Methods and dressings for sealing internal injuries
a technology for internal injuries and dressings, applied in the direction of drug compositions, metabolic disorders, cardiovascular disorders, etc., can solve the problems of increased expense, significant morbidity, blood vessel injuries, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing the flow of fluid
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0126]In order to apply the haemostatic test articles to the surface of an injured artery surrounded by a tissue stimulant, the test articles were housed in cylindrical molds made of 10 or 3 mL polypropylene syringes (Becton Dickinson) with the luer-lock end removed. The plungers were withdrawn to the 6 mL and 2 mL mark respectively. For dressings utilizing a backing, the support material was cut and placed into each mold and pushed down until it was adjacent to the plunger. Once prepared the molds were placed upright and surrounded by dry ice, leaving the opening exposed at the top. 1 ml of fibrinogen and 0.15 mL of thrombin (with or without backing material dispersed within) were dispensed into the 10 mL molds and 1 ml of fibrinogen and 0.15 mL of thrombin (with or without support material dispersed within) were dispensed into the 3 mL molds, which were allowed to freeze for 5 minutes. The molds were then placed into the −80° C. freezer for at least two hours before being placed i...
example 2
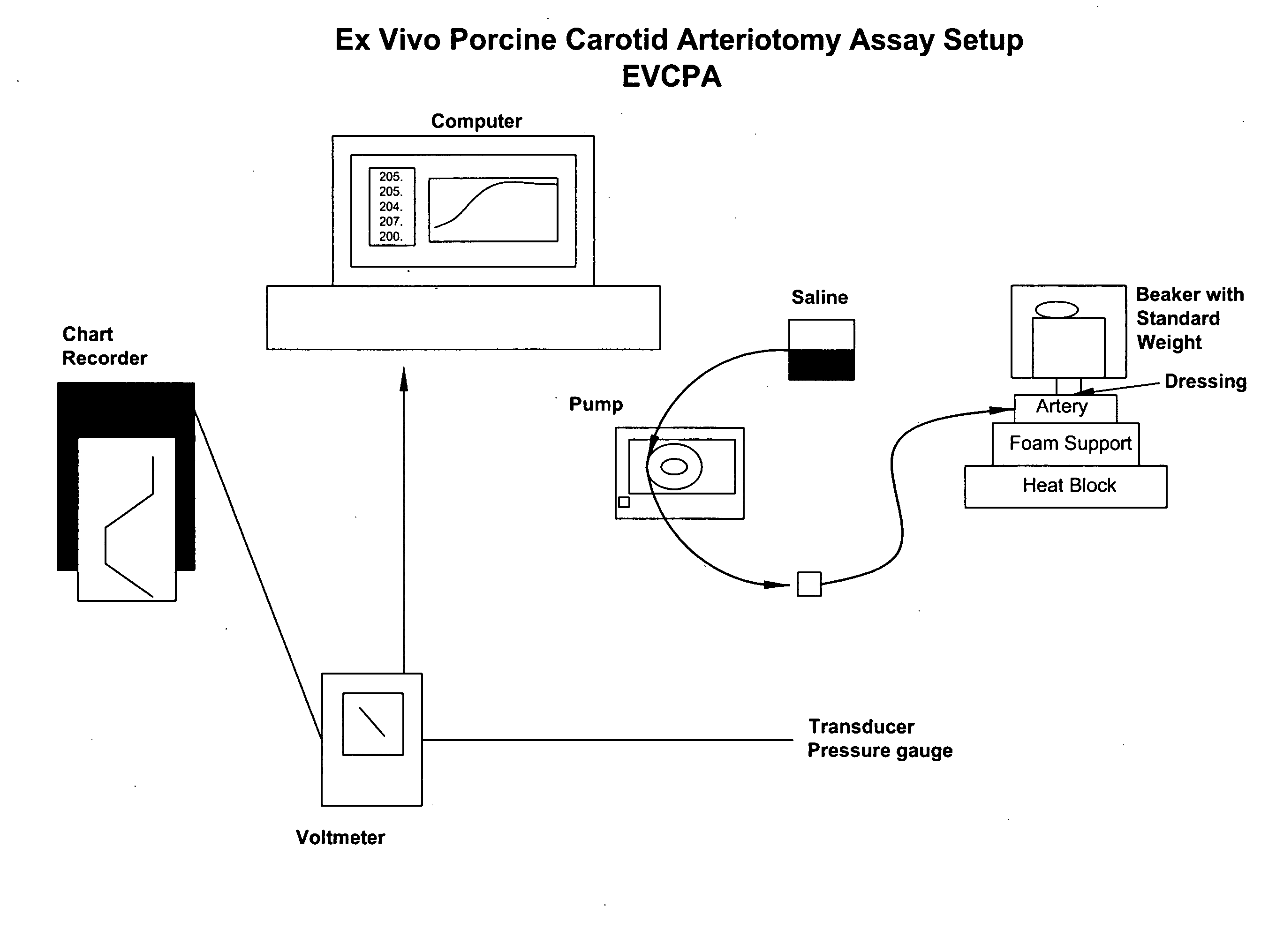
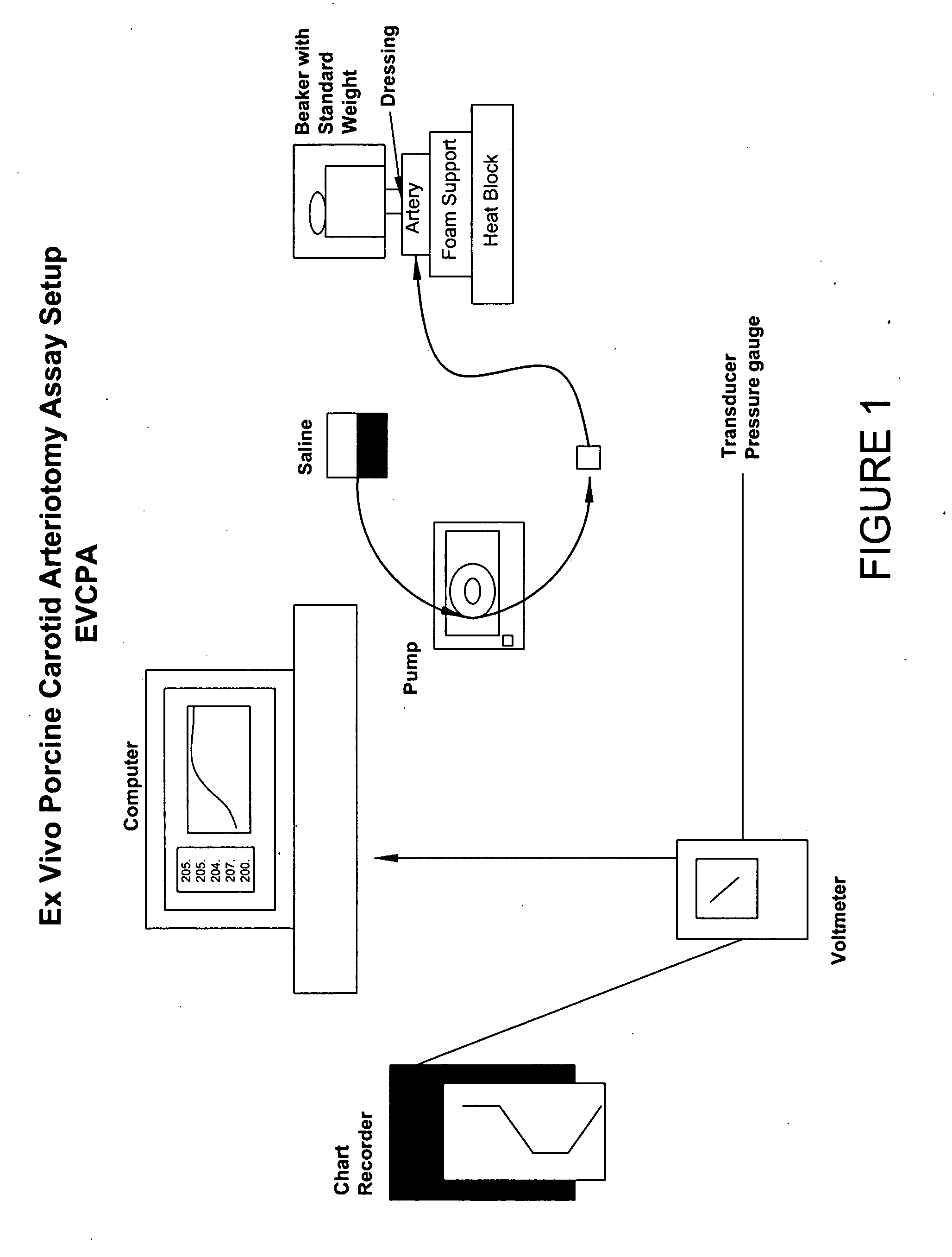
[0206]Similar to the need to evaluate a test article in the context of sealing and injury deep within surrounding tissue, there was also a need to test products that can seal injured tissue where the injured vessels are smaller and thinner-walled than an aorta. The following assay accomplishes this goal.
