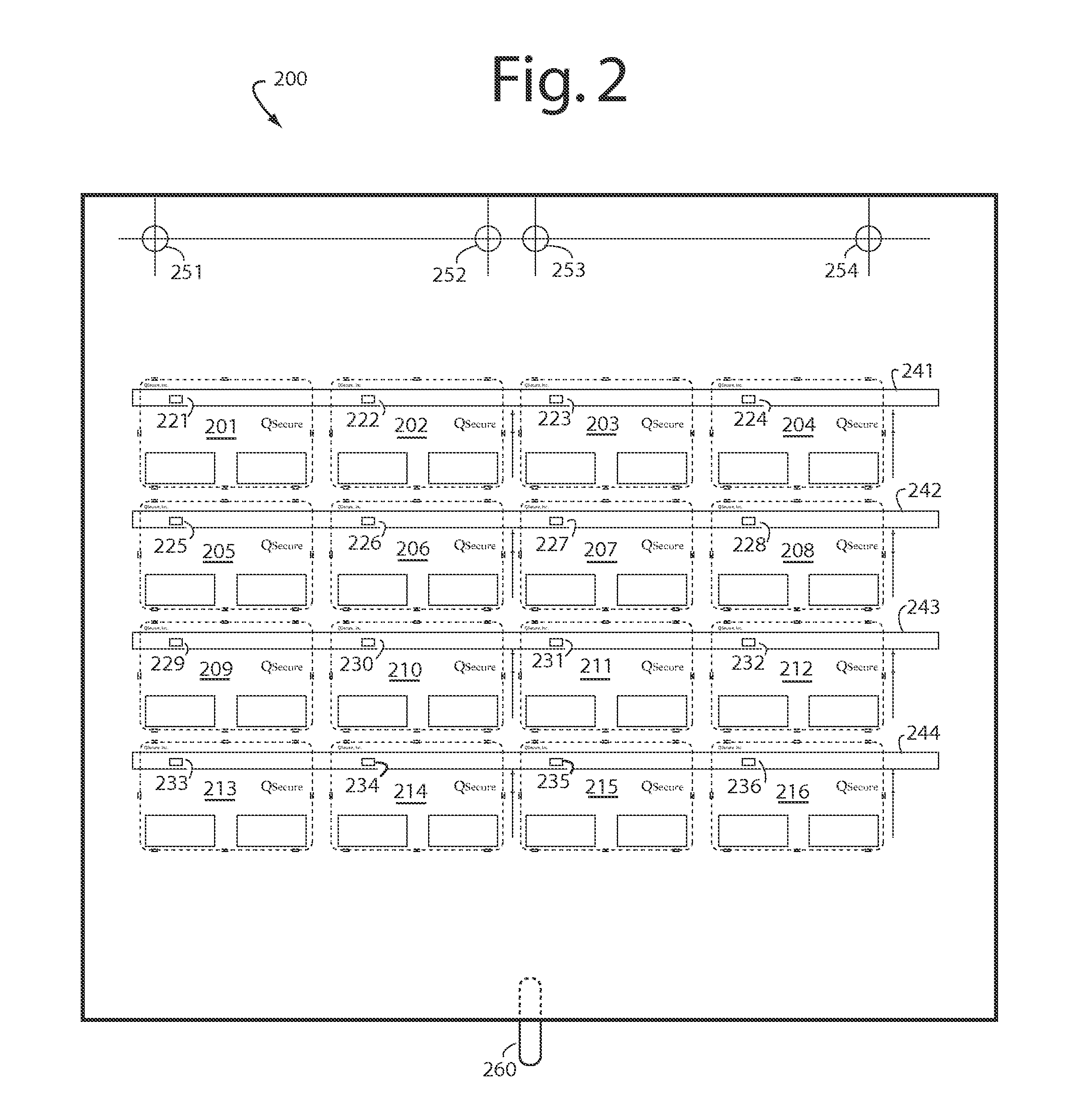
Patents
Literature
114 results about "Magnetic transitions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
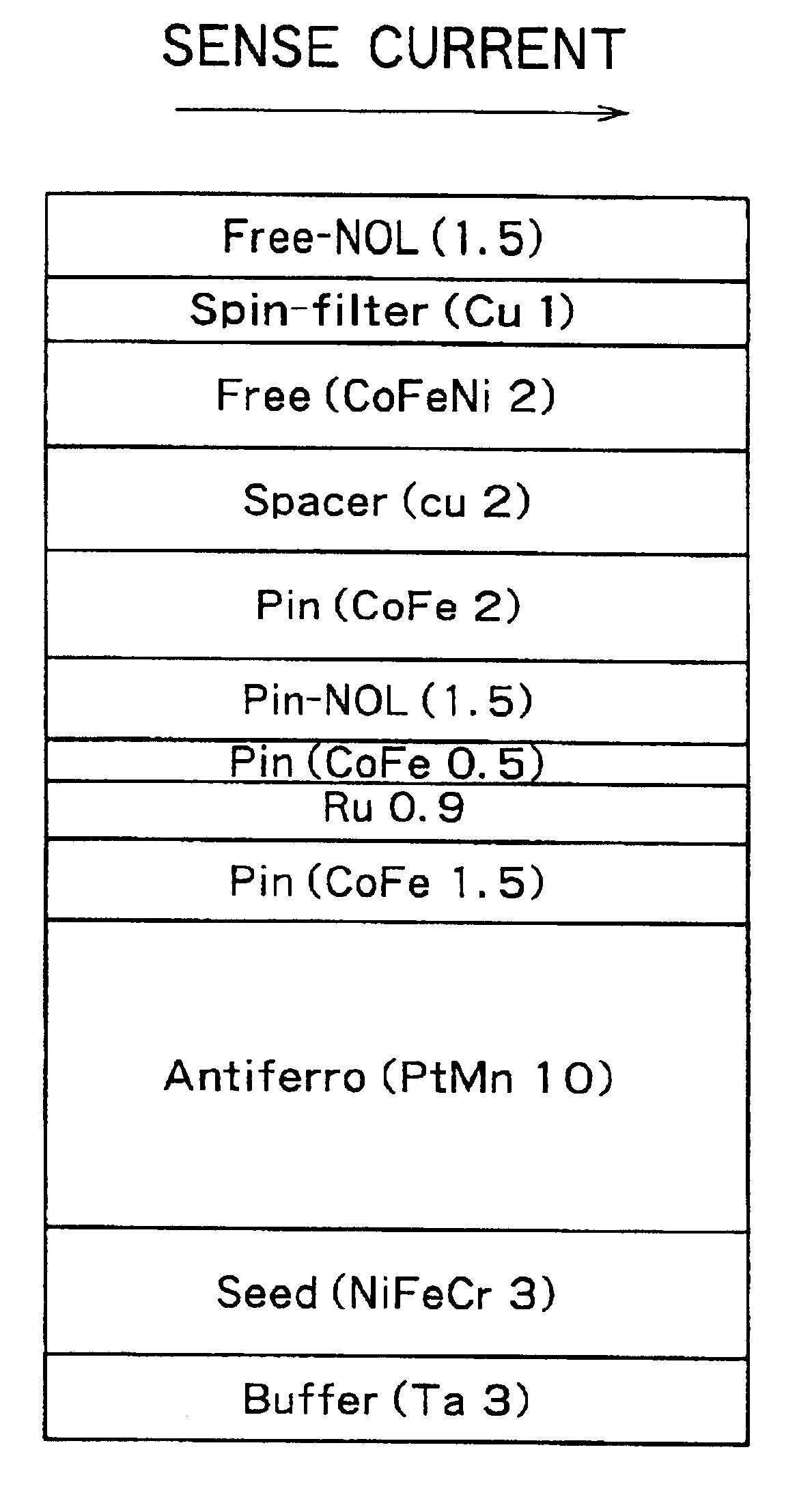
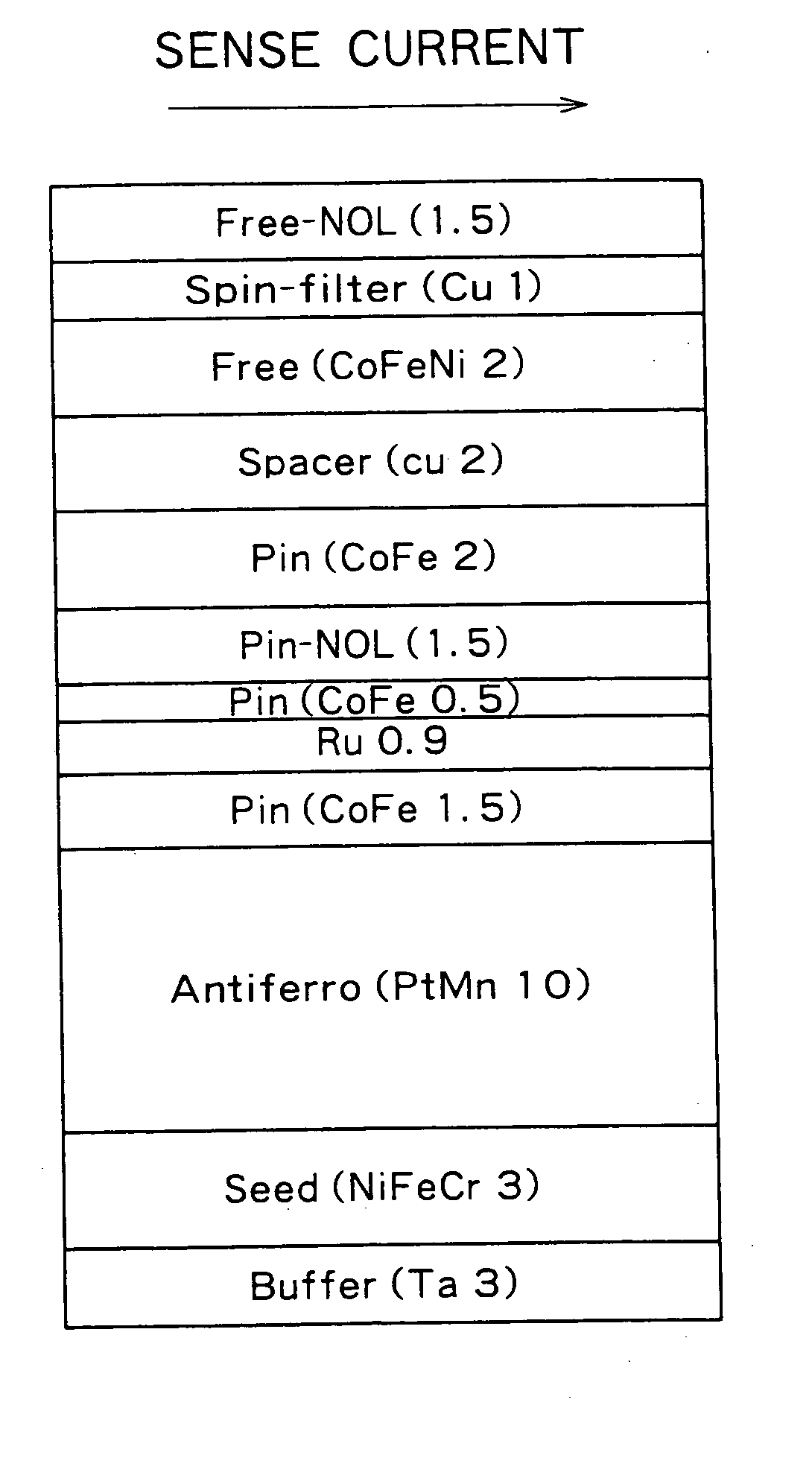
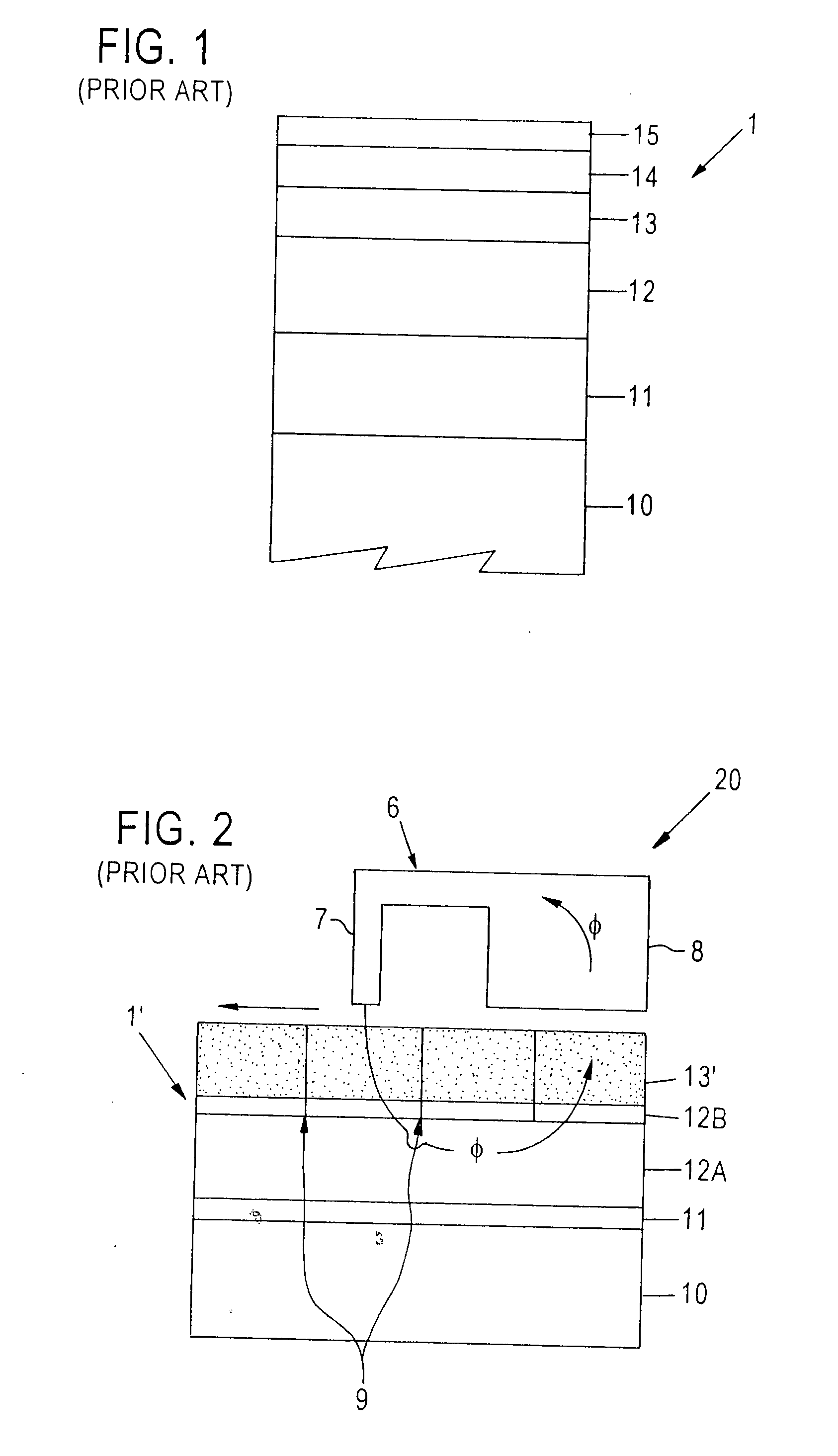
Magnetoresistance effect element
InactiveUS6853520B2High sensitivityImprove reliabilityNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsMagnetic transitionsNitrogen
There are provided a magnetoresistance effect element, a magnetic head, a magnetic head assembly and a magnetic recording system, which have high sensitivity and high reliability. The magnetoresistance effect element has two ferromagnetic layers, a non-magnetic layer provided between the ferromagnetic layers, and a layer containing an oxide or nitride as a principal component, wherein the layer containing the oxide or nitride as the principal component contains a magnetic transition metal element which does not bond to oxygen and nitrogen and which is at least one of Co, Fe and Ni.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
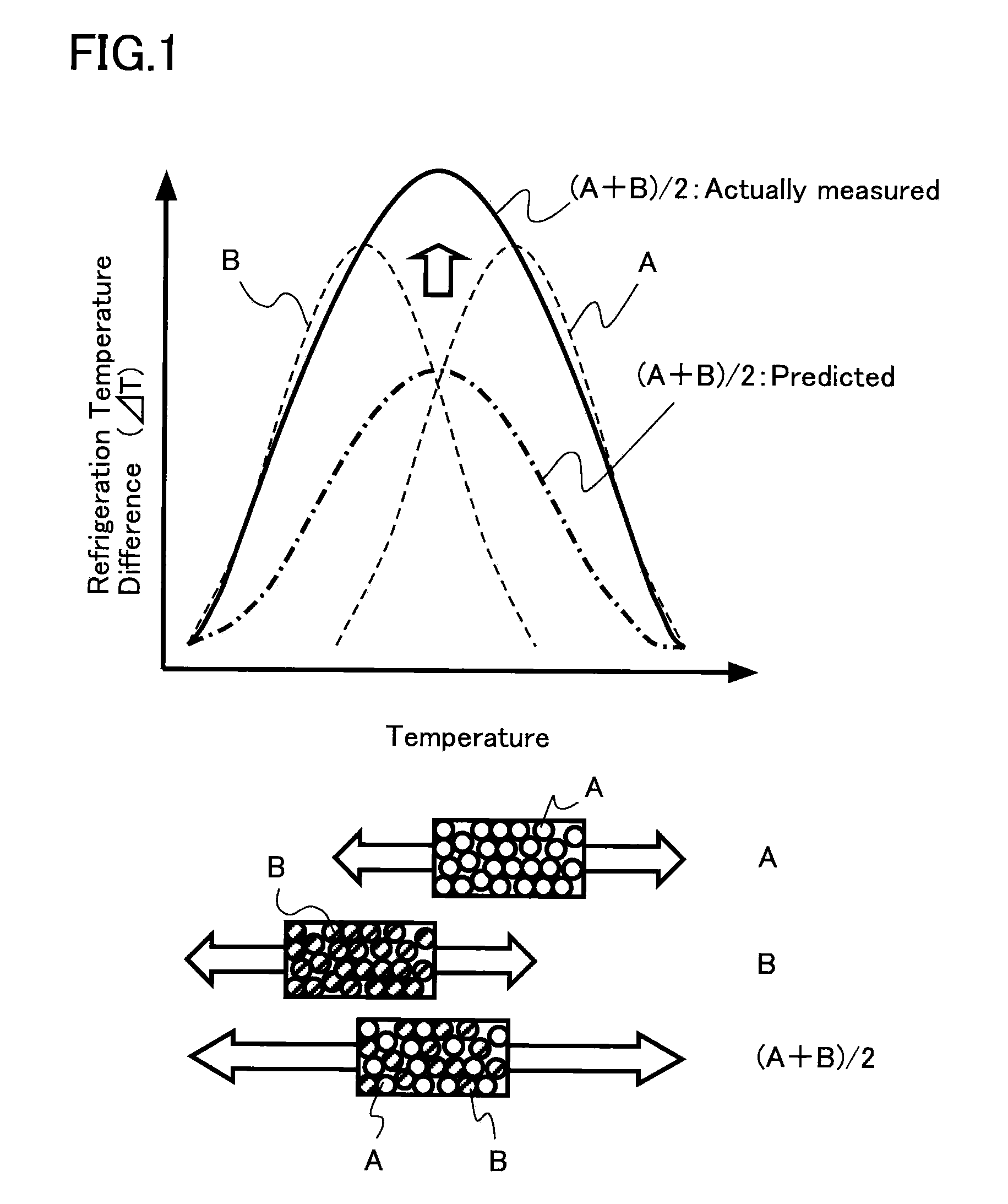
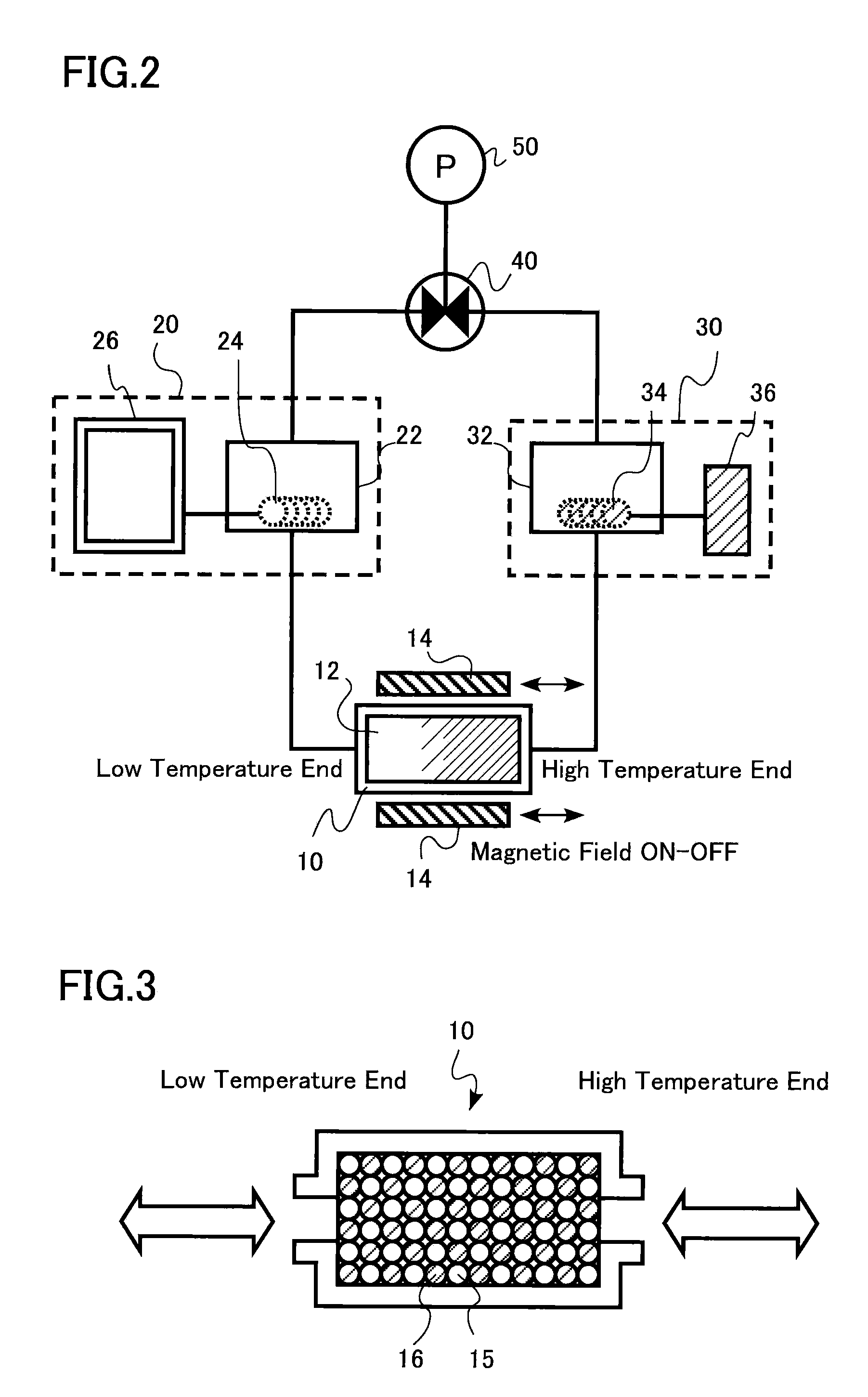
Magnetic material for magnetic refrigeration apparatus, amr bed, and magnetic refrigeration apparatus
InactiveUS20090217674A1Improve cooling efficiencyWide operationEnergy efficient heating/coolingMachines using electric/magnetic effectsMagnetic transitionsMaximum diameter
There are provided a magnetic material for a magnetic refrigeration apparatus, which improves magnetic refrigeration efficiency by the wide operation temperature range of it, AMR bed using the magnetic material, and a magnetic refrigeration apparatus. The magnetic material is used for the magnetic refrigeration apparatus using a liquid refrigerant, formed by approximately uniformly blending at least two kinds of magnetic particles having different magnetic transition temperatures, and the magnetic particles exhibit an approximately spherical shape with maximum diameter of 0.3 mm or more to 2 mm or less. The AMR bed is filled with the magnetic particles.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
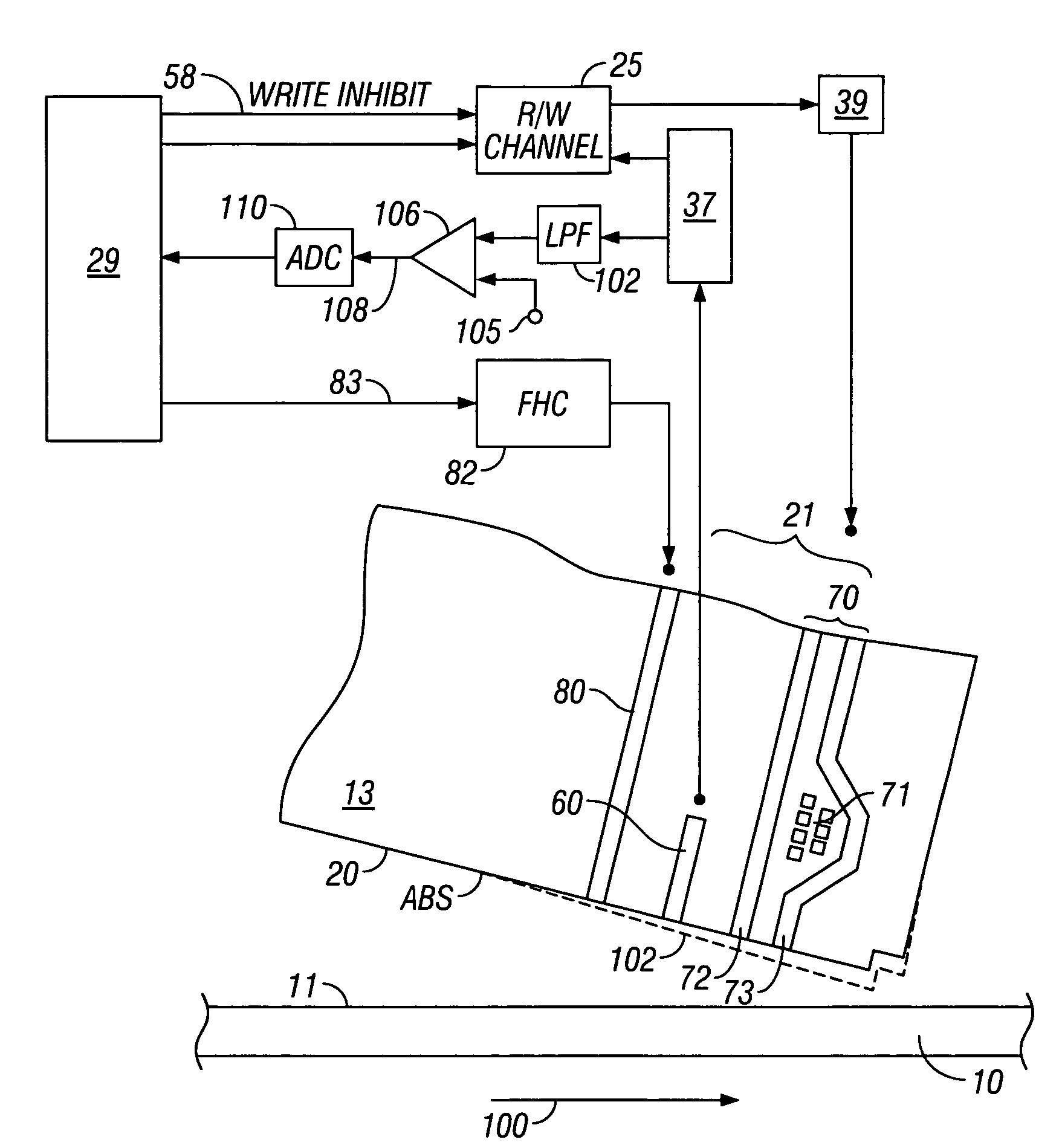
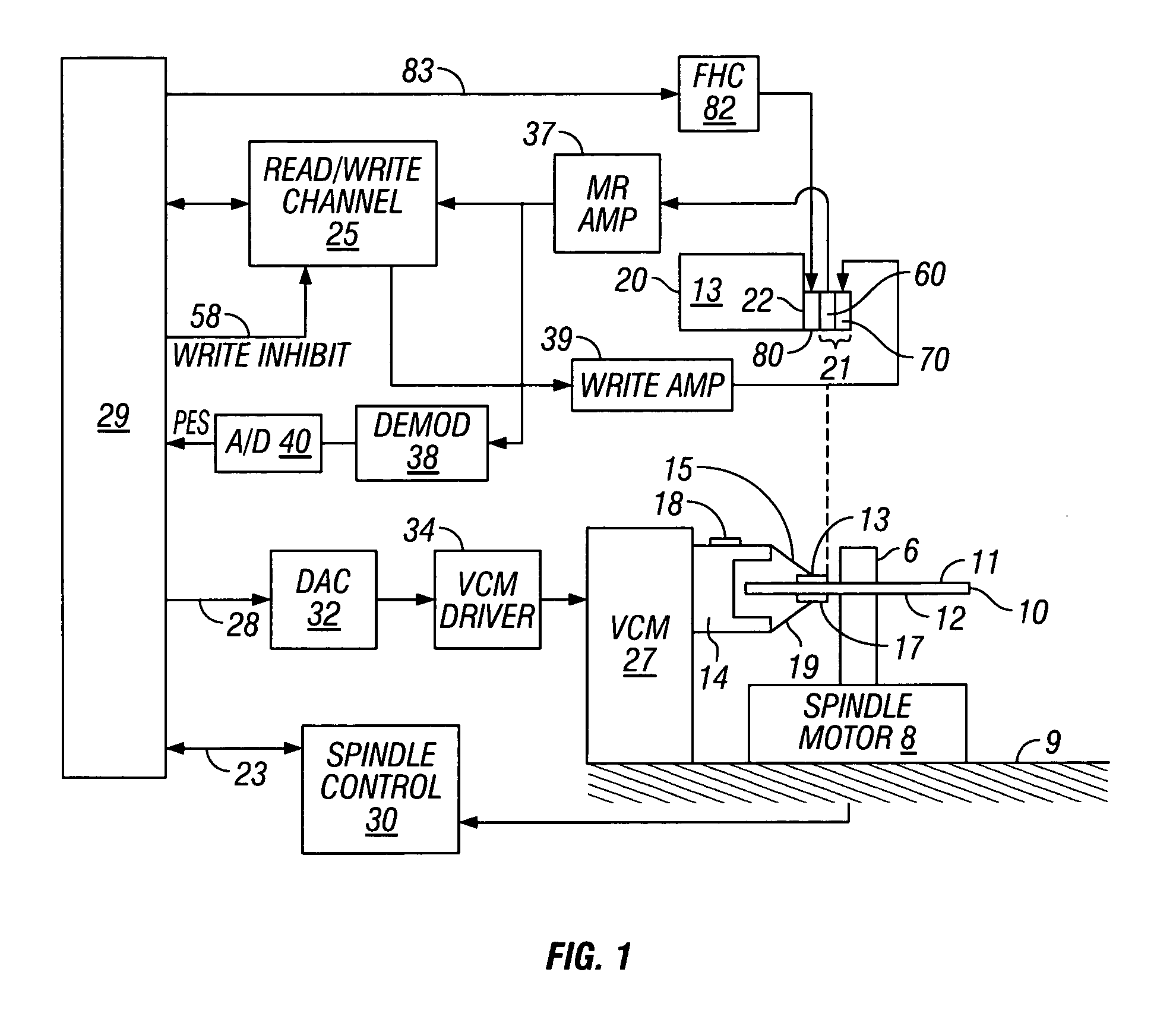
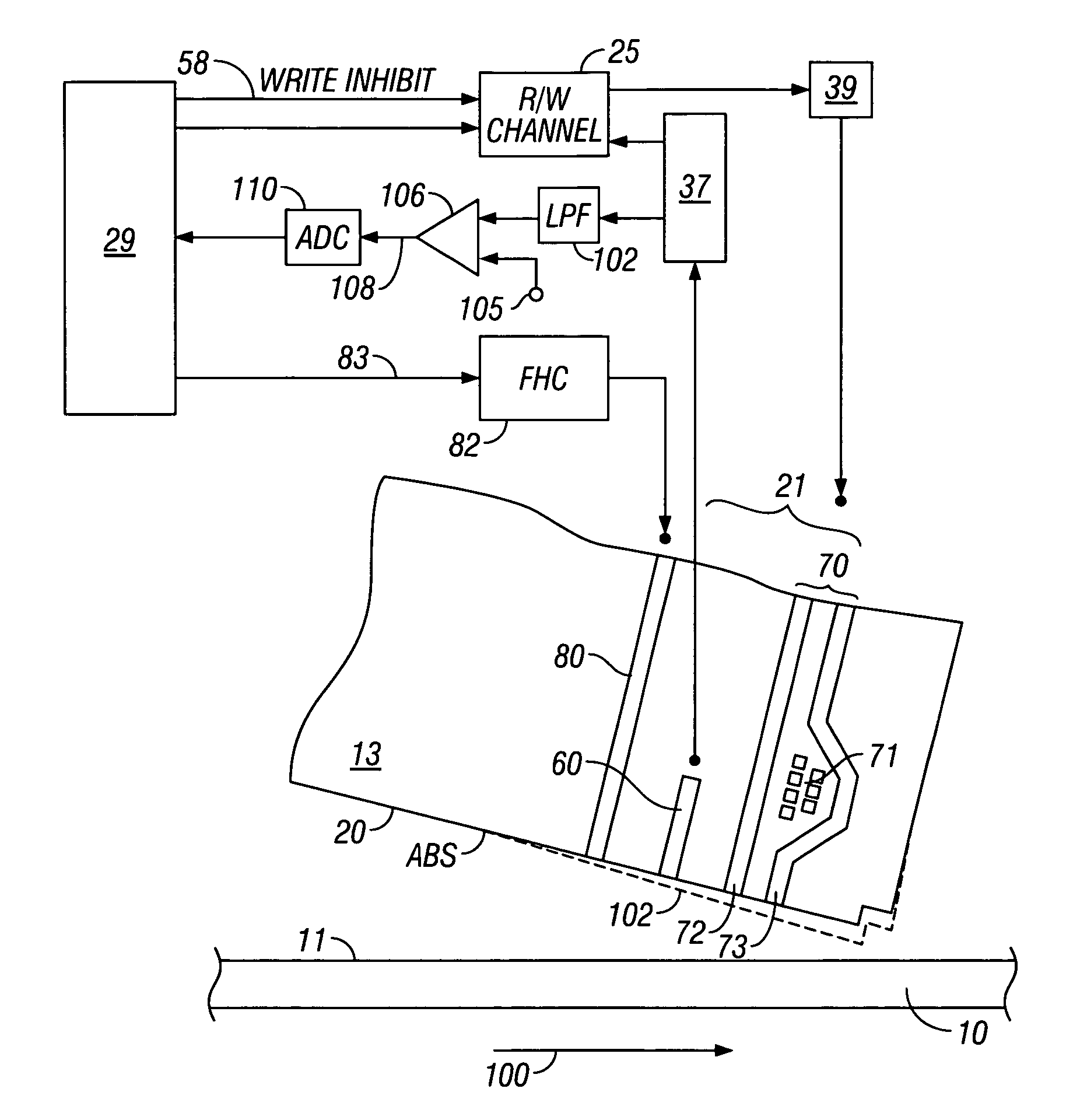
