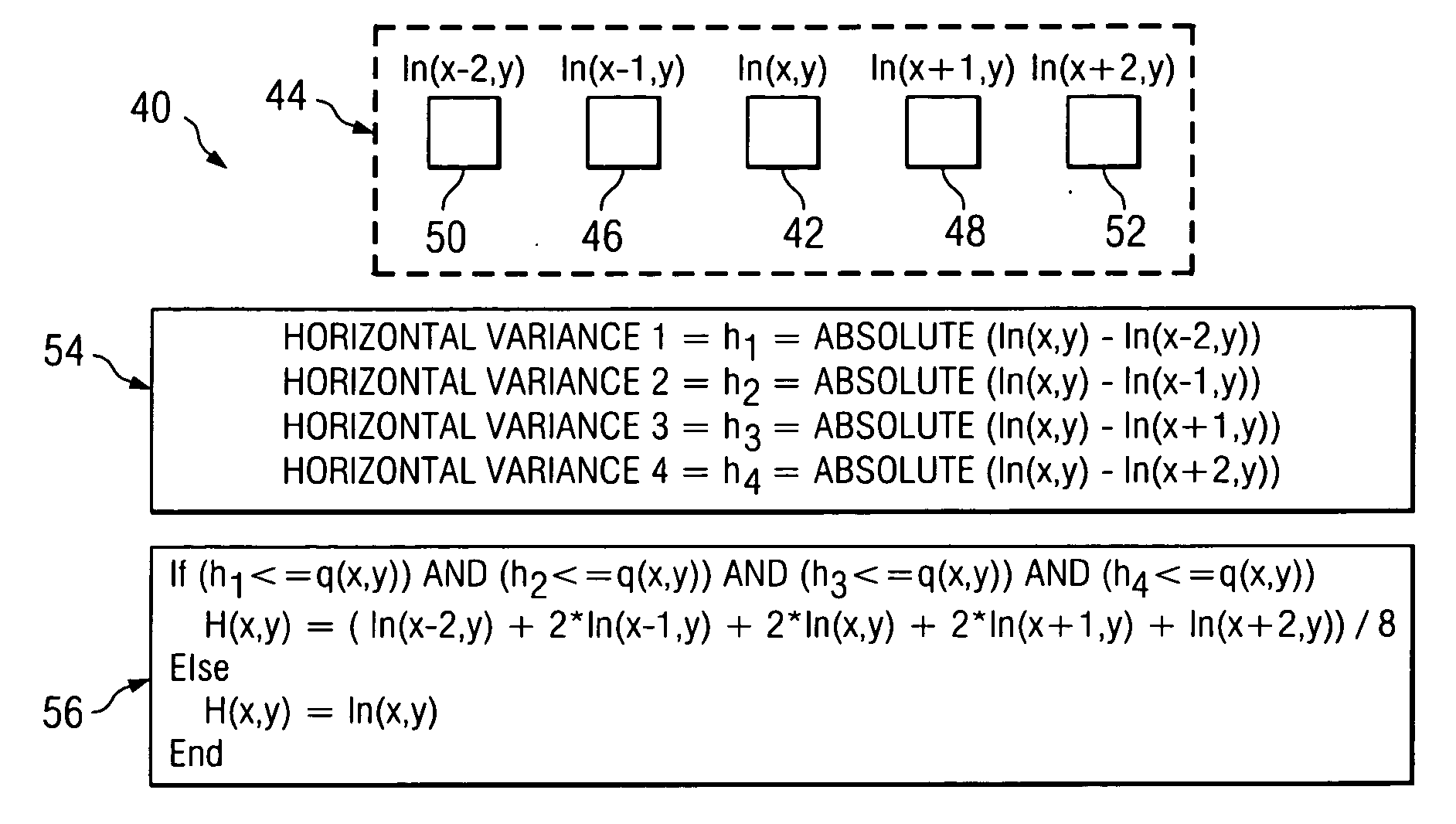
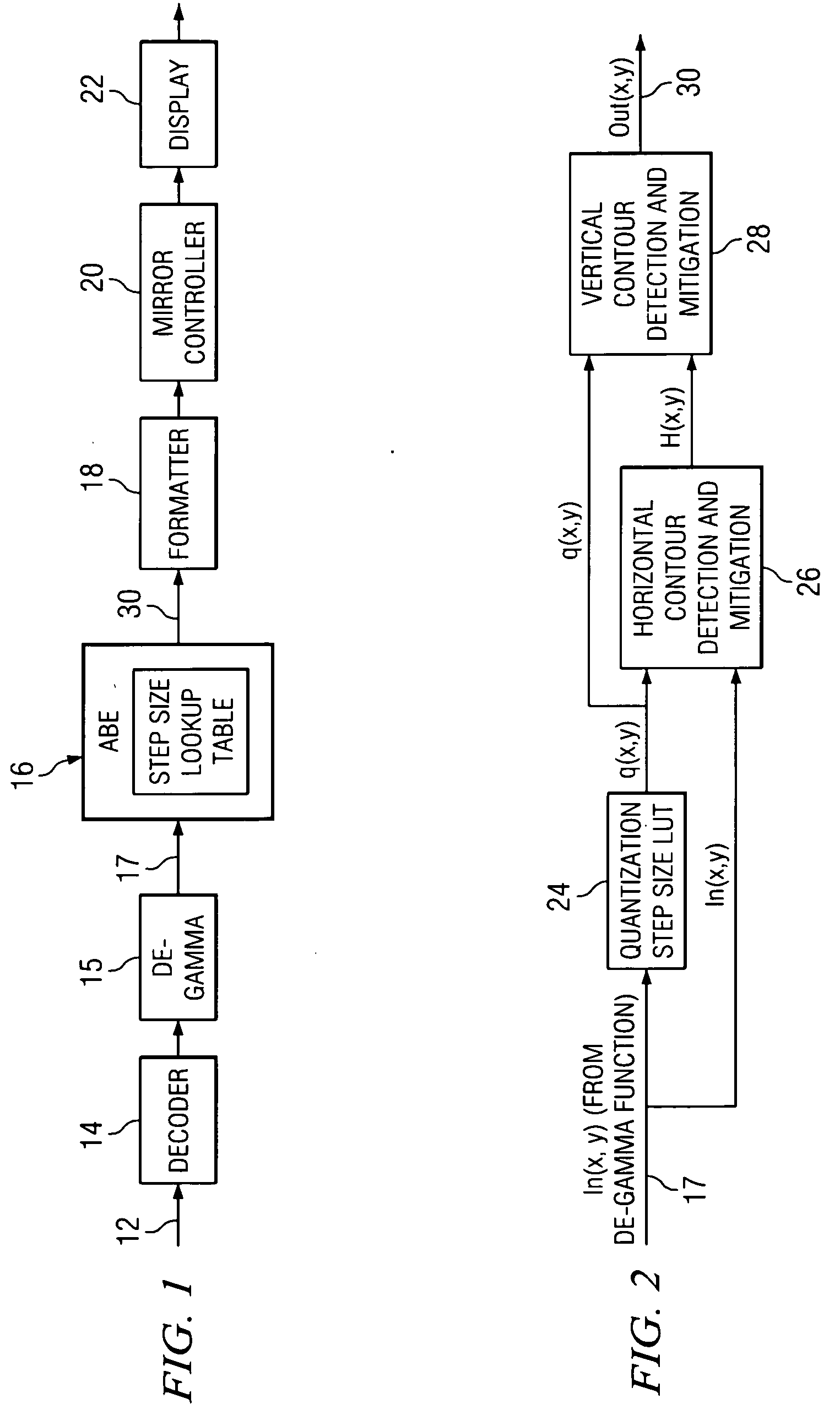
According to one embodiment, a method for compensating for inadequate bit resolution in a light processing system includes receiving a plurality of values each indicative of an intensity level for a pixel to be displayed. Each of the values is represented by a plurality of bits of data. The method also includes determining a quantization step size for the plurality of bits of data. For at least one particular pixel of the pixels, a set of consecutive pixels including the particular pixel is selected. The method also includes determining a difference between the value associated with the particular pixel in the set and each value associated with the other pixels in the set, and also determining that all of the determined differences are less than or equal to the quantization step size. In response, a filtered value for the particular pixel in the set is generated based at least on some of the pixels in the set in addition to the particular pixel.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Image bit depth enhancing method