[0207]According to this modification, the porcine carotid artery is attached to a barbed female connector using cotton thread with the connective tissue side exposed. This is in contrast to the standard EVPA where the internal side is exposed. As the carotid arteries used in the VA model are more elastic and friable than the aorta, it is more difficult to treat or abrade the surface without damaging and compromising the artery. To ensure that no tears have occurred during the removal of the bulk of the connective tissue, the artery is connected to the barbed connector and solution is pumped into it. If the artery is intact, a 1.5 mm hole is punched into the artery using a biopsy punc...
example 3
[0286]For all dressings, ERL fibrinogen lot 3130 was formulated in CFB. The final pH of the fibrinogen was 7.4±0.1. The fibrinogen concentration was adjusted to 37.5 mg / ml. Once prepared the fibrinogen was placed on ice until use. Thrombin was formulated in CTB. The final pH of the thrombin was 7.4±0.1. The thrombin was adjusted to deliver 0.1 units / mg of Fibrinogen or 25 Units / ml thrombin. For the group with shredded support material dispersed within, it was cut into approximately 1 mm×1 mm pieces and dispersed within the thrombin solution prior to filling the molds. Once prepared the thrombin was placed on ice until use. The temperature of the fibrinogen and thrombin prior to dispensing was 4° C.±2° C. Cylindrical molds made of 10 or 3 mL polypropylene syringes (Becton Dickinson) with the luer-lock end removed were used. The plungers were withdrawn to the 6 mL and 2 mL mark respectively. For dressings utilizing a support material, the support material was cut and placed into each ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com