A 3D image registration method for AR system
A technology of 3D images and reference images, which is applied in image data processing, instruments, biological neural network models, etc., can solve the problems that the accuracy of 3D image registration cannot be guaranteed, so as to reduce training time, improve efficiency, ensure stability and The effect of precision
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
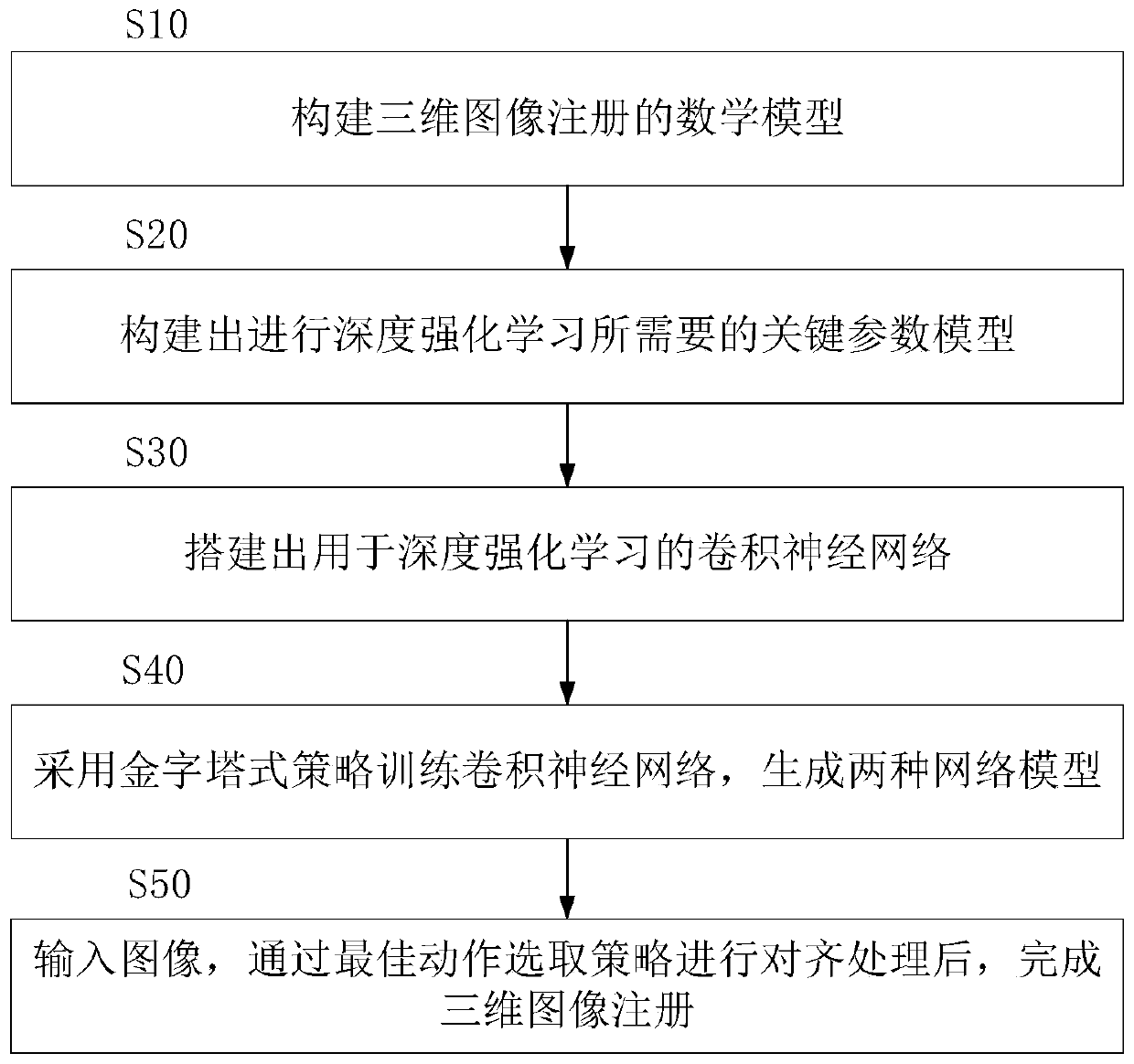
[0045] Such as figure 1 As shown, the three-dimensional image registration method for the AR system provided in Embodiment 1 of the present invention includes the following steps:
[0046] Step S10, constructing a mathematical model T(t of three-dimensional image registration x ,t y ,t z ,θ x ,θ y ,θ z ):
[0047]
[0048] Where: parameter t x ,t y ,tz Indicates the translation amount of the 3D image along the x, y, z axes, θ x ,θ y ,θ z Indicates the rotation angle of the 3D image along the x, y, and z axes;
[0049] The foundation of the mathematical model is as follows:
[0050] Order I r Denotes a reference image or a target image, I f Indicates the need to register with the I r random image (registration image), then T g is a 4×4 homogeneous transformation matrix, representing the transformation matrix that needs to be estimated (that is, the direct means to realize 3D image registration), the purpose of this mathematical model is to obtain T g × I f ...