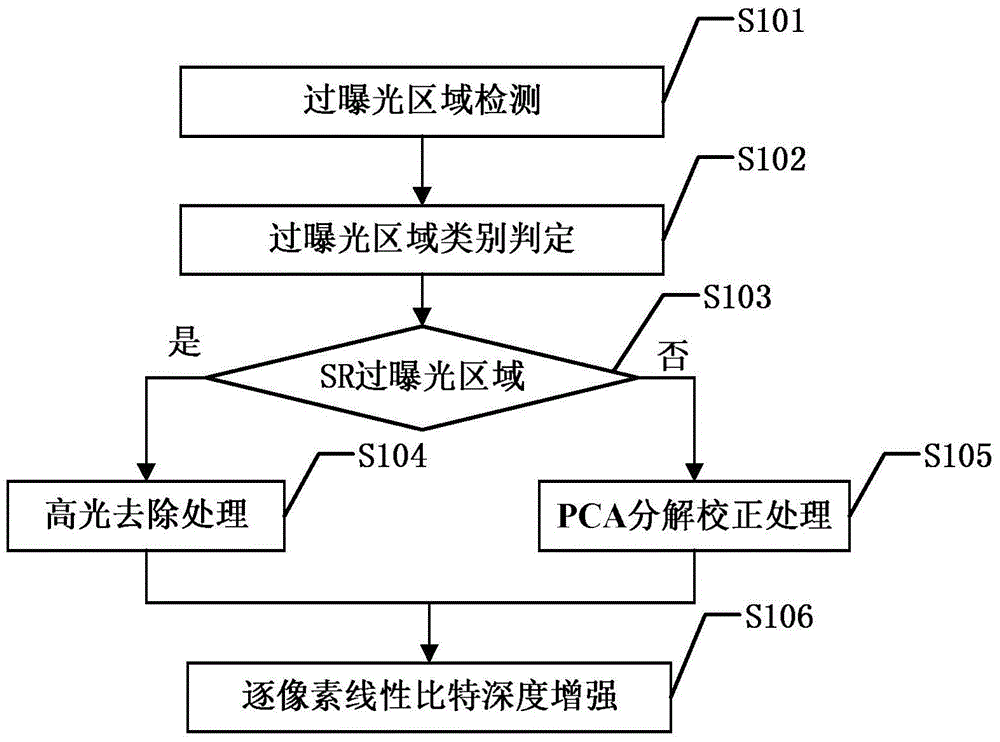
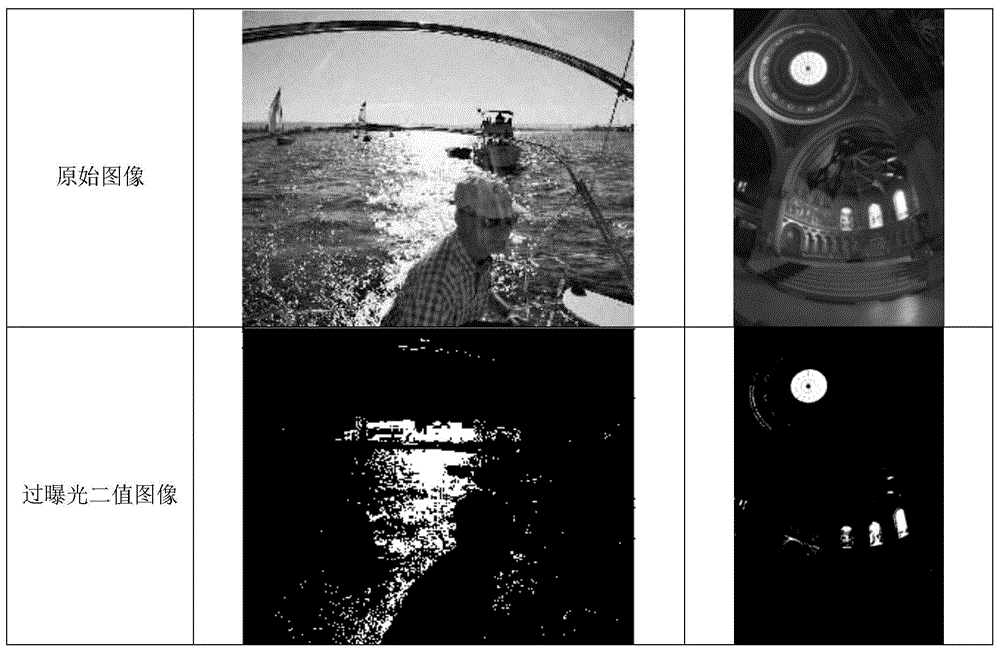
InactiveCN105184748AImprove efficiencyBit depth enhancementImage enhancementDepth enhancementComputer vision
The invention discloses an image bit depth enhancing method. The image bit depth enhancing method includes the steps: detecting an original image to obtain an overexposure area, and then determining whether the overexposure area is an SR overexposure area or an LS overexposure area; utilizing corresponding overexposure processing methods to perform overexposure processing of the original image; and utilizing a bit depth enhancing algorithm of a normal exposure image to perform bit depth enhancement of the image after overexposure processing. Compared with the overall transformation, the image bit depth enhancing method takes the characteristics of different areas in the image into account. Compared with the local transformation, the image bit depth enhancing method processes the overexposure area in advance, and can utilize the same transformation function for the whole image during the subsequent bit depth enhancing process so that the complexity of bit depth enhancement is reduced and the efficiency of the whole algorithm is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
