Radar device and method for adjusting among radar sites
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0019] Hereinafter, an embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
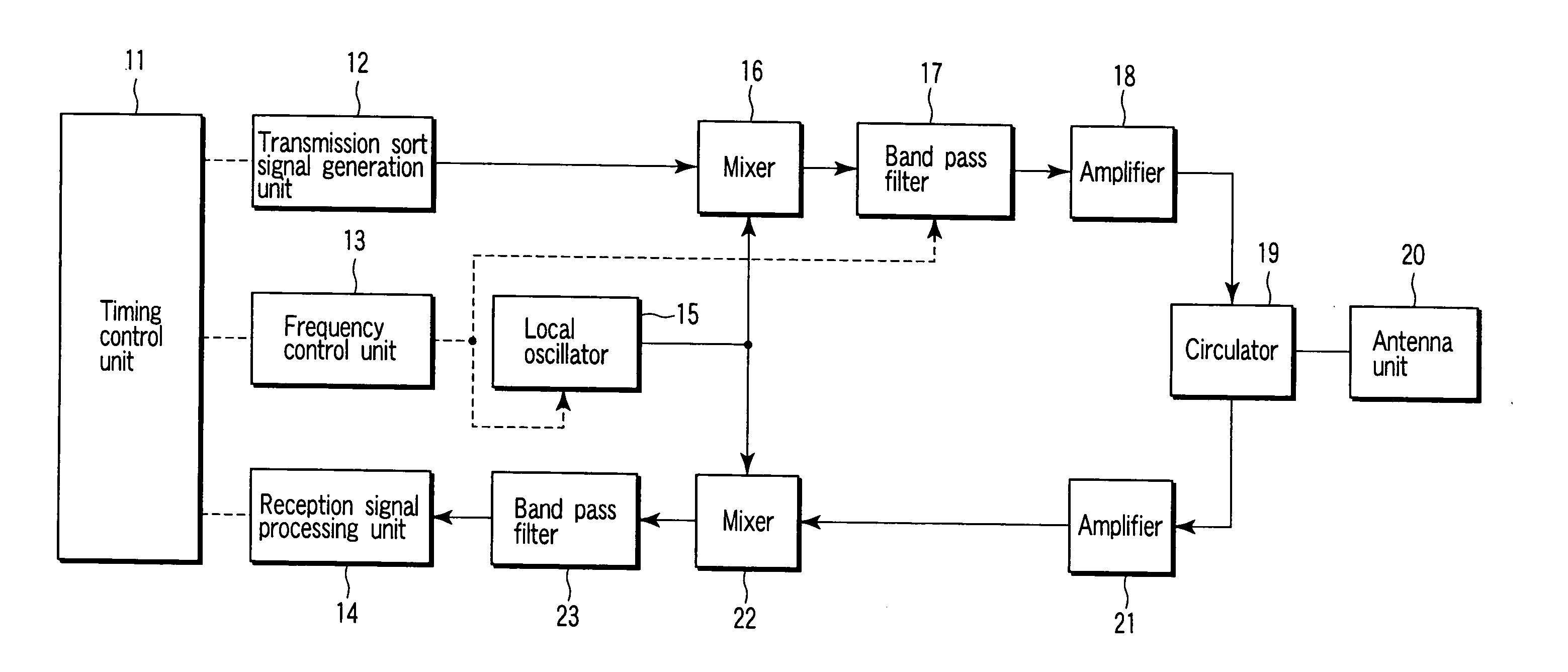
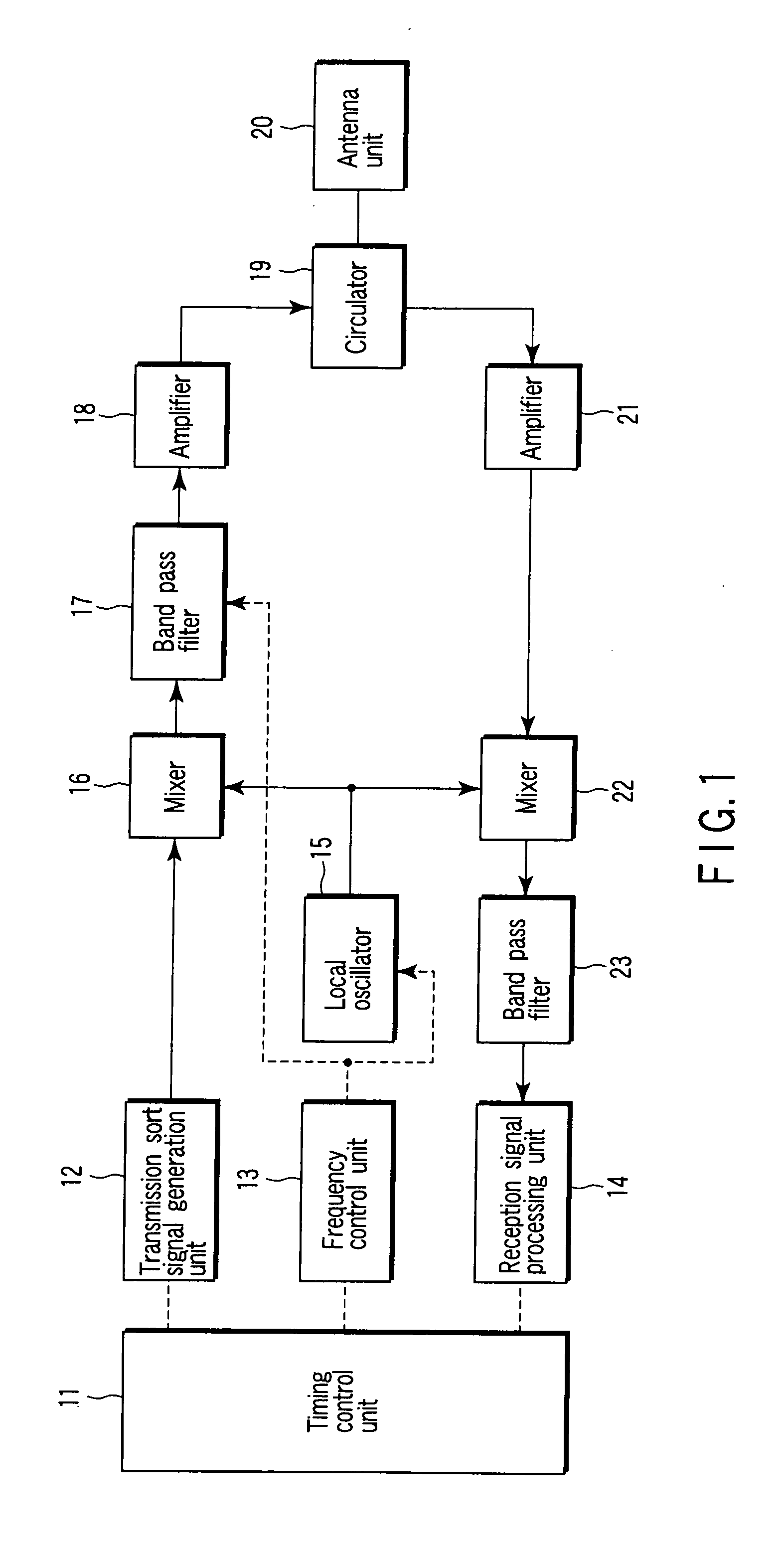
[0020]FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing an example of a configuration of a radar device regarding one embodiment of the invention. In FIG. 1, a timing control unit 11 controls processing of the whole of the device, and mainly controls the processing timings of a transmission sort signal generation unit 12, a frequency control unit 13 and a reception signal processing unit 14.
[0021] The generation unit 12 generates a transmission sort signal of a preset RPF, pulse width and modulation method in accordance with an instruction from the timing control unit 11. The frequency control unit 13 controls an oscillation frequency from a local oscillator 15 and a passing frequency band of a first band pass filter 17, and the reception signal processing unit 14 performs processing to detect a target from a received echo signal.
[0022] By drive control performed by the timing co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com