Automated lean methods in anatomical pathology
a technology of anatomic pathology and automatic leaning, applied in the field of anatomical pathology, can solve the problems of high work in progress inventories, inefficiency in output, and limiting effects, and achieve the effects of reducing labor intensity, reducing labor intensity, and improving the quality of li
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
A. Introduction
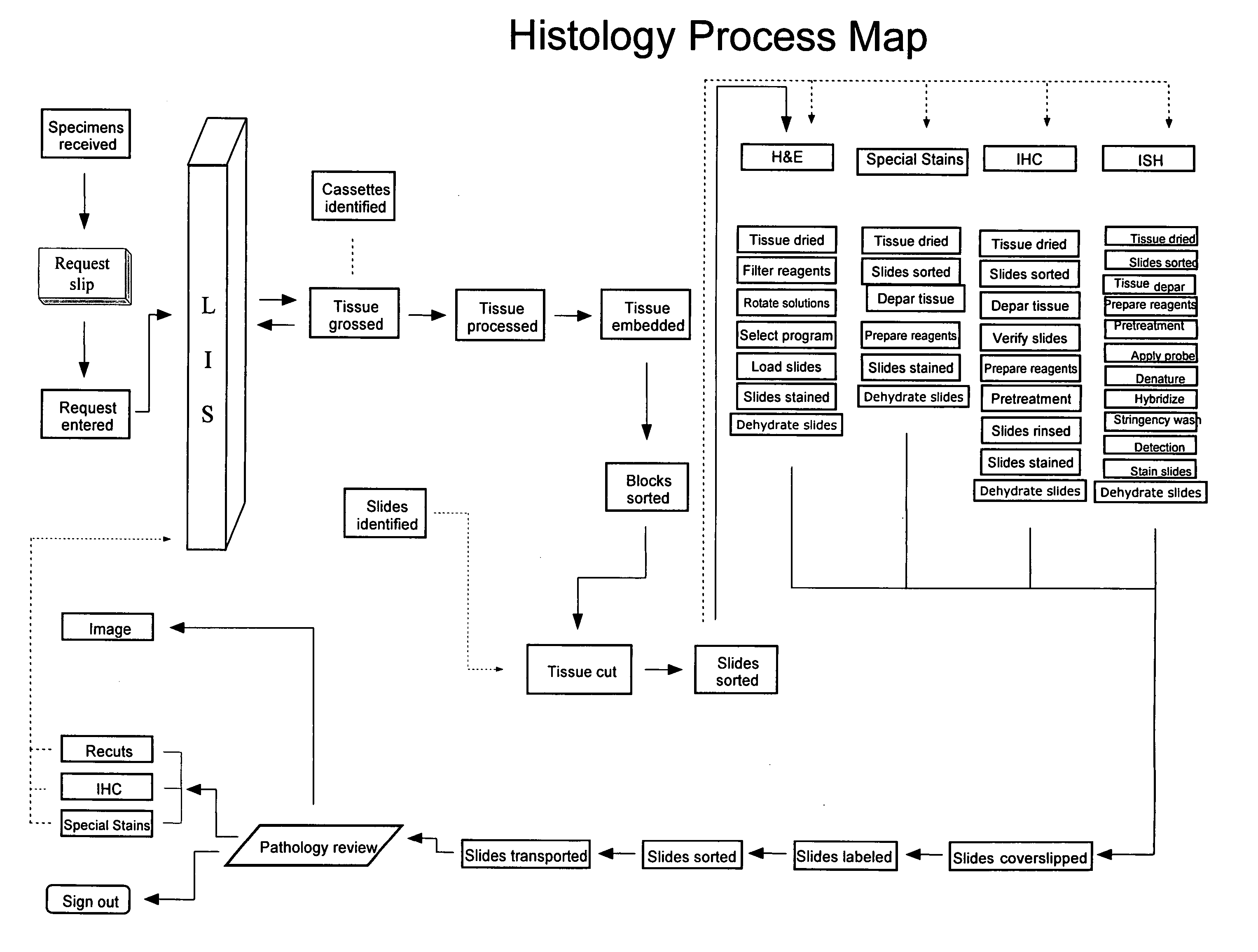
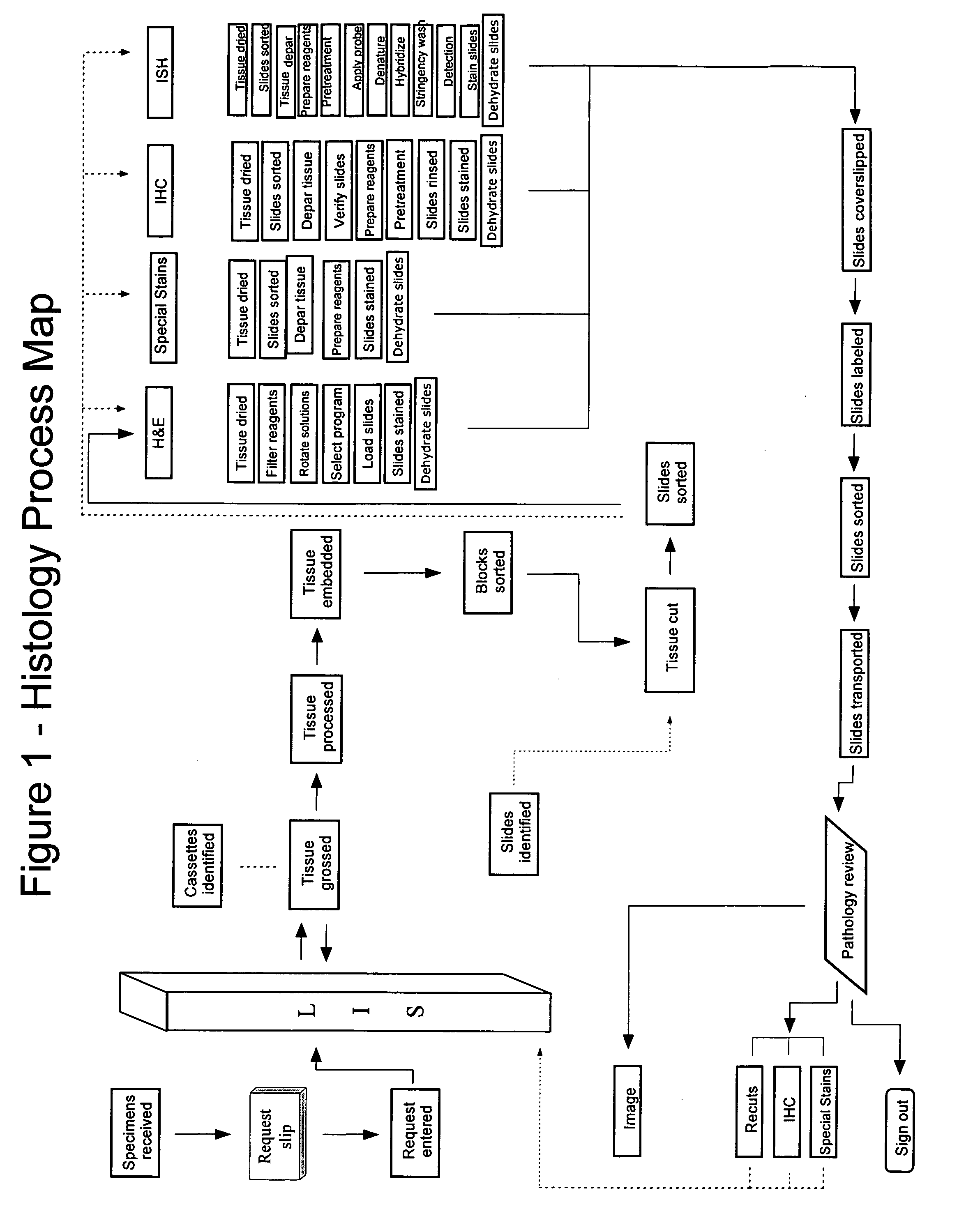
