Passive Thermal Management System
a passive thermal management and thermal management technology, applied in the field of thermal management, can solve the problems of not improving the heat transfer coefficient, the shape of the fin can be critical, and the heat sink is substantially ineffective, so as to achieve the effect of dissipating heat and dissipating hea
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
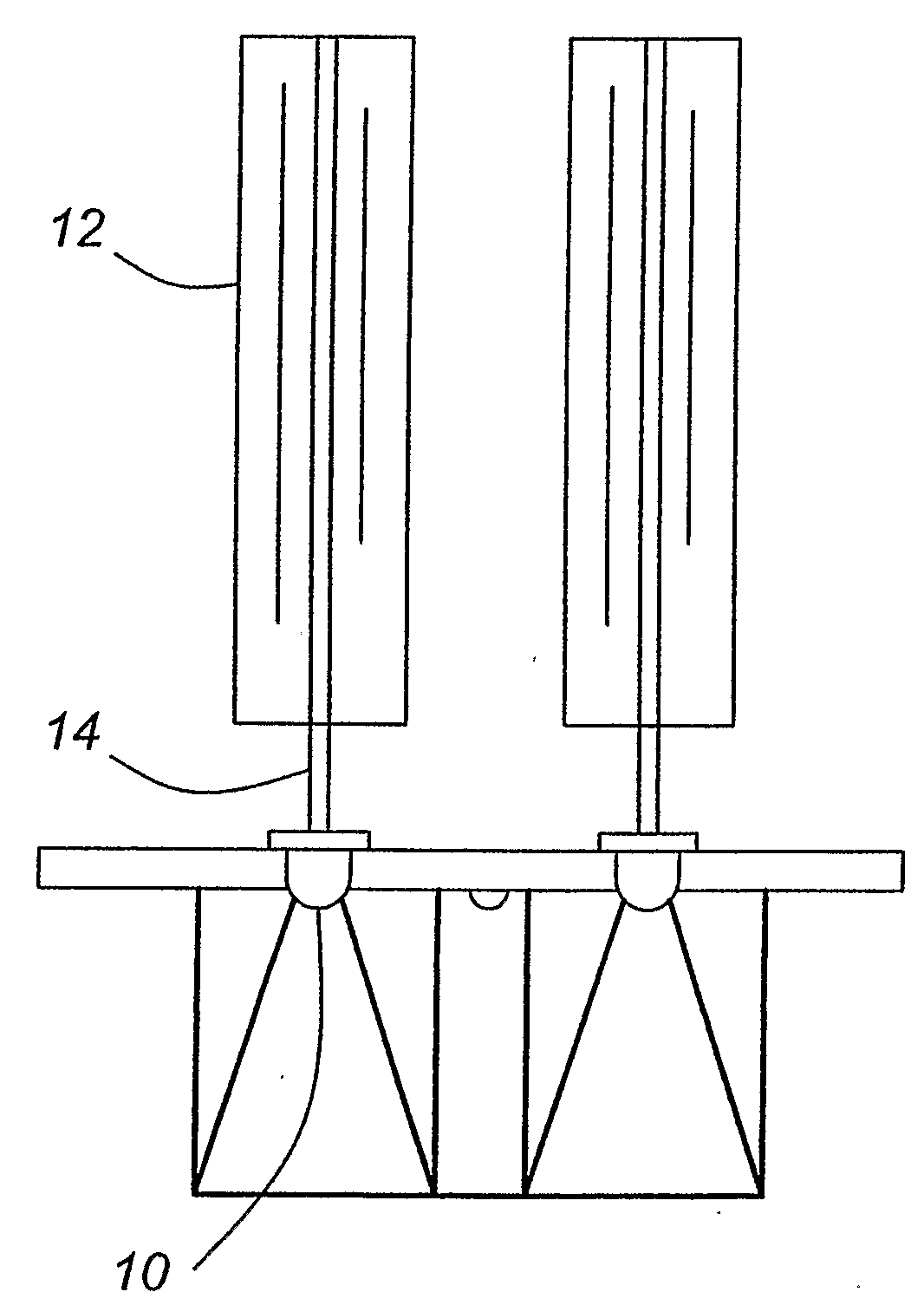
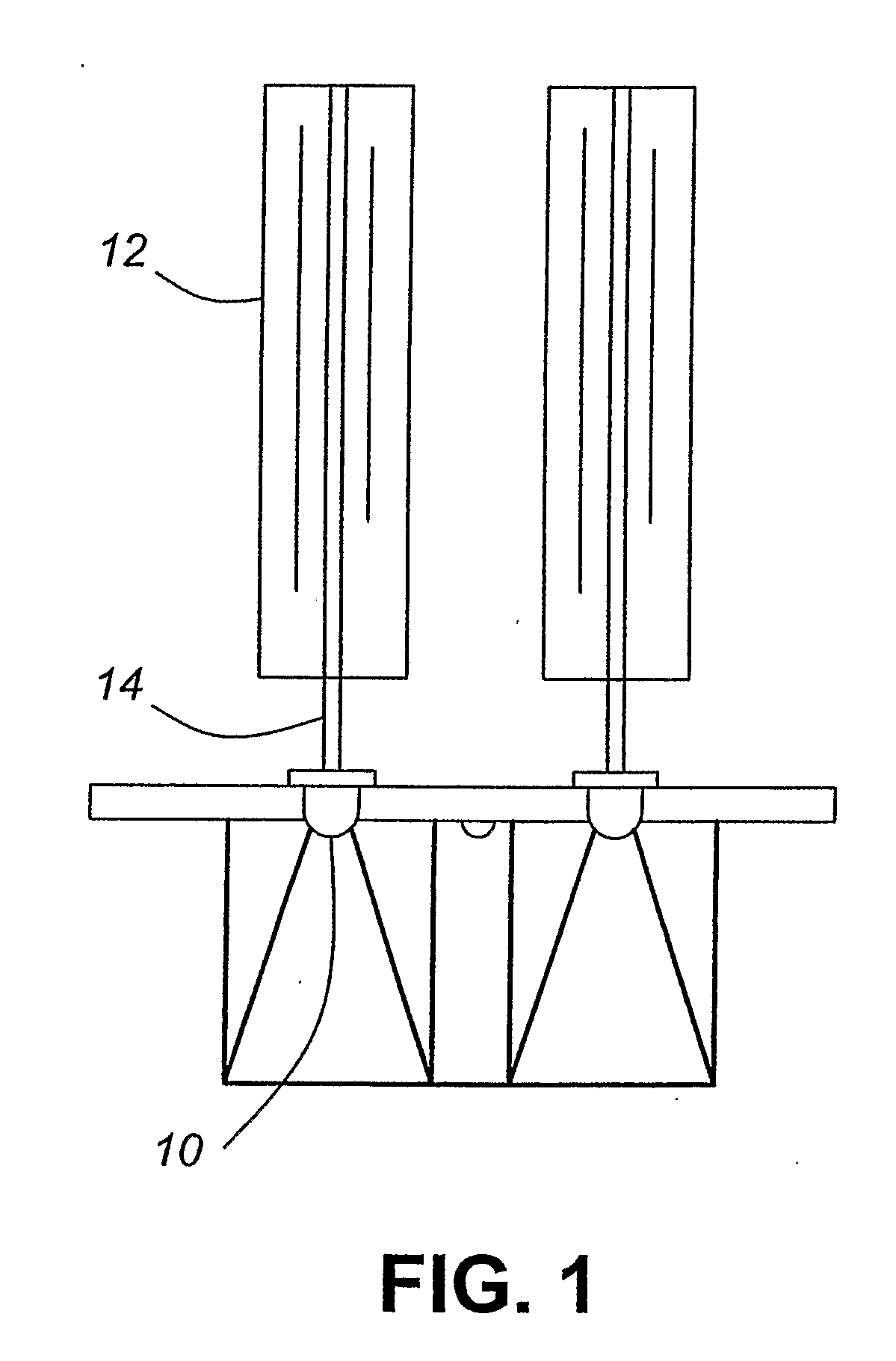
[0059]FIG. 1 illustrates a passive thermal management system according to one embodiment of the present invention. The thermal management system provides for the dissipation of heat that is generated by one or more light-emitting diodes 10 which are thermally coupled to the passive thermal management system, and more specifically heat pipe 14. For example, the thermal connection between the one or more light-emitting diodes and a heat pipe can be provided via substantially direct contact, through a LED package or via a thermally conductive substrate upon which the one or more light-emitting diodes are mounted. The thermal management system comprises heat pipes 14 which are thermally connected to a fin system 12 which is configured as a sleeve of fins. Each of the fins of the sleeve of fins are substantially aligned along the length of a heat pipe. The sleeve of fins functions as a heat sink and thereby passively transfers heat from a heat pipe to the surrounding environment, thereby...