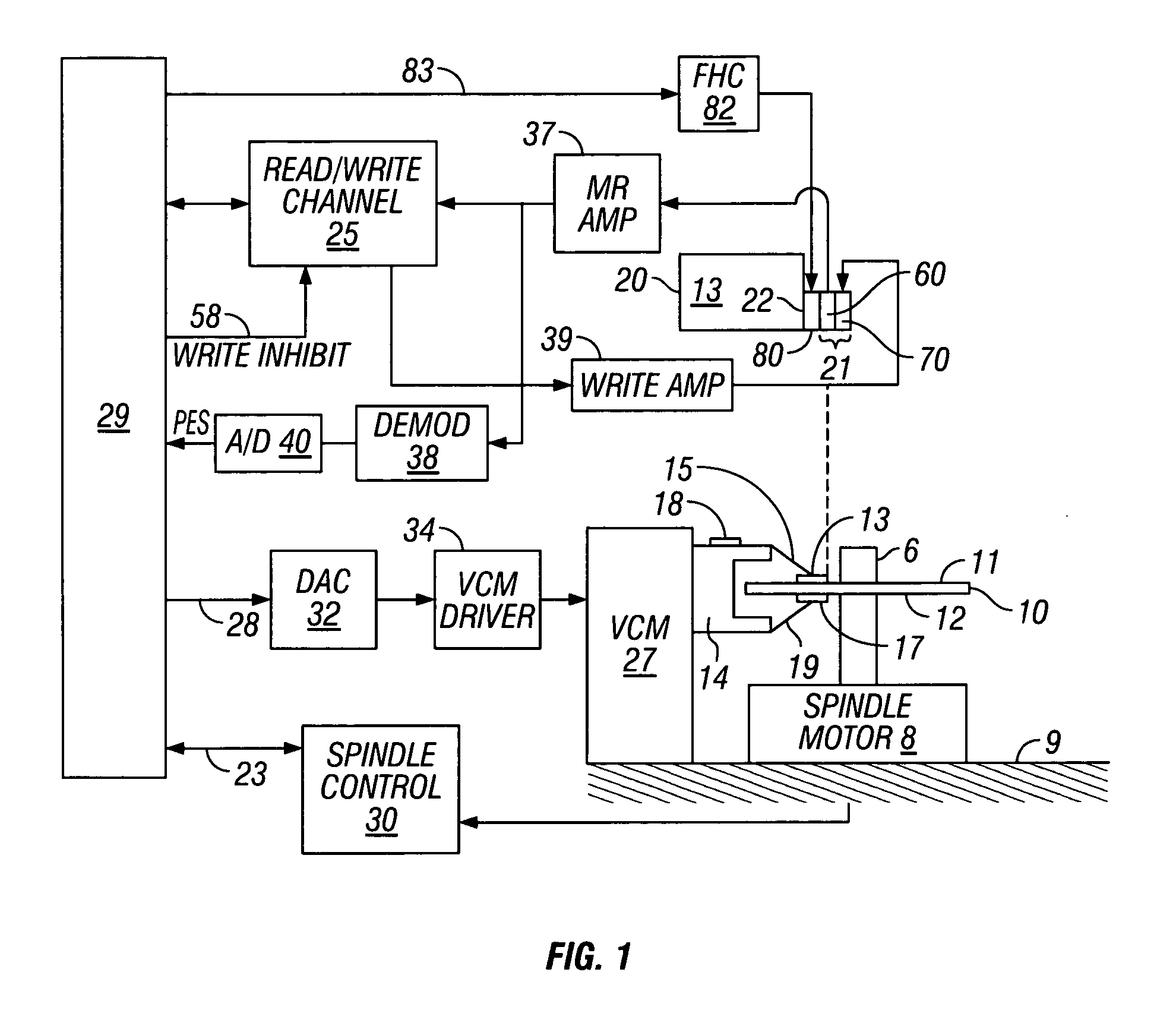
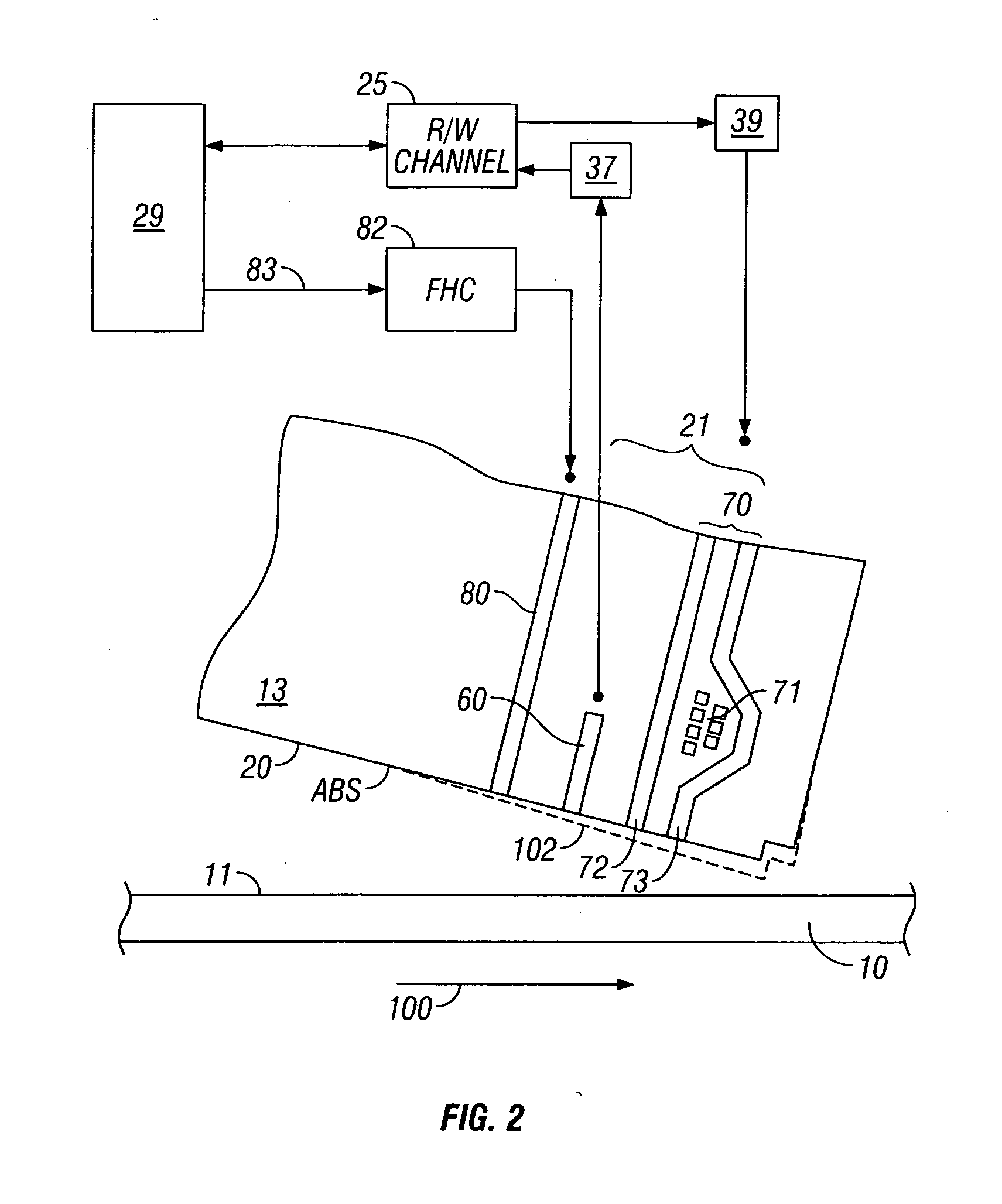
System and method for determining head-disk contact in a magnetic recording disk drive by magnetoresistive signal amplitude
InactiveUS7292401B2Driving/moving recording headsFilamentary/web record carriersMagnetic transitionsControl signal
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Multi dimensional read head array
InactiveUS20080290166A1Sensing record carriersRecord carriers used with machinesMagnetic transitionsMulti dimensional
Owner:SEMTEK INNOVATIVE SOLUTIONS
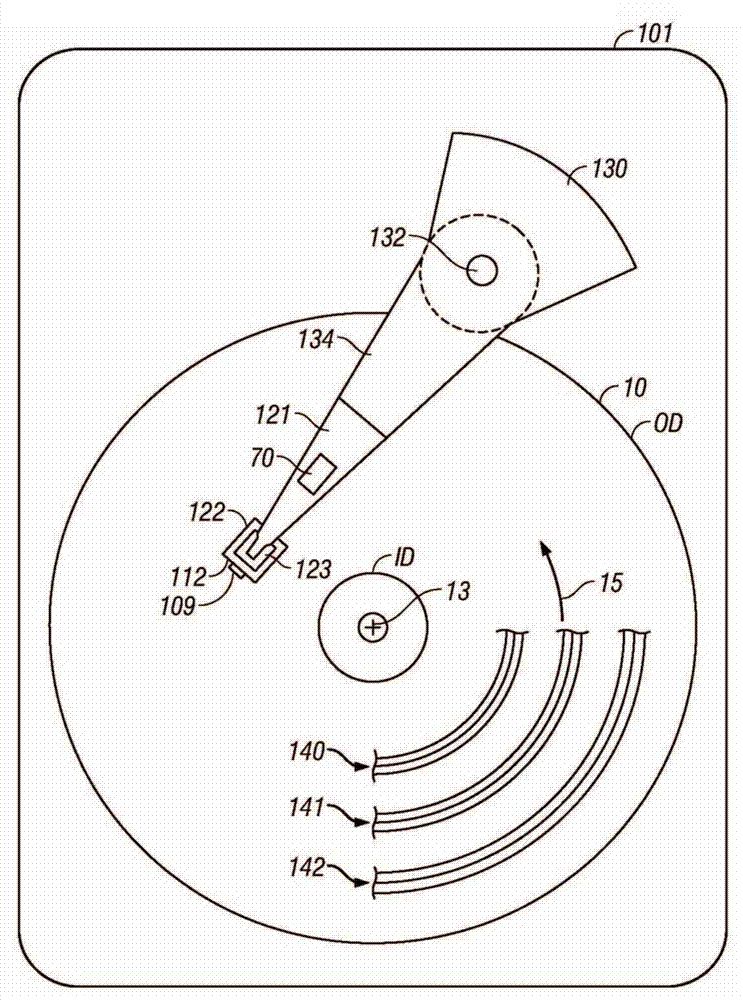
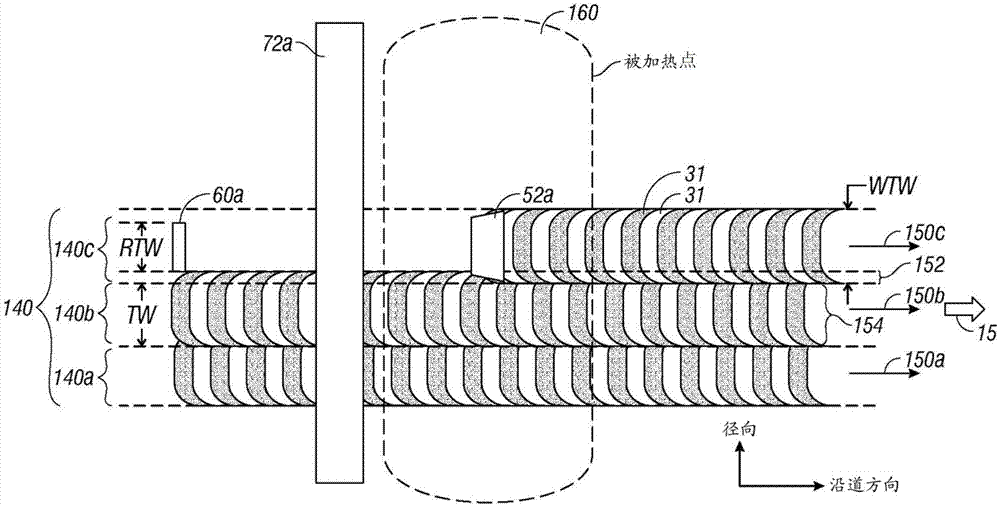
Magnetic recording disk drive with shingled writing and wide-area thermal assistance
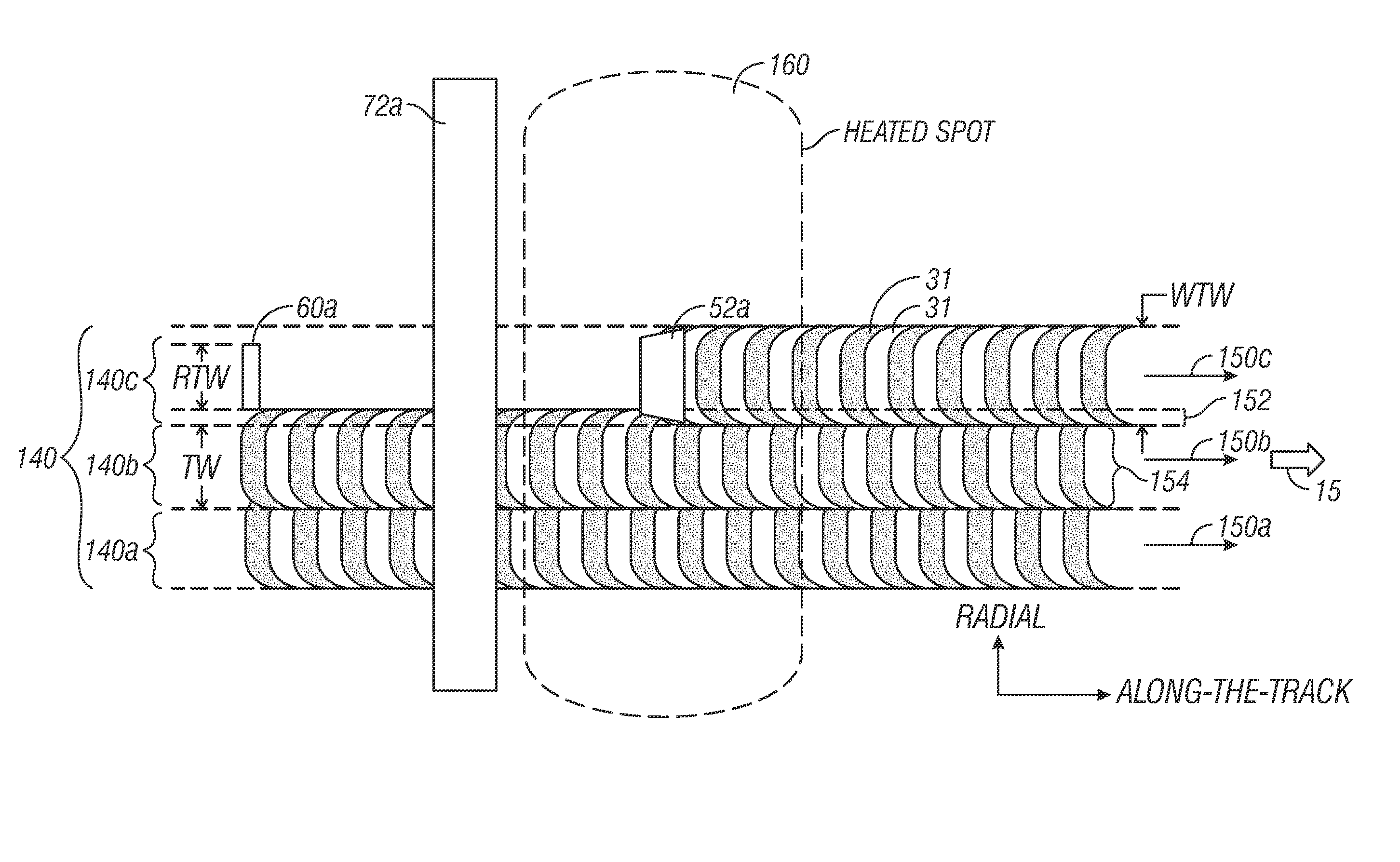
A thermally-assisted recording (TAR) disk drive uses a “wide-area” heater with “shingled” recording. In shingled recording, the write head pole tip is wider than the read head in the cross-track direction and writes magnetic transitions by making a plurality of consecutive circular paths that partially overlap. The non-overlapped portions of adjacent paths form the data tracks, which are thus narrower than the width of the write pole tip. The data tracks are grouped into annular bands and when data is to be rewritten, all of the data tracks in an annular band are also rewritten. The wide-area heater may be a waveguide with an output end that generates a heated area on the disk recording layer which is wider than the cross-track width of the write pole tip. It has been determined that the use of a wide-area heater with shingled recording does not result in any significant adjacent track erasure (ATE).
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Magnetic recording head for perpendicular recording and including a portion protruding toward a mail pole and magnetic disc storage apparatus mounting the magnetic head
InactiveUS7054105B2Improve recording densityReduce widthManufacture head surfaceHeads using thin filmsMagnetic transitionsEngineering
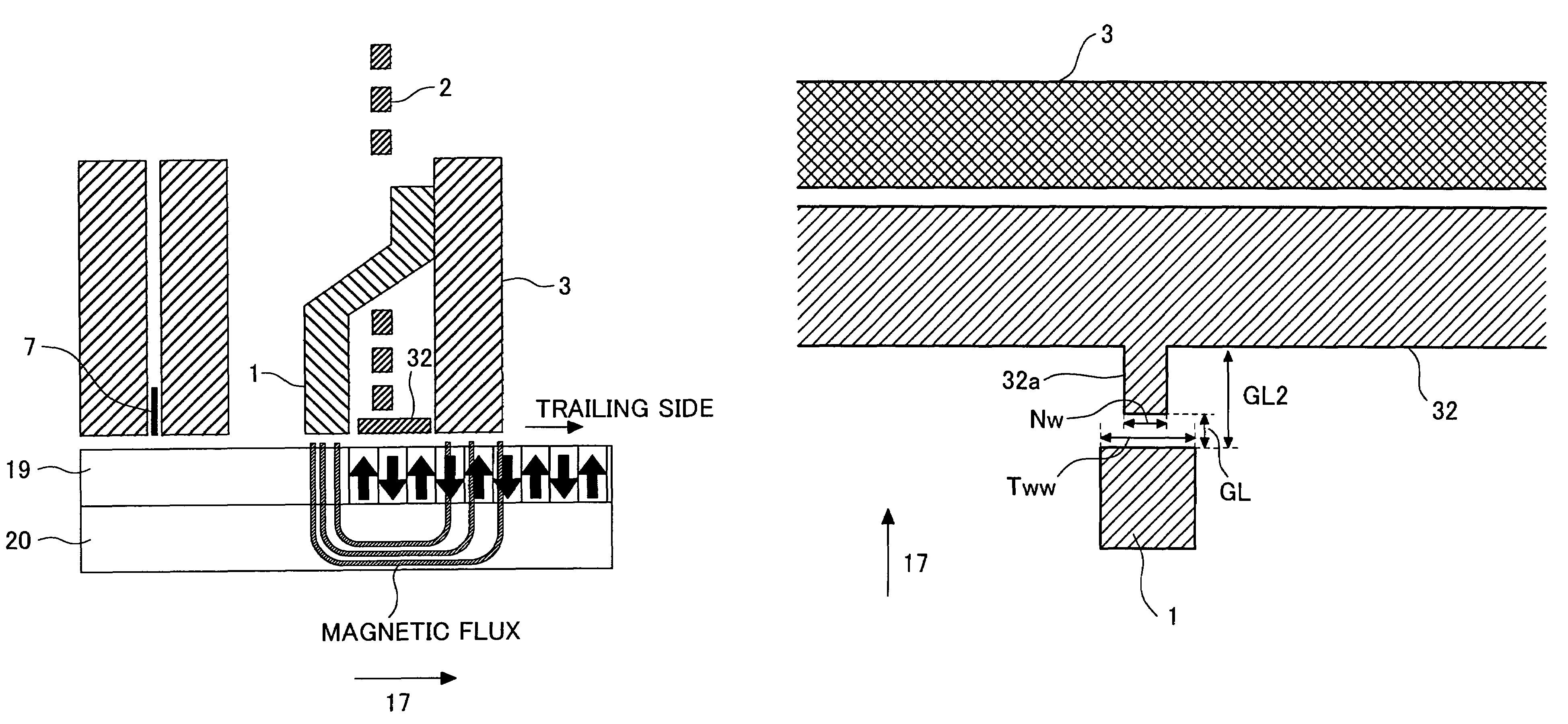