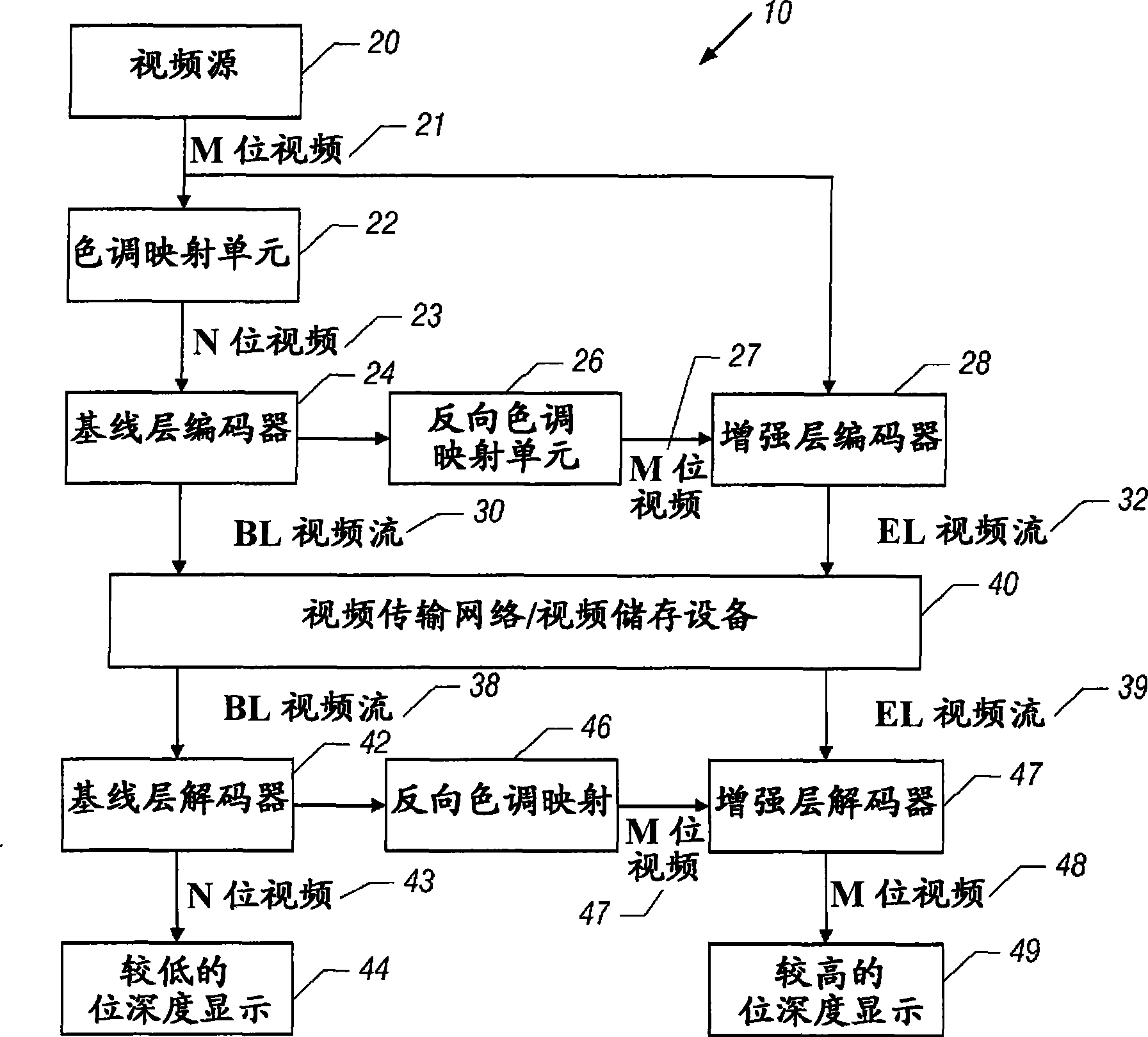
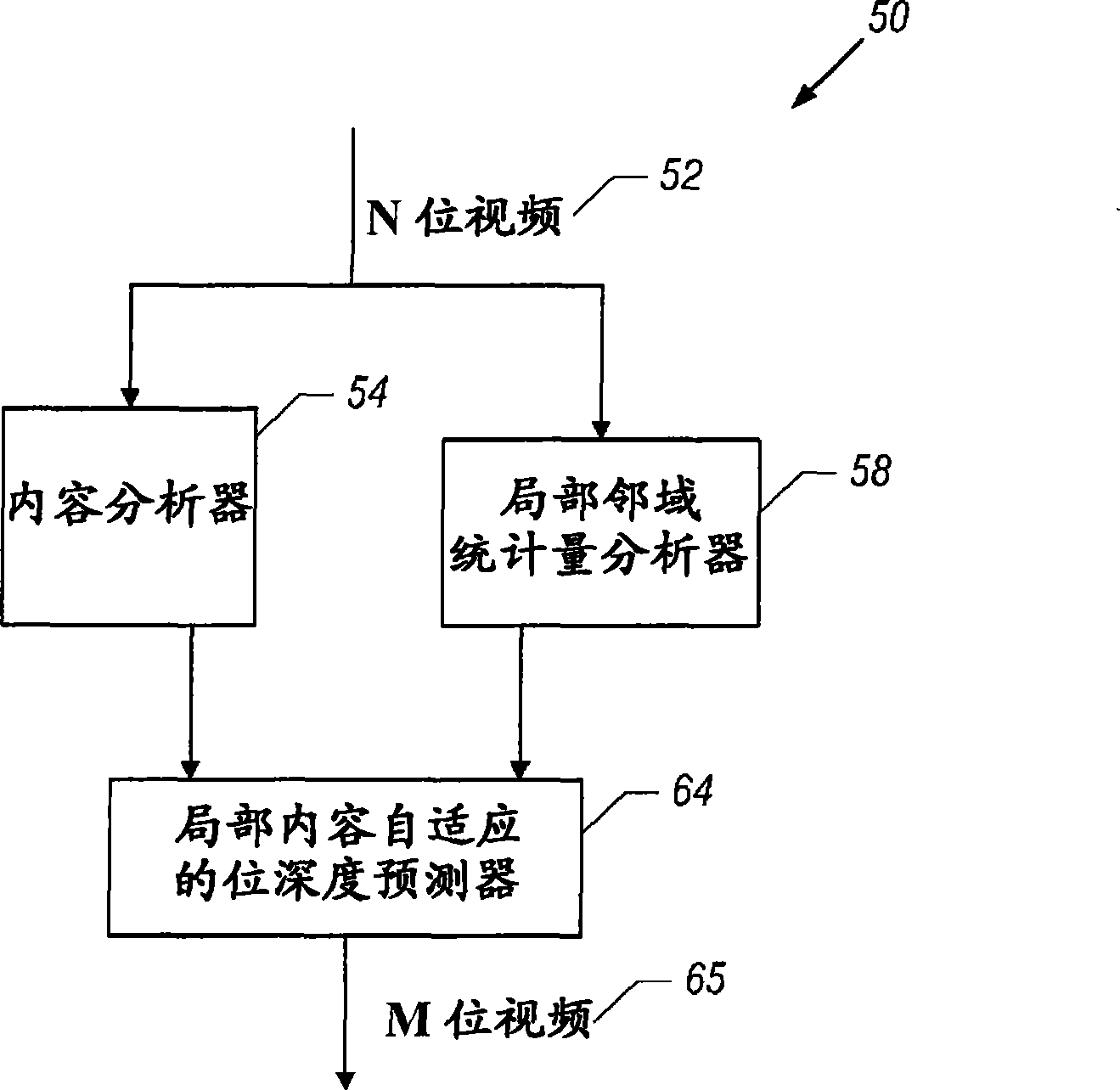
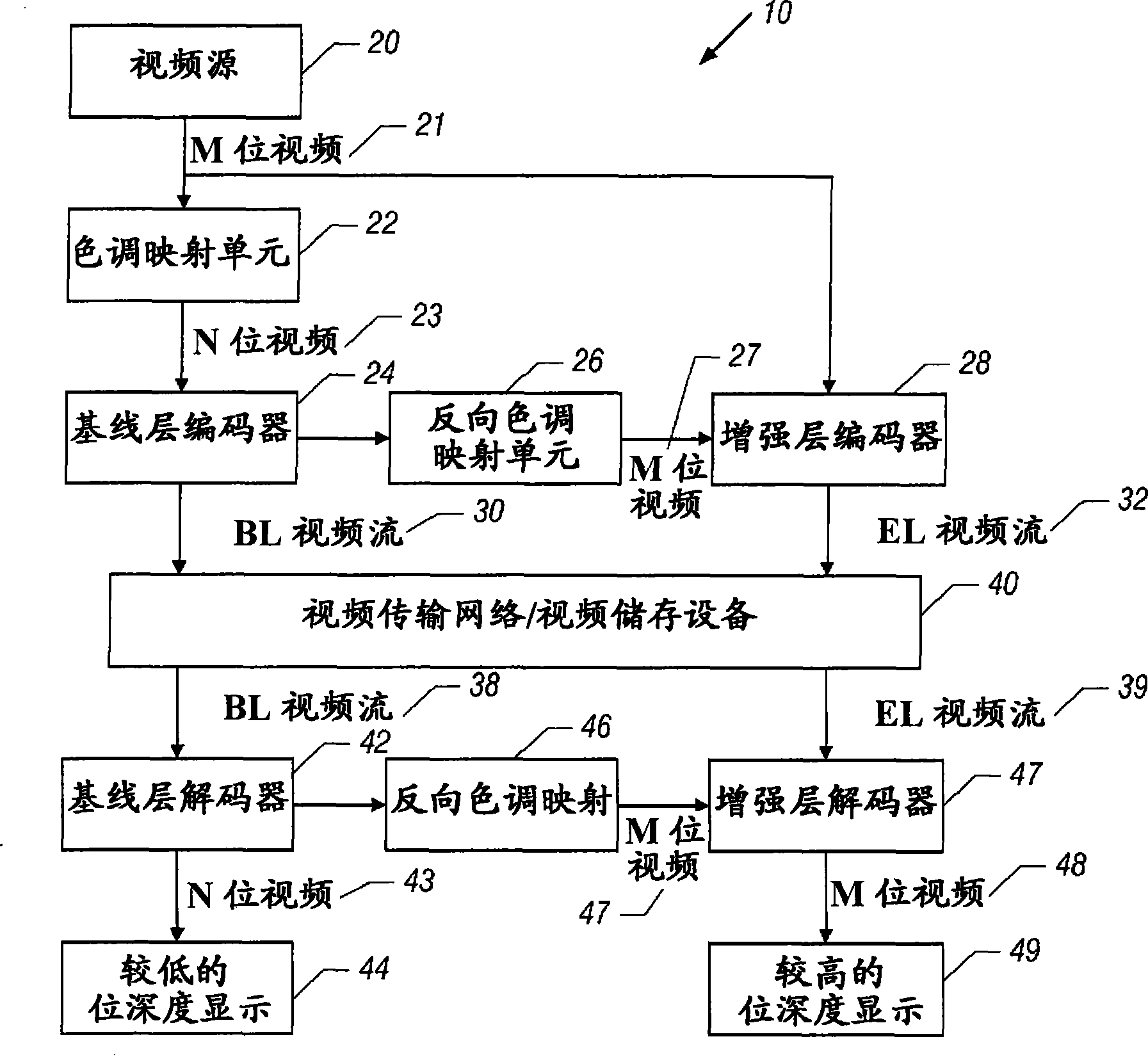
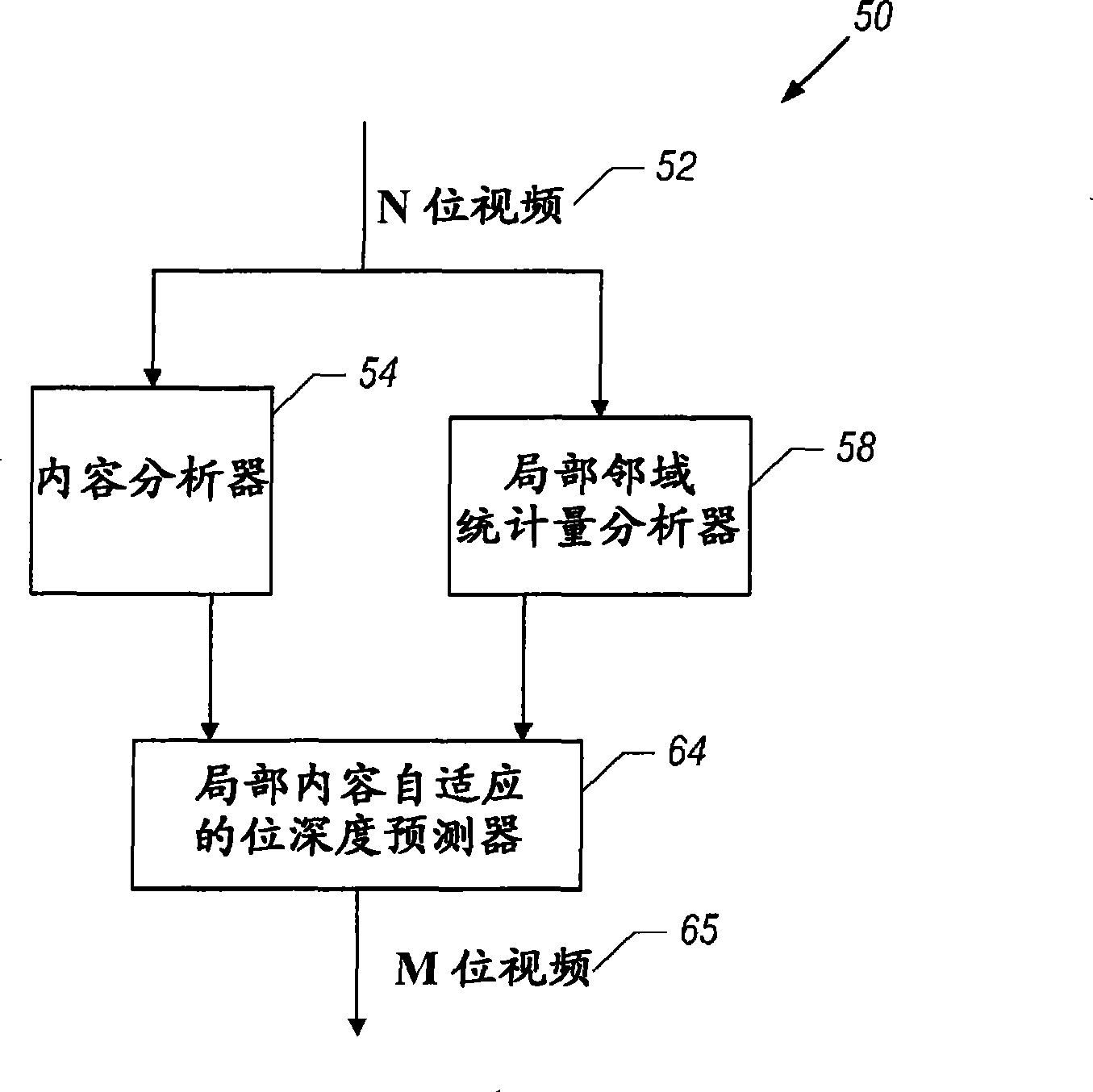
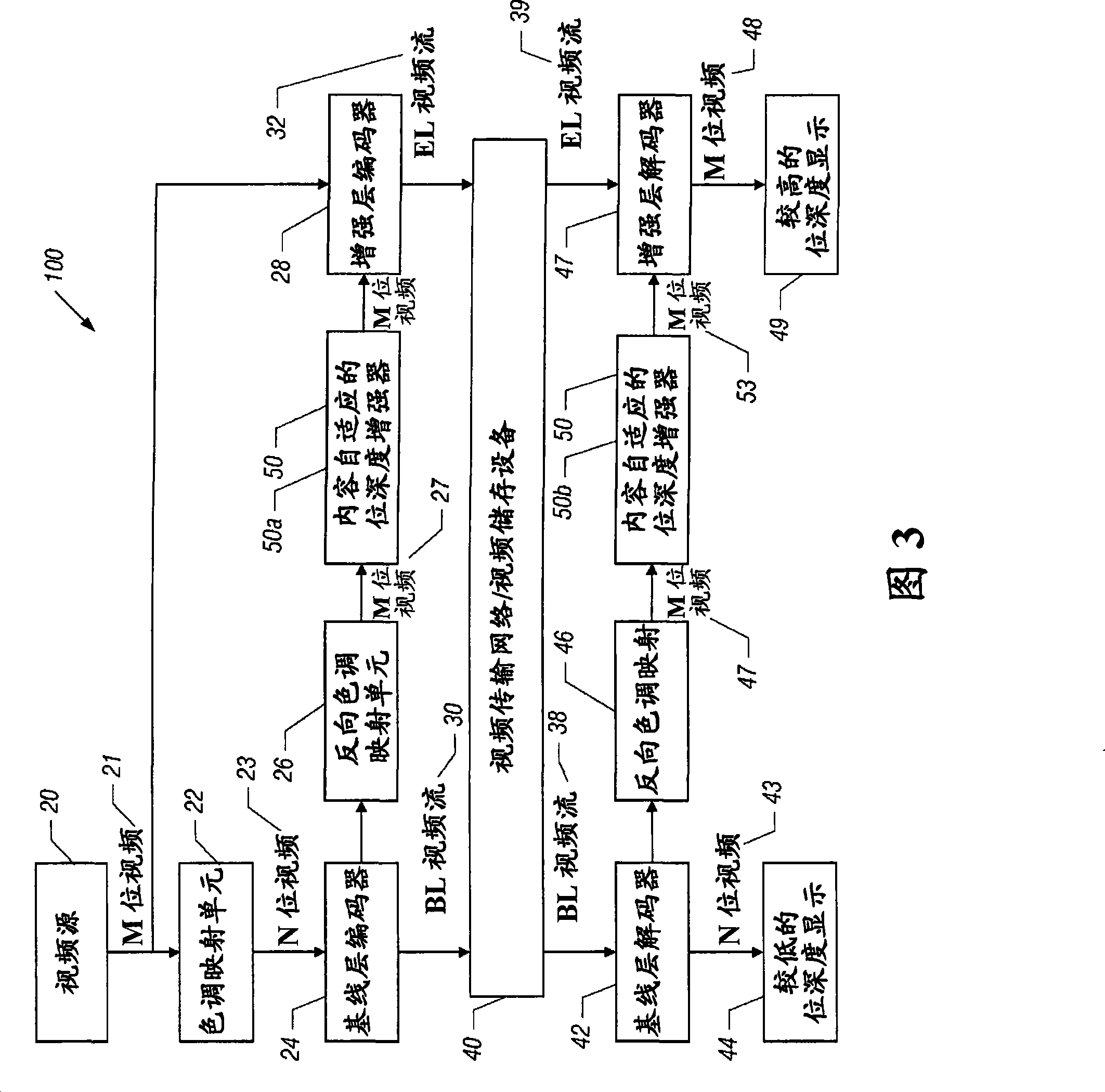
Bit depth enhancement for scalable video coding
InactiveCN101459845AHigh coding efficiencyImprove coding efficiencyTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationDepth enhancementComputer graphics (images)
A video system includes an analyzer and a bit depth predictor. The analyzer receives a first coded video signal, which is indicative of first values for pixels. The first values are associated with a first bit depth. The analyzer, for each pixel, analyzes the first values for the pixels located in a neighborhood that contains said each pixel. The bit depth predictor, based at least in part on the analysis, generates a second coded video signal that is indicative of second values for the pixels. The second values are associated with a second bit depth that is different than the first bit depth.
