Methods for preventing fixed pattern programming
a technology of fixed pattern and programming method, which is applied in the direction of read-only memories, instruments, and static storage, etc., can solve the problems of long erase time and lower performanc, over-erased cells may become leaky, and over-erased cells may become difficult to program, so as to prevent fixed pattern programming and prevent large differences in program.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
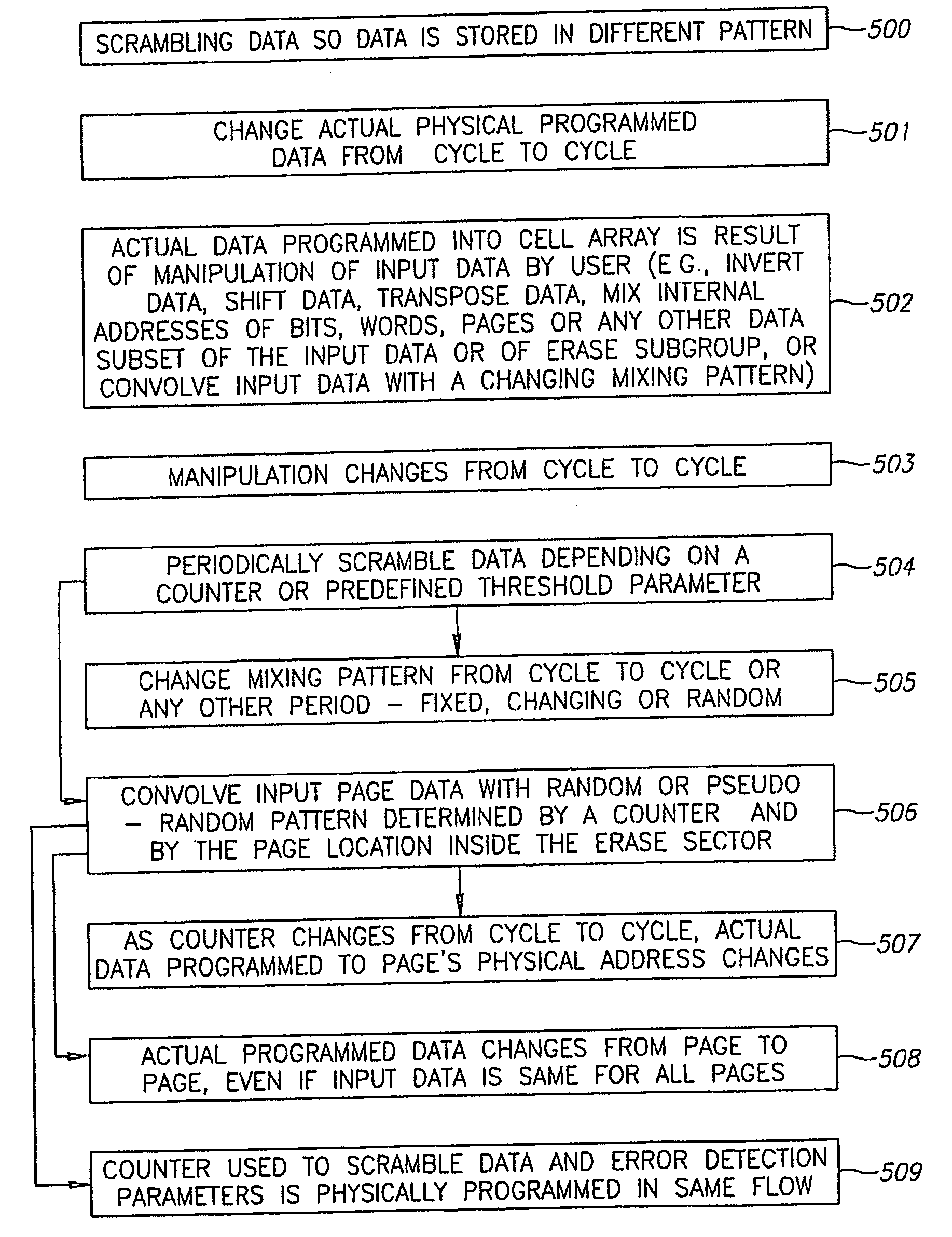
[0026] Reference is now made to FIG. 5, which illustrates a method for preventing fixed pattern programming in a non-volatile memory cell array, in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention. Specifically, FIG. 5 is a simplified flow chart of the programming flow in a data scrambling implementation, as is now explained.
[0027] In accordance with an embodiment of the present invention, after programming data into a pattern of memory cells in a memory array, fixed pattern programming is prevented by periodically scrambling the data so that the data is stored in a different pattern of memory cells in the memory array (step 500). In a non-limiting embodiment of the present invention, the actual physical programmed data is forced to change from cycle to cycle (step 501). Thus the rate at which systematic differences can develop, due to fix pattern programming, may be substantially reduced. The actual data programmed into the cell array may be a result of a manipulation of the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com