example 2
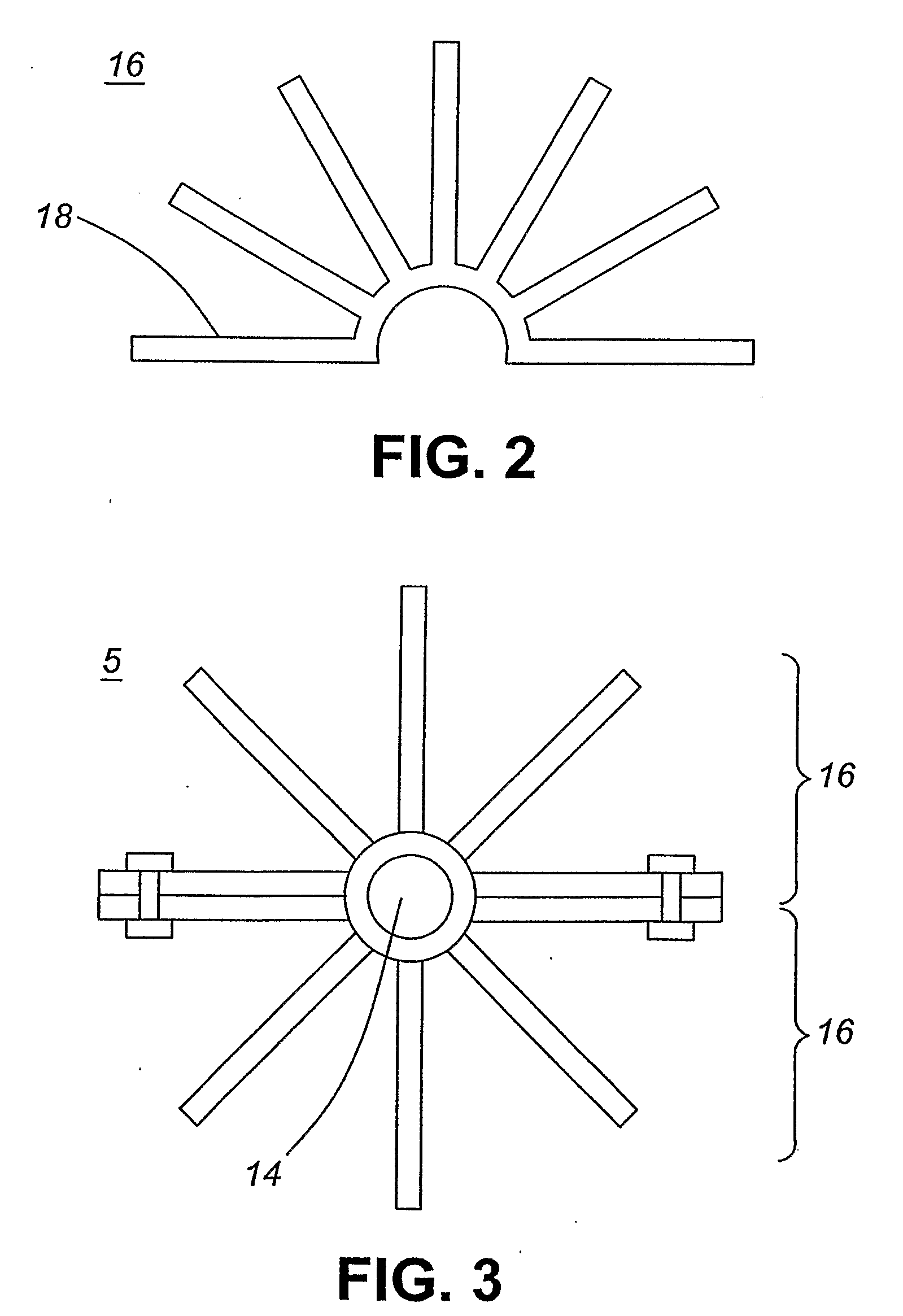
[0064]In another embodiment of the present invention, the thermal management system comprises a fin system including two or more flat plate fins 34 that are thermally connected to one or more heat pipes 36 transverse to the length of each of heat pipes as illustrated in FIG. 7. These plate fins can be manufactured with one or more holes 38 therein for the insertion of a heat pipe therethrough as illustrated in FIG. 8.
[0065]In another embodiment, the plate fins can be manufactured with a plurality of holes 41 for the insertion of heat pipes and additionally include secondary holes 40 and 42 therein which can enable the passage of air therethrough, as shown in FIG. 9. The secondary holes 40 and 42 in adjacent plate fins can be aligned along the length of the heat pipes. Alternately the secondary holes in adjacent plate fins can be offset thereby providing a means for changing the direction of air movement along the length of the heat pipe, wherein the change in directional movement of...
example 3
[0066]FIG. 10A illustrates a configuration of the passive thermal management system for dissipating heat generated by a heat source located at end 45 according to another embodiment of the present invention. The thermal management system comprises one or more heat pipes 46 and a fin system comprising a plurality of curved fins 44. A single curved fin of the fin system is illustrated in FIG. 10B. The shape of the fins of the fin system is configured wherein the cool air enters into the passive thermal management system at a first velocity in a first direction 48 and is subsequently slowed, increasing thermal transfer thereto. The heated air thereafter exits the thermal management system at a second velocity in a second direction 50.
[0067]FIG. 11A illustrates a configuration of the passive thermal management system for dissipating heat generated by a heat source located at end 56 according to another embodiment of the present invention. The thermal management system comprises one or m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com