A magnetic field distribution of a recording head is made linear so that a curvature of the magnetic-transition pattern in recording bit cells can be corrected. In a SPT head having a main pole 1 and an auxiliary pole 3, a magnetic layer 32 is disposed on a trailing side of the main pole. The magnetic layer is provided with a protruding portion 32a protruding towards the main pole. A width Nw of a side of the protruding portion opposite the main pole of the protruding portion is made smaller than a width Tww of the main pole on the trailing side.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC +1
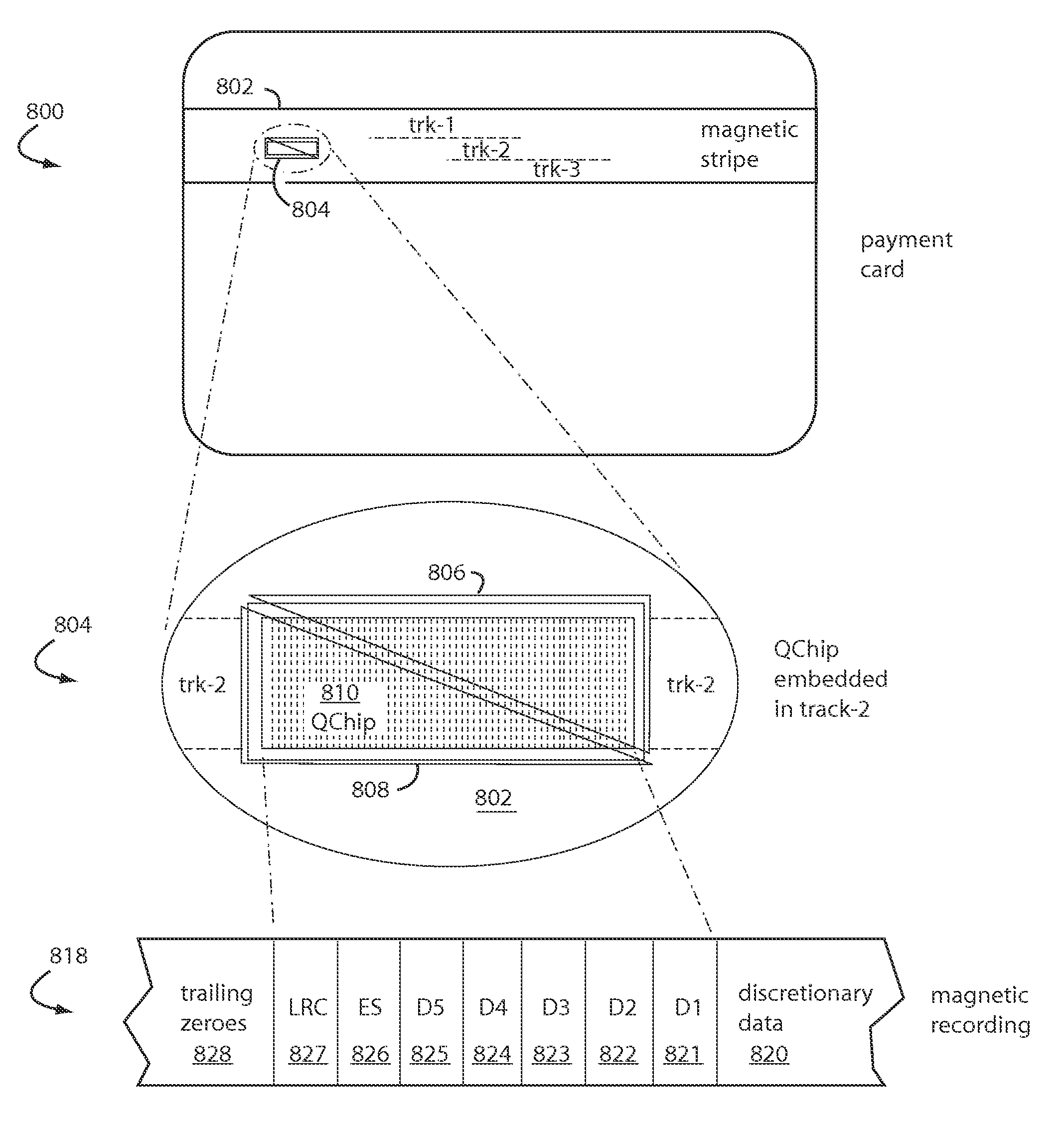
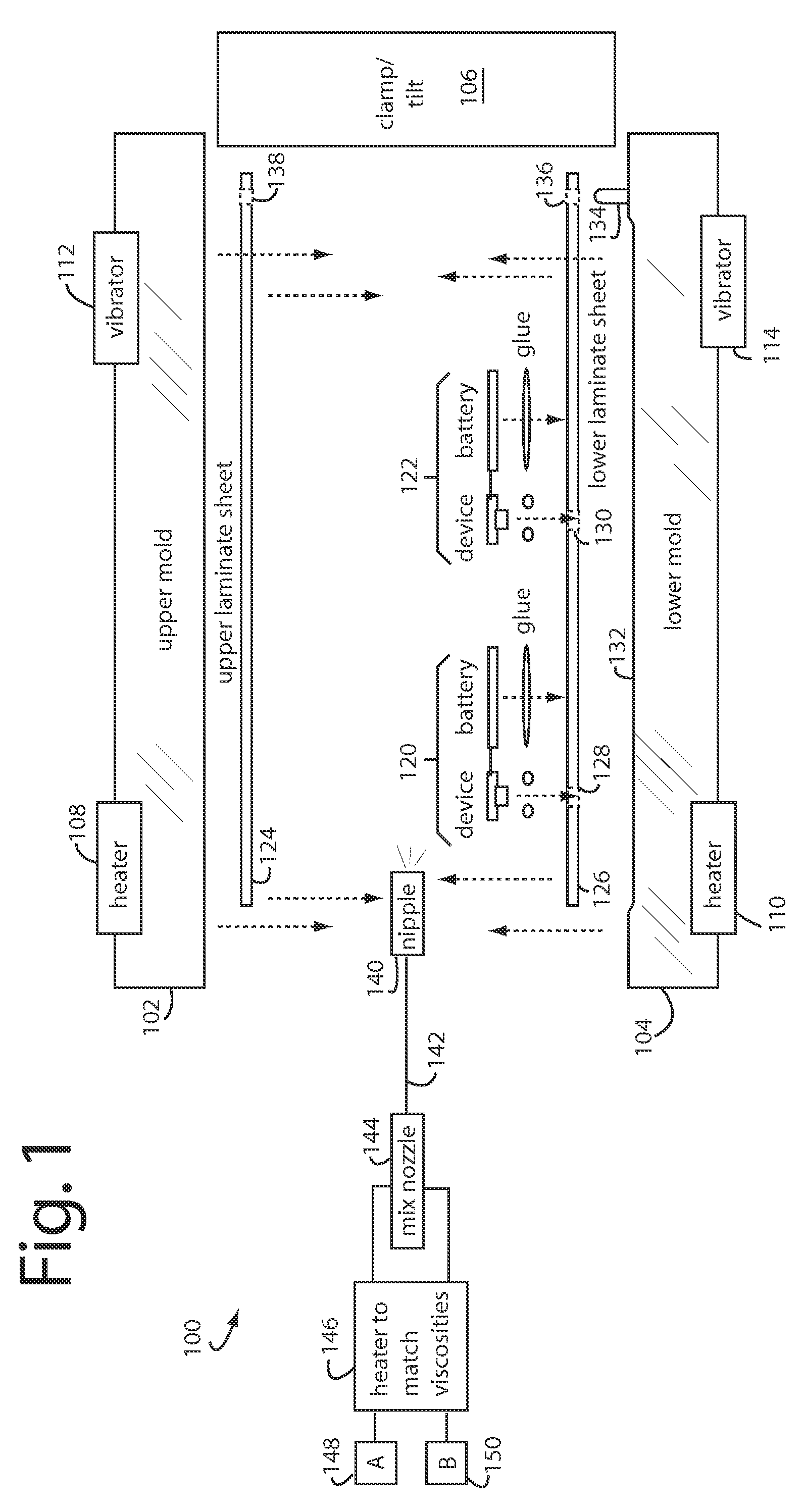
Payment card manufacturing technology
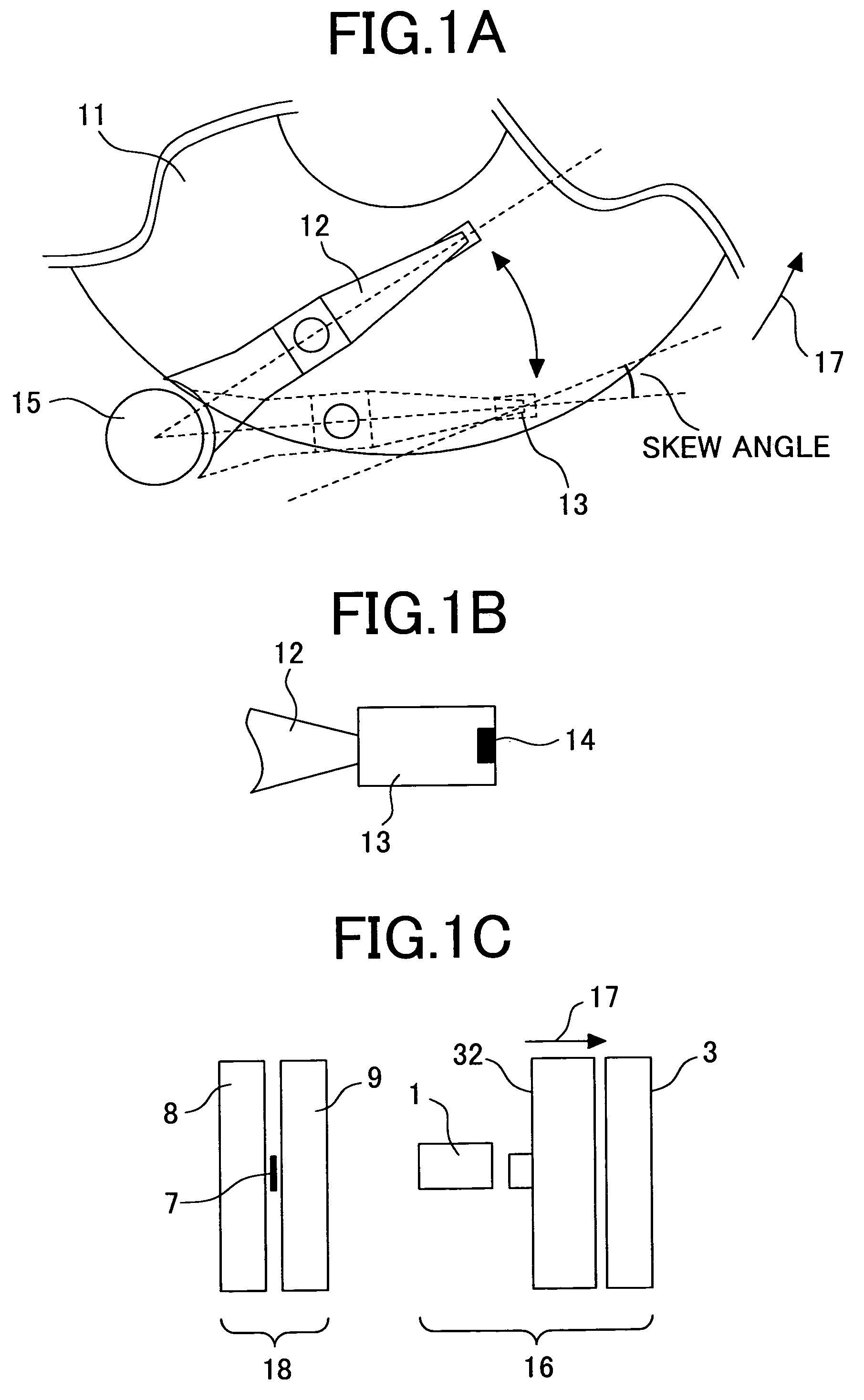
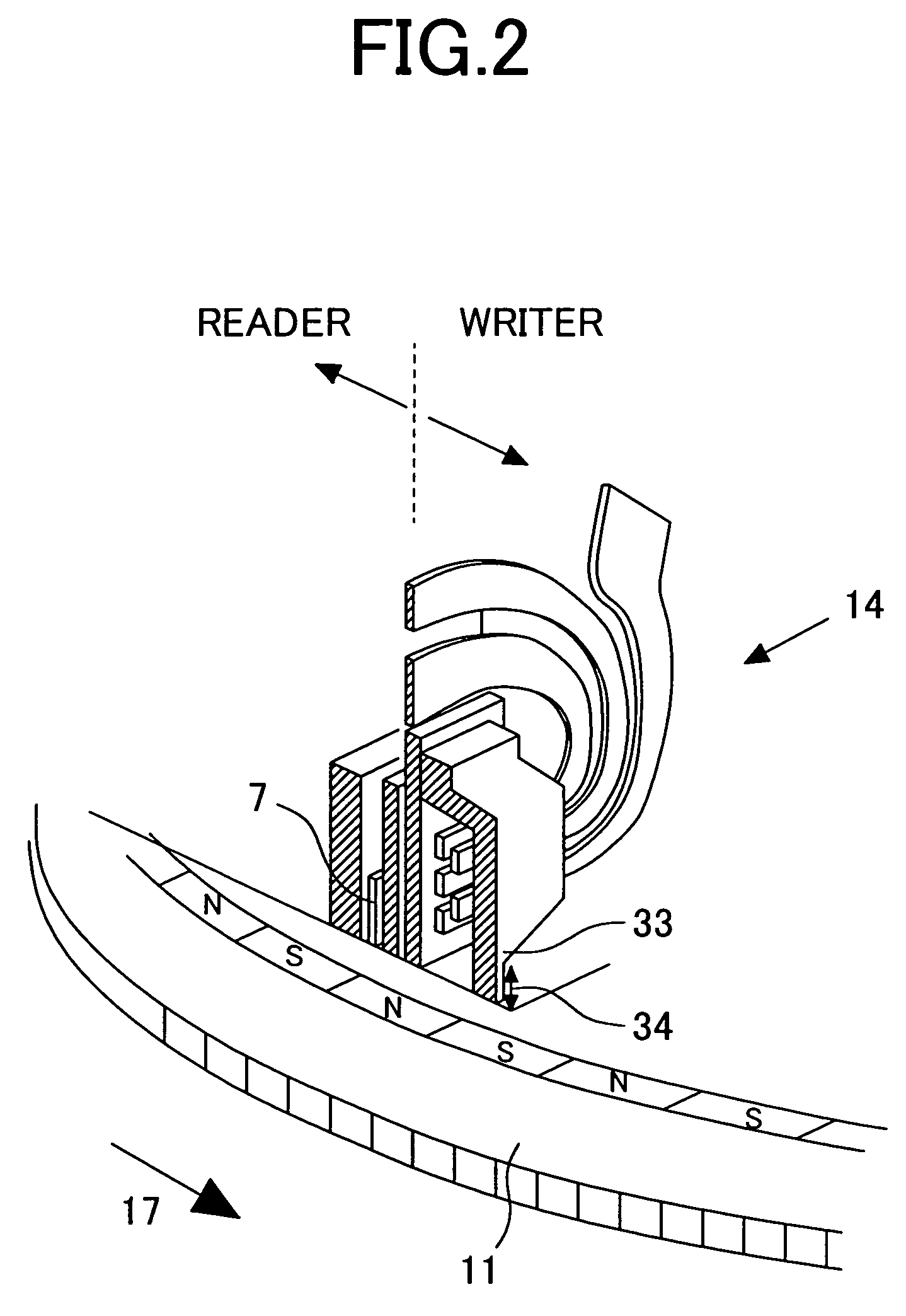
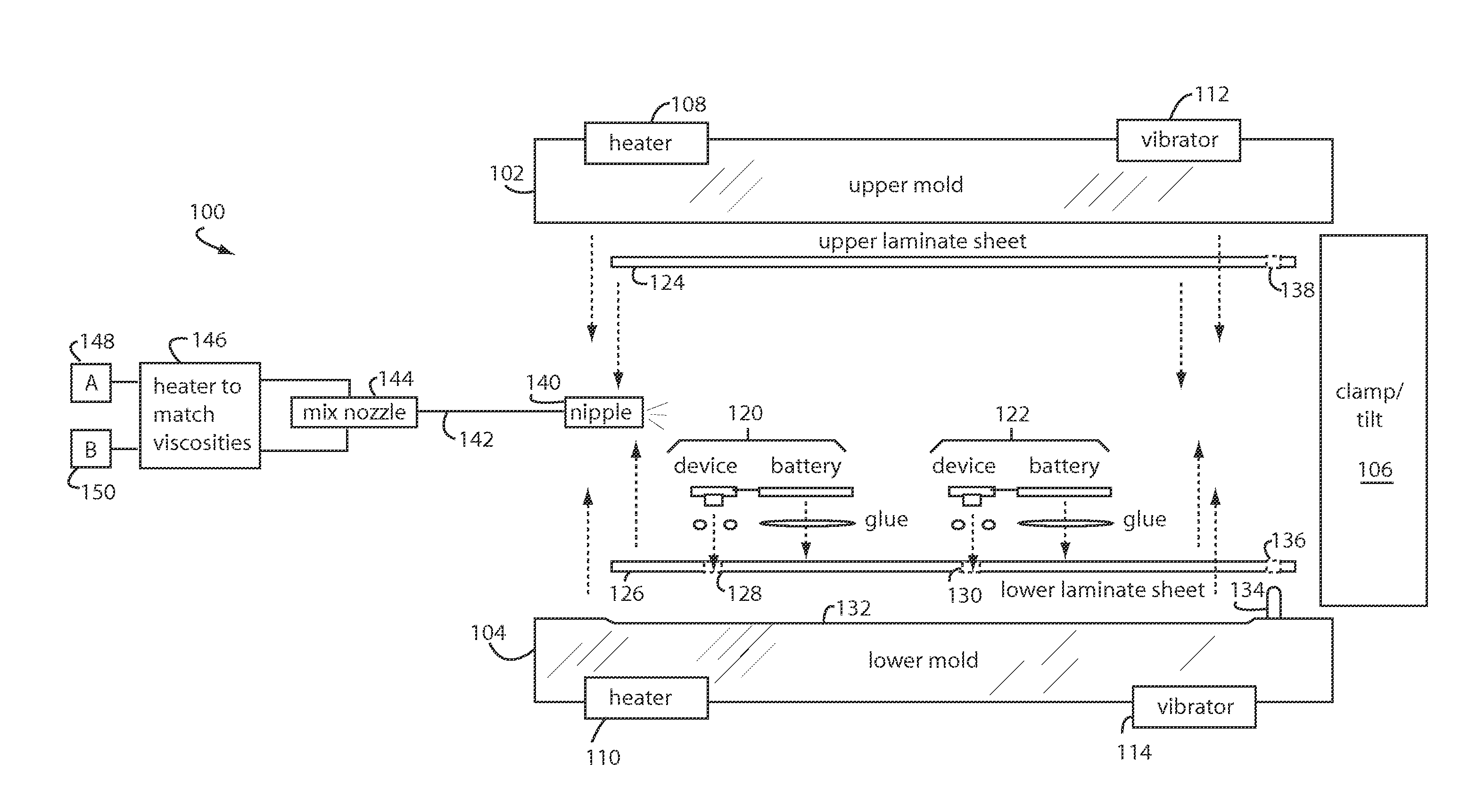
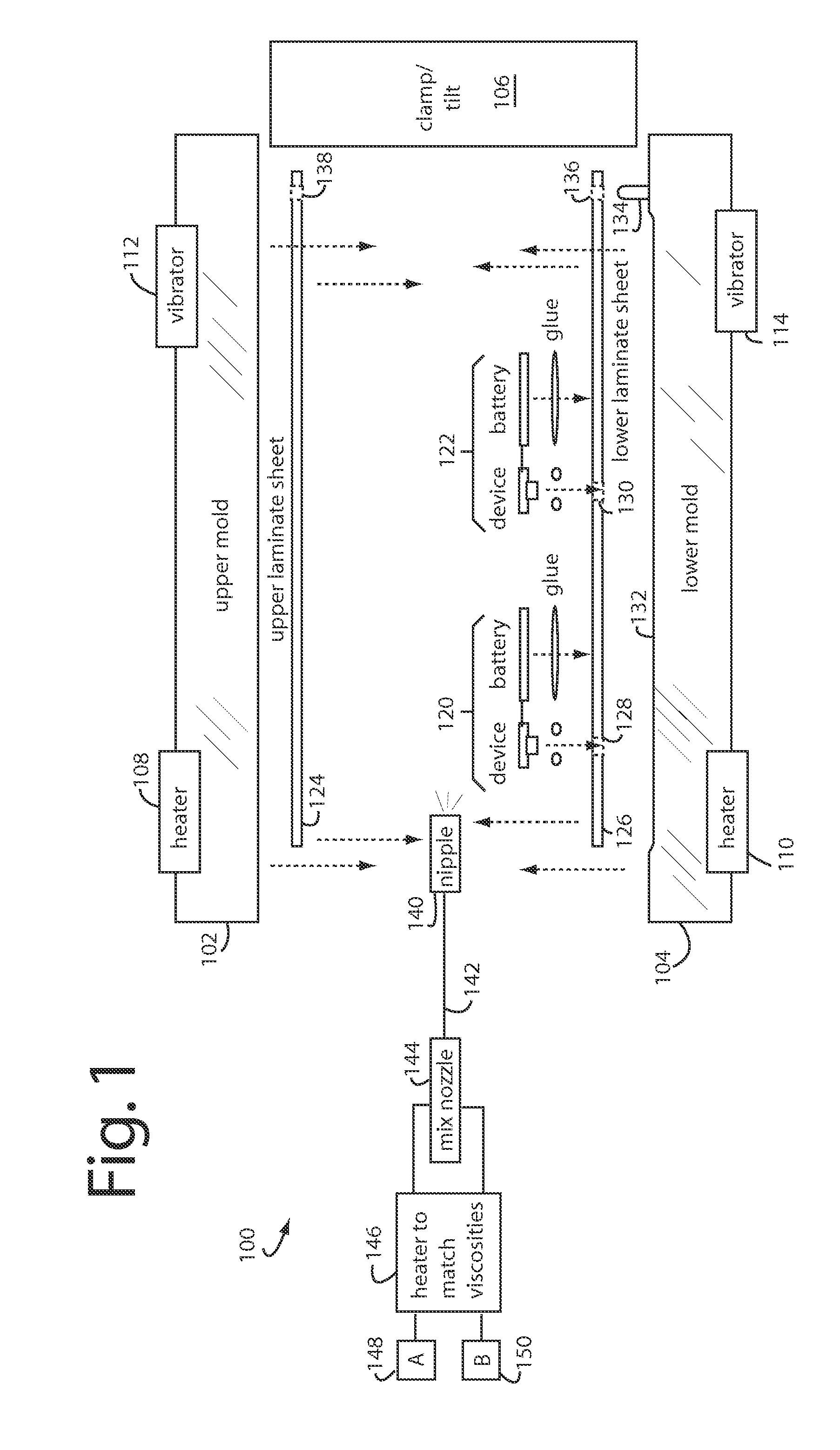
A payment card manufacturing process glues a thin battery and an autonomously reprogrammable magnetic device to the inside surface of one of two outer front and rear laminate sheets. The magnetic device is pressed through a precisely cut rectangular hole provided for it in the rear laminate sheet, and is sealed with a gasket bead. Such magnetic device is critically placed flush in a magnetic stripe area, and the end gaps are such that they will minimize adverse magnetic transitions seen by a reader between the magnetic stripe field and the autonomously reprogrammable magnetic device. The surfaces of the battery, electronics, and laminate sheets, are plasma treated to promote adhesion. These are then all sandwiched together inside a heated mold that is tilted or vibrated just before a two-part polyurethane is injected. Each of the two polyurethane parts is temperature adjusted to match viscosities and thus improve mixing. The liquid polyurethane is injected through a nozzle and manifold to fill all the voids between the laminate sheets, and air escapes or is vacuumed out the top edge of the mold. The polyurethane sets quickly and sheets of sixteen or more payment cards can then be de-molded and singulated.
Owner:FITBIT INC
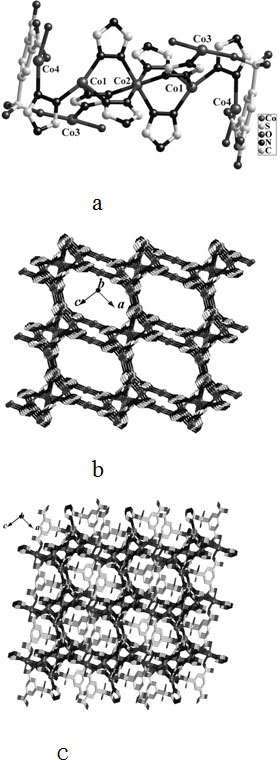
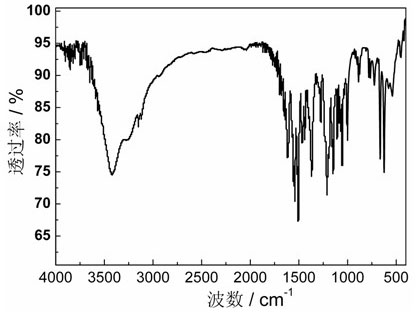
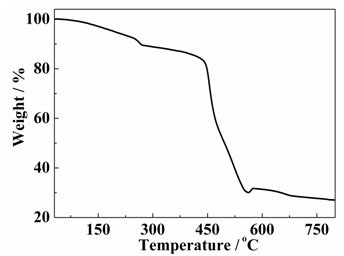
Mixed ligand cobalt (ii) complex and its preparation method and application
InactiveCN102276658AImprove thermal stabilityHigh yieldCobalt organic compoundsMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsMagnetic transitionsPhysical chemistry
