Electromagnetically Driven Valve
a technology of electric drive valve and drive valve body, which is applied in the direction of valve operating means/release devices, machines/engines, non-mechanical valves, etc., can solve the problems of increased slide resistance and failure to smooth reciprocating motion of the driven valve, and achieve smooth housing, suppressing surface abrasion, and reducing slide resistance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
[0024] (First Embodiment)
[0025] The electromagnetically driven valve according to the present embodiment implements an engine valve (an intake valve or an exhaust valve) in an internal combustion engine such as a gasoline engine or a diesel engine. In the present embodiment, description will be given assuming that the electromagnetically driven valve implements an intake valve, however, it is noted that the electromagnetically driven valve is similarly structured also when it implements an exhaust valve.
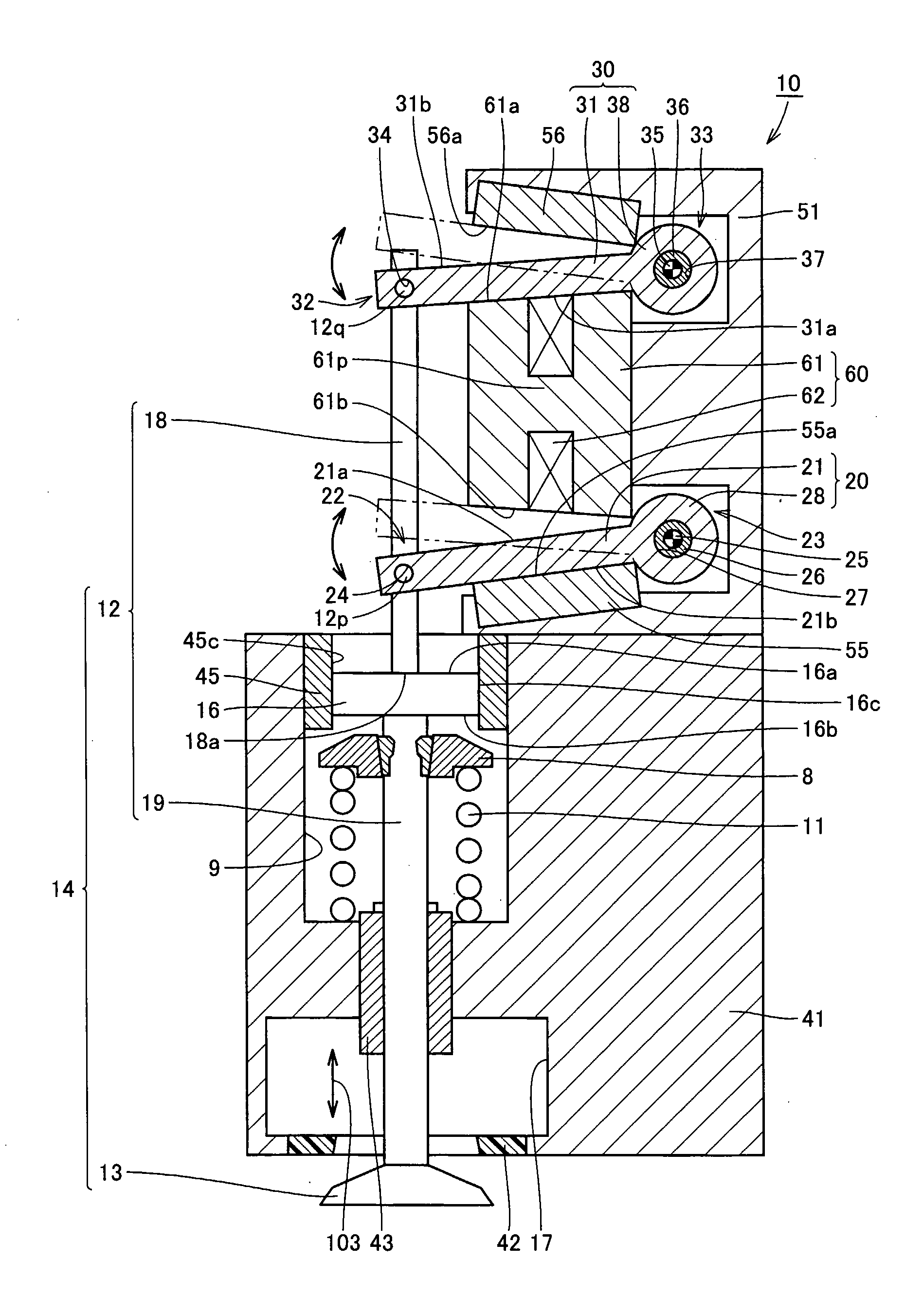
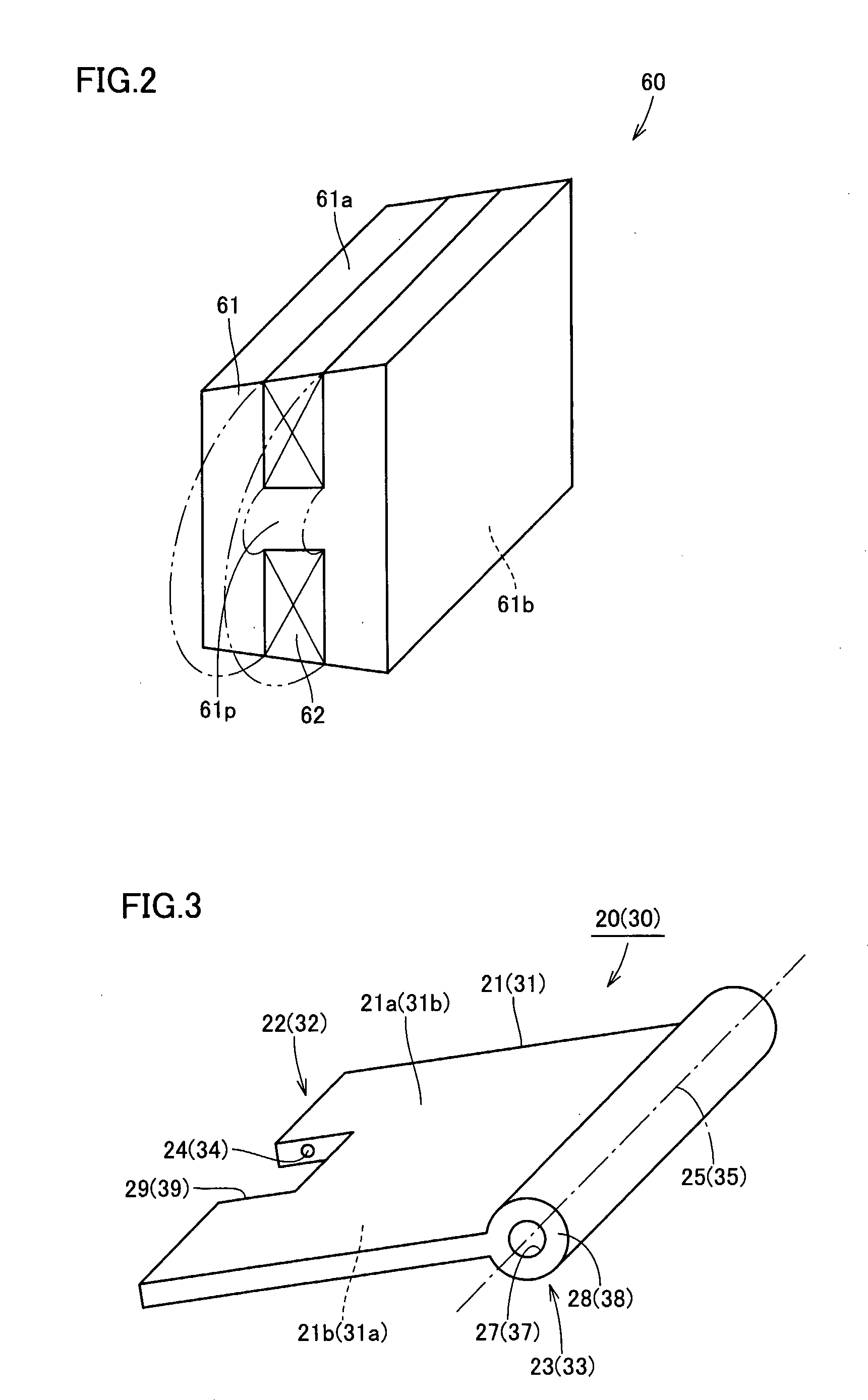
[0026] Referring to FIG. 1, an electromagnetically driven valve 10 is a rotary drive type electromagnetically driven valve. As an operation mechanism for the electromagnetically driven valve, a parallel link mechanism is applied.
[0027] Electromagnetically driven valve 10 includes a driven valve 14 having a stem 12 extending in one direction and an umbrella-shaped portion 13 formed at a tip end of stem 12, and a lower disc 20 and an upper disc 30 coupled to different positions on st...
second embodiment
[0061] (Second Embodiment)
[0062] An electromagnetically driven valve according to the present embodiment is structured in a manner basically similar to the electromagnetically driven valve in the first embodiment. Therefore, description of a redundant structure will not be repeated.