Owner:INTEL CORP
System and method for increasing the bit depth of images
Processing an image having a first bit depth includes performing two or more iterations of a bit depth enhancement operation that increases the bit depth of the image to a second bit depth that is higher than the first bit depth. The bit depth enhancement operation includes dividing the image into a plurality of areas, performing an edge detection operation to identify one or more areas from the plurality of areas that do not contain edge features, and applying a blur to the one or more areas from the plurality of areas that do not contain edge features. In a first iteration of the of the bit depth enhancement operation, the plurality of areas includes a first number of areas, and the number of areas included in the plurality of areas decreases with each subsequent iteration of the bit depth enhancement operation.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Minimal artifact image sequence depth enhancement system and method
Motion picture scenes to be colorized / depth enhanced (2D→3D) are broken into separate elements, backgrounds / sets or motion / onscreen-action. Background and motion elements are combined into composite frame which becomes a visual reference database that includes data for all frame offsets used later for the computer controlled application of masks within a sequence of frames. Masks are applied to subsequent frames of motion objects based on various differentiating image processing methods, including automated mask fitting / reshaping. Colors and / or depths are automatically applied to masks throughout a scene from the composite background and to motion objects. Areas never exposed by motion or foreground objects in a series of images may be partially or fully realistically drawn or rendered and applied to the occluded areas of the background and then automatically applied throughout the images to generate of minimal artifact or artifact-free secondary viewpoints when translating foreground objects horizontally during 2D→3D conversion.
Owner:LEGEND FILMS INC
Method and system for adaptive bit depth enhancement for displays
ActiveUS7265766B2False contours may be mitigatedBackground splotchiness smoothed outCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsDepth enhancementDisplay device
According to one embodiment, a method for compensating for inadequate bit resolution in a light processing system includes receiving a plurality of values each indicative of an intensity level for a pixel to be displayed. Each of the values is represented by a plurality of bits of data. The method also includes determining a quantization step size for the plurality of bits of data. For at least one particular pixel of the pixels, a set of consecutive pixels including the particular pixel is selected. The method also includes determining a difference between the value associated with the particular pixel in the set and each value associated with the other pixels in the set, and also determining that all of the determined differences are less than or equal to the quantization step size. In response, a filtered value for the particular pixel in the set is generated based at least on some of the pixels in the set in addition to the particular pixel.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
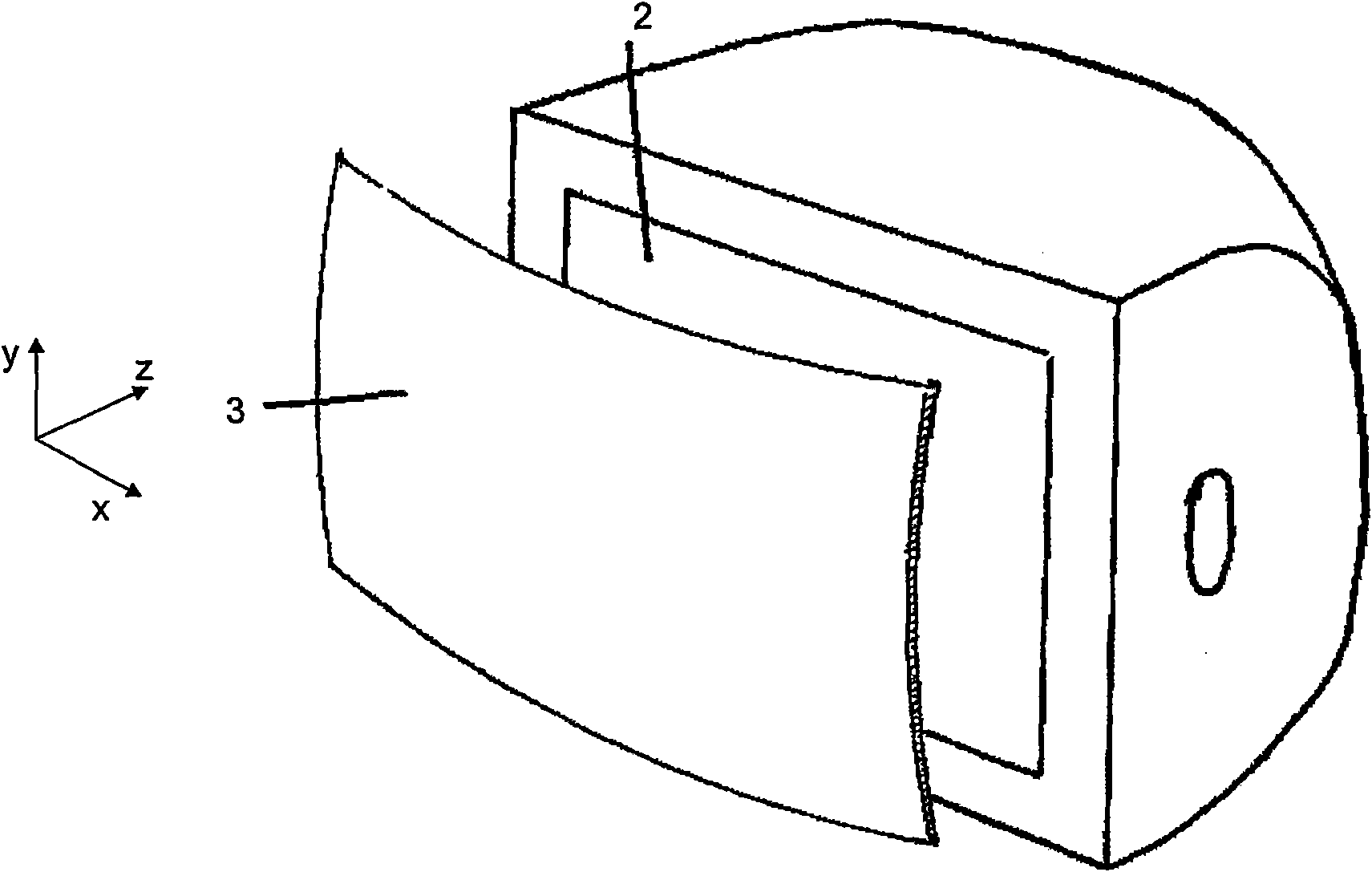
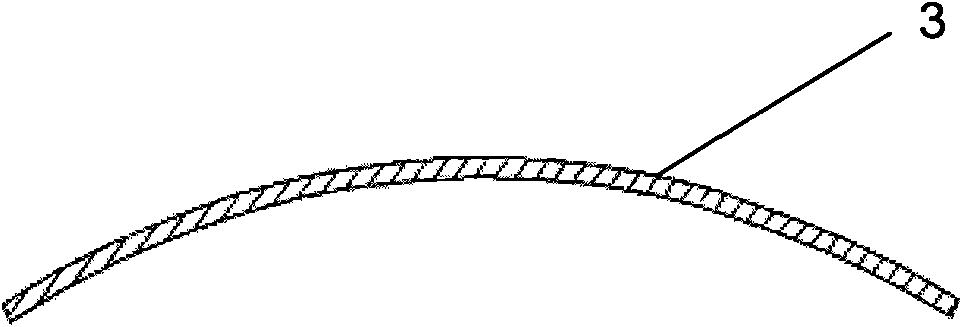
Depth enhancing screen
The present disclosure relates to a depth-enhancing screen for producing a simulated 3D image. The screen comprises a multi-curved Fresnel lens which when viewed in cross-section along the or each longest line linking two points on the edge of the lens, has a curved cross-section with an apex in the central region of the lens, and wherein each end of the curve flattens before it reaches the edge of the lens.
Owner:REALVIEW INNOVATIONS
Minimal artifact image sequence depth enhancement system and method
InactiveUS8073247B1Texturing/coloringCharacter and pattern recognitionReference databaseImaging processing
Motion picture scenes to be colorized / depth enhanced (2D->3D) are broken into separate elements, backgrounds / sets or motion / onscreen-action. Background and motion elements are combined into composite frame which becomes a visual reference database that includes data for all frame offsets used later for the computer controlled application of masks within a sequence of frames. Masks are applied to subsequent frames of motion objects based on various differentiating image processing methods, including automated mask fitting / reshaping. Colors and / or depths are automatically applied to masks throughout a scene from the composite background and to motion objects. Areas never exposed by motion or foreground objects in a series of images may be partially or fully realistically drawn or rendered and applied to the occluded areas of the background and then automatically applied throughout the images to generate of minimal artifact or artifact-free secondary viewpoints when translating foreground objects horizontally during 2D->3D conversion.