The invention relates to a 1,2,4-triazole and 5-sulfonyl m-phthalic acid mixed ligand cobalt (II) coordination compound magnetic material as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The chemical formula of the coordination compound magnetic material is {[Co3.5(H2O)2(trz)4(sip)].1.5H2O}, wherein trz is 1,2,4-triazole monovalent anion; and sip is trivalent anion of 5-sulfonyl m-phthalic acid. The coordination compound magnetic material is prepared by using a solvothermal method and has higher yield and good repeatability. The coordination compound magnetic material is the first case of cobalt (II) compound containing the 1,2,4-triazole and 5-sulfonyl m-phthalic acid mixed ligand, shows a magnetic transition phenomenon induced by a three-step field under different external magnetic fields, can be used as a molecule-based magnetic material and has great application value in the field of material science.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Payment card manufacturing technology
A payment card manufacturing process glues a thin battery and an autonomously reprogrammable magnetic device to the inside surface of one of two outer front and rear laminate sheets. The magnetic device is pressed through a precisely cut rectangular hole provided for it in the rear laminate sheet, and is sealed with a gasket bead. Such magnetic device is critically placed flush in a magnetic stripe area, and the end gaps are such that they will minimize adverse magnetic transitions seen by a reader between the magnetic stripe field and the autonomously reprogrammable magnetic device. The surfaces of the battery, electronics, and laminate sheets, are plasma treated to promote adhesion. These are then all sandwiched together inside a heated mold that is tilted or vibrated just before a two-part polyurethane is injected. Each of the two polyurethane parts is temperature adjusted to match viscosities and thus improve mixing. The liquid polyurethane is injected through a nozzle and manifold to fill all the voids between the laminate sheets, and air escapes or is vacuumed out the top edge of the mold. The polyurethane sets quickly and sheets of sixteen or more payment cards can then be de-molded and singulated.
