Stent/graft assembly
a graft and stent technology, applied in the field of stent and graft assembly, can solve the problems of occlusion, emboli production, prone to aneurysm, etc., and achieve the effects of enhancing fixation, and reducing the risk of emboli production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
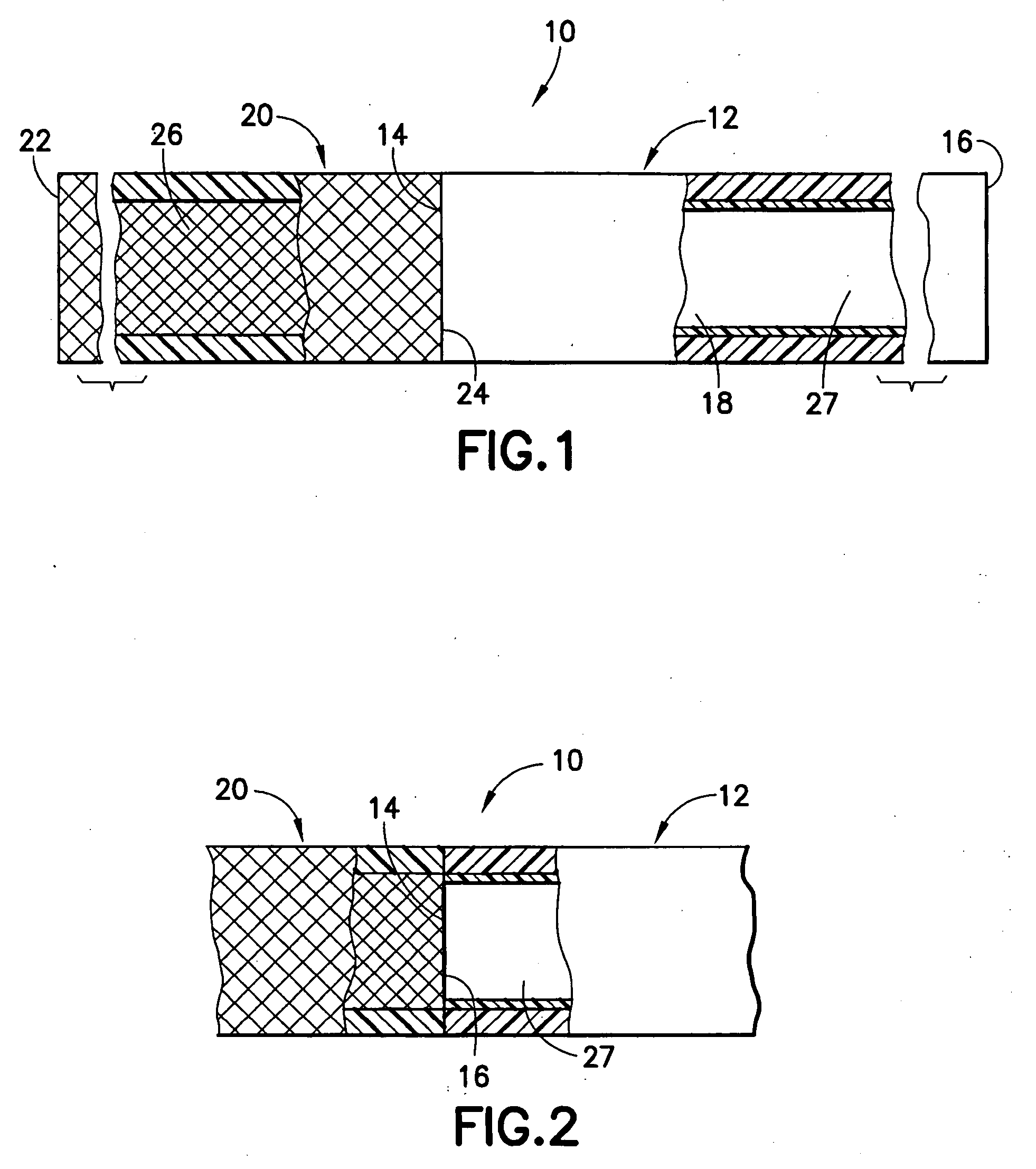
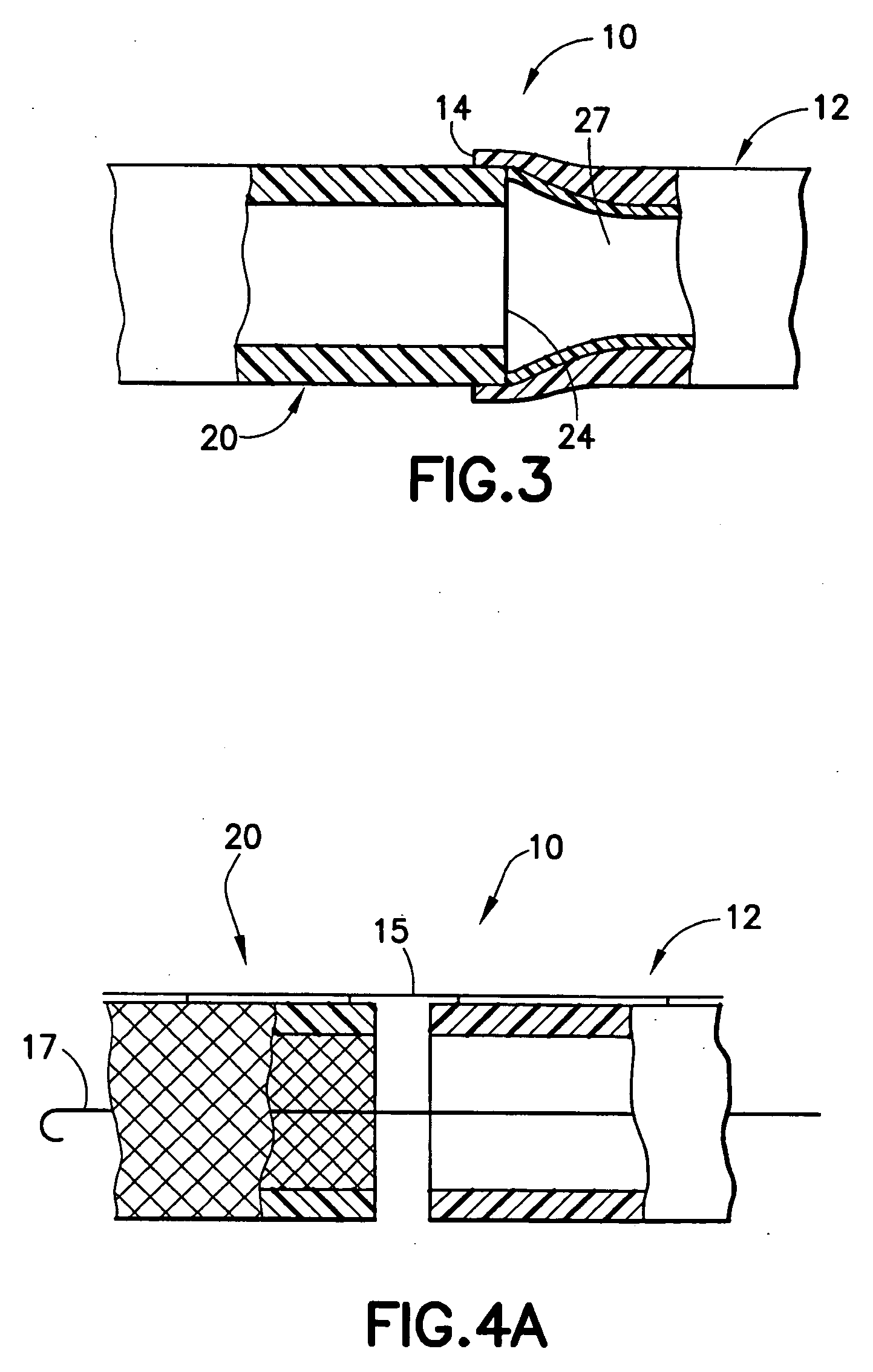
[0047] An endovascular stent / graft assembly in accordance with the invention is identified generally by the numeral 10 in FIG. 1. The endovascular stent / graft assembly 10 includes a substantially tubular graft 12 having a flexible wall formed from a synthetic material, such as a polyester material that is substantially impervious to fluid transmission or that becomes substantially impervious after exposure to blood. The tubular graft 12 has an upstream end 14, a downstream end 16 and a fluid passage 18 extending between the ends. The endovascular stent / graft assembly 10 further comprises a tubular stent 20 having an upstream end 22, a downstream end 24 and a passage 26 extending between the ends. The tubular stent 20 may be of known construction and may be formed from materials that are known to those skilled in the art of treating vascular anomalies with endovascular stent / graft assemblies, such as polyethylene terepthalate and PTFE, including materials sold under the trademarks DA...
