Method for controlling an expansion valve and expansion valve, in particular for vehicle air-conditioning systems operated with CO2 as the refrigerant
a technology of expansion valve and expansion valve, which is applied in the direction of gas cycle refrigeration machines, compression machines, mechanical equipment, etc., can solve the problem of generally taking too long for the maximum cooling power to be obtained under high ambient temperatur
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
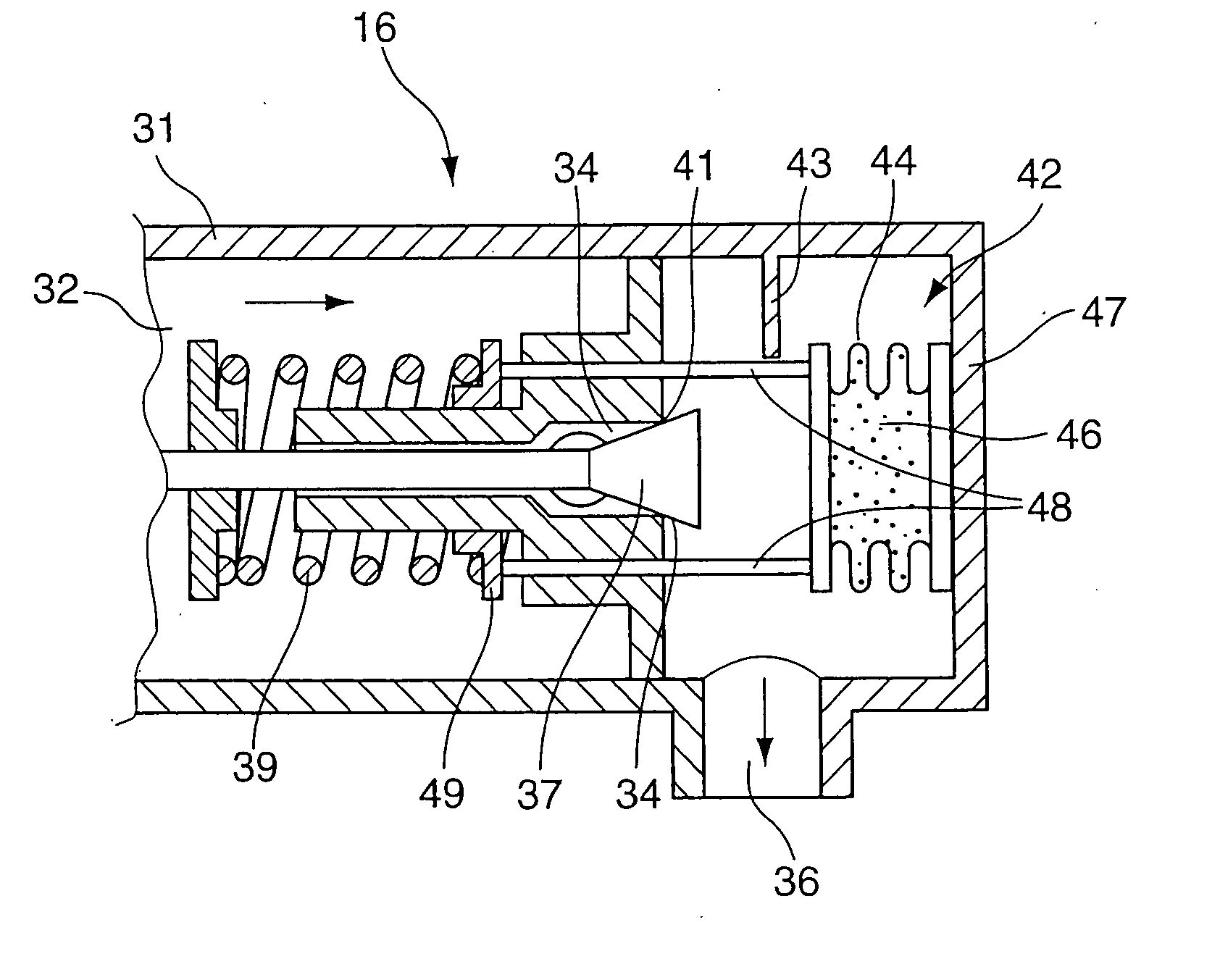