Owner:FITBIT INC
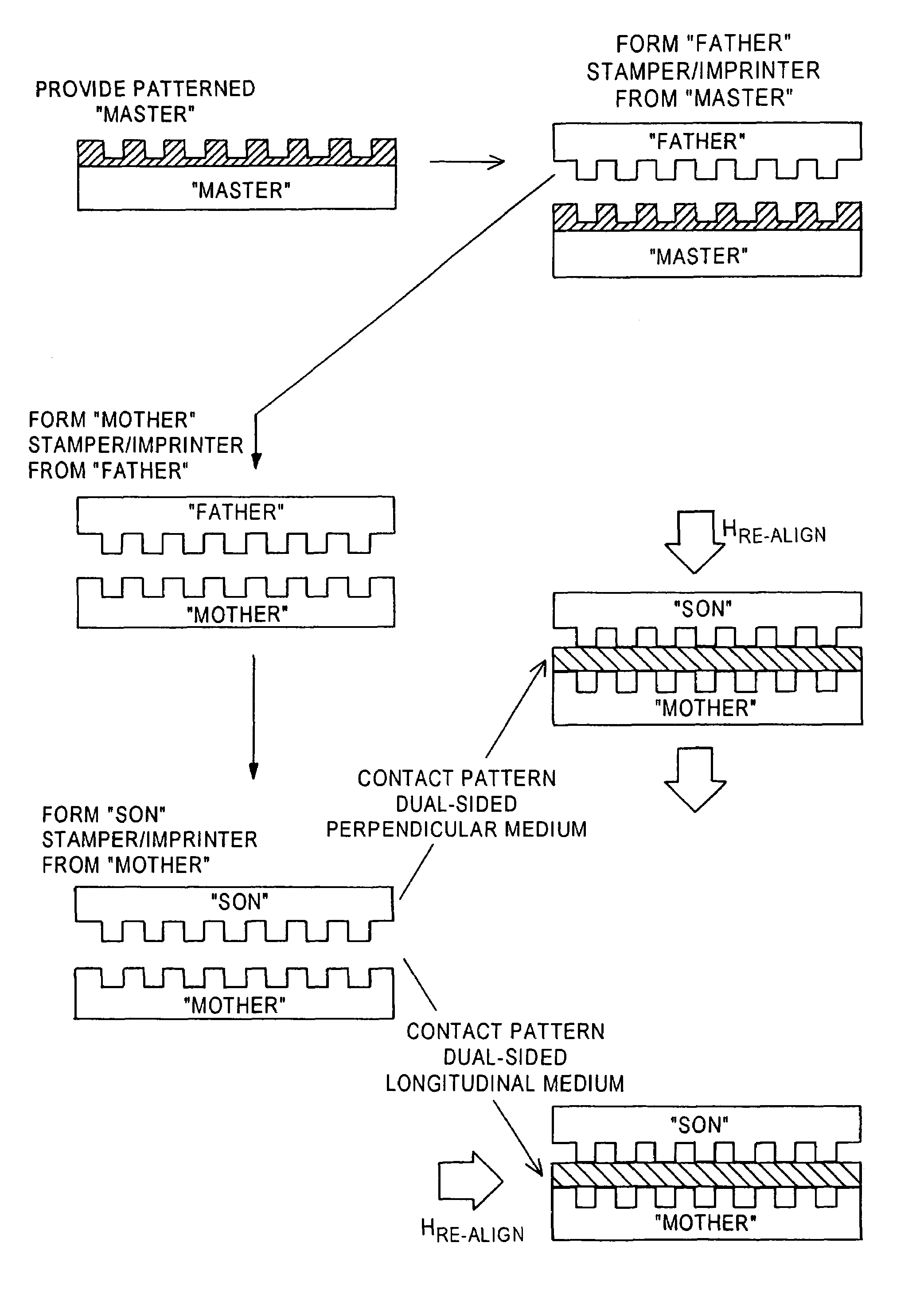
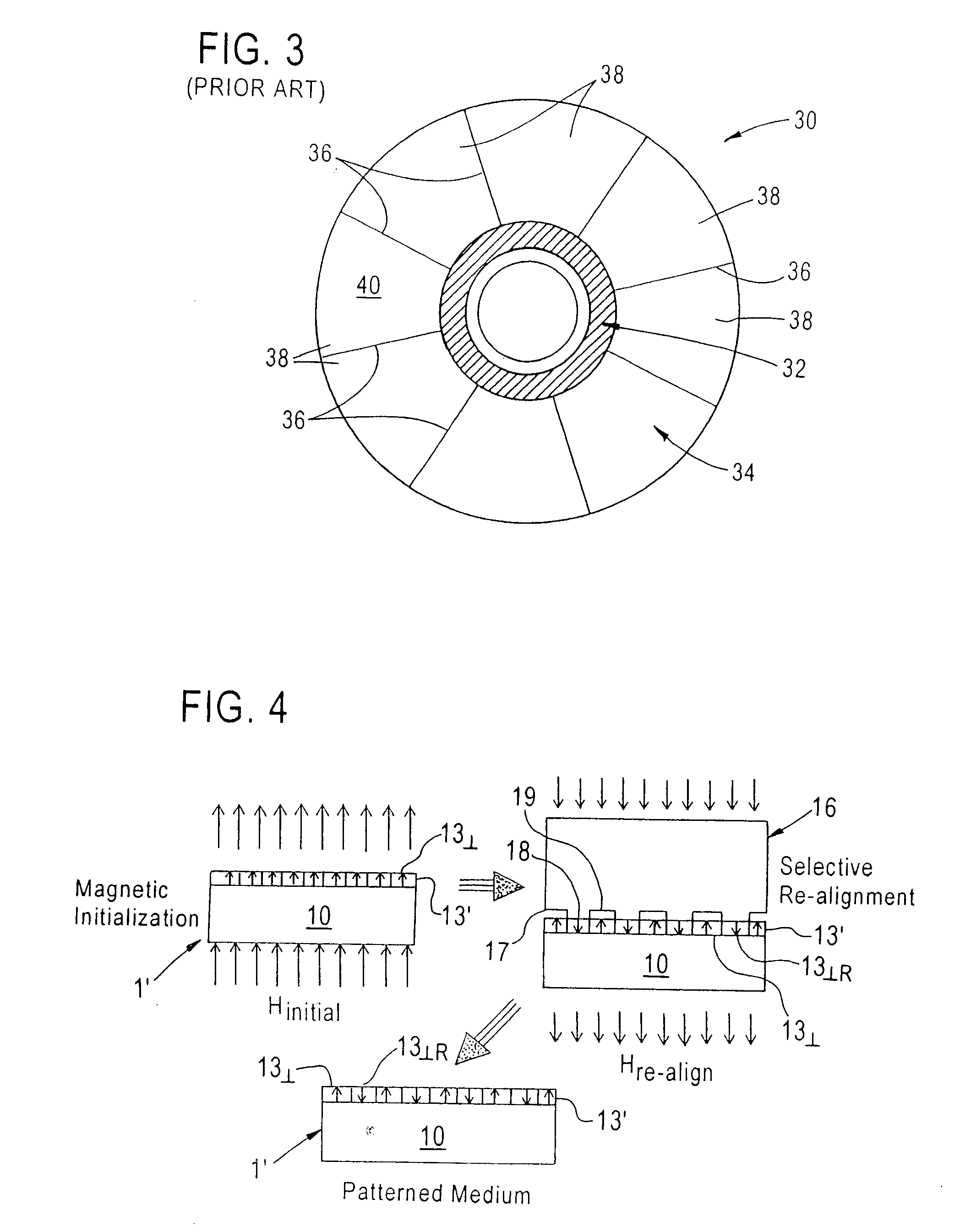
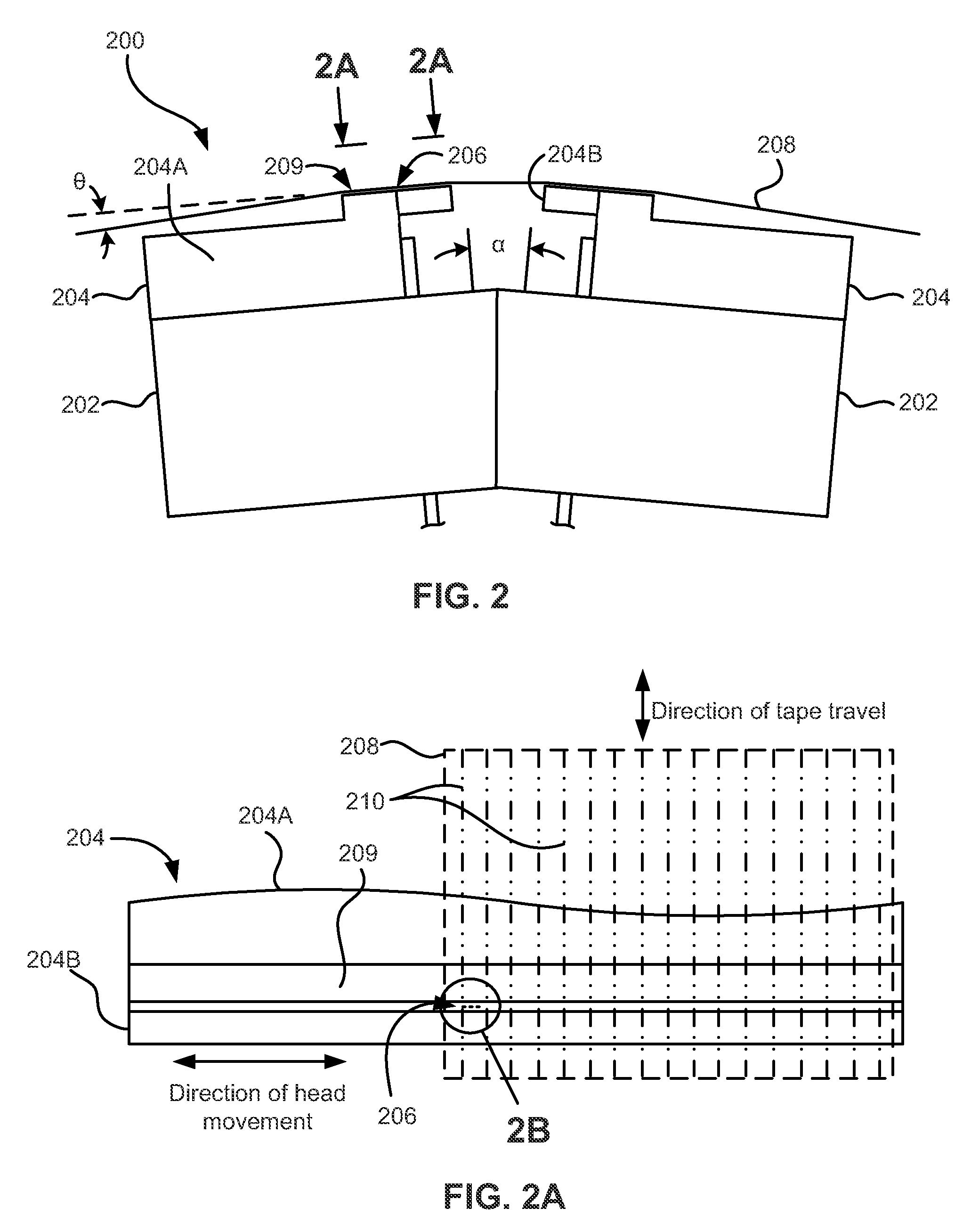
Method of simultaneously forming magnetic transition patterns of a dual side recording medium
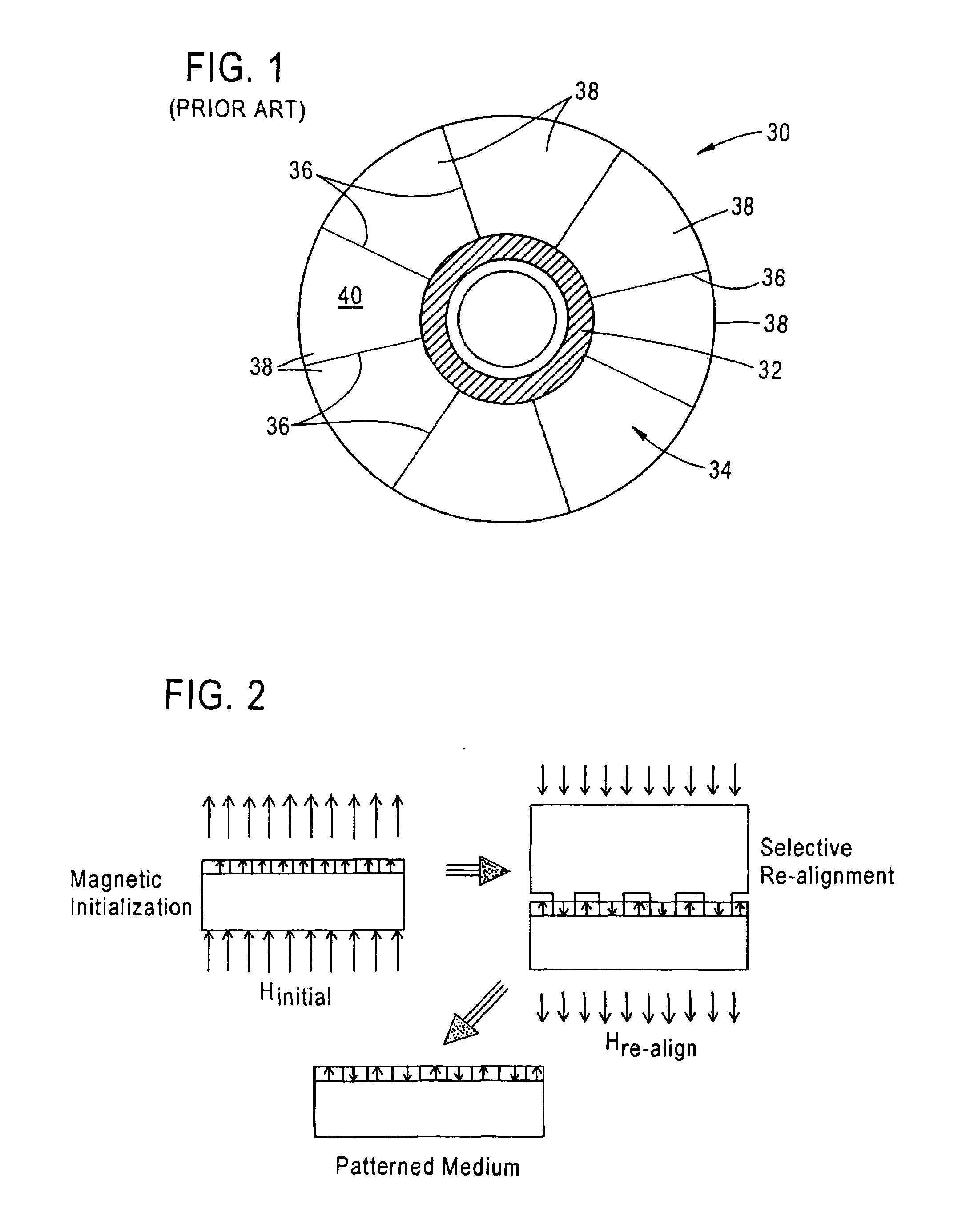
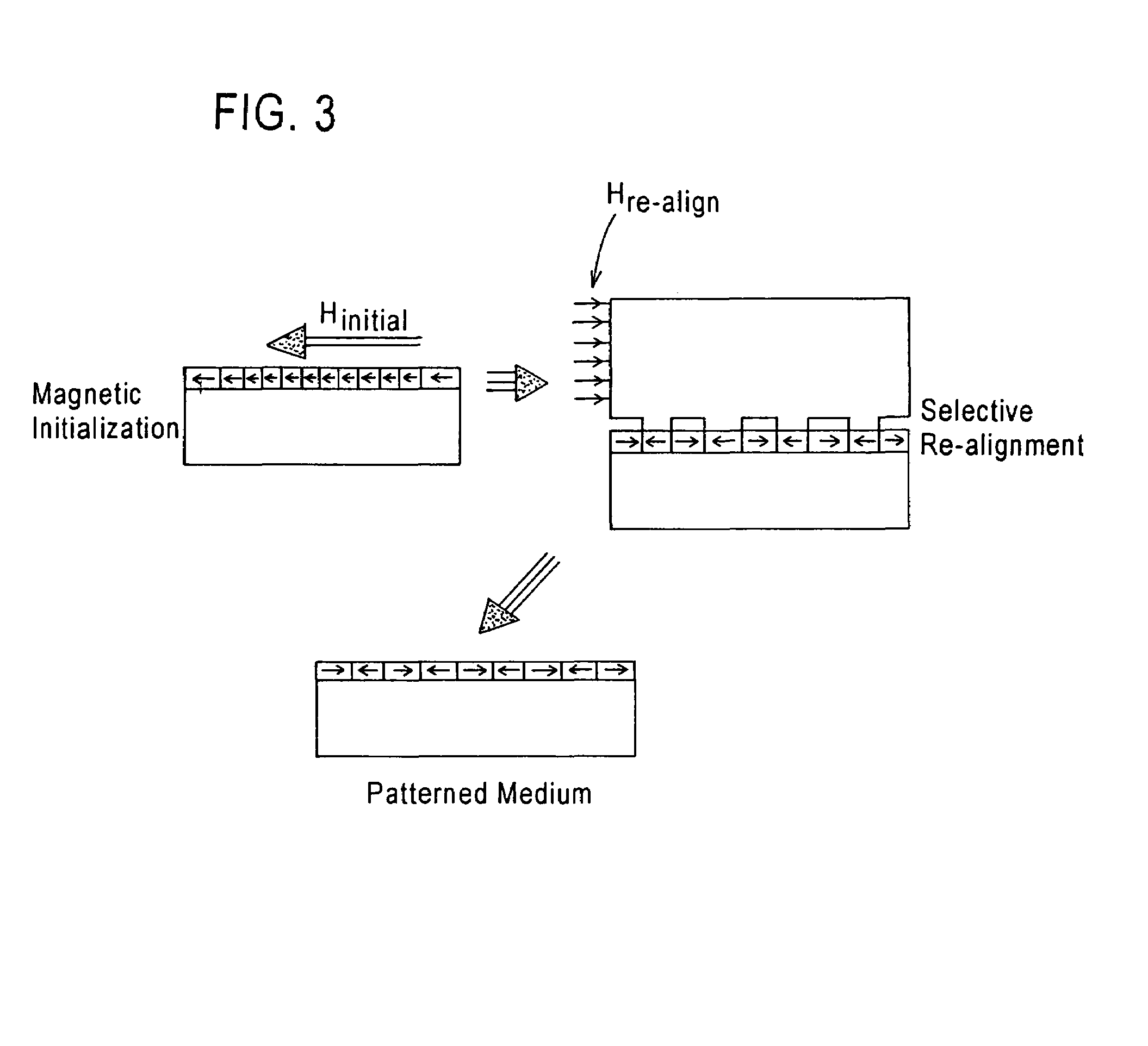
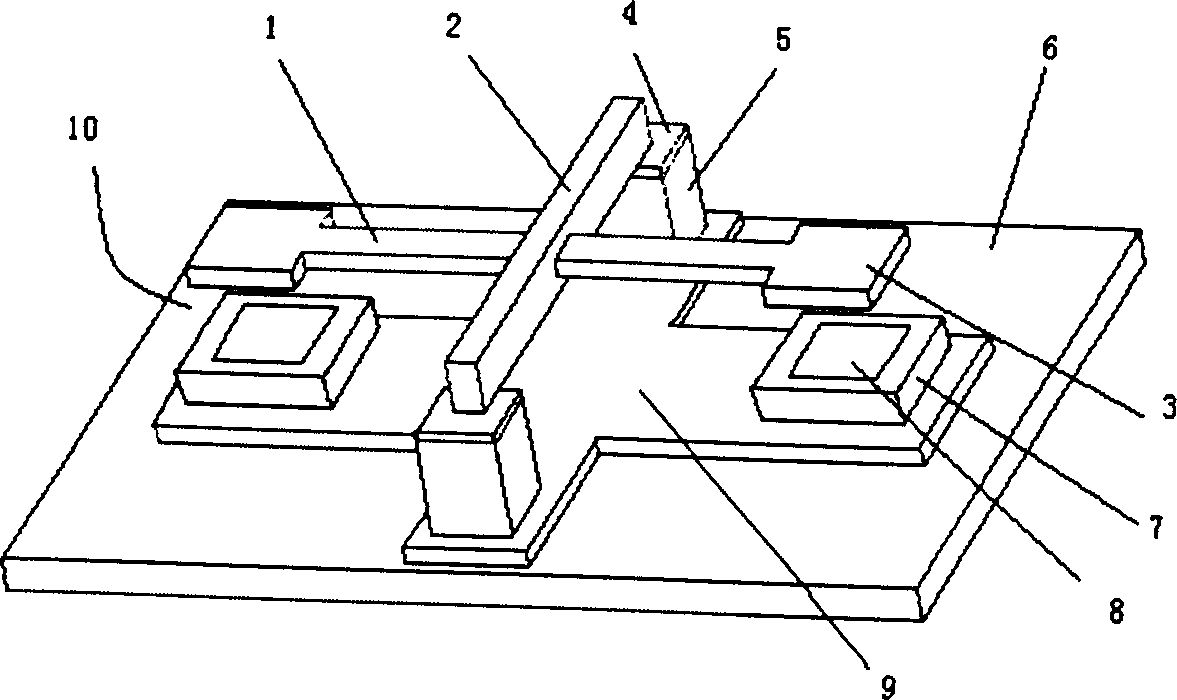
InactiveUS7036209B1Simple methodImprove methodCombination recordingElectrical transducersMagnetic transitionsEngineering
A method of simultaneously forming magnetic transition patterns in both side surfaces of a dual-sided magnetic or magneto-optical (MO) recording medium comprises steps of:(a) providing a dual-sided magnetic or MO recording medium having first and second opposing side surfaces;(b) providing a first magnetic stamper / imprinter having a first topographically patterned imprinting surface comprising a plurality of projections and depressions arranged in a first pattern corresponding to a first magnetic transition pattern to be formed in the first side surface;(c) providing a second magnetic stamper / imprinter having a second topographically patterned imprinting surface comprising a plurality of projections and depressions arranged in a second pattern corresponding to a second magnetic transition pattern to be formed in the second side surface, the second magnetic stamper / imprinter being formed from the first magnetic stamper / imprinter in a “mother” / “son” relationship;(d) contacting the first side surface with the first topographically patterned imprinting surface of the first magnetic stamper / imprinter;(e) contacting the second side surface with the second topographically patterned imprinting surface of the second magnetic stamper / imprinter; and(f) simultaneously forming magnetic transition patterns in both side surfaces of the medium by contact printing.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Bistable electromagnetic microdriver and mfg. method thereof
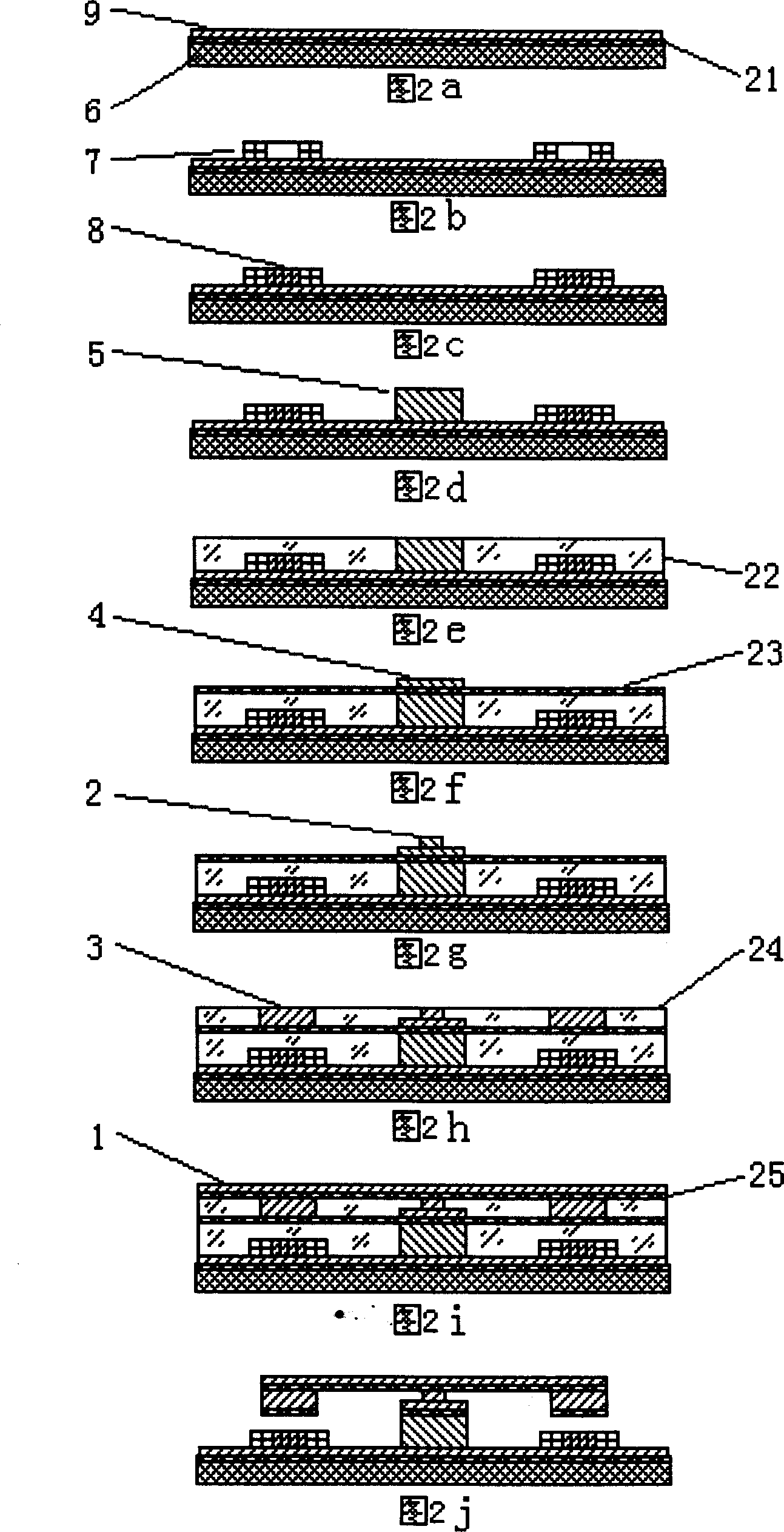
InactiveCN1452202AReduce power consumptionEfficient electromagnetic interactionDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingCantilevered beamMagnetic transitions
A bistable electromagnetic microdriver is structurally characterized by that a pair of permanent-magnet bases are symmetrically arranged on a soft-magnetic liner on base, a soft-magnetic torsional beams is arranged via soft-magnetic transition layer on said two bases to form a bridge structure, and a pair of soft-magnetic cantilevers are horizontally and symmetrically extended from the middle part of torsional beam to make their ends above the planar windings containing iron core on said liner. An air gap is between the end of cantilever and planar winding.