second embodiment
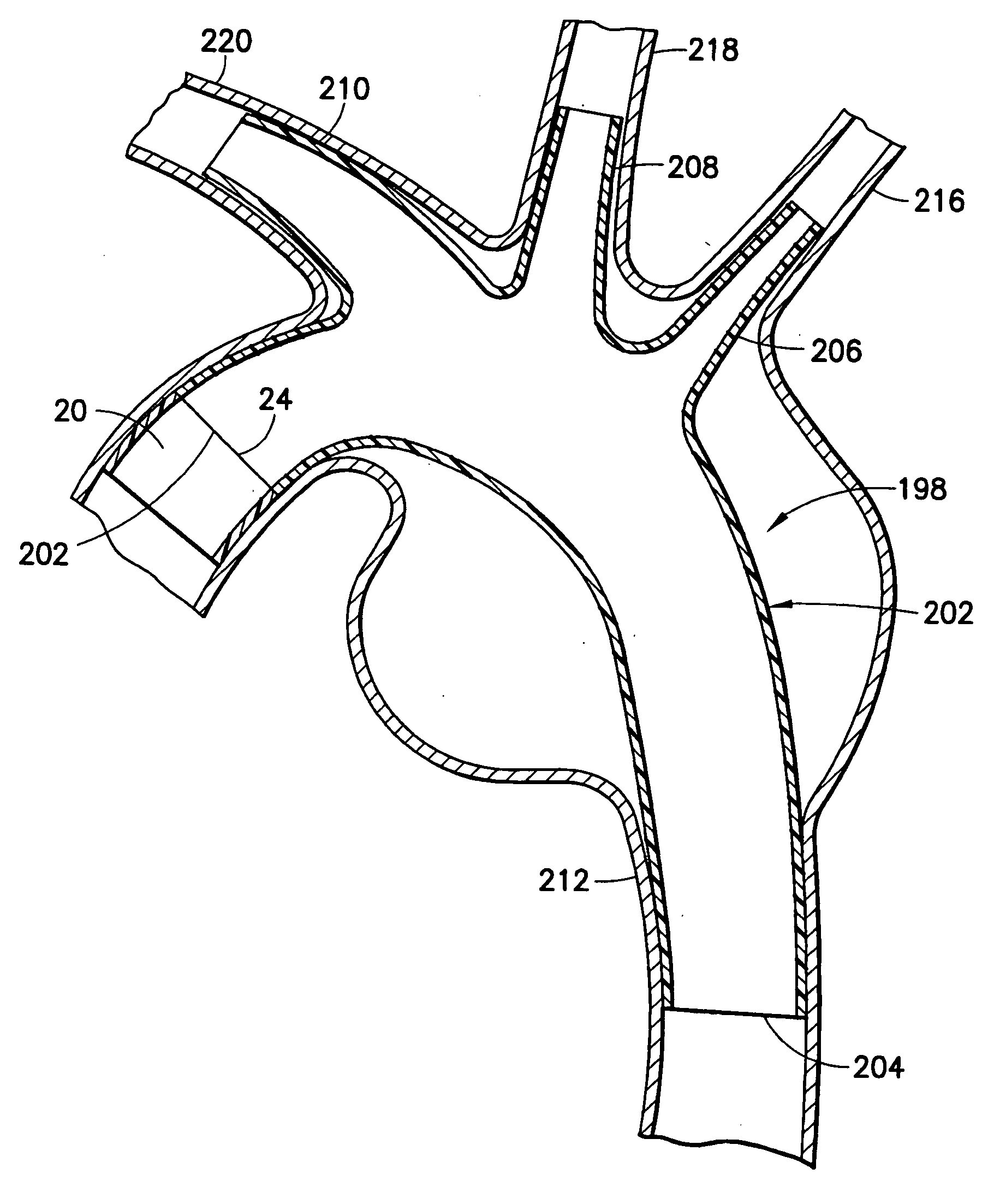
[0055]FIG. 7 shows an endovascular stent / graft assembly 32 in accordance with the invention. The endovascular stent / graft assembly 32 includes a tubular graft 12 substantially identical to the tubular graft 12 in the embodiment of FIG. 1. The stent / graft assembly 32 further includes an upstream tubular stent 20 substantially identical to the tubular stent 20 in the embodiment of FIG. 1. However, the stent / graft assembly 32 further includes a downstream stent 34. The downstream stent 34 has an upstream end 36, a downstream end 38 and a tubular passage 40 extending between the ends. The upstream end 36 of the downstream stent 34 is connected in substantially end-to-end relationship with the downstream end 16 of the tubular graft 12 by any of the connection arrangements depicted respectively in FIGS. 2-6. The downstream stent 34 can be connected to the tubular graft prior to insertion of the stent / graft assembly 32 into the blood vessel. Alternatively, the sub-assembly of the tubular g...
fourth embodiment
[0059] the endovascular stent / graft assembly is identified by the numeral 50 in FIG. 12. The endovascular stent / graft assembly 50 is a variation of the stent / graft assembly 46 of FIG. 11 in that a plurality of wires 52 extend axially from the stent 20 substantially to the downstream end 16 of the tubular graft 12 where the wires 52 are affixed to the tubular graft 12. The stent / graft assembly 50 prevents axial collapsing of the tubular stent 20, substantially as with the embodiment of FIG. 11. However, the wires 52 will further provide radially support for the tubular graft 12 and will resist radially collapsing of the graft 12.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com