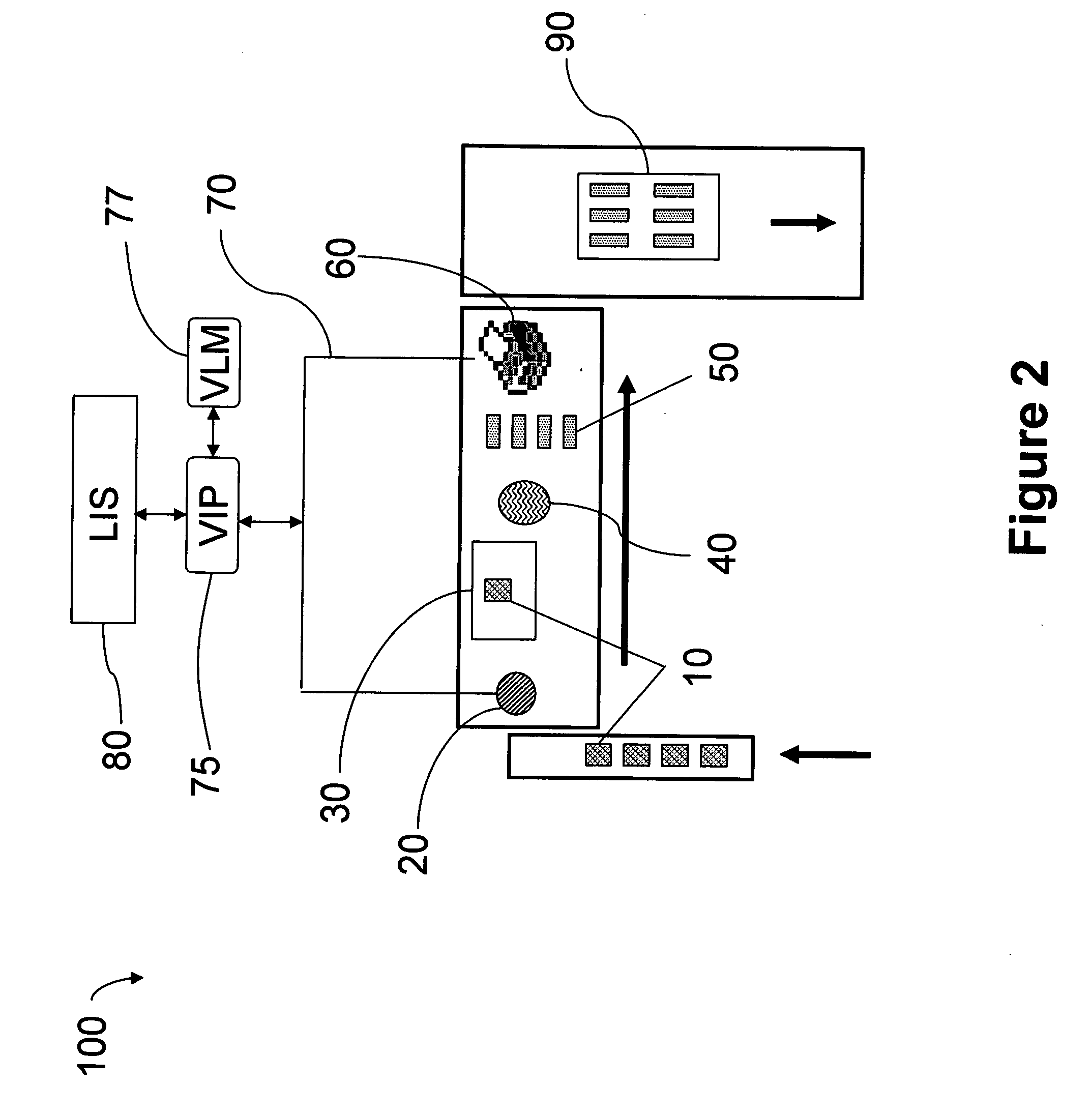
[0017] Lean methodology comprises 5 basic steps: 1) observe the process you wish to model, 2) define that process, 3) define opportunities within the existing process, 4) develop improvement opportunities, and 5) implement and sustain the improvements. Lean principles as applied to the Anatomical Pathology lab suggest that developing a map of the existing process is a recommended starting point. In FIG. 1 is shown a Histology Process Map, which is a visualization of one particular histology production path, including both materials and information. At the left side of the figure the sample is first received (“Specimens Received”), then a Request Slip is generated for the tests to be performed, which is entered via the hospital's Lab Information System (“LIS”). Typically the LIS is a networked software enterprise that links requesters and providers with test request and test status and result information. The system normally is all-inclusive: anyone in the hospital who...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com