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Layered perovskite multiferroic material and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a layered perovskite multiferroic material which is prepared by performing a ball milling for a bismuth layered perovskite ferroelectric material and a magnetic material containing transition metal elements, and then mixing, drying and sintering, wherein the bismuth layered perovskite ferroelectric material has a molecular formula (Bi2O2)<2+>(An-1BnO3n+1)<2-> as shown in a formula I, A is selected from any one or several of Na, K, Ca, Sr, Ba, Pb, Bi, La, Y, Gd and Pr, B is selected from any one or several of Ti, Nb, W and Ta, and n is positive integers. According to the invention, the bismuth layered perovskite ferroelectric material is inserted with magnetic transition metal elements, so as to prepare the multiferroic material, thereby effectively inhibiting electric leakage phenomena common in the magnetic materials and at the same time improving ferroelectric properties; and by together inserting different magnetic ions into interlayer of ferroelectric, different magnetic ions can be fully coupled, thereby improving ferromagnetic properties of the materials.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Magnetic anisotropy adjusted laminated magnetic thin films for magnetic recording
InactiveUS6939626B2Recording head field is reducedIncrease distanceDifferent record carrier formsRecord information storageMagnetic transitionsMagnetic media
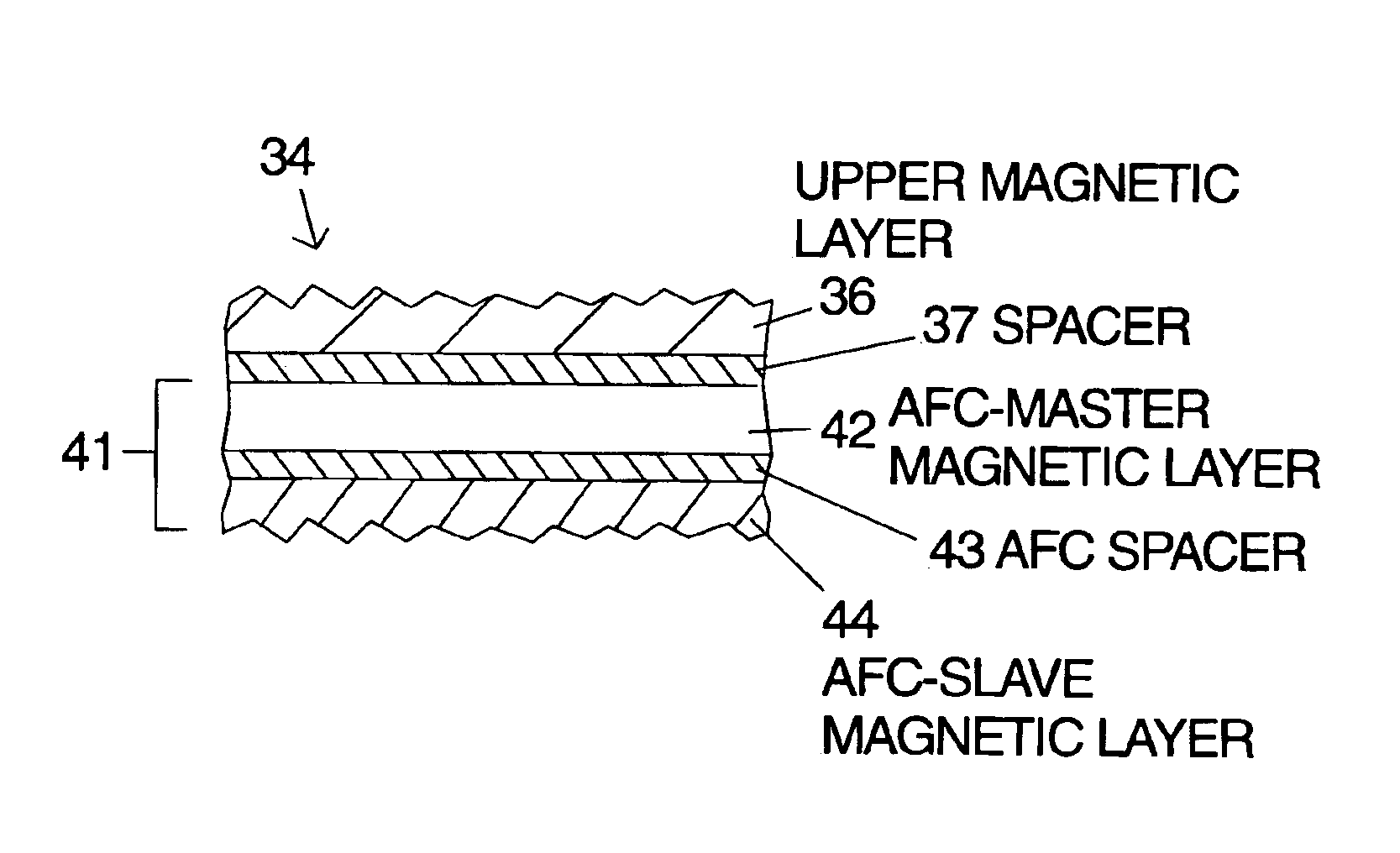
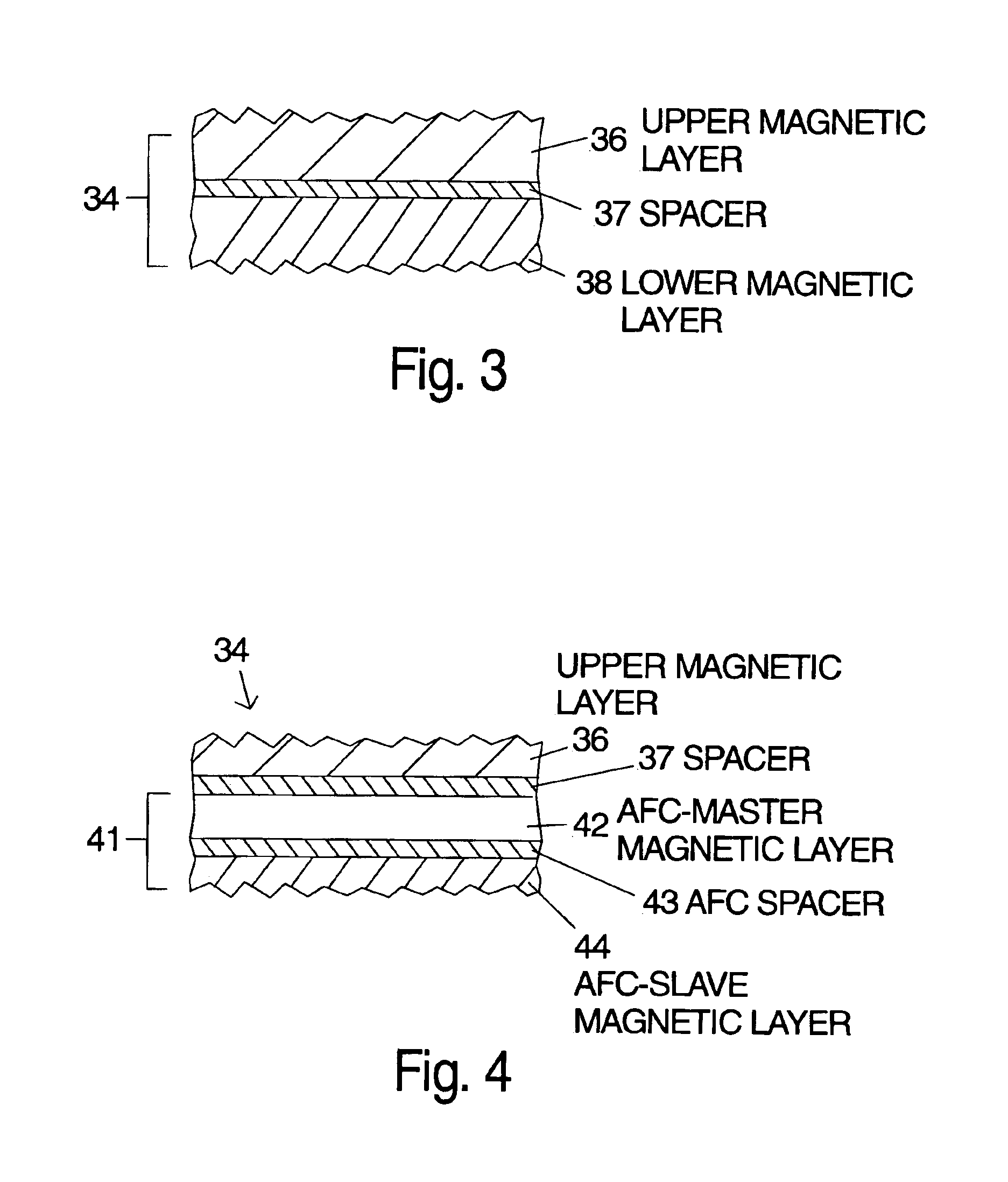
Multiple embodiments of the invention are described which include at least two laminated ferromagnetic layers with differing magnetic anisotropy. The independent magnetic layer farther away from the recording head is selected to have a lower magnetic anisotropy to allow magnetic switching of the multiple magnetic layers to occur at approximately the same head write current even though the recording head field is reduced with increased distance from the head. The improved switching yields improved magnetic recording performance. Laminated magnetic media according to the invention can have a single peak in the normalized DC erase noise vs. head write current plot indicating that the magnetic transitions in the non-slave magnetic layers are written at the same head write current. As a result the magnetic pulse width (PW50) is reduced, overwrite (OW) is improved and media signal-to-noise ratio (SoNR) is improved. Alternatively one or both of the laminated ferromagnetic layers can be replaced with an antiferromagnetically (AF) coupled layer structure that has an AFC-master and an AFC-slave layer separated by a spacer layer selected to antiferromagnetically couple the AFC-master and AFC-slave layers.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Magnetic data storage system
InactiveUS7586828B1Large storage densityMechanical recordingNanoinformaticsMagnetic transitionsFerromagnetism
A magnetic data storage system having a scanning tip array based system and a shape memory thin film-based data storage medium. Prior to storing data, the medium is in its non-ferromagnetic austenitic phase. Indentation stress locally induces martensitic transformation of the medium, which in turn generates a locally ferromagnetized surface. By measuring the magnetic force interaction between the tip and the medium surface, inscribed magnetic information can be read. The shape memory thin film enables the stress-induced local magnetic transition to provide a fast data storage system with high data storage density.