Owner:LEGEND FILMS INC
Distribution type laser spot alloying method
InactiveCN100417746CImprove wear performanceOvercoming temper softening problemsMetallic material coating processesLaser beam welding apparatusDepth enhancementAlloy
The invention relates to a distributed laser point-shaped alloying method that uses the small-hole effect caused by high power density laser effect to form mixing liquid bath by metal base and high performance alloy power sent by powder sending machine, the alloying point would be formed in the following rapid concreting. Controlling the laser beam processing point to point to form alloying points on the surface of the material, the distributed laser depth enhancement would be realized. The invention optimizes the alloying points and the distributing state to improve abrasion resistance of the surface, and the useful life of the component would be improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Vascular model extraction method based on depth neural network
ActiveCN109472807AReduced responseImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionDepth enhancement
The invention discloses a blood vessel model extraction method based on a depth neural network. The method comprises the following steps: 1. Blood vessel data is enhanced by T_Frangi algorithm according to the spatial scale theory so as to enhance the blood vessel data; 2, reserve candidate data; 3, calculate that characteristics of the blood vessel connection region; Step 4: Deep neural network training, using the tuple of blood vessel features as input to train the neural network, so as to obtain the blood vessel extraction model. The blood vessel model extraction method based on the depth neural network, In the candidate region of blood vessel after depth enhancement, Using the connectivity of blood vessels, the five-element feature set of each connected region is constructed, and the neural network model is trained to extract blood vessels. This method does not need to train the whole volume data, only needs to consider the calculation of candidate blood vessel connectivity regions. It can effectively remove the outliers, and has high extraction accuracy and flexibility.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
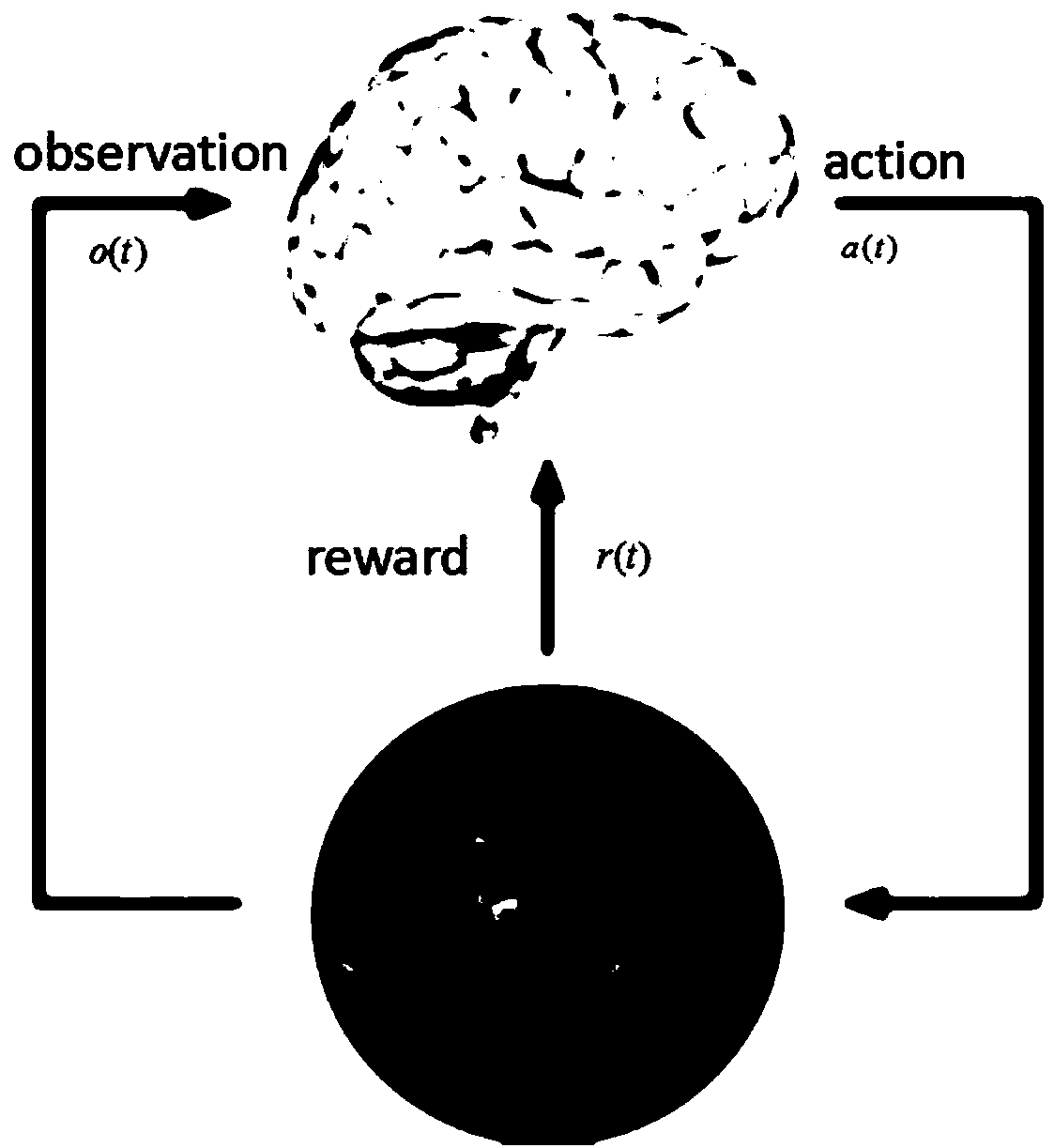
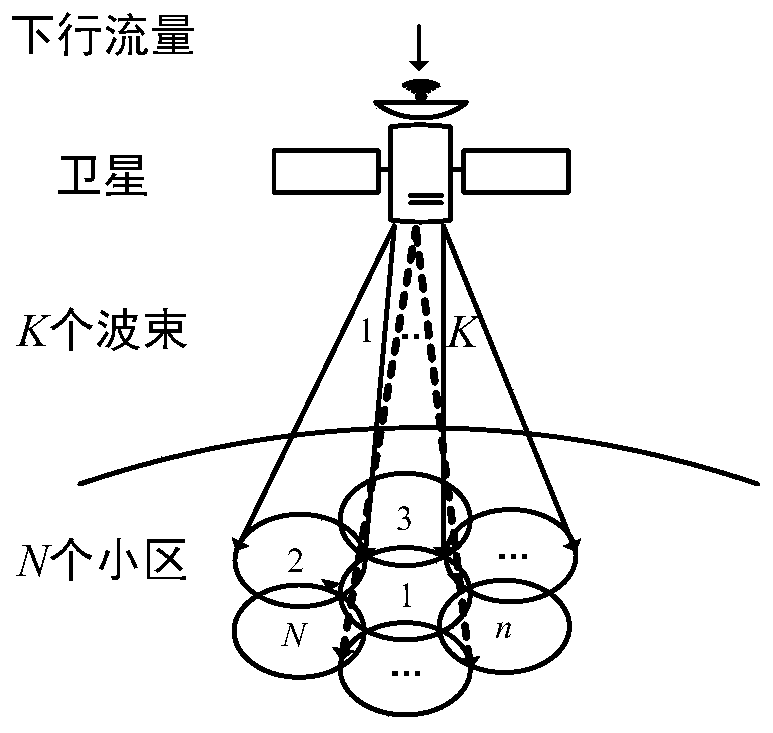
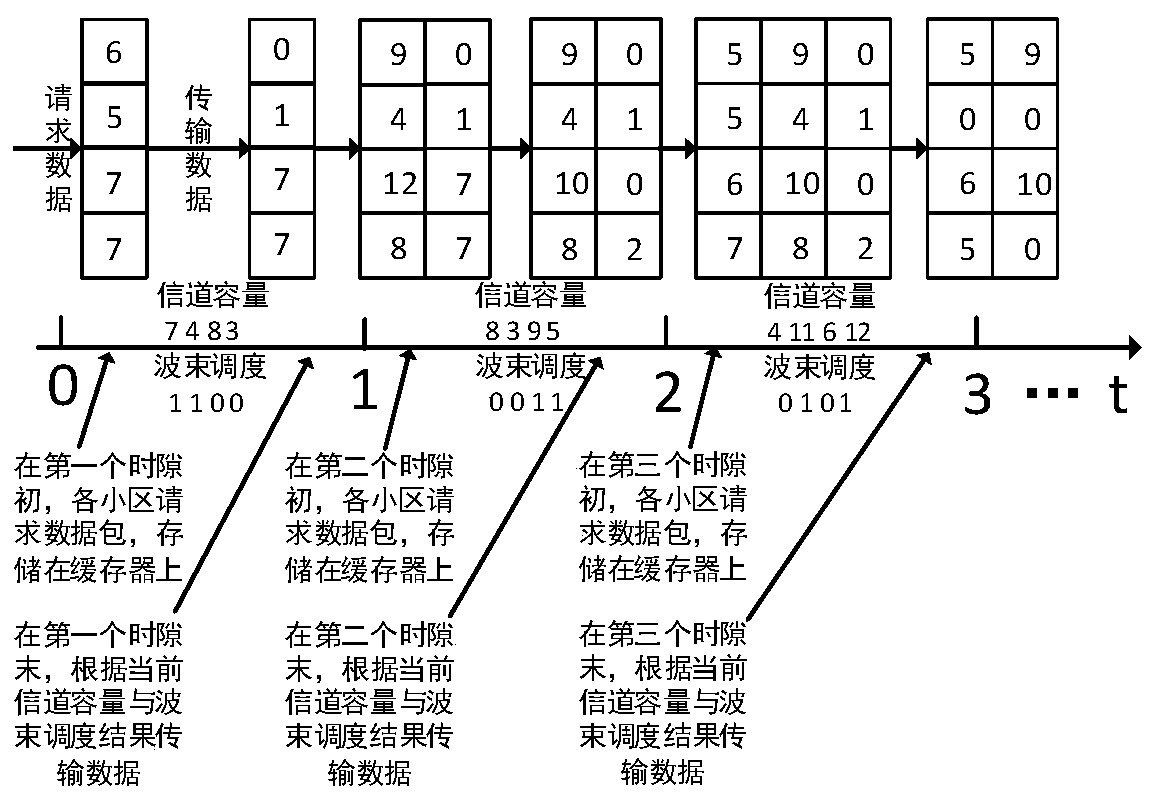
Dynamic beam scheduling method based on deep reinforcement learning
ActiveCN108966352BSpecific beam scheduling actionsWith online learning functionRadio transmissionWireless communicationDepth enhancementNetwork packet
The invention provides a dynamic beam scheduling method based on deep reinforcement learning, which belongs to the field of multi-beam satellite communication systems. The dynamic beam scheduling method comprises the steps of: firstly, modeling a dynamic beam scheduling problem into a Markov decision process, wherein states of each time slot comprise a data matrix, a delay matrix and a channel capacity matrix in a satellite buffer, actions represent a dynamic beam scheduling strategy, and a target is the long-term reduction of accumulated waiting delay of all data packets; and secondly, solving a best action strategy by utilizing a deep reinforcement learning algorithm, establishing a Q network of a CNN+DNN structure, training the Q network, using the trained Q network to make action decisions, and acquiring the best action strategy. According to the dynamic beam scheduling method, a satellite directly outputs a current beam scheduling result according to the environment state at the moment through a large amount of autonomous learning, maximizes the overall performance of the system in the long term, and greatly reduces the transmission waiting delay of the data packets while keeping the system throughput almost unchanged.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Depth enhancing screen
The present disclosure relates to a depth-enhancing screen for producing a simulated 3D image. The screen comprises a multi-curved Fresnel lens which when viewed in cross-section along the or each longest line linking two points on the edge of the lens, has a curved cross-section with an apex in the central region of the lens, and wherein each end of the curve flattens before it reaches the edge of the lens.
Owner:REALVIEW INNOVATIONS
Bit depth enhancement for scalable video coding
InactiveCN101459845BHigh coding efficiencyImprove coding efficiencyTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationDepth enhancementComputer graphics (images)
A video system includes an analyzer and a bit depth predictor. The analyzer receives a first coded video signal, which is indicative of first values for pixels. The first values are associated with a first bit depth. The analyzer, for each pixel, analyzes the first values for the pixels located in a neighborhood that contains said each pixel. The bit depth predictor, based at least in part on theanalysis, generates a second coded video signal that is indicative of second values for the pixels. The second values are associated with a second bit depth that is different than the first bit depth.