[0063]FIG. 9 is an enlarged view of a region of the electromagnetically driven valve where the lash adjuster is provided. Referring to FIG. 9, an end surface 19a is defined at a position of lower stem 19 connected to bottom surface 16b of lash adjuster 16. In the present embodiment, the tip end of upper stem 18 is formed like a collar, such that end surface 18a has an area larger than an area of end surface 19a.
[0064] According to the electromagnetically driven valve in the second embodiment of the present invention structured as above, an effect similar to that in the first embodiment can be obtained. In addition, a contact area between end surface 18a and top surface 16a is reduced, so that smoother s...
third embodiment
[0065] (Third Embodiment)
[0066] An electromagnetically driven valve according to the present embodiment is structured in a manner basically similar to the electromagnetically driven valve in the first embodiment. Therefore, description of a redundant structure will not be repeated.
[0067]FIG. 10 is an enlarged view of a region of the electromagnetically driven valve where the lash adjuster is provided. Referring to FIG. 10, lash adjuster 16 is constituted of an upper lid 81 having top surface 16a, a lower lid 83 arranged with a prescribed distance from upper lid 81 and having bottom surface 16b, and a viscous member 82 filling a gap between upper lid 81 and lower lid 83, such as grease and oil. In the present embodiment, lower retainer 8 in FIG. 1 is not provided in lower stem 19. Lower spring 11 is housed in hollow portion 9 between the bottom surface of hollow portion 9 and lower lid 83.
[0068] In the electromagnetically driven valve according to third embodiment of the present in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com