Owner:TINI ALLOY
Preparation method of alloy thin strip magnet of Sm(Co,Cu,Fe,Zr)-z type
InactiveCN101620928AMagnetsInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic transitionsMischmetal
The invention relates to a preparation method of alloy thin strip magnets of Sm(Co,Cu,Fe,Zr)-z types and relates to a magnet containing hard magnetic materials of a rare-earth metal and magnetic transition metals. The preparation method comprises the following steps: presenting a chemical composition formula in a melt of Sm(Cox Cuy Feu Zrv) z; rapidly quenching the melt on a cooling molybdenum roller or a copper roller rotating at a peripheral speed of 5-40 m / s by a melt rapidly quenching furnace or a vacuum melting rapidly quenching continuous furnace to obtain melt thin strips of Sm(Co,Cu,Fe,Zr)-z types; pulverizing the melt thin strips into powder; pressing the powder into blocks in a magnetic field larger than 1T; and compacting the blocks in a cold isostatic press before final heat treatment. The invention provides three heat treatment processes and accordingly obtains the practical block alloy thin strip magnets of Sm(Co,Cu,Fe,Zr)-z types with different characteristics.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of Sm-Co-based amorphous nanocrystalline thin-strip magnet
ActiveCN102403117AHigh glass forming abilityHigh curie temperaturePermanent magnetsInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic transitionsHigh resistance
The invention relates to a preparation method of a Sm-Co-based amorphous nanocrystalline thin-strip magnet, and relates to a rare earth metal and magnetic transition metal containing magnet made of a hard magnetic material. The Sm-Co-based amorphous nanocrystalline thin-strip magnet has a chemical formula of SmxCoyFezZruBvQw, wherein the symbols of qualified elements metered by atomic percentage meet the following conditions: x + y + z + u + v + w = 100, x = 9.0-14.0, y = 45.0-70.5, z = 2.8-18.4 , u = 1.1-7.0, v = 3.8-19.0, w = 1.0-21.2, and Q is one to four elements of Nb, Al, Si, Cu and C. The Sm-Co-based amorphous nanocrystalline thin-strip magnet prepared by a centrifugal fast quenching and strip throwing technology has the advantages of high room temperature intrinsic coercivity, high resistance to corrosion and high strength.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Piezoelectric element and method for manufacturing
InactiveUS20060131680A1Well formedImprove heat resistancePiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblySubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementMagnetic transitionsCrystal structure
A lower electrode is formed on a silica glass substrate or a stainless substrate. Through a sputtering process, a thin film of aluminum nitride and / or zinc oxide is formed on the lower substrate so that the degree of dipole-orientation becomes 55% or more, and thereby a piezoelectric thin film is formed. And an upper electrode is formed on the piezoelectric thin film. A piezoelectric device has a piezoelectric layer made of aluminum nitride and / or zinc oxide. Aluminum nitride and zinc oxide with a crystal structure have inborn piezoelectric characteristics because their crystal structures are not symmetrical, they do not have Curie temperature unlike ferroelectrics, and in aluminum nitride and zinc oxide, magnetic transition does not occur even at high temperature, so that they never lose piezoelectric characteristics until crystal melts or sublimates.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Contact printing of magnetic media with mechanically reinforced and/or gas venting stamper
InactiveUS7218466B1Smooth connectionApparatus is enlargedPatterned record carriersNanoinformaticsMagnetic transitionsMagnetic media
An apparatus for performing contact printing of a magnetic transition pattern in a magnetic recording medium, comprising:(a) a stamper / imprinter including a body formed of at least one magnetic material having a high saturation magnetization Bsat and a high permeability, including an imprinting surface adapted to be placed in intimate contact with a surface of a magnetic layer, the imprinting surface comprised of a plurality of patterned areas which separate a plurality of areas which are not patterned, each of the areas which is not patterned being provided with at least one of:(i) mechanical reinforcing means for preventing deformation of the body when the imprinting surface is urged into contact with the surface of the magnetic layer; and(ii) gas venting means for facilitating removal of air or other gas from between the imprinting surface and the surface of the magnetic layer when the former is urged into contact with the latter.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
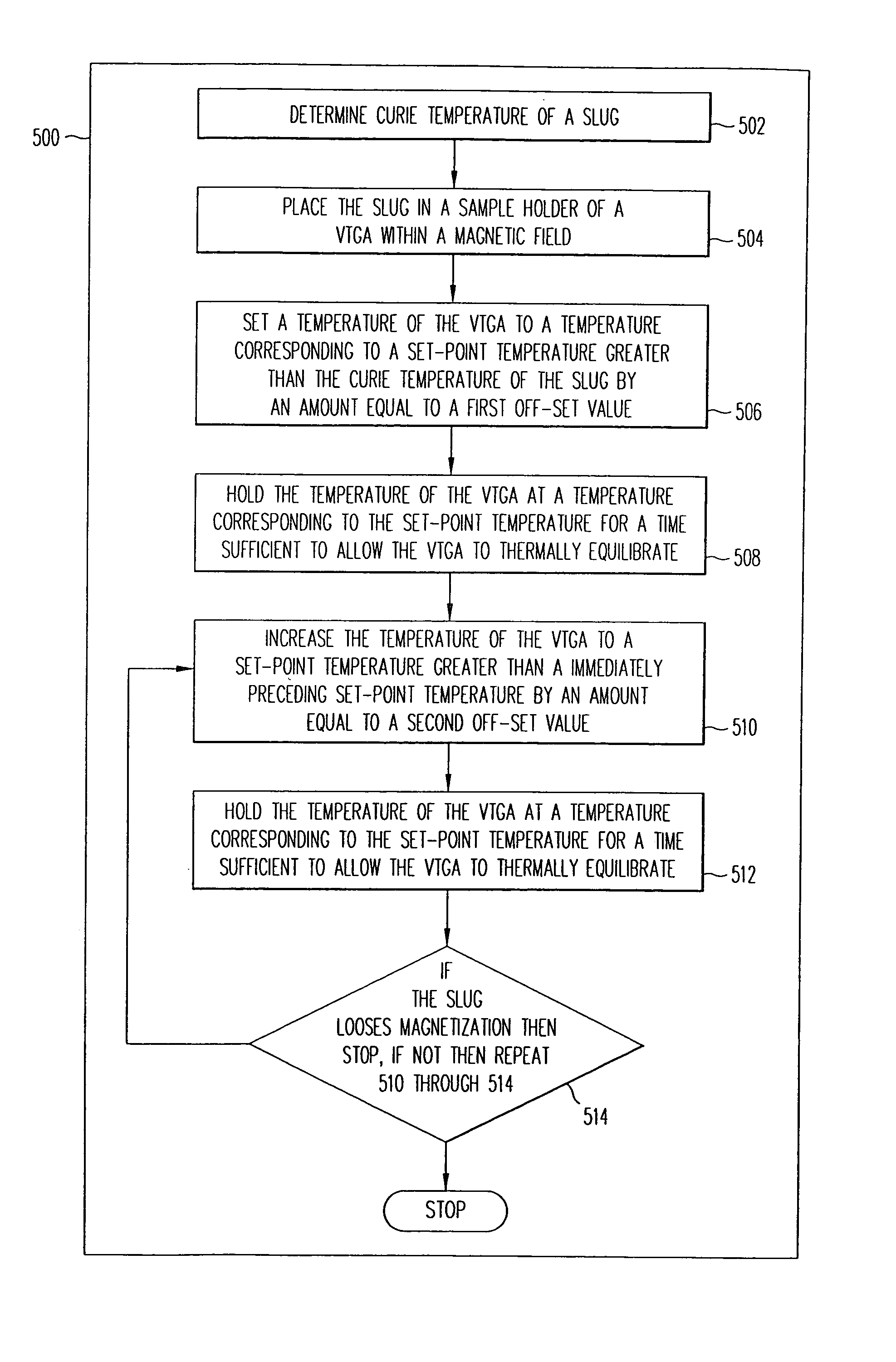
Standards for the calibration of a vacuum thermogravimetric analyzer for determination of vapor pressures of compounds
InactiveUS20050025212A1Improve magnetic propertiesHomogenize microstructureThermometers using physical/chemical changesThermometer testing/calibrationMagnetic transitionsAlloy
The invention provides a set of standards for accurately calibrating a vacuum thermogravimetric analyzer (VTGA). The invention solves the problem of calibrating a VTGA by using the actual magnetic transitions and associated transition temperatures, or Curie temperatures, TC's, of a set of standards which can be used in-situ at the location of the sample holder obviating the difficulties associated with indirect methods of calibration. The set of standards permits accurate calibration through sufficiently numerous calibration points over a rather limited low-temperature range for determining vapor pressures of compounds. The set of temperature calibration standards is fabricated from slugs of ferromagnetic material. The composition of the ferromagnetic material in each slug is altered by alloying a ferromagnetic constituent with a non-ferromagnetic constituent to provide a plurality of standards with different Curie temperature over the limited temperature range. In particular, an embodiment of the invention using alloys of Ni and Cu where the amount of Cu varies between less than 10% up to approximately 50% by weight provides a set of standards that can span temperatures in any selected range from approximately 300 C to −150 C respectively.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
System and method for determining head-disk contact in a magnetic recording disk drive by magnetoresistive signal amplitude
InactiveUS20070217051A1Easy to testIncrease head-disk spacingDriving/moving recording headsFilamentary/web record carriersMagnetic transitionsLow-pass filter
A system and method for determining head-disk contact (HDC) in a disk drive uses the signal from the magnetoresistive (MR) read head and does not require the presence of magnetic transitions on the disk. The method thus has application in head-disk testers or “spin stands” to facilitate the design and testing of slider-suspension assemblies and fly-height actuators, as well as in disk drives to take corrective action before HDC and / or to control fly-height actuators. The invention is also a magnetic recording disk drive that has a fly-height actuator and a low-pass filter and comparator circuit for the MR signal. When the output of the filter exceeds a threshold the comparator circuit output indicates the onset of HDC. The comparator circuit output is input to a digital processor or controller. When the controller determines the onset of HDC or that HDC has occurred, it generates a control signal that can be used to cause the disk drive to take corrective action.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Magnetoresistance effect element
InactiveUS20050047028A1High sensitivityImprove reliabilityNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsMagnetic transitionsNitrogen
There are provided a magnetoresistance effect element, a magnetic head, a magnetic head assembly and a magnetic recording system, which have high sensitivity and high reliability. The magnetoresistance effect element has two ferromagnetic layers, a non-magnetic layer provided between the ferromagnetic layers, and a layer containing an oxide or nitride as a principal component, wherein the layer containing the oxide or nitride as the principal component contains a magnetic transition metal element which does not bond to oxygen and nitrogen and which is at least one of Co, Fe and Ni.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
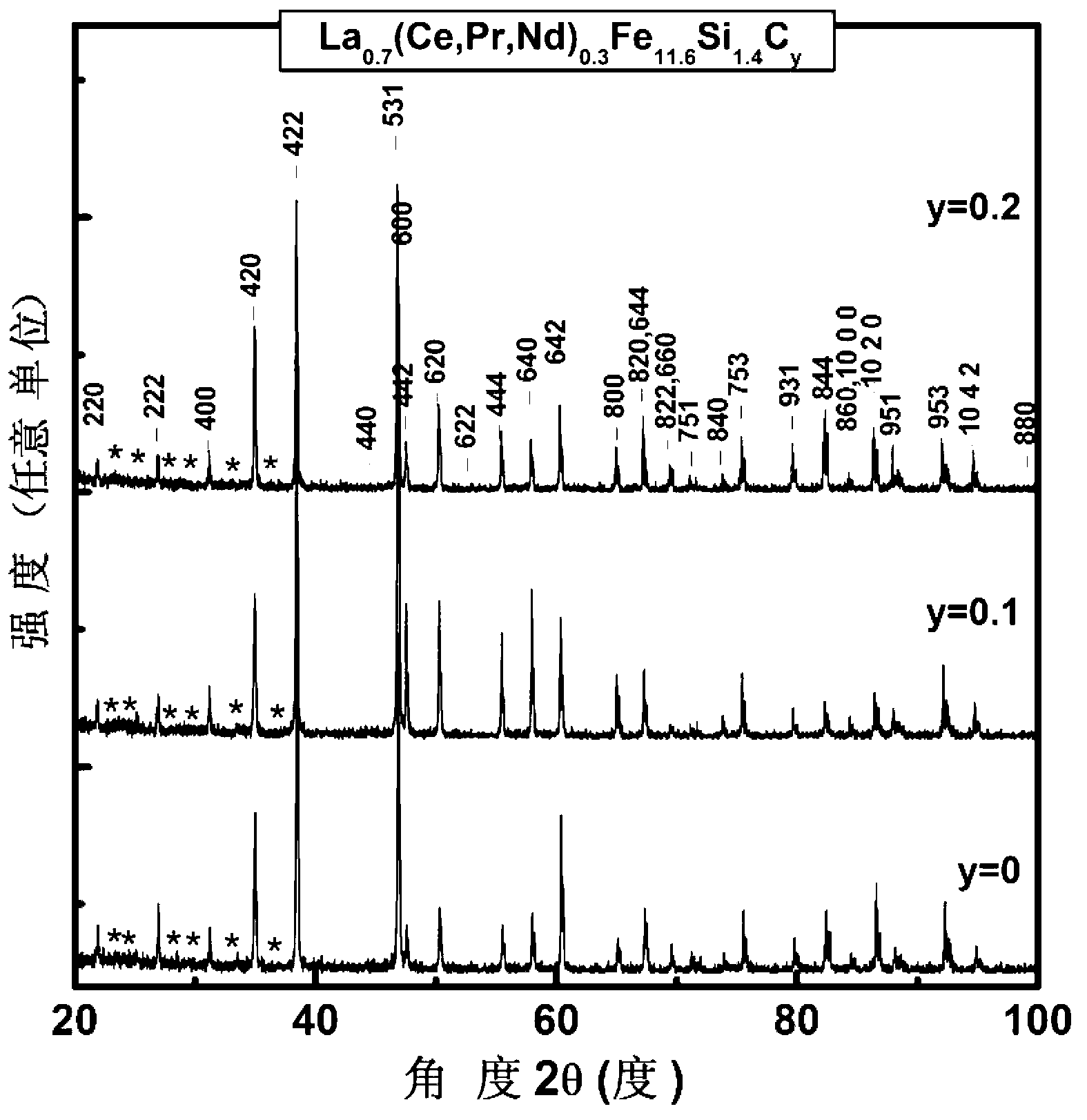
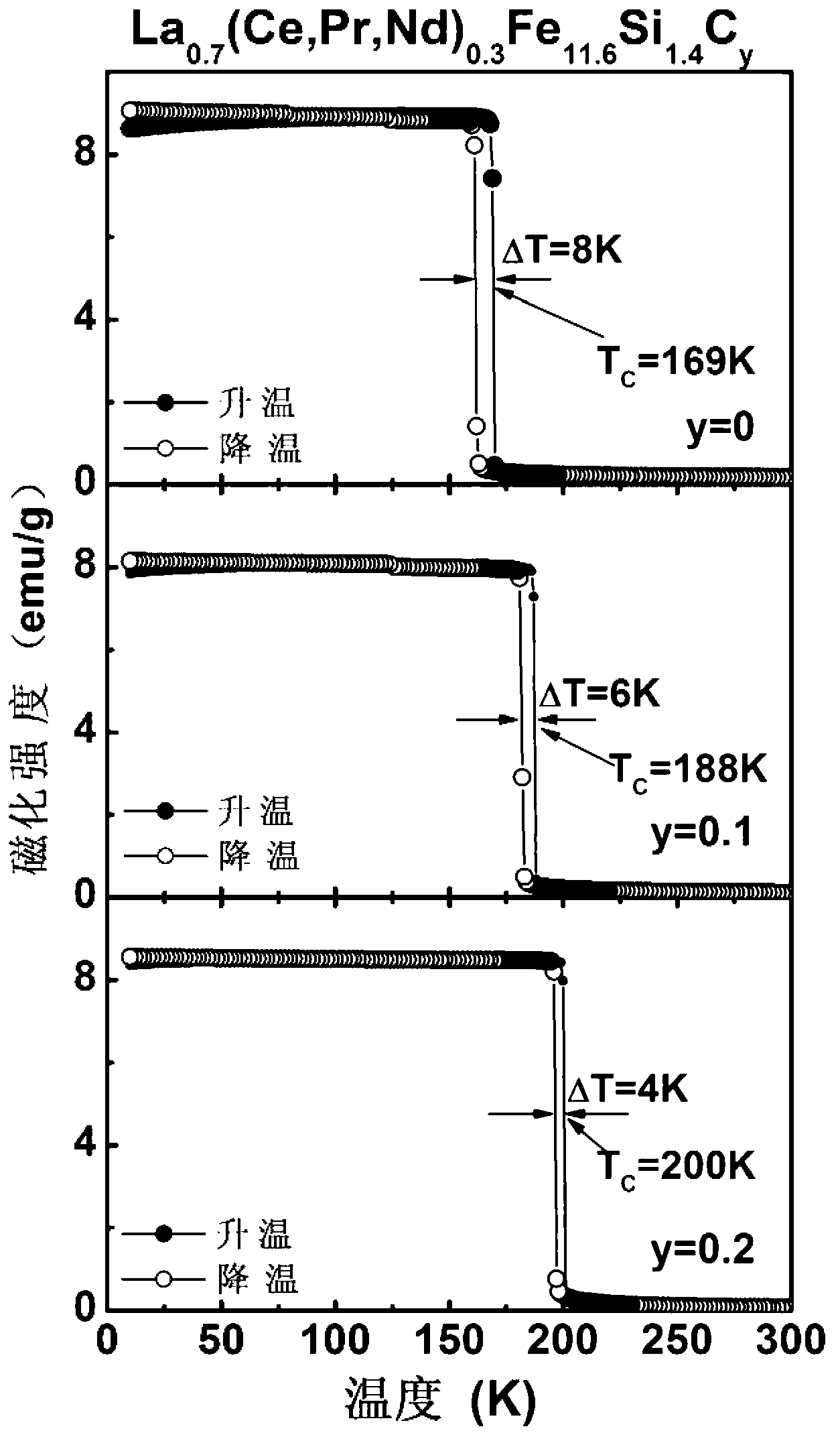
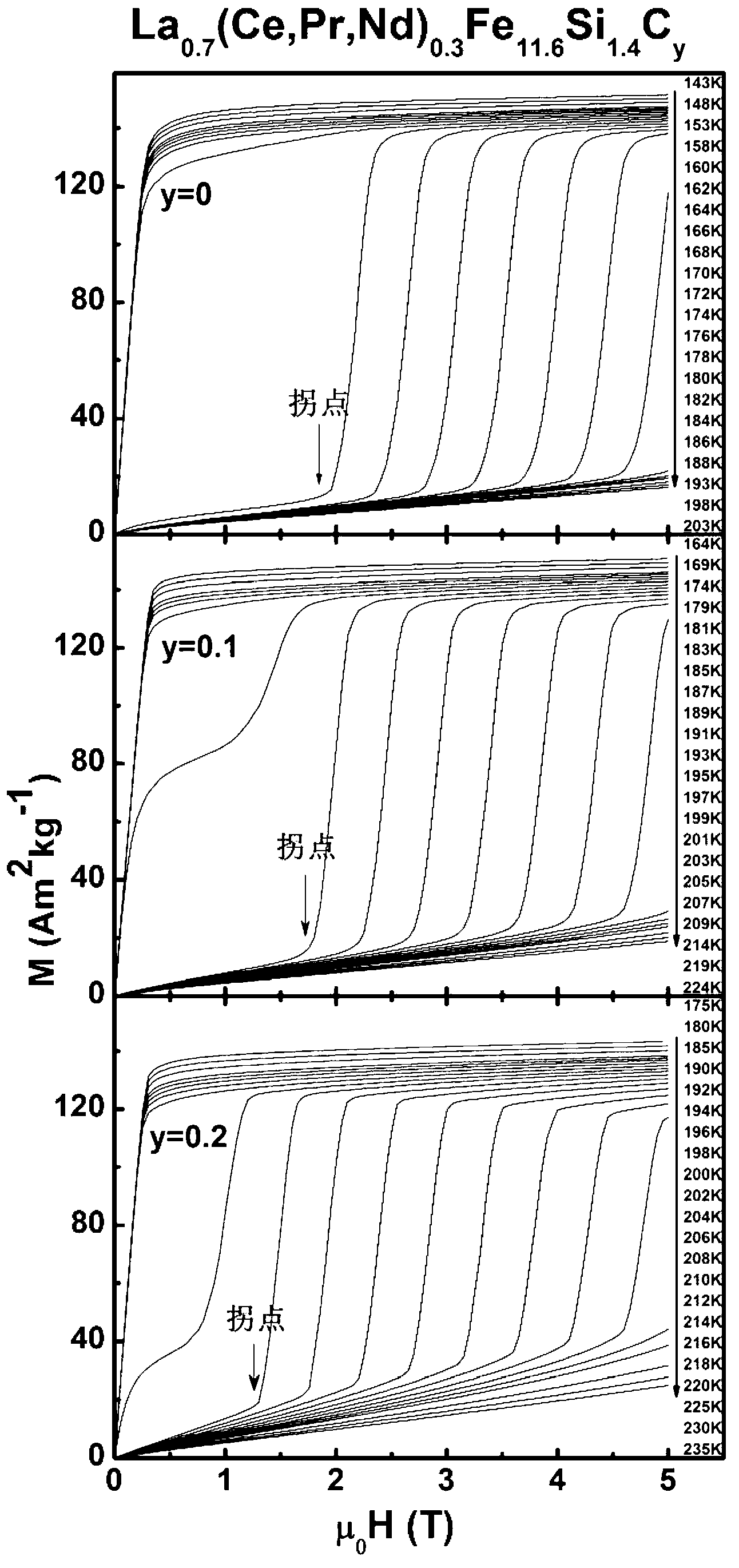
La(Fe,Si)13 based magnetic refrigeration material by taking high-Ce industrial pure mixed rare earth as raw material as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103045177AReduce manufacturing costReduce dependenceHeat-exchange elementsMagnetic transitionsSingle substance
The invention provides a La(Fe,Si)13 based magnetic refrigeration material by taking high-Ce industrial pure mixed rare earth as a raw material. The chemical formula is La1-x(Ce,Pr,Nd)x(Fe1-p-qCopMnq)13-ySiyaalpha and is provided with an NaZn12 type structure. The invention further provides a preparation method and an application of the material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: smelting and annealing to prepare the La1-x(Ce,Pr,Nd)x(Fe1-p-qCopMnq)13-ySiyaalpha magnetic refrigeration material by taking the high-Ce industrial pure mixed rare earth as the raw material. Impurities in the raw material high-Ce industrial pure mixed rare earth do not influence the generation of a 1: 13 phase and the appearance of first order phase transformation and variable magnetic transition behavior, so that the dependence on a high-purity single-substance rare earth raw material is reduced, the preparation cost of the material is reduced, and the La(Fe,Si)13 based magnetic refrigeration material has important actual meanings on developing the magnetic refrigeration application of the material.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