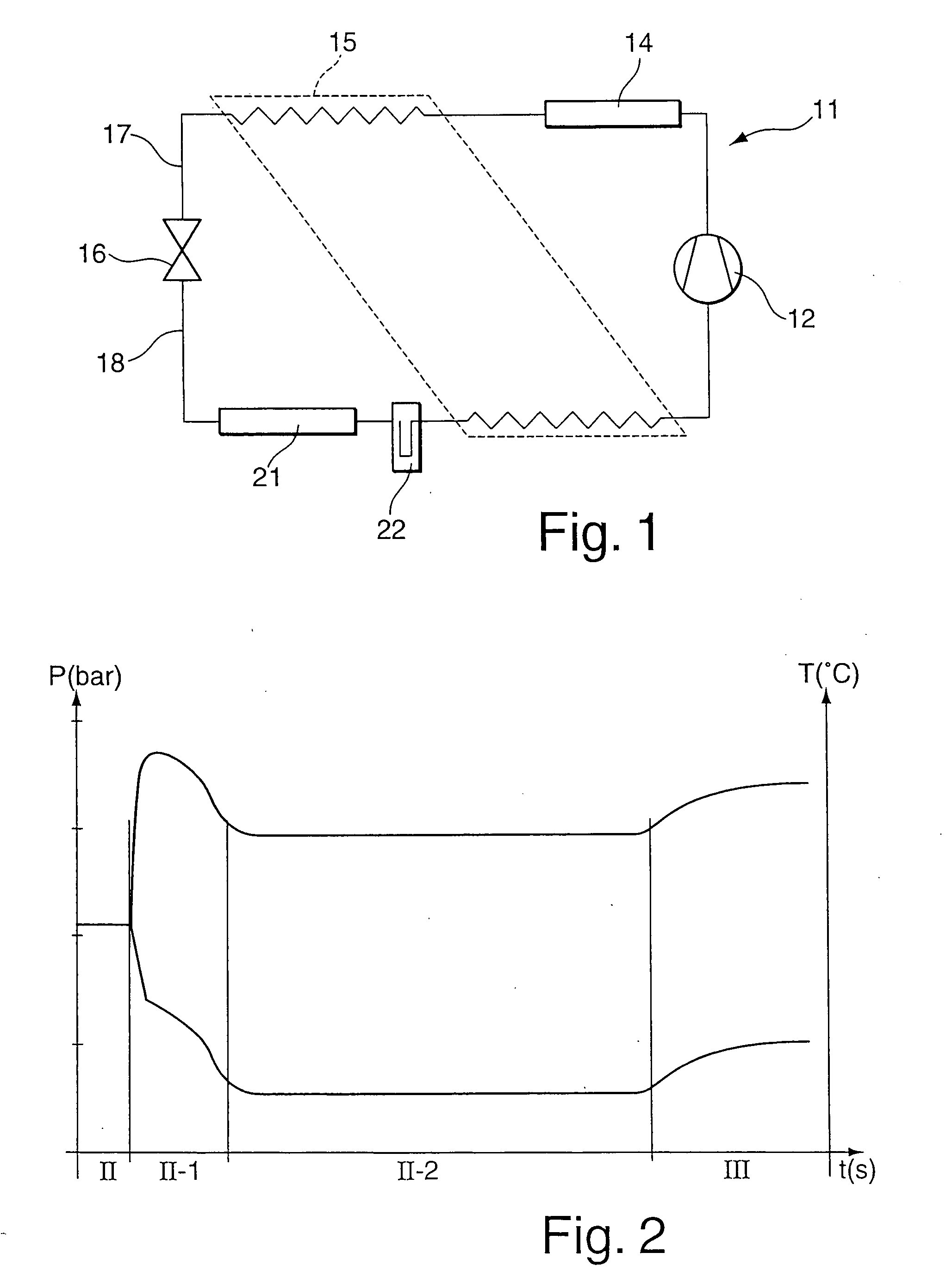
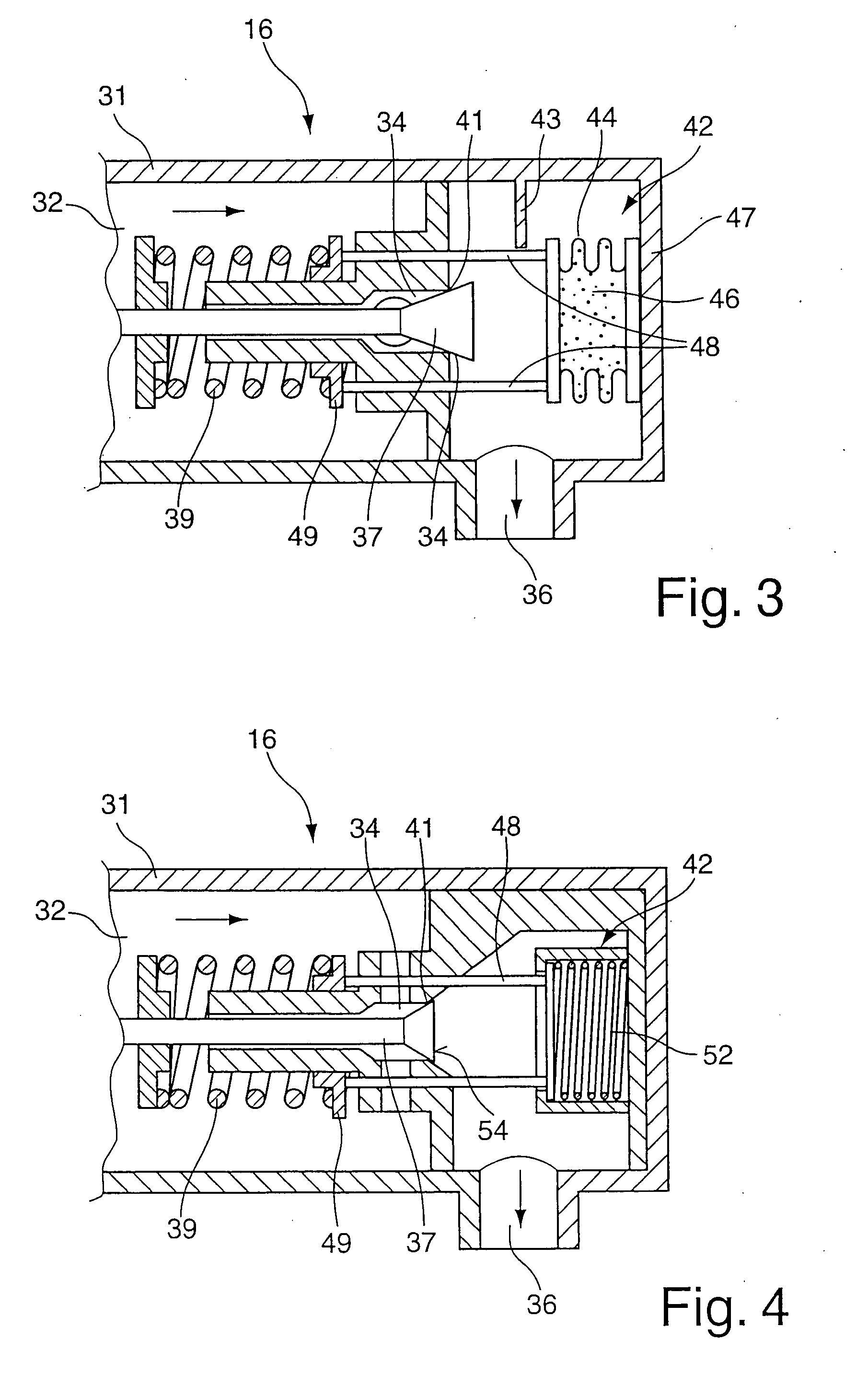
[0027]FIG. 1 illustrates a refrigerant circuit 11 which is preferably operated with CO2. This refrigerant circuit 11 is used, for example, as a vehicle air-conditioning system. A compressor 12 feeds the compressed refrigerant on the high-pressure side to an outside heat exchanger 14. The latter is connected to the surroundings and outputs heat outwards. Connected downstream of the latter is an inside heat exchanger 15 which feeds the refrigerant to an expansion valve 16 via a feed line 17. Upstream of the expansion valve 16 on the high-pressure side there is an input pressure which, for example in summer, can be 120 bar. The refrigerant flows through the expansion valve 16 and passes to the low-pressure side. On the output side, the expansion valve 16 has pressures of between 35 and 45 bar under stationary conditions. The refrigerant, which is cooled by the relaxation of the pressure, passes via a removal line 18 into the inside heat exchanger 21 and will remove heat from the surrou...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com