Media servowriting system
a technology of servowriters and media, applied in the direction of maintaining head carrier alignment, recording information storage, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of previously available systems, inability to support custom read/write heads, and system performance issues of previous available servowriters
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
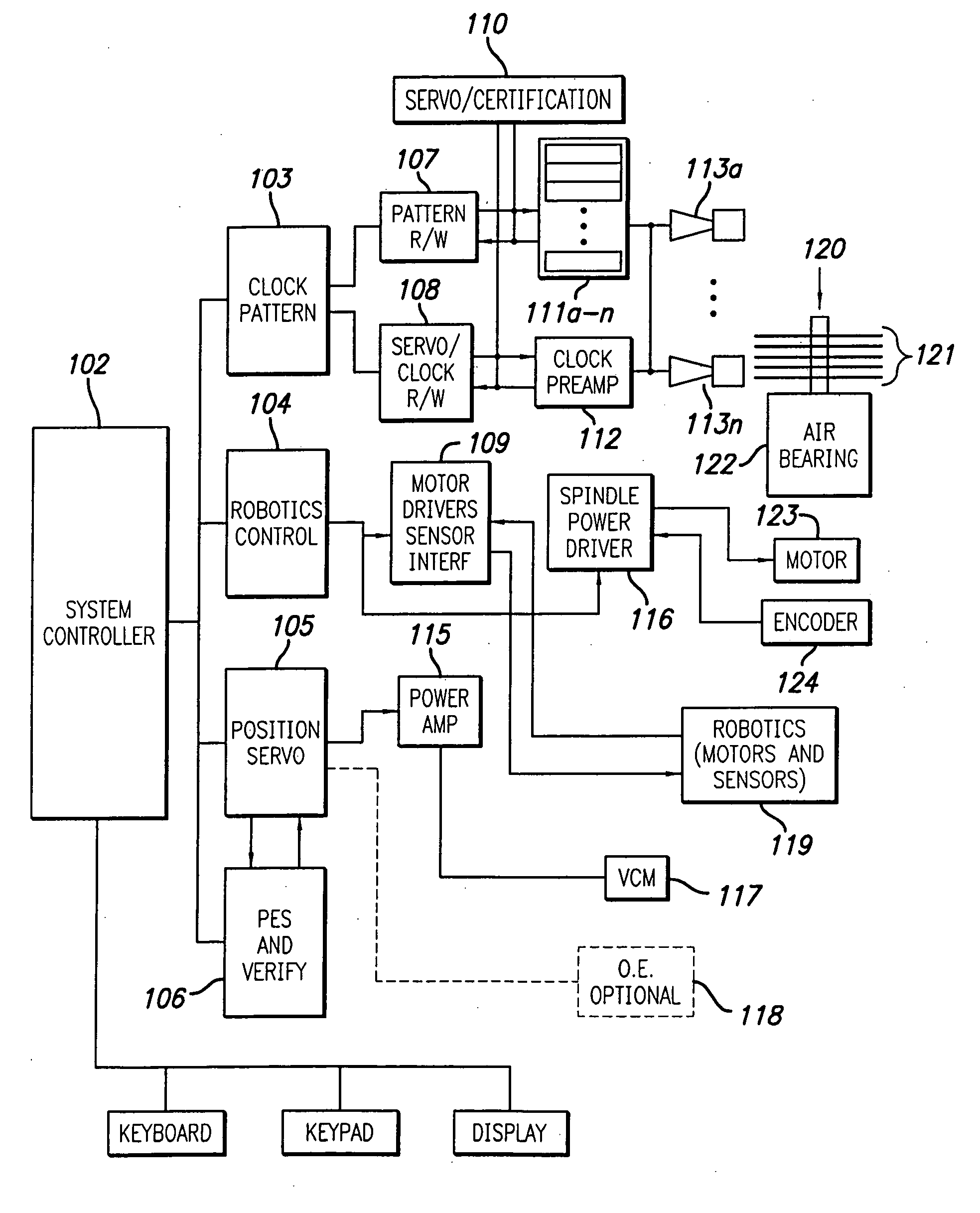
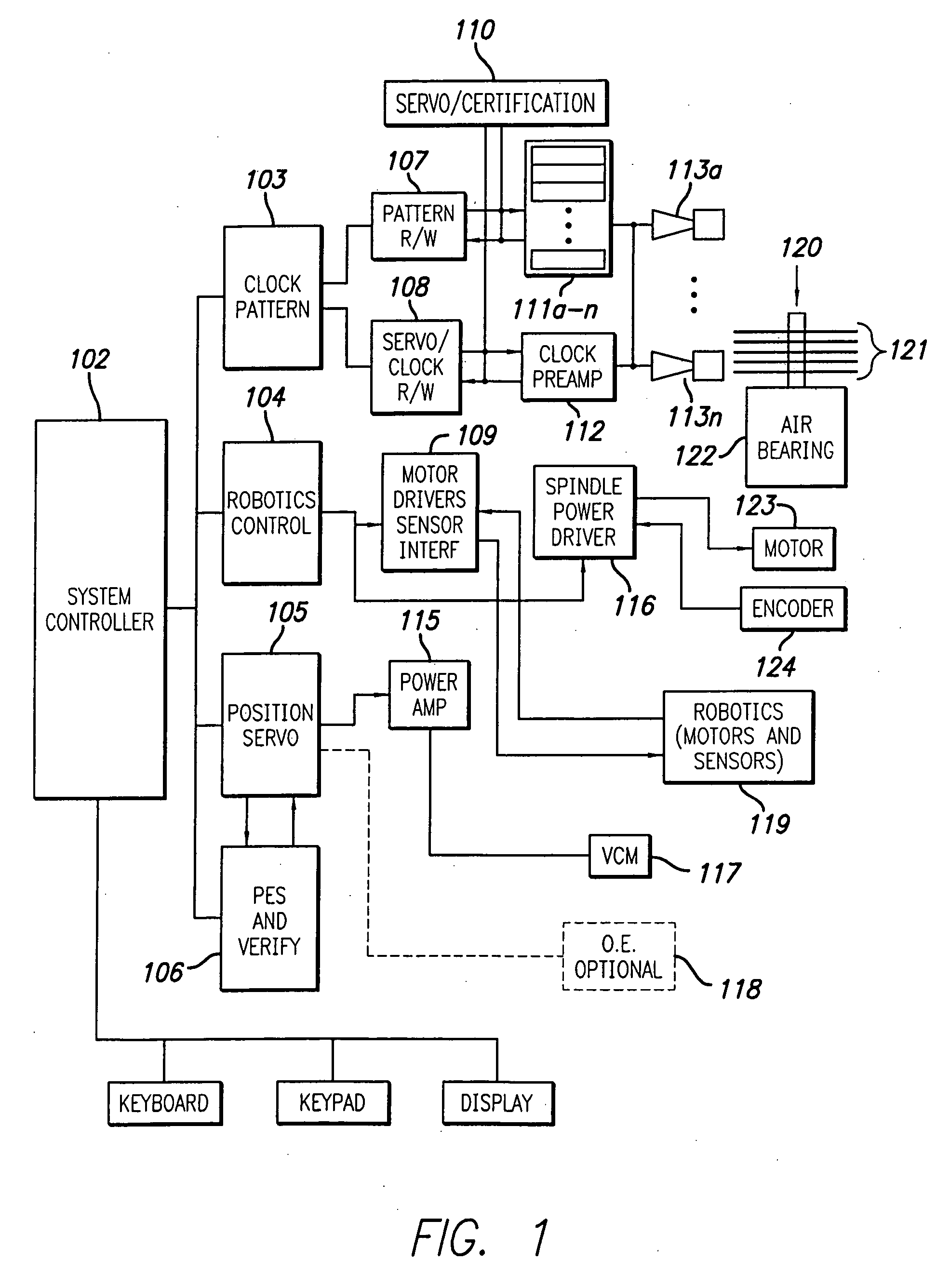
[0093] According to the present invention, there is provided an enhanced media servowriter having several aspects constituting improvements over previously known designs. An aspect of the present invention is a system and method for tracking disk and spindle position, typically in a multiple media disk arrangement, whereby data from the disks or spindle are fed back to hardware and / or software to compensate for position errors during reading and / or writing to the media.