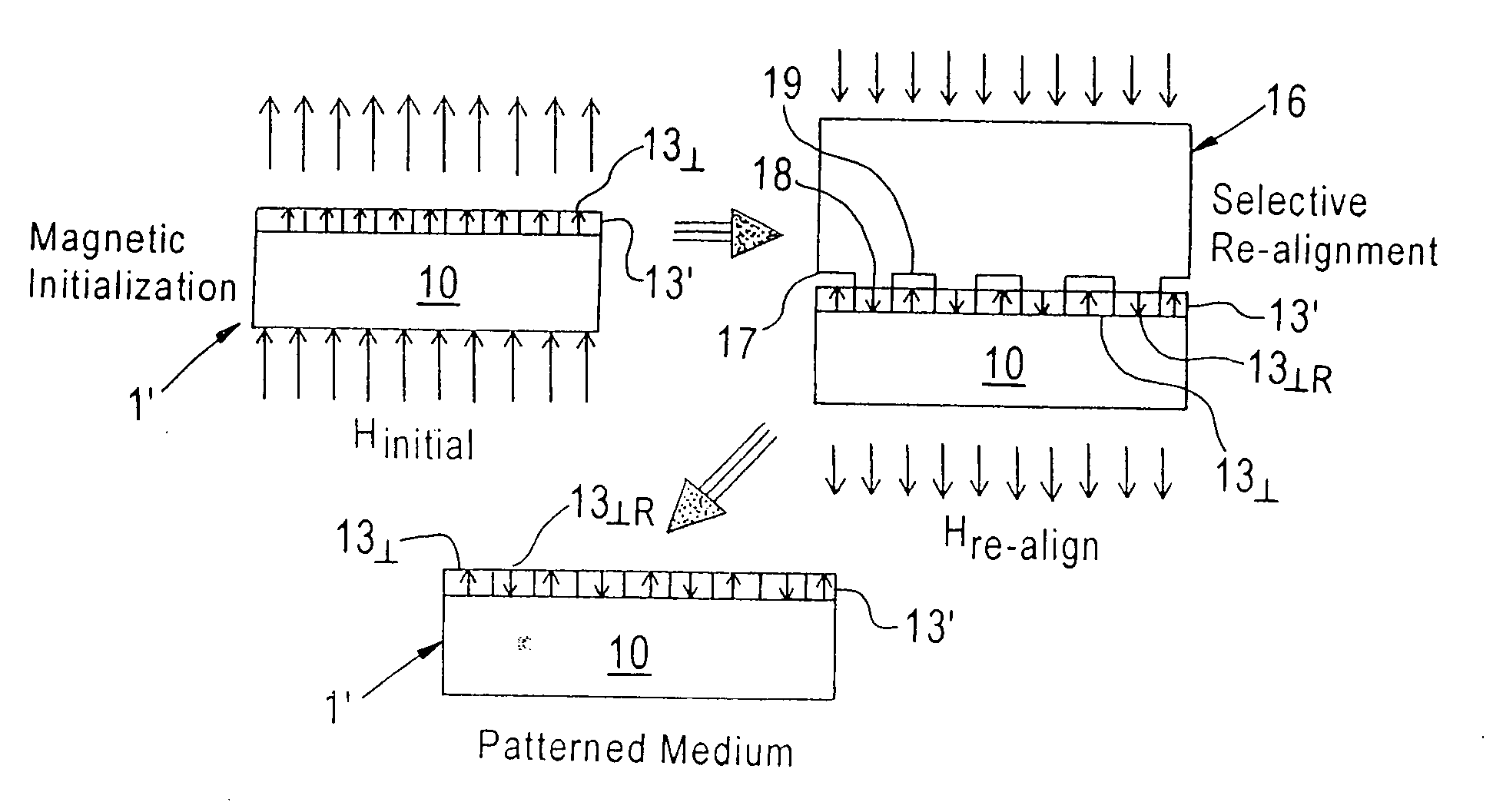
Magnetic media patterning via contact printing utilizing stamper having magnetic pattern formed in non-magnetic substrate
InactiveUS20070285816A1Easy to manufactureSimple methodNanoinformaticsPatterned record carriersMagnetic transitionsMagnetic media
Owner:SEAGATE TECH HDD HLDG +3
Preparing method of porous graphene oxide
The invention provides a preparing method of porous graphene oxide. The method includes the following steps of a, preparing a composite of graphene oxide / magnetic transition metal oxide nanoparticles;b, conducting seed crystal growth and reduction on the composite of graphene oxide / magnetic transition metal oxide nanoparticles; c, conducting microwave reaction on the processed composite of graphene oxide / magnetic transition metal oxide nanoparticles to obtain a porous graphene oxide coarse product; d, conducting acid pickling on the obtained coarse product. By means of the preparing method, the size and number of nanometer pores in the surface of a prepared porous graphene oxide slice layer can be controlled by preparing the magnetic transition metal oxide nanoparticles of different sizesand densities on the surface of graphene oxide.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Magnetic recording disk drive with shingled writing and wide-area thermal assistance
InactiveCN102779528ADisposition/mounting of recording headsRecord information storageMagnetic transitionsRecording layer
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
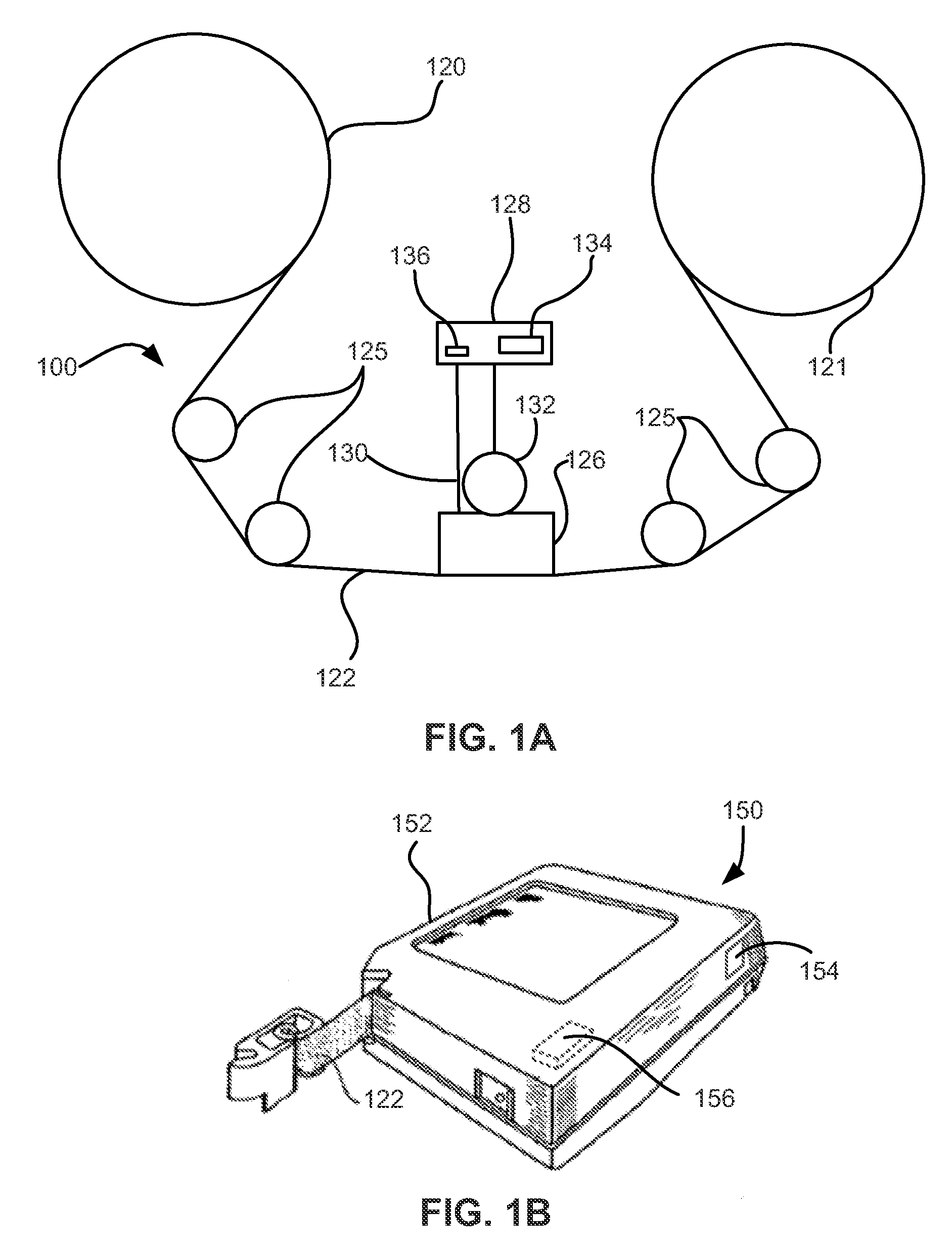
Write delay to de-skew data in read while write function for tape storage devices
InactiveUS9117470B1Alignment for track following on tapesRecord information storageMagnetic transitionsMagnetic media
According to one general embodiment, a method includes determining an offset between first and second arrays of transducers on a magnetic head in a direction perpendicular to an intended direction of media travel when the magnetic head is positioned at a first position, tilting the magnetic head to a second position, and delaying writing by at least some of the write transducers to provide magnetic transitions on a magnetic medium as if the longitudinal axis of the array was aligned in the direction perpendicular to the intended direction of media travel. At least one of the arrays of transducers includes write transducers. Moreover, the arrays of transducers have longitudinal axes aligned at the second position greater or less than 0 degrees from the longitudinal axes of the arrays of transducers aligned at the first position.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for preparing Sm-Co based magnetic nano-material
ActiveCN103586465AHighlight substantive featuresDistributeInorganic material magnetismNanotechnologyMagnetic transitionsCompound (substance)
The invention discloses a method for preparing Sm-Co based magnetic nano-material and relates to a magnetic material containing rare earth metals and magnetic transition metals. The method for preparing the Sm-Co based magnetic nano-material combines physical methods and chemical methods in the following manner: hard magnetic SmCo6.9Hf0.1 nano-particles are obtained as a core in a ball-milling mode, the outer layers of the SmCo6.9Hf0.1 nano-particles are coated with soft magnetic elementary substance Co or Fe shells in combination with the polyol reduction method, and thus the Sm-Co based magnetic nano-material with the core-shell structure is prepared. Because the outer layer of the Sm-Co based magnetic nano-material is coated with the soft magnetic transition metal elementary substance shells, the Sm-Co based magnetic nano-material is prevented from being oxidized to a certain extent, and meanwhile possibility is provided for further pressing and sintering blocky materials with higher magnetic performance.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Production method for Sm(Co,M)7 type alloy thin strip magnet
InactiveCN101430958AOptimized grain size microstructureImprove intrinsic coercive forceInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic transitionsMicro structure
The invention provides a preparation method used for Sm(Co, M)7 typed alloy ligature magnet, belonging to the magnet technical field of hard magnetic material containing rare earth metal and magnetic transition metal. The preparation method comprises the steps as follows: the molecular formula of the fuse is SmCo<7-x>Mx(CNT)y; wherein, M is Hf, Ga or Si; CNT is carbon nano-tube; according to the atom percentage, the symbols which limits the composition meets the following formulas: x is not less 0.05 and not more than 1.6; y is not less than 0.01 and not more than 0.1; the fuse is rapidly quenched on a cooling molybdenum roller wheel or a copper roller wheel which rotates at a circumferential velocity of 10-60m / s, thus preparing the Sm(Co, M)7 typed alloy ligature magnet which has the mass magnetization intensity of 40.0-105.0Am<2> / kg, has the intrinsic coercivity of 480.0-1840.0kA / m after being magnetized in an external magnetic field of 4.8MA / m, has the intrinsic coercivity of 480.0-2,000.0kA / m after being magnetized in an external magnetic field of 7.2MA / m, has the thickness of 20-120 microns and has the average grain size of 10-200nm. The carbon nano-tube which is used as an ideal pinning phase stabilizes the phase structure of the Sm(Co, M)7 typed alloy ligature magnet when in a quick quenching state and a heat disposal state, optimizes the micro-structure of the grain size and leads the alloy to be practical permanent magnet with high coercivity.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Standards for the calibration of a vacuum thermogravimetric analyzer for determination of vapor pressures of compounds
InactiveUS20050163191A1Improve magnetic propertiesHomogenize microstructureThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsInorganic material magnetismMagnetic transitionsAlloy
The invention provides a set of standards for accurately calibrating a vacuum thermogravimetric analyzer (VTGA). The invention solves the problem of calibrating a VTGA by using the actual magnetic transitions and associated transition temperatures, or Curie temperatures, TC's, of a set of standards which can be used in-situ at the location of the sample holder obviating the difficulties associated with indirect methods of calibration. The set of standards permits accurate calibration through sufficiently numerous calibration points over a rather limited low-temperature range for determining vapor pressures of compounds. The set of temperature calibration standards is fabricated from slugs of ferromagnetic material. The composition of the ferromagnetic material in each slug is altered by alloying a ferromagnetic constituent with a non-ferromagnetic constituent to provide a plurality of standards with different Curie temperature over the limited temperature range. In particular, an embodiment of the invention using alloys of Ni and Cu where the amount of Cu varies between less than 0% up to approximately 50% by weight provides a set of standards that can span temperatures in any selected range from approximately 300 C to −150 C respectively. Prior to use in calibration, each slug is preferably placed in a magnetic field having a magnitude sufficient to provide a well defined magnetic transition at the Curie temperature.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
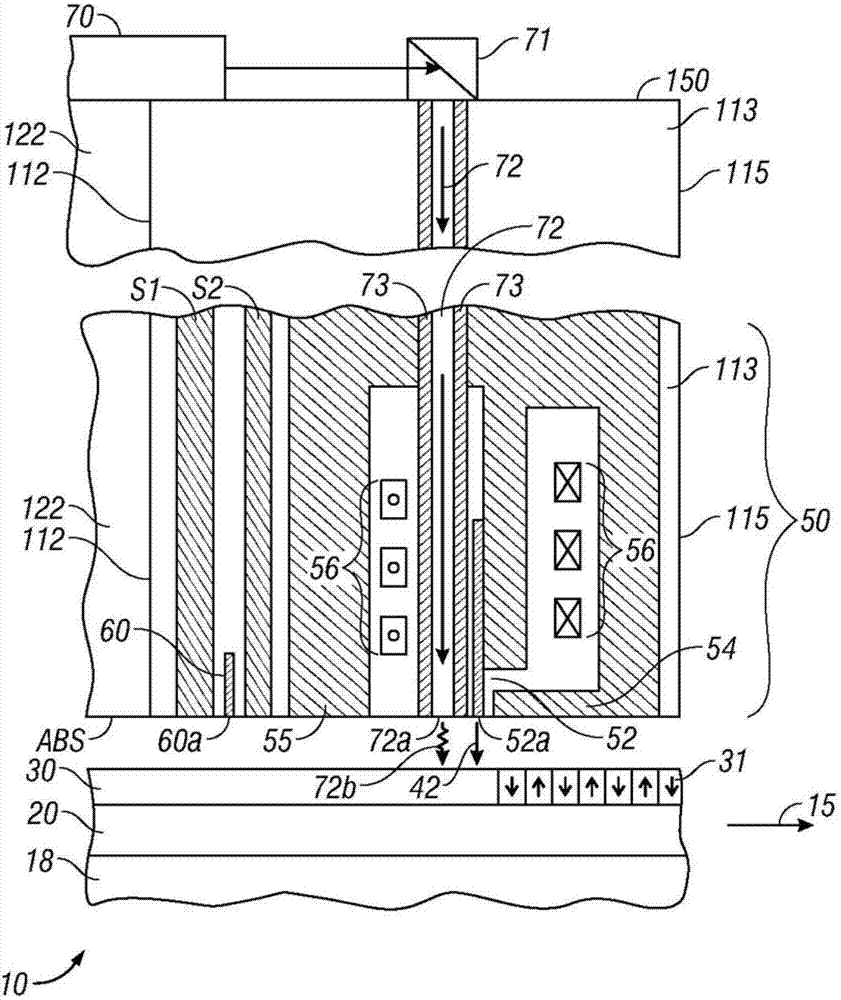
Perpendicular magnetic recording system with medium having thin soft underlayer and recording head having thick-throat trailing shield
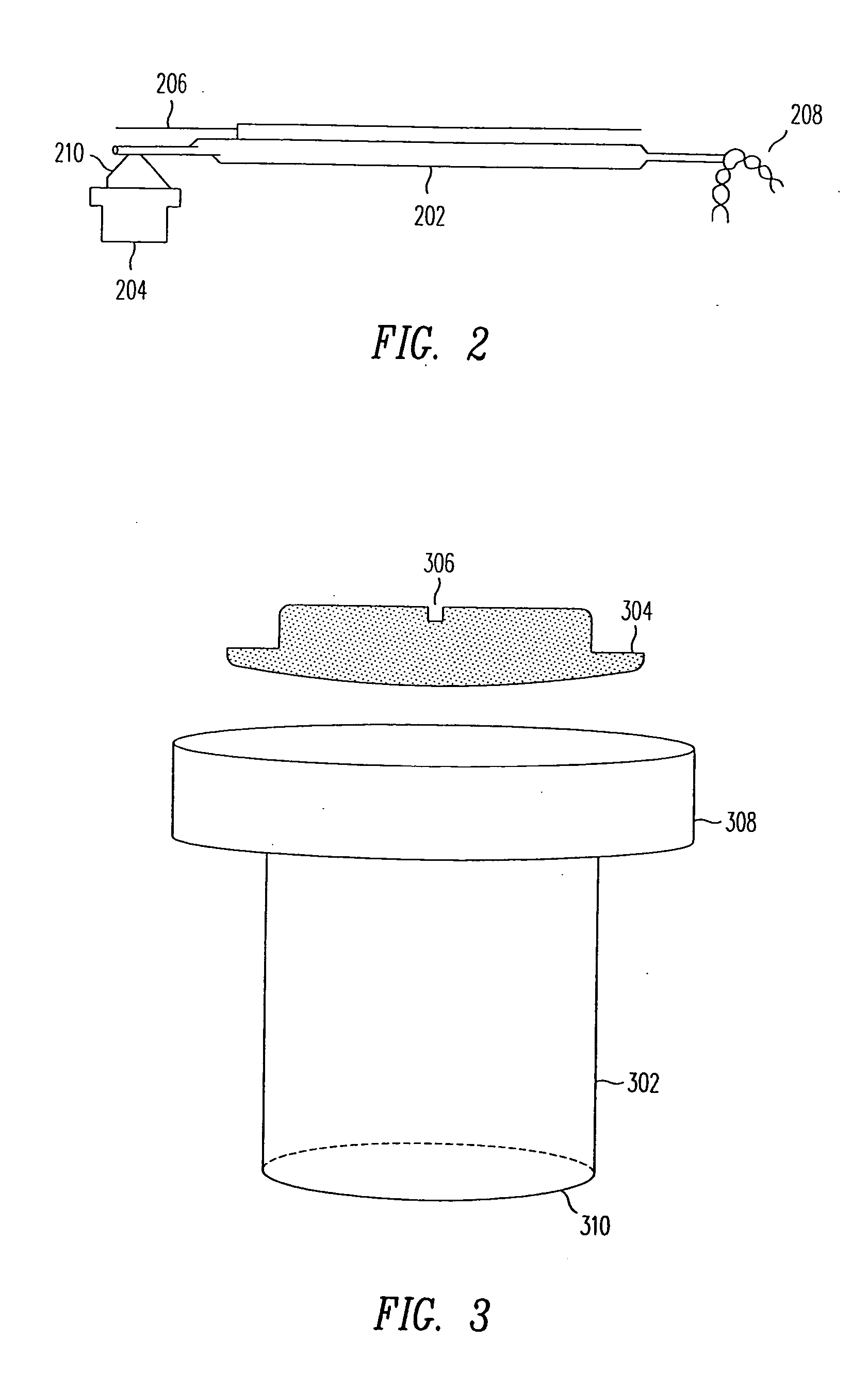
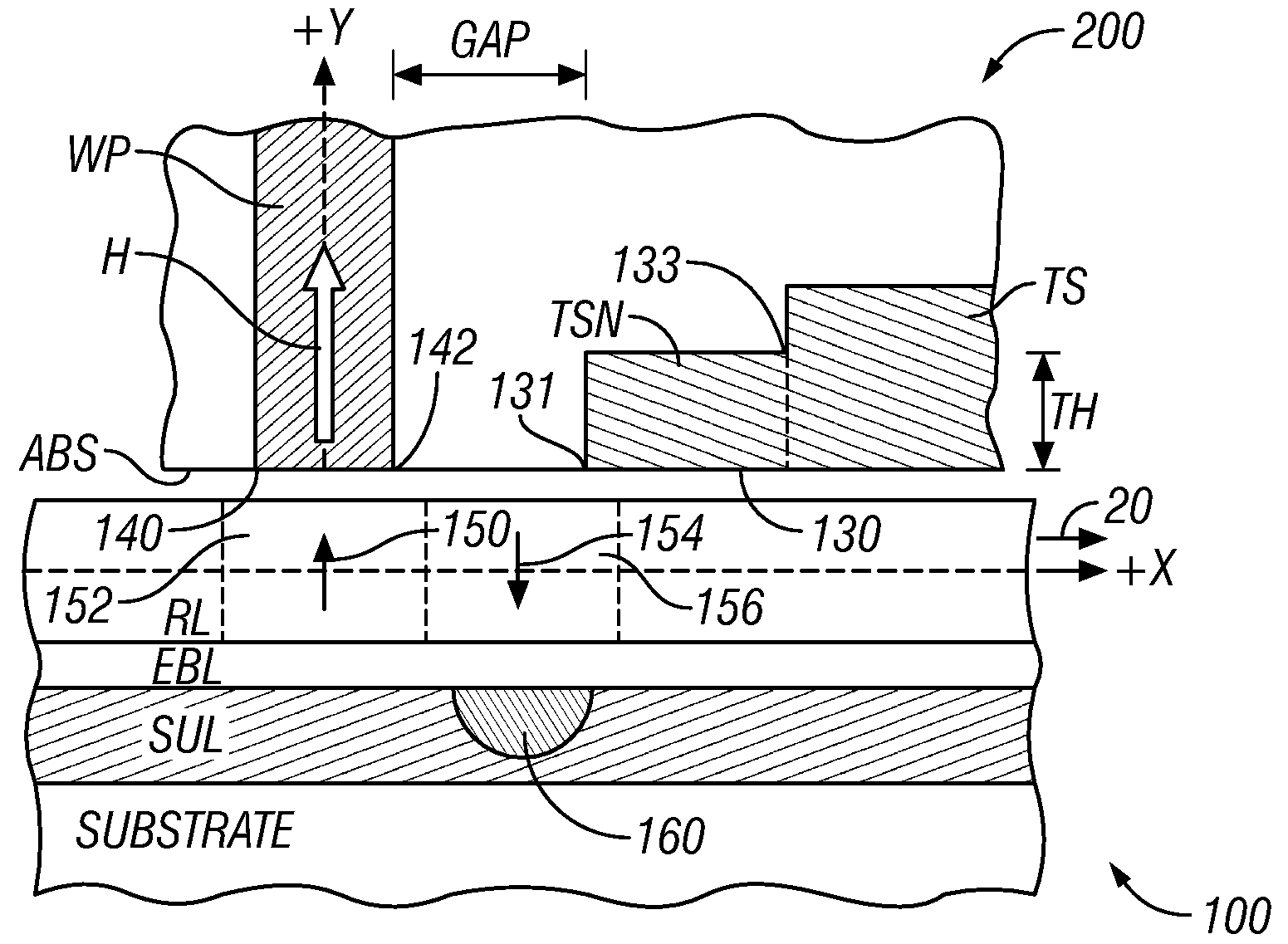
InactiveUS7532432B2Low enough magnetic permeabilityHigh gradientManufacture head surfaceRecord information storageThroatMagnetic transitions
A perpendicular magnetic recording data storage system combines a perpendicular medium that has a thin low-magnetic-permeability or “soft” underlayer (SUL) with a recording head that has a trailing shield (TS) with a thick throat height, i.e., a thickness in a direction orthogonal to the recording layer of the medium. The SUL is thin enough and has a low enough magnetic permeability to become saturated in a region beneath the trailing gap of the head during writing, but the throat height of the TS is thick enough to prevent the TS from becoming magnetically saturated during writing. The magnetic saturation of the SUL during writing changes the magnetic reluctance such that more of the magnetic flux going through the SUL changes direction (“field undershoot”) and goes to the TS. If the permeability of the SUL is so low (e.g., close to unity) that the SUL does not magnetically saturate, field undershoot may still occur because the reluctance from the SUL to the TS is still smaller than the reluctance from the SUL to the return pole (RP). Field undershoot enables a high write field gradient, which results in narrower magnetic transitions.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com