Liquid crystal display device
a liquid crystal display and display technology, applied in semiconductor devices, instruments, optics, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the panel size of the liquid crystal display device, prone to degradation in the quality of display, and becoming eviden
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
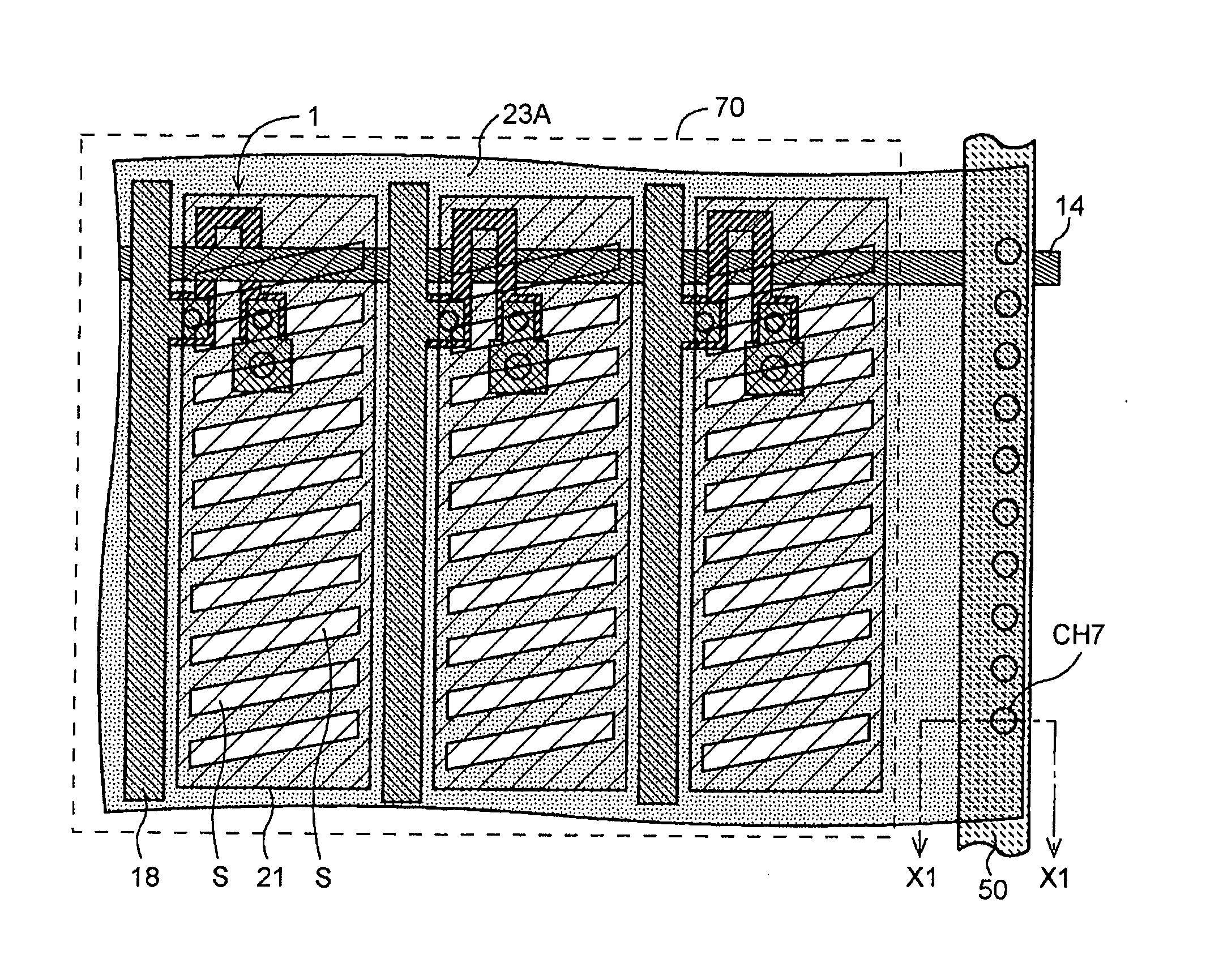
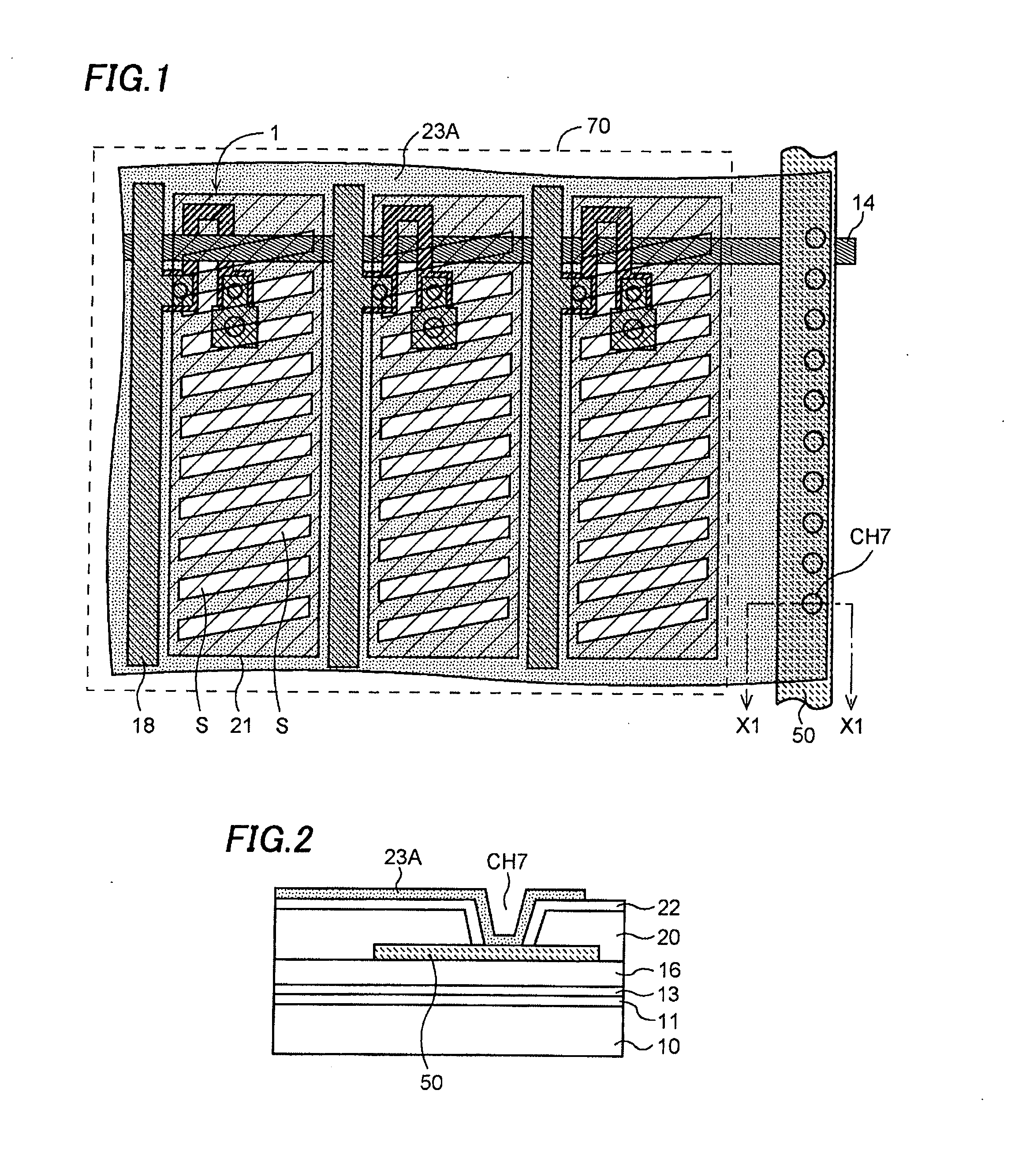
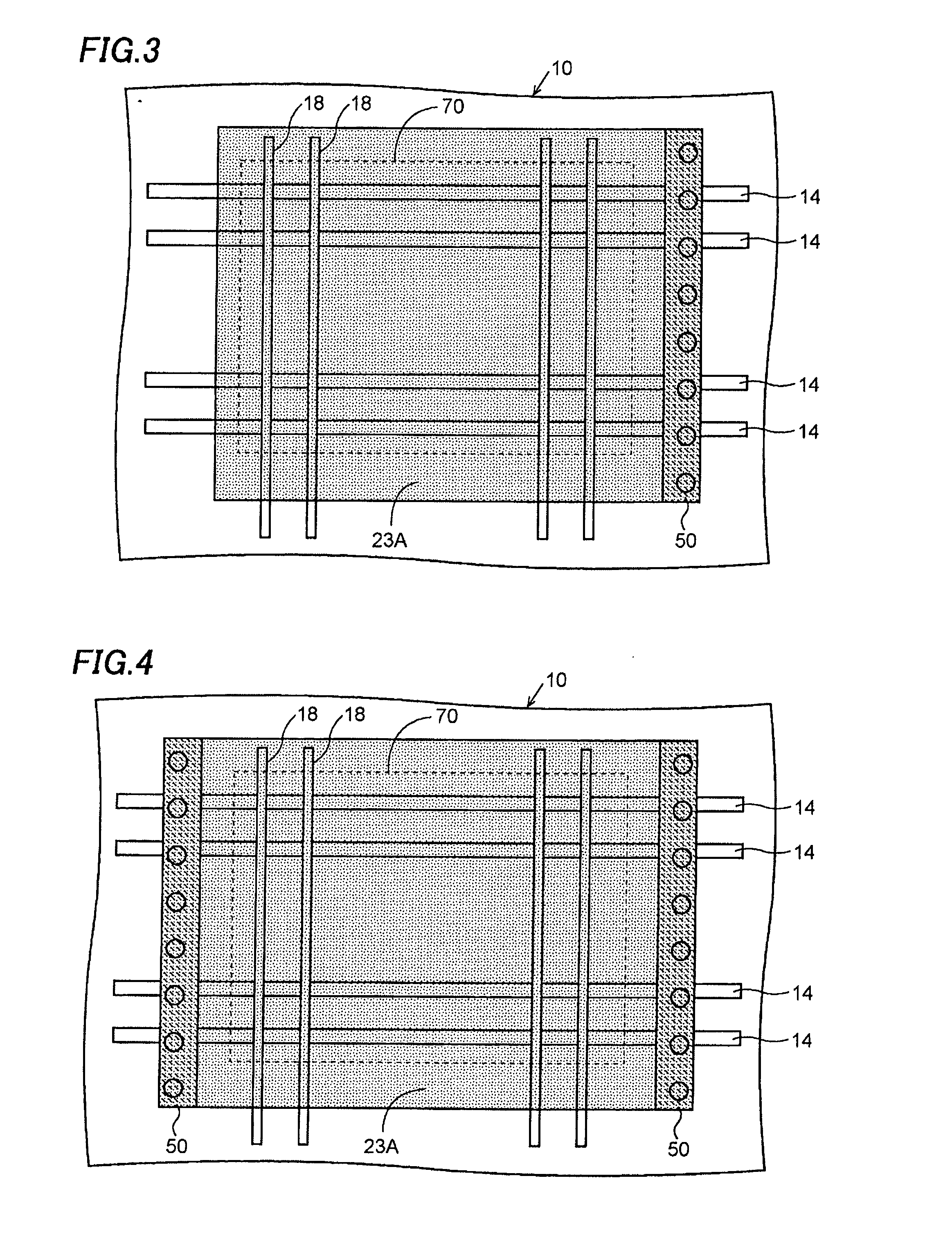
[0039]A liquid crystal display device according to this invention will be explained referring to the drawings. FIG. 1 is a plan view showing a portion of a display region in the liquid crystal display device. FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view showing a section X1-X1 in FIG. 1. Although a large number of pixels are disposed in a matrix form in the display region 70 in the actual liquid crystal display device, only three pixels are shown in the plan view.
[0040]A pixel electrode 21 is formed of a first layer transparent electrode. A common electrode 23A made of a second layer transparent electrode is formed above the pixel electrode 21 interposing an insulation film 22 between them. The