specific Embodiment 2
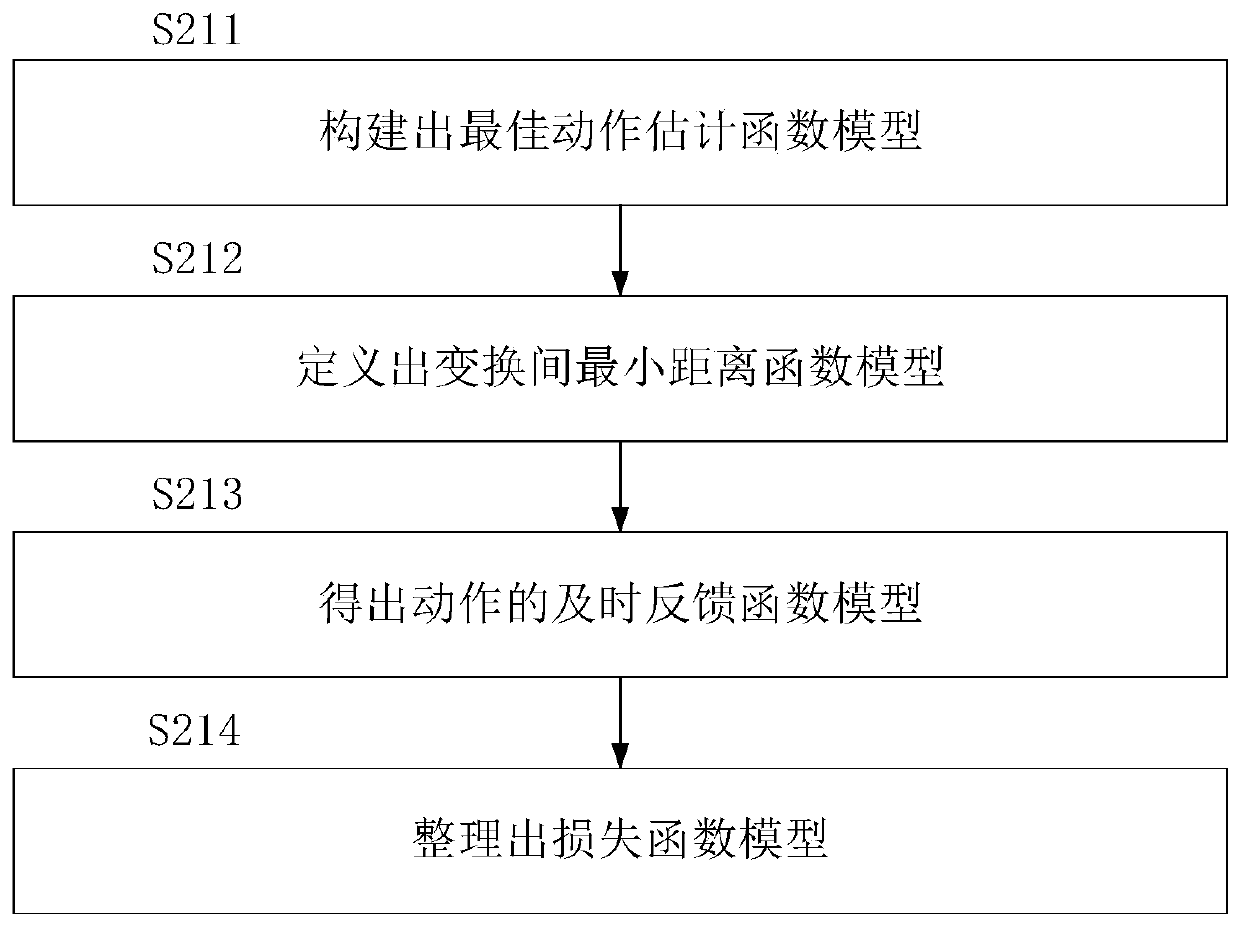
[0069] This specific embodiment 2 is a specific refinement of the four key parameter models constructed in step S20, thereby constructing the action estimation function model required for deep learning and the key parameter model required for training.
[0070] Such as figure 2 As shown, in this embodiment, step S20 specifically includes the following steps:
[0071] Step S211, constructing an optimal motion estimation function model;
[0072] Step S212, defining a minimum distance function model between transformations;
[0073] Step S213, obtain the timely feedback function model of the action;
[0074] Step S214, sort out the loss function model.
[0075] The core problem of 3D image registration is to find an optimal action execution strategy to command the intelligent agent to make decisions.
