Write precompensation method for perpendicular magnetic recording
a perpendicular magnetic and precompensation technology, applied in the direction of magnetic recording, recording/reproducing/erasing methods, digital recording, etc., can solve the problems of limiting the data recording rate of the disk drive, standardized lengths of the regions in which data bits are written, and errors in reading data from the disk
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
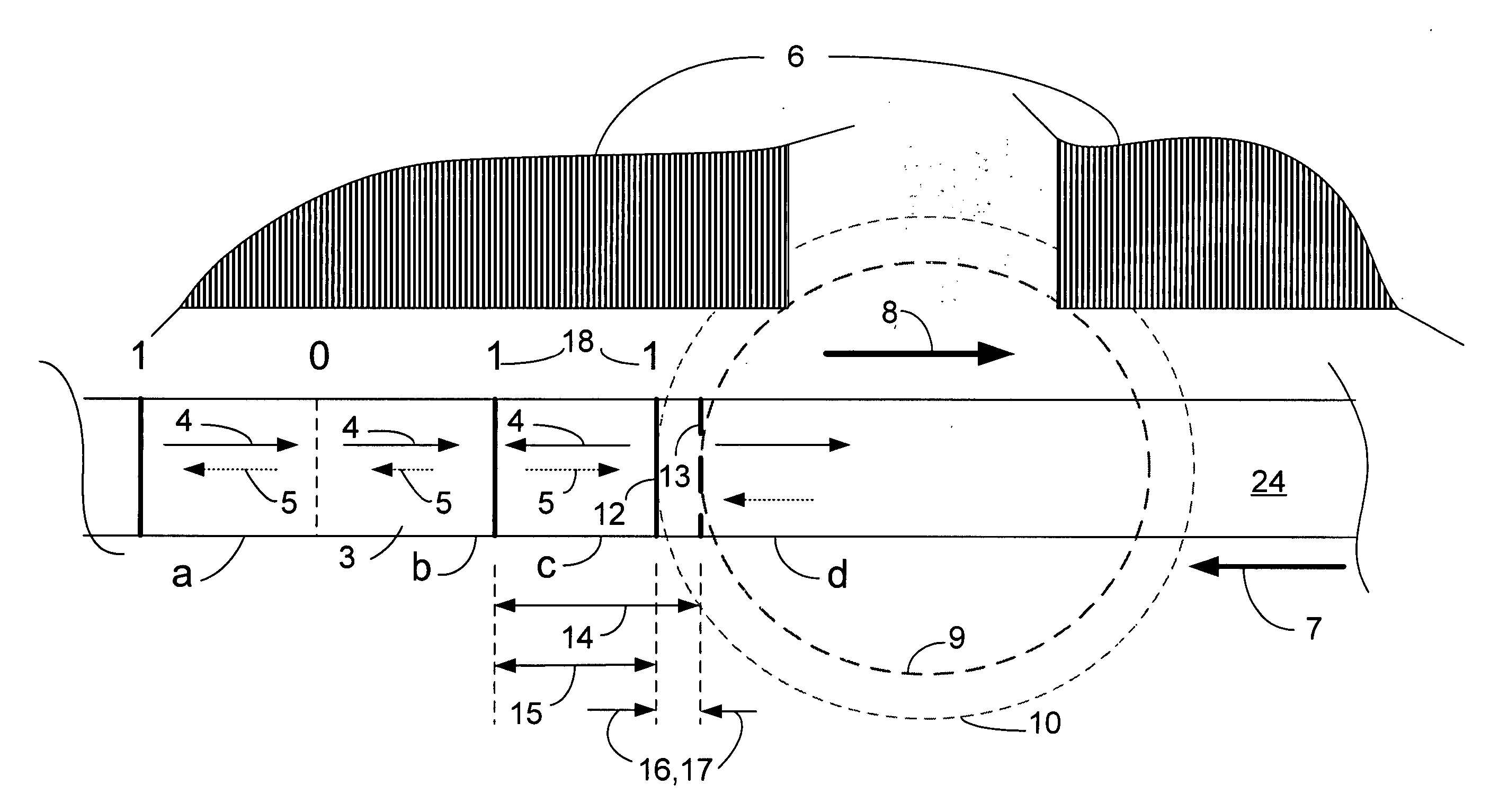
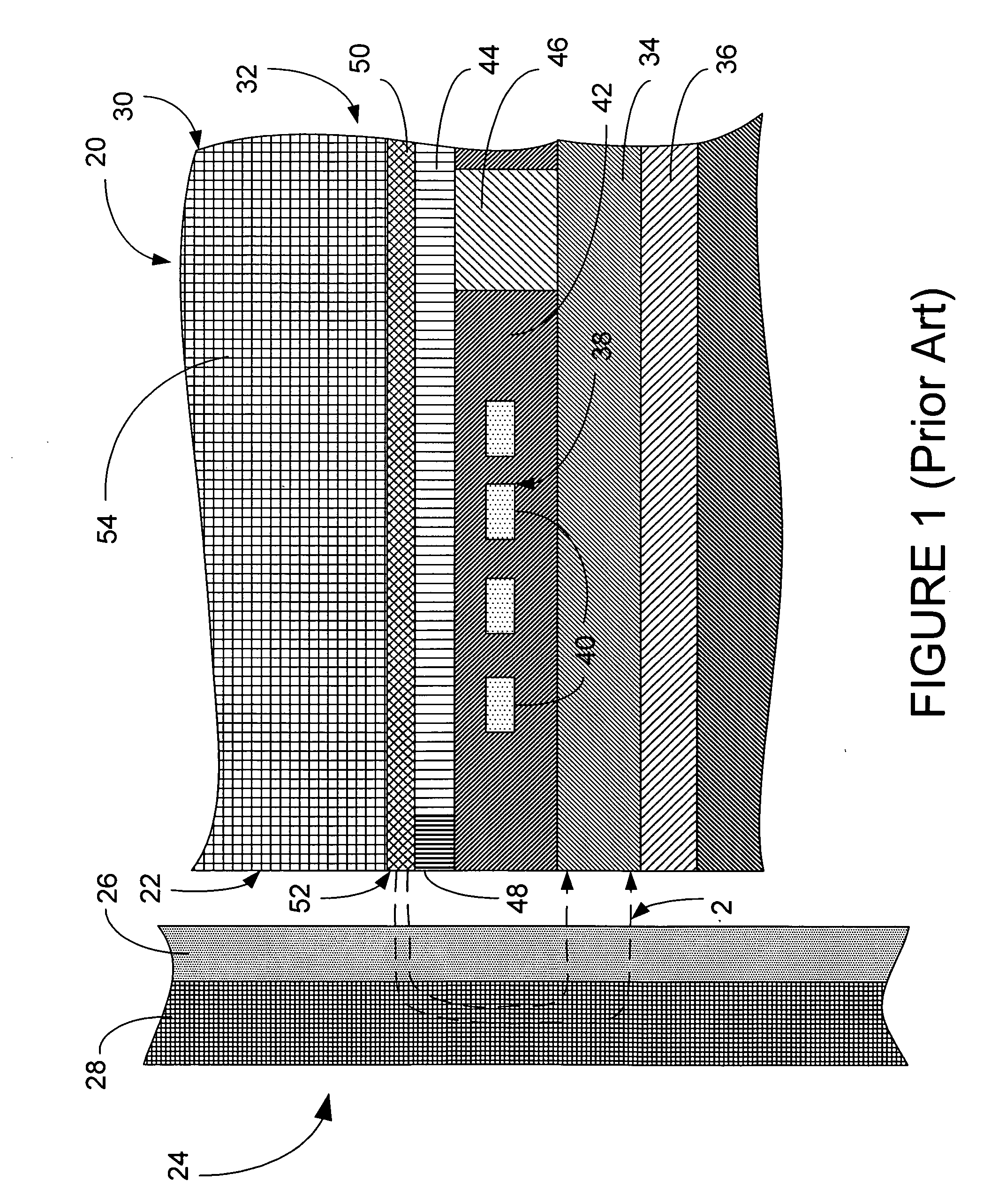
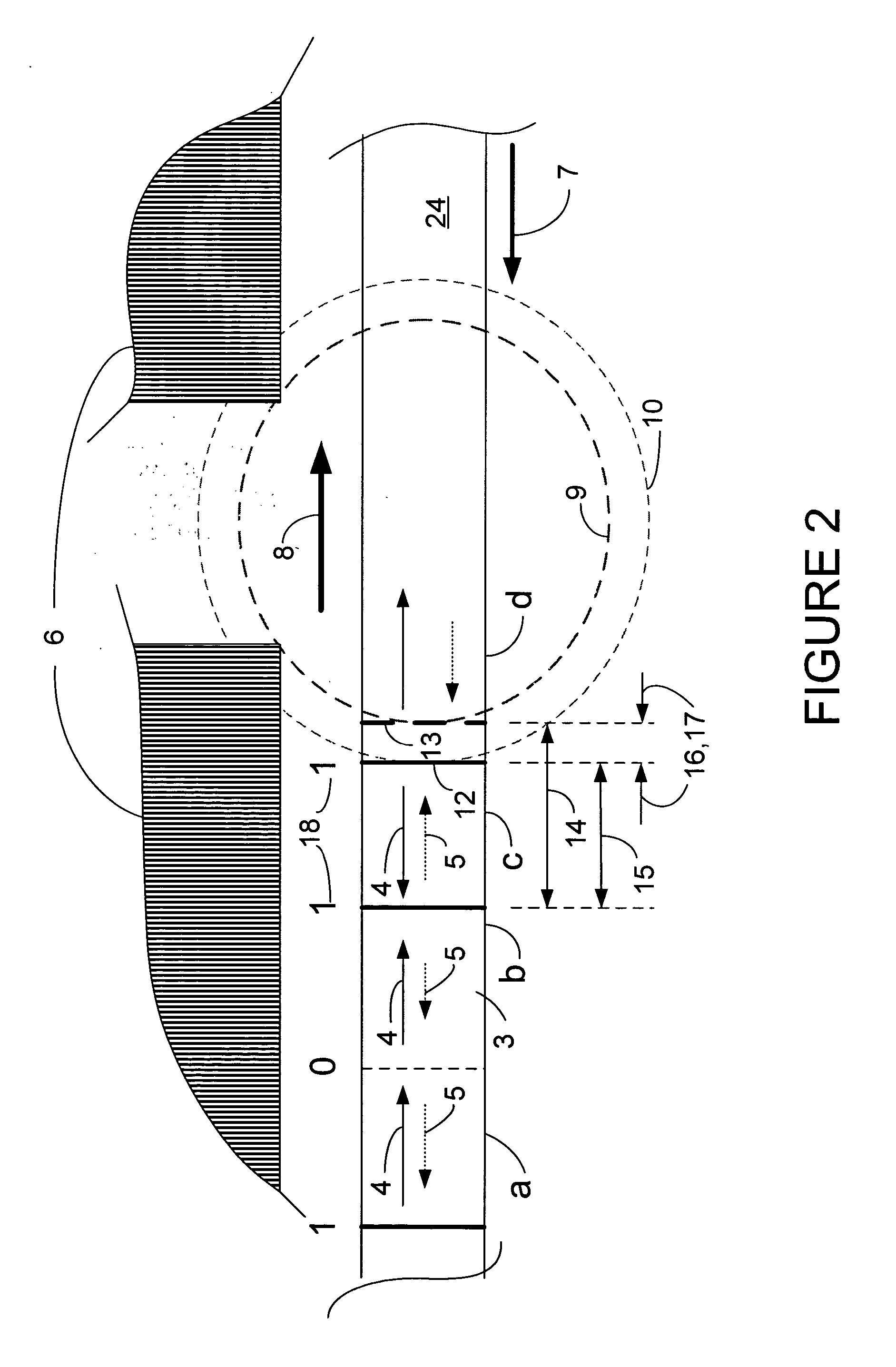
[0043]FIG. 1 (prior art) is a side cross-sectional diagram of the write head portion of a typical prior art perpendicular magnetic head. A slider 20 has an air bearing surface (ABS) 22 which flies above the surface of a hard disk 24. The disk 24 includes a high coercivity magnetic layer, also referred to as the hard layer 26, that is fabricated on top of a magnetically soft layer 28.
[0044] The perpendicular head 30 typically includes a read head, which is not shown here. The write head portion, includes a first magnetic pole P134 is fabricated upon an insulation layer 36. An induction coil structure 38, which includes coils 40, is fabricated upon the P1 pole 34. The coil turns 40 are typically formed within electrical insulation layers 42. A second magnetic pole layer, typically termed a P2 shaping layer 44, is fabricated on top of the induction coil structure 38. A magnetic back gap piece 46 joins the back portions of the P1 pole 34 and the P2 shaping layer 44, such that magnetic ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| magnetic polarity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| track density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| magnetic field | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com