common electrode 23A in an upper layer is provided with a plurality of slits S. The structures described above are generally common to the structure shown in FIGS. 20A and 20B. In the embodiment, however, the common electrode 23A extends over all the pixels in the display region 70. An end of the common ...
second embodiment
[0048]A liquid crystal display device according to this invention will be explained referring to the drawings. FIG. 9 is a plan view showing a portion of a display region in the liquid crystal display device. FIG. 10 is a cross-sectional view showing a section X2-X2 in FIG. 9. FIG. 11 is a cross-sectional view showing a section Y1-Y1 in FIG. 9. Although a large number of pixels are disposed in a matrix form in the display region in the actual liquid crystal display device, only three pixels are shown in the plan view.
[0049]A relationship between vertical locations of the pixel electrode 21 and the common electrode 23A in the liquid crystal display device according to the first embodiment is reversed in the liquid crystal display device according to the second embodiment. A common electrode 23B is formed of the first layer transparent electrode and a pixel electrode 21B is formed of the second layer transparent electrode above it interposing the insulation film 22 between them. The p...
fourth embodiment
[0063]A liquid crystal display device according to this invention will be explained referring to the drawings. FIG. 15 is a plan view showing a portion of a display region in the liquid crystal display device. FIG. 16 is a cross-sectional view showing a section X4-X4 in FIG. 15. FIG. 16 is a cross-sectional view showing a section Y3-Y3 in FIG. 15. Although a large number of pixels are disposed in a matrix form in the display region in the actual liquid crystal display device, only three pixels are shown in the plan view.
[0064]A relationship between vertical locations of the pixel electrode 121B and the common electrode 123B in the liquid crystal display device according to the third embodiment is reversed in the liquid crystal display device according to the fourth embodiment. A pixel electrode 121A is formed of a first layer transparent electrode and a common electrode 123A is formed of a second layer transparent electrode above it interposing a gate insulation film 101 and an inte...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com