[0076] In the present invention, at first obtain the best action estimation function model according to the Bellman equation:
[0077] Q t (s t ,a t ) = max τ E[r t +γr ...
specific Embodiment 3
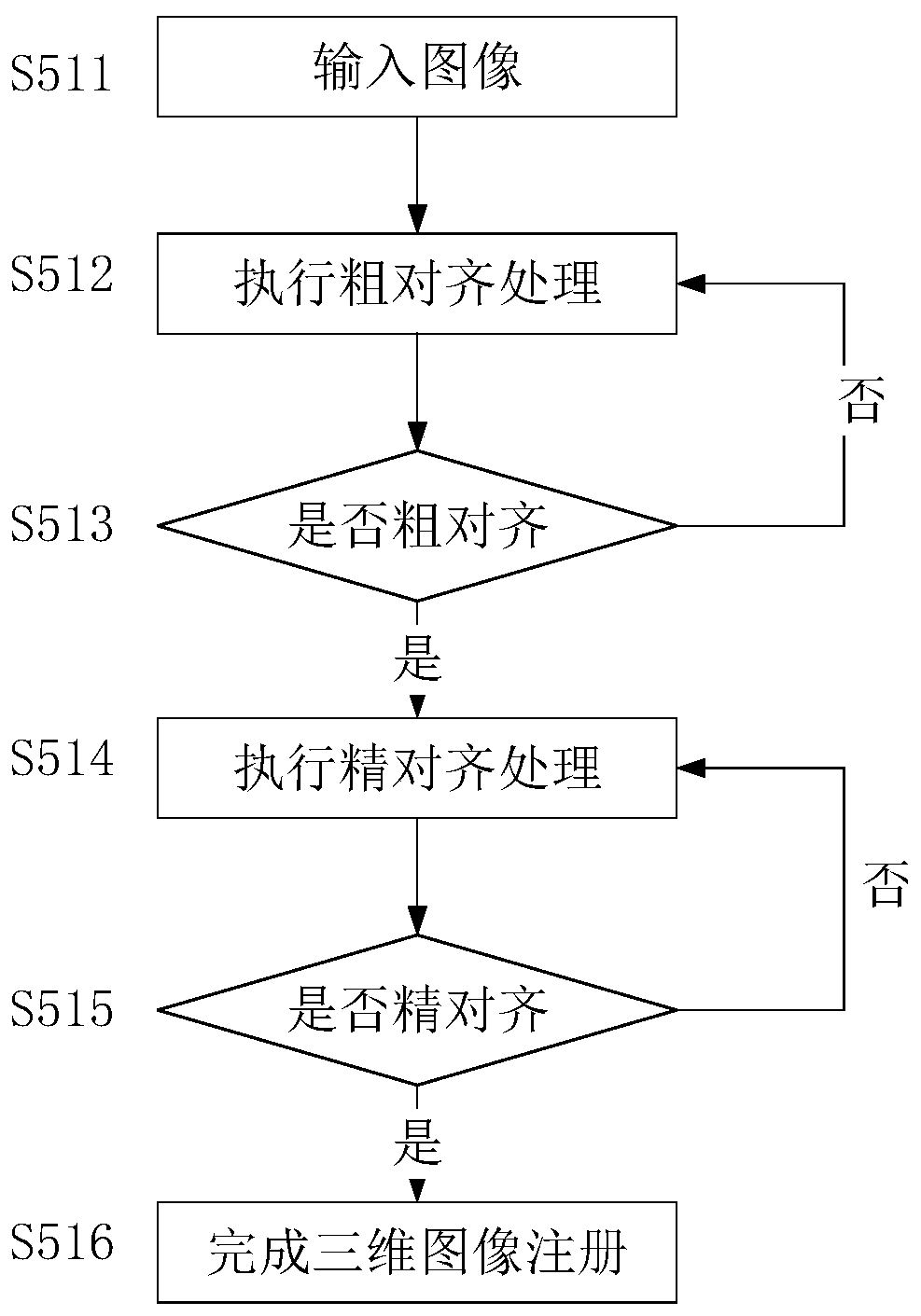
[0095] Such as image 3 As shown, in this embodiment, step S50 specifically includes the following steps:
[0096] Step S511, input image;
[0097] Step S512, performing coarse alignment processing;
[0098] Step S513, judging whether the coarse alignment is successful, if the coarse alignment is successful, go to step S514, otherwise go to step S512;
[0099] Step S514, perform fine alignment processing;
[0100] Step S515, judging whether the fine alignment is successful, if successful, go to step S516, otherwise go to step S514;
[0101] Step S516, completing the three-dimensional image registration.
[0102] Fine alignment is carried out starting from the last action position of the coarse alignment. Firstly, the coarse alignment and then the fine alignment can quickly converge to obtain the 3D registration result of the current image, which gradually improves the 3D registration accuracy and efficiency of the image in the present invention, which is different from the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com