Owner:INTEL CORP
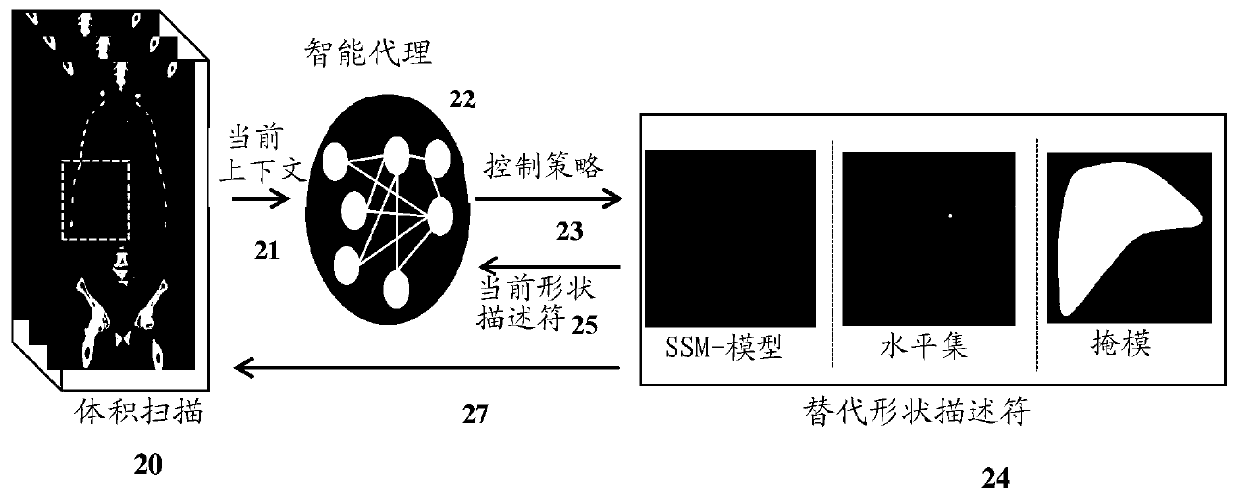
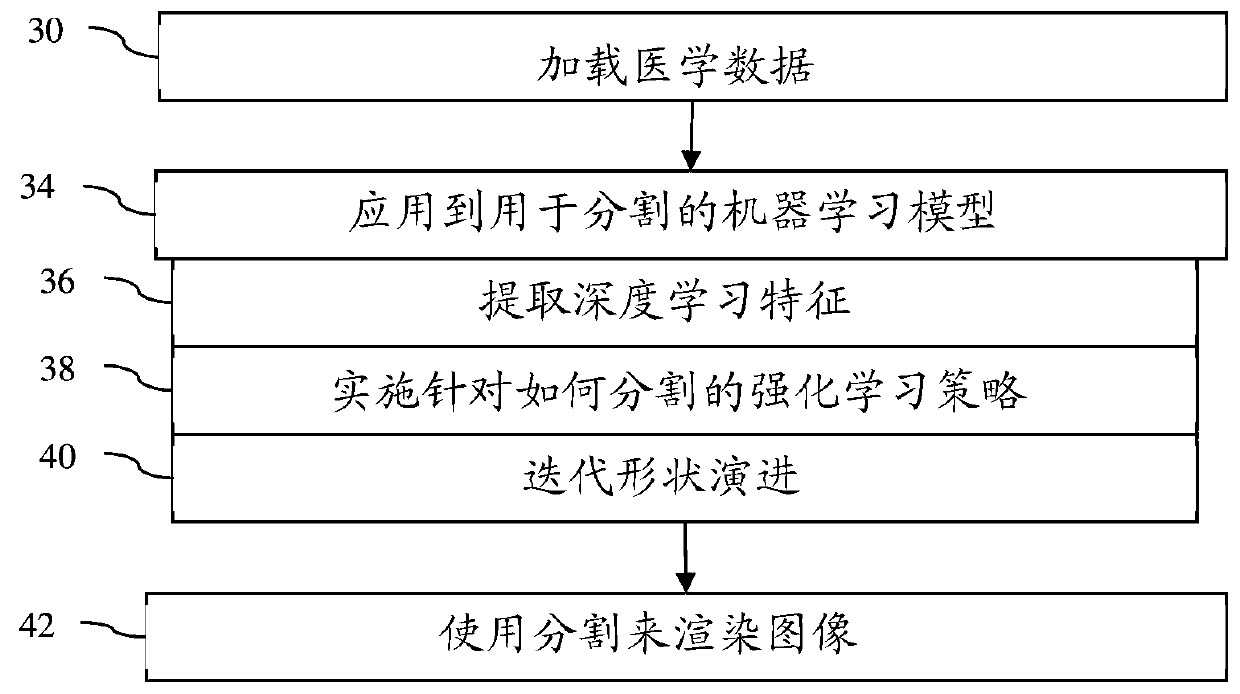
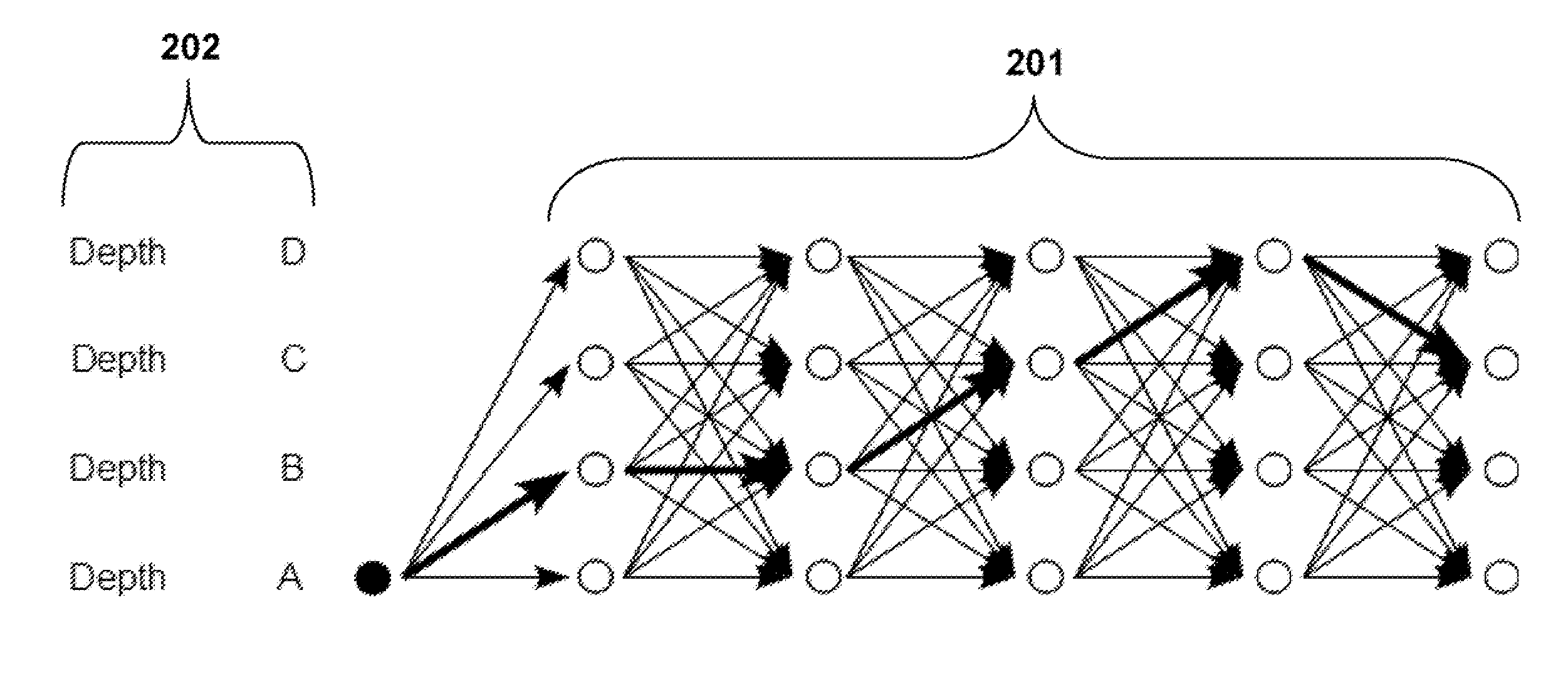
Multiscale deep reinforcement machine learning for n-dimensional segmentation in medical imaging
Multiscale deep reinforcement machine learning for N-dimensional segmentation in medical imaging. Multiscale deep reinforcement learning produces multiscale deep reinforcement models for multidimensional (e.g., 3D) segmentation of objects (22). In this context, segmentation is formulated as learning an image-driven policy (38) for shape evolution (40) that converges to object boundaries. This segmentation is treated as a reinforcement learning problem, and scale-space theory is used to achieve robust and efficient multi-scale shape estimation. The learning challenge of end-to-end regression systems can be addressed by learning an iterative strategy to find segmentations.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method for enhancing depth images of scenes using trellis structures
InactiveUS8994722B2Reduce artifactsQuality improvementCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingDepth enhancementLeast cost
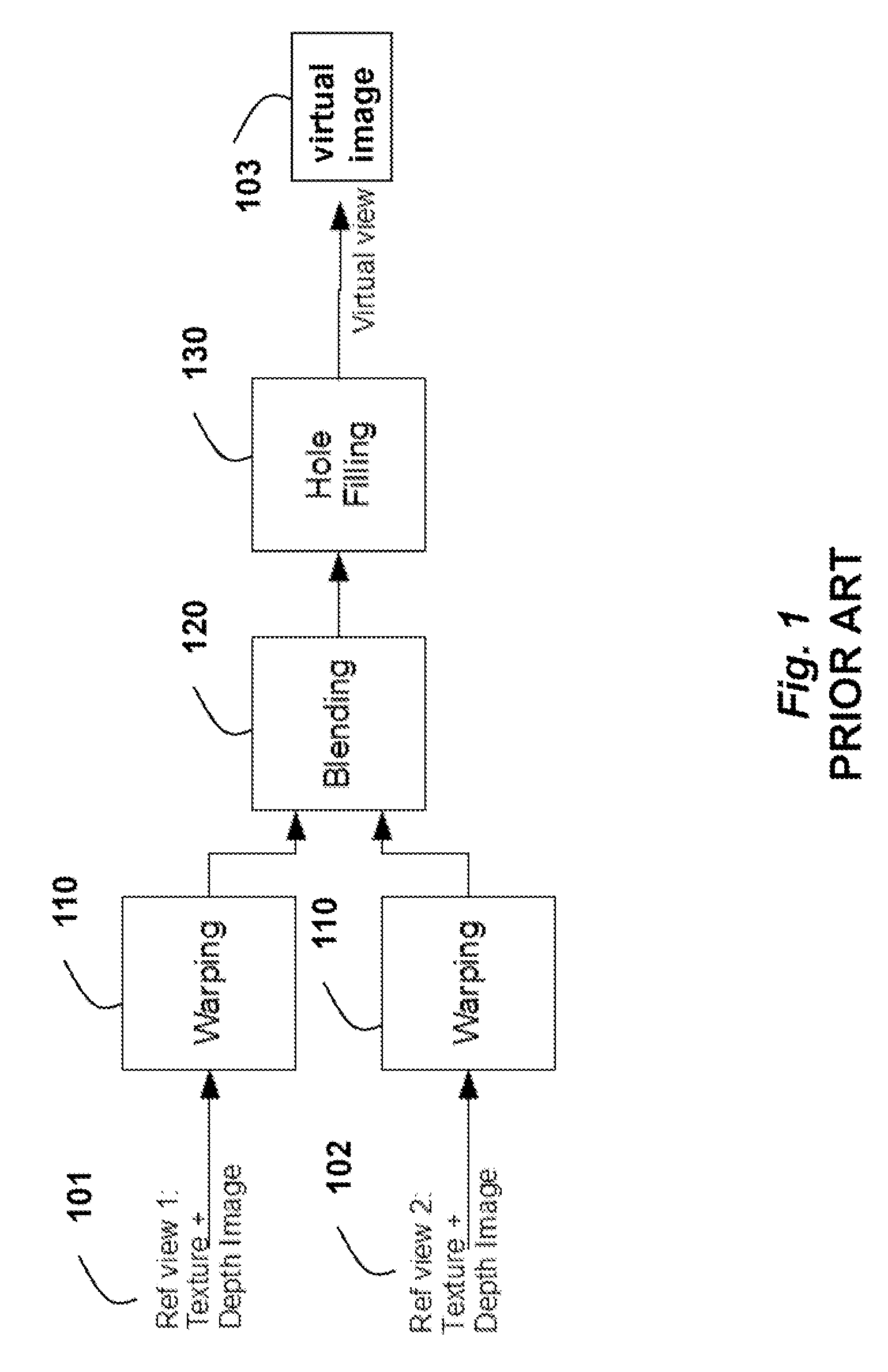
An image for a virtual view of a scene is generated based on a set of texture images and a corresponding set of depth images acquired of the scene. A set of candidate depths associated with each pixel of a selected image is determined. For each candidate depth, a cost that estimates a synthesis quality of the virtual image is determined. The candidate depth with a least cost is selected to produce an optimal depth for the pixel. Then, the virtual image is synthesized based on the optimal depth of each pixel and the texture images. The method also applies first and second depth enhancement before, and during view synthesis to correct errors or suppress noise due to the estimation or acquisition of the dense depth images and sparse depth features.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Texture-based depth boundary correction method
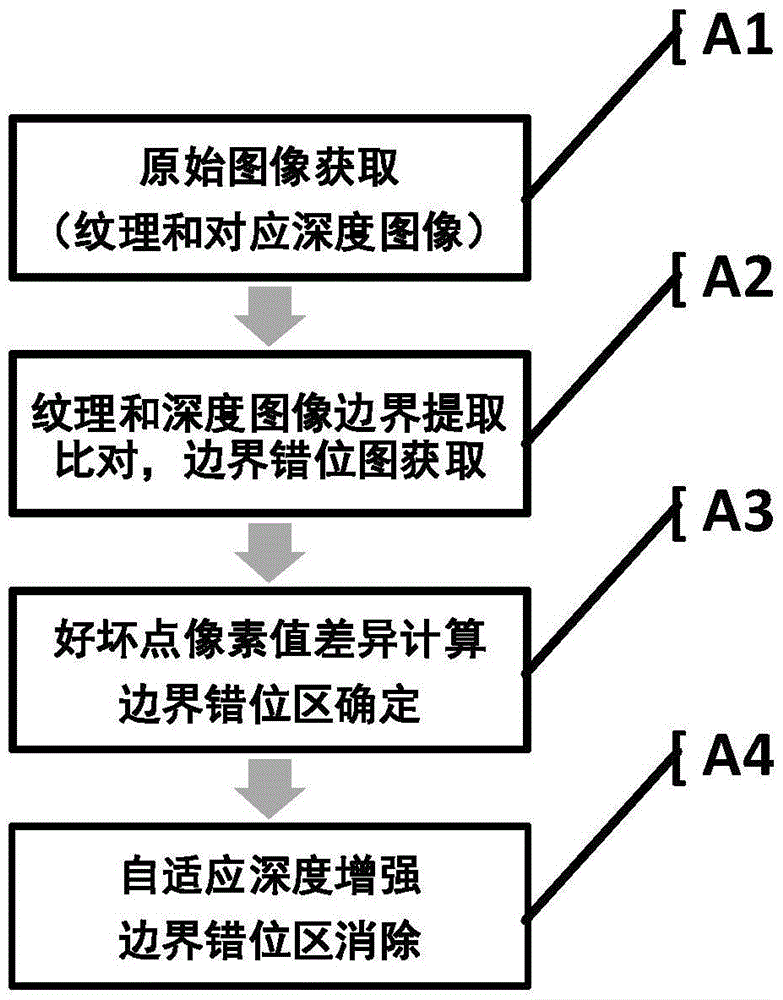
ActiveCN105678765AIncrease depth-weighted meanGuaranteed robustnessImage enhancementImage analysisTime domainDepth enhancement