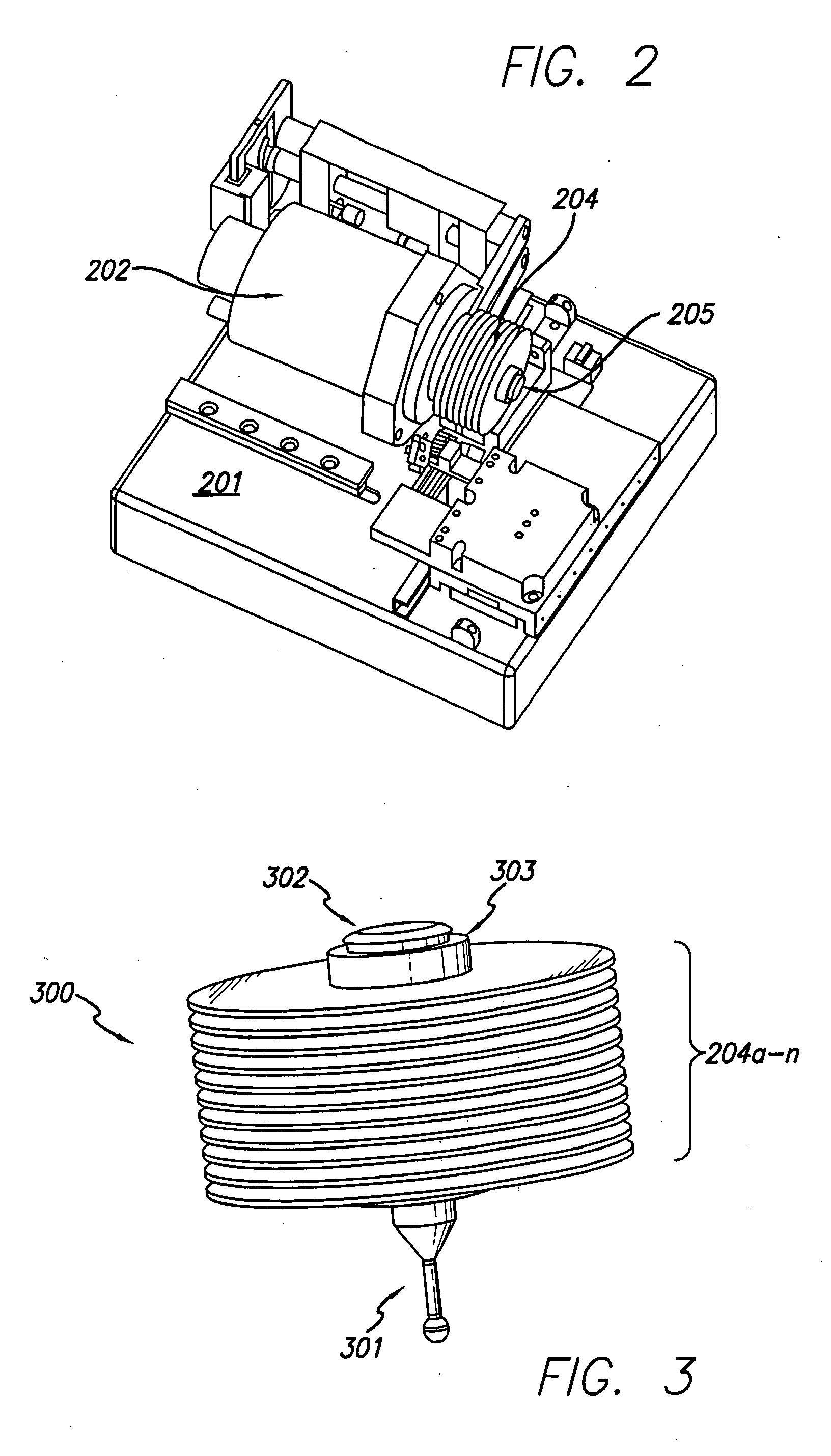
[0094] In a particular aspect of the present invention, a non-contact radiation detection system cooperates with an ideal disk produced using patterning technology to detect movement of disks mechanically coupled to a spindle. The system further utilizes an ideal magnetic disk to detect movement of disks mechanically coupled to a spindle. Further, the system and method disclosed herein detect spindle and disk (or disks) movement with respect to a common base by detecting radiation reflected by a rotating part of the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| distances | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com