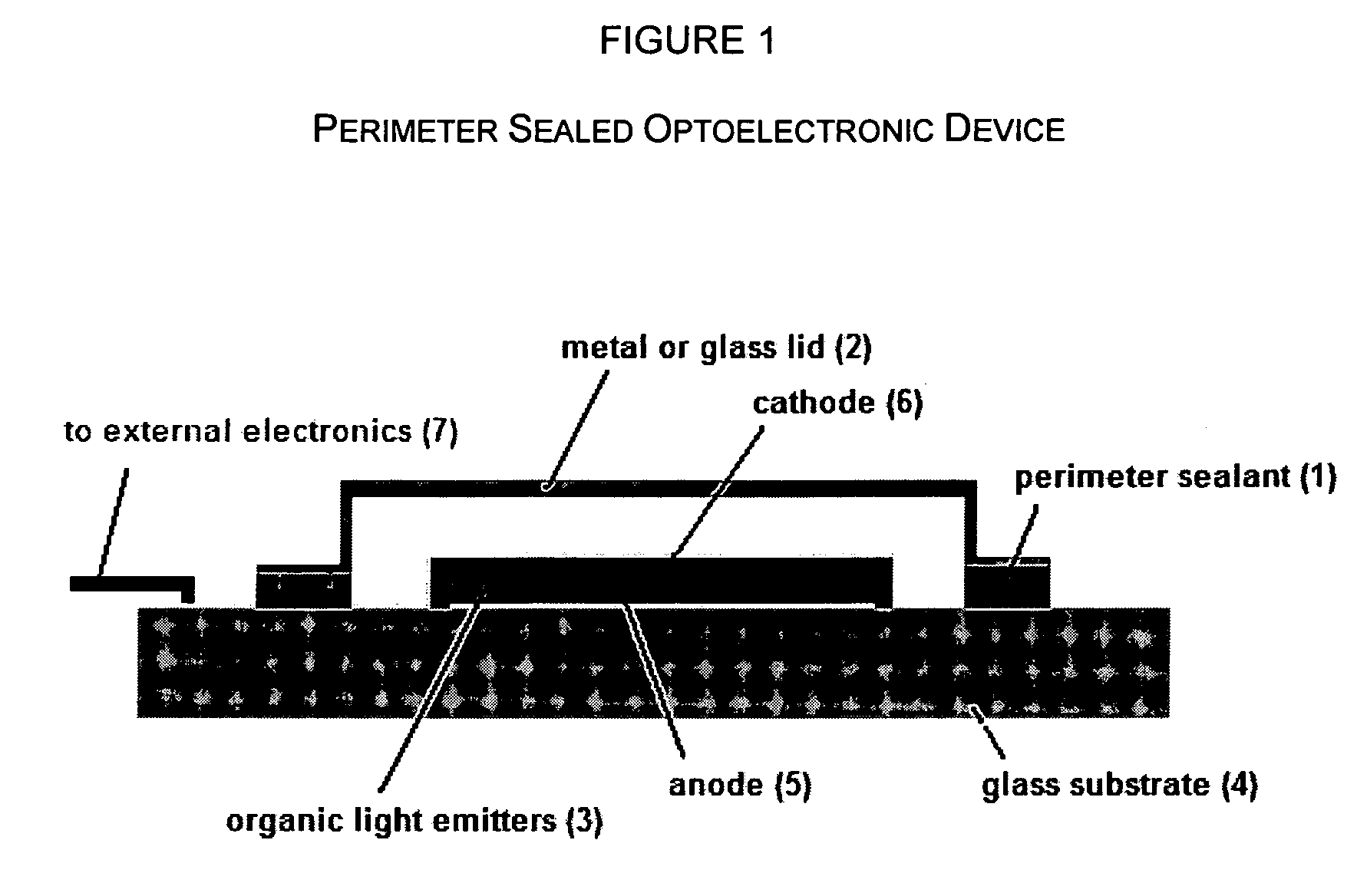
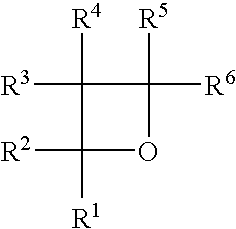
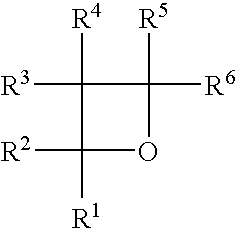
Radiation- or thermally-curable oxetane barrier sealants
a technology of oxetane and barrier sealants, which is applied in the direction of refrigeration components, electrodialysis, refrigeration machines, etc., can solve the problems of many systems that are merely hydrophobic not good barrier materials, and cannot be sufficient to have only a low solubility, and achieve the effect of superior barrier performan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Synthesis of Oxethane, 3,3′-[1,3-Phenylenebis (Methyleneoxymethylene)]bis[3-Methyl-
[0035]
[0036] Into a 250 mL three-neck round bottom flask equipped with a reflux condenser, a mechanic stirrerwere added 12.0 g NaOH (0.3 mol), 0.6 g n-Bu4N+Br−(0.0019 mol), 30.0 g 3-methyl-3-hydroxymethyl-oxetane (0.29 mol), 25.0 g α, α′-dibromo-m-xylene (0.095 mol), and 100 mL of toluene. The reaction was brought to 110° C. for 3.5 hours. The organic phase was collected by filtration and the solvents were removed. The light yellow crude product was redissolved in 200 mL of toluene and washed with deionized water three times. After drying over magnesium sulfate, the toluene solution was passed through a short column of neutral alumina to remove trace amount of the ammonium salt phase transfer catalyst. Finally, the solvents were removed with rotary evaporator and Kugelrohr and the sample was purified by distillation. 1H NMR (CDCl3): δppm 1.36 (6H), 3.56 (4H), 4.38-4.55 (8H), 4.60 (4H), 7.18-7.38 (4H)...
example 2
Synthesis of Oxetane, 3,3′-[1,4-phenylenebis(methyleneoxymethylene)]bis[3-methyl-
[0037]
[0038] The reaction conditions of Example 1 were adopted except 25.0 g α, α′-dibromo-p-xylene (0.095 mol) was used instead of 25.0 g α,α′-dibromo-m-xylene (0.095 mol). 1H NMR (CDCl3): δppm 1.36 (6H), 3.55 (4H), 4.37-4.55 (8H), 4.59 (4H), 7.36 (4H)
example 3
Synthesis of Oxetane, 3,3′-[1,3-phenylenebis(methyleneoxymethylene)]bis[3-ethyl-
[0039]
[0040] The reaction conditions of Example 1 were adopted except 34.1 g 3-ethyl-3-hydroxymethyl-oxetane (0.29 mol) was used instead of 30.0 g 3-methyl-3-hydroxymethyl-oxetane (0.29 mol). 1H NMR (CDCl3): δppm 0.87-0.91 (6H), 1.77-1.83 (4H) 3.61 (4H), 4.40-4.49 (8H), 4.59 (4H), 7.28-7.38 (4H)
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com