The present invention relates to a texture-based depth boundary correction method. The method comprises the steps of A1, inputting a texture image and a corresponding depth image, wherein the images are acquired by a depth sensor (such as a Kinect); A2, extracting the boundary of the texture image and the boundary of the depth image, and acquiring a depth boundary dislocation figure with the boundary of the texture image as the reference; A3, calculating the pixel value difference between an accurate depth point (sweet spot) and an error depth point (dead point) and determining a boundary dislocation area; A4, according to the distribution characteristics of the boundary dislocation area, adaptively determining the side length of a square window for depth enhancement processing, correcting the depth of the dead point in the window, eliminating the boundary dislocation area. According to the invention, the accuracy and the time-domain stability of the boundary of the depth image, acquired by the Kinect and other low-end depth sensors, are significantly improved. The method is applied to the fields of three-dimensional reconstruction, free viewpoint video coding and the like, and can effectively improve the scene three-dimensional reconstruction quality and the coding efficiency.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF FUTURE MEDIA TECH +1
A Resampling Method Based on Depth Enhancement for 3D Video Coding
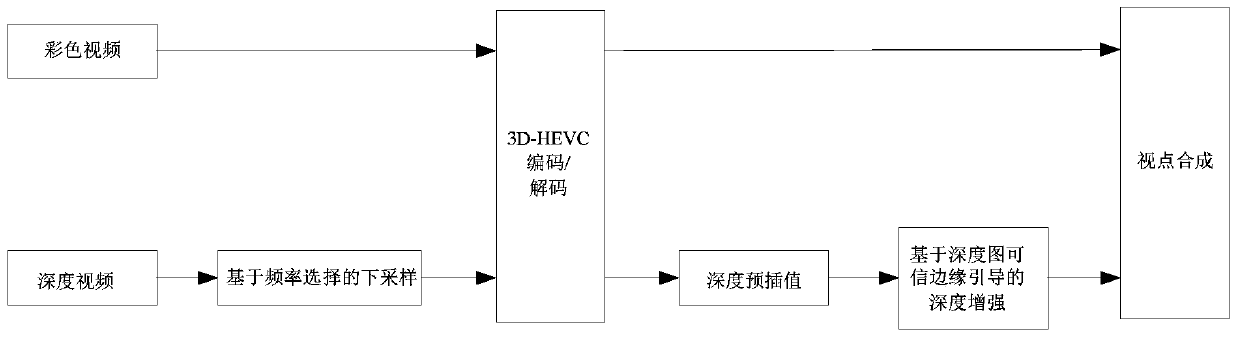
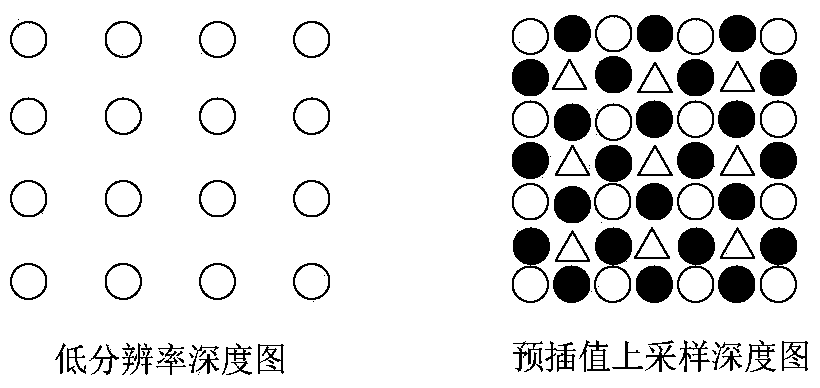
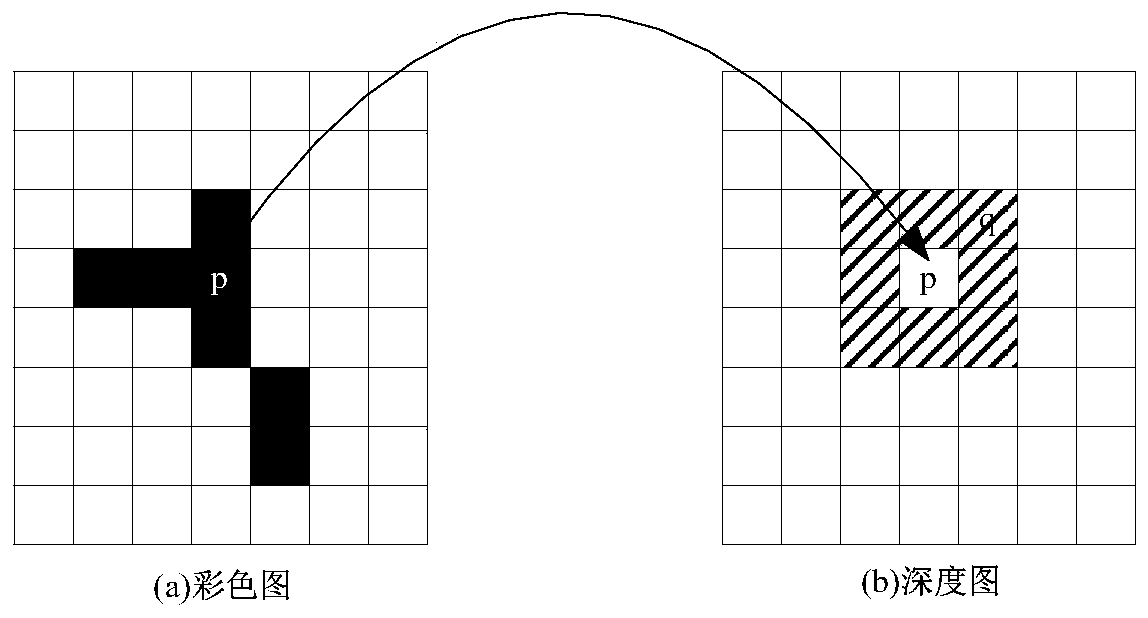
ActiveCN105635742BRestoring and Preserving Edge FeaturesQuality improvementDigital video signal modificationDepth enhancementViewpoints
The invention relates to a depth-enhancement-based resampling method facing 3D video coding. The method comprises: a color video is coded according to an original resolution ratio and resolution-rate reduction coding is carried out on a depth ratio; downsampling is carried out on the depth video by using a frequency-selection-based method before depth video coding, and for the decoded depth ratio, a depth video with an original resolution rate is generated by using a pre interpolation method and then upsampling is carried out on the depth video by using a depth enhancement method based on depth graph trusted edge guiding; and a view-point synthesis is carried out on the color video obtained by decoding and the upsampling depth video to obtain a needed multi-viewpoint video. With the method, distortion of resampling depth video during the 3D video coding and decoding processes can be reduced; the depth video edge is protected; and the quality of the synthesized viewpoint is improved.
Owner:XIAMEN TONGJING INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
A 3D image registration method for AR system
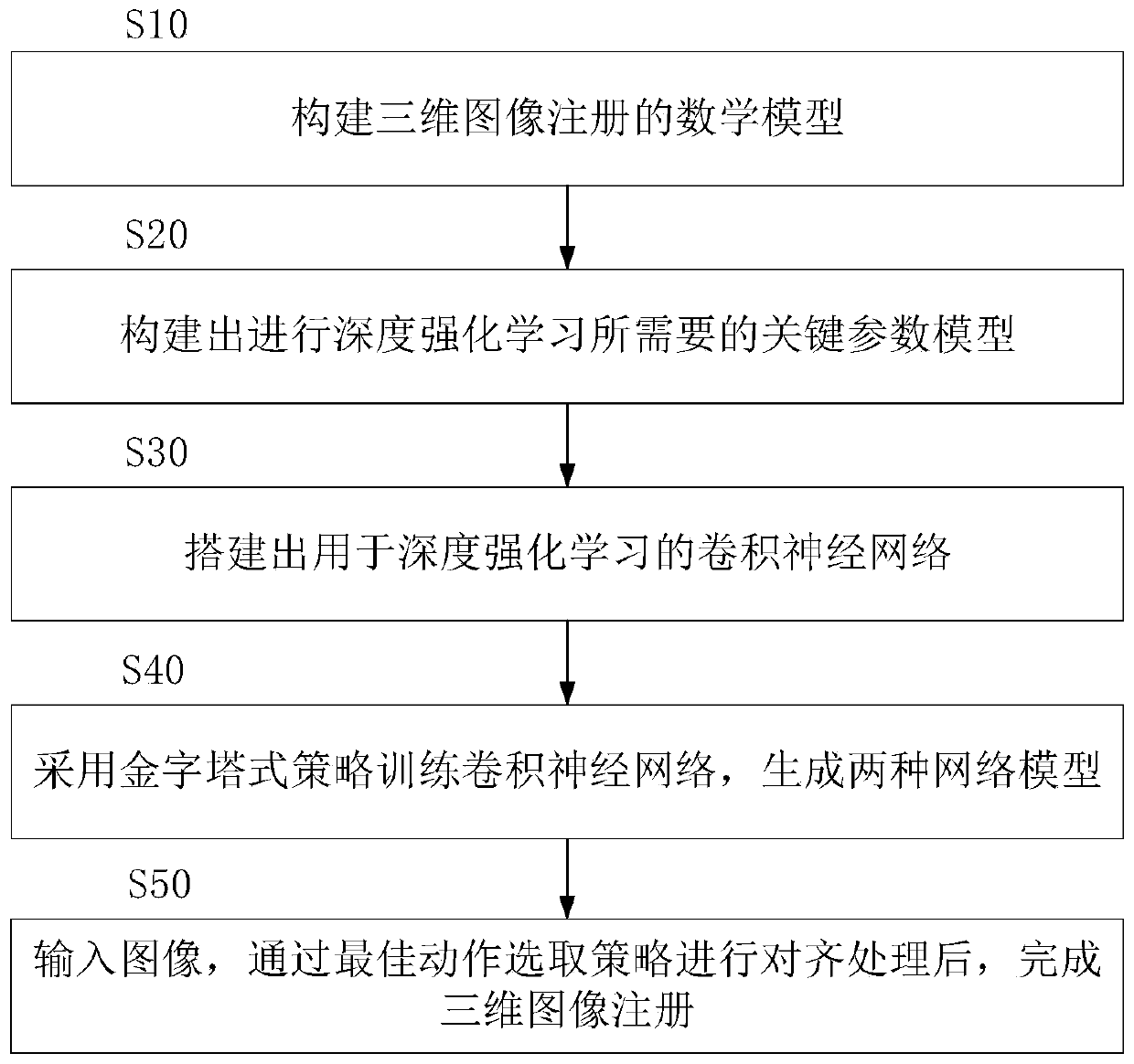
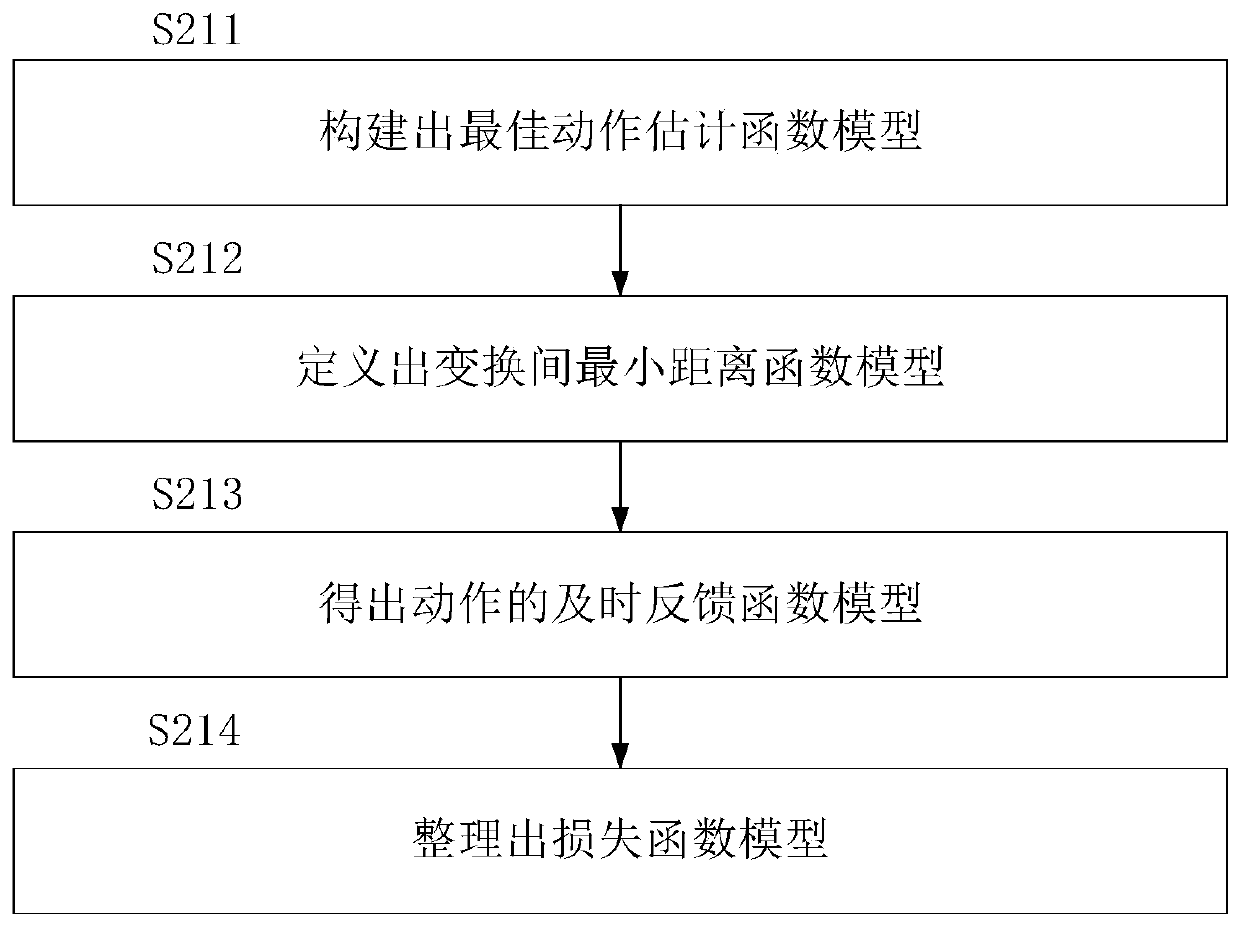
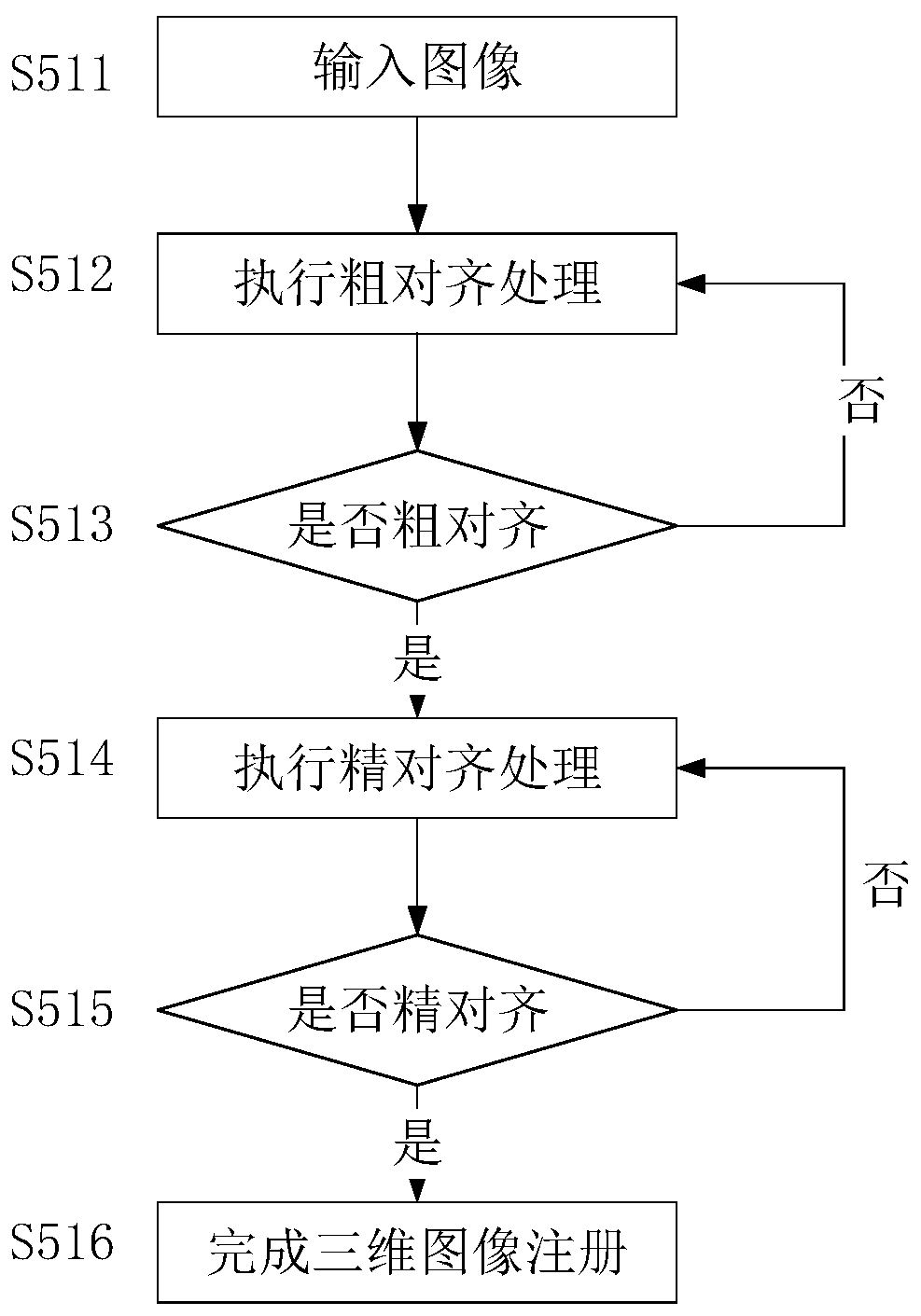
InactiveCN108460829BGuaranteed accuracyEasy alignmentCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesDepth enhancement3d image
The invention discloses a three-dimensional image registration method for an AR system. The "estimation" of the best action of the reference image; the convolutional neural network training is performed on the sample image using a pyramid strategy, and two network models are generated for coarse alignment and fine alignment; the input scene image and the target image are used, and the key parameter model and The two network models perform coarse alignment and fine alignment respectively to complete 3D image registration. The present invention, based on the registration strategy of deep reinforcement learning, defines the three-dimensional image registration problem as a series of continuous actions to achieve image alignment and operation, and finds the best action in a limited solution to improve the alignment effect, which can ensure that The globally optimal alignment parameters ensure the accuracy of 3D image registration.
Owner:广州智能装备研究院有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com