Data distribution management device and data distribution management method
a data distribution management and data technology, applied in the field of data distribution management devices and data distribution management methods, can solve the problems of increasing processing load, deteriorating speed performance, and data segments whose protocols are deteriorating in transmission efficiency, so as to prevent the downfall of throughput
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
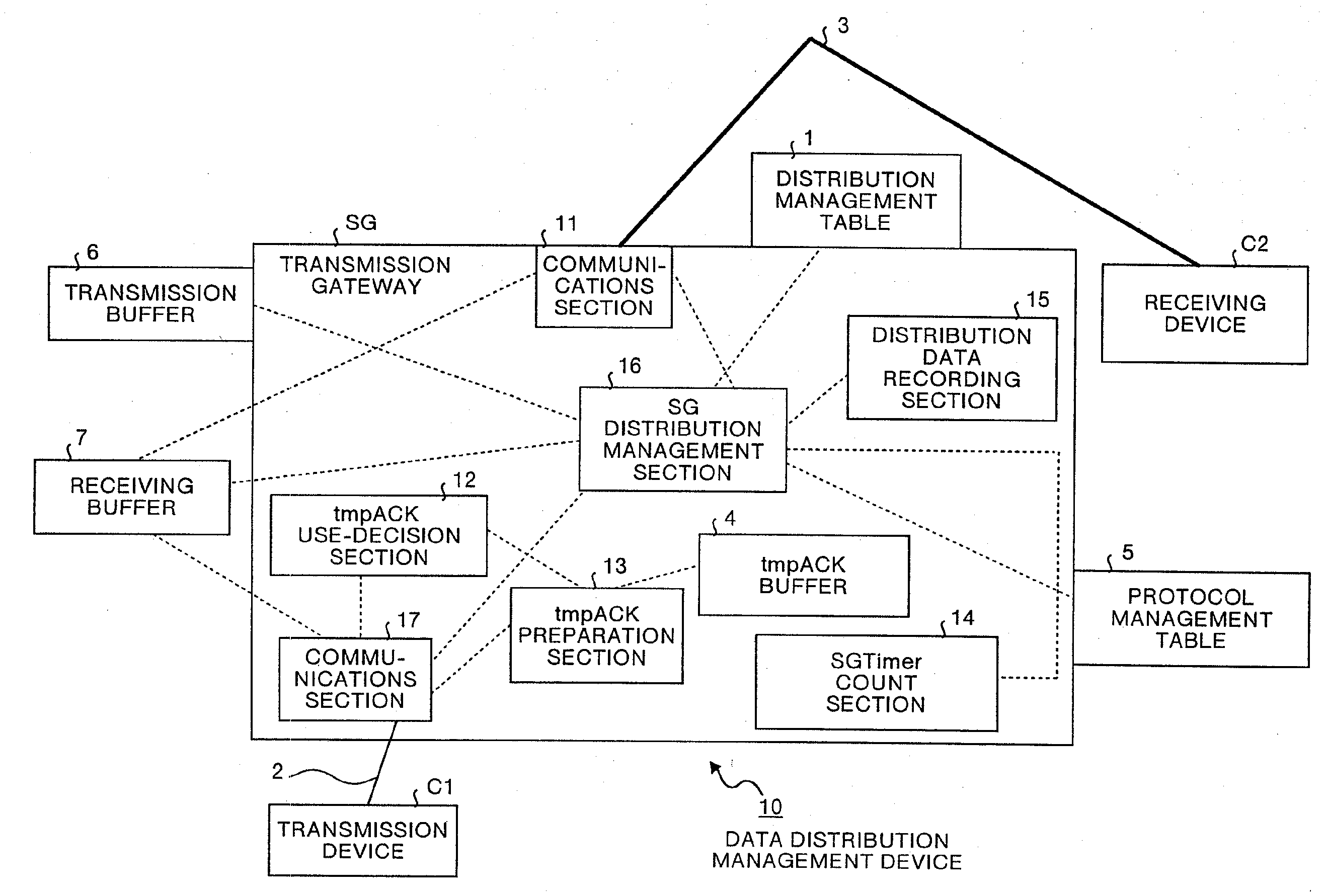
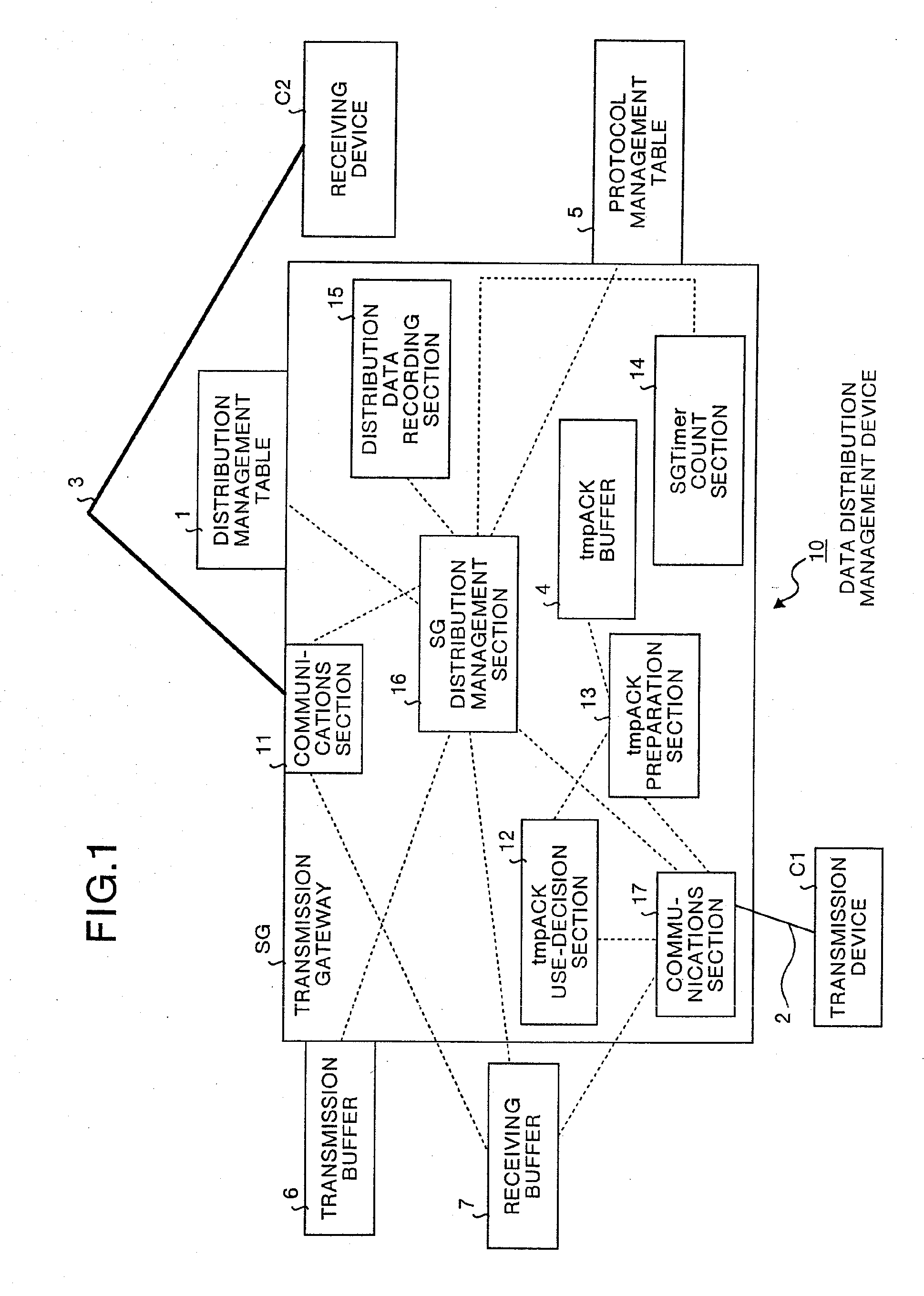
[0110]FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing the configuration of the data distribution management system including the data distribution management device according to the first embodiment of this invention. In FIG. 1, the data distribution management system is configured so that a transmission device C1 is connected to a data distribution management device 10 through a circuit 2, whereas the data distribution management device 10 is connected to a receiving device C2 through a circuit 3. The circuit 3, like satellite circuits, is a circuit having a large transmission delay, and the circuit 2 is smaller in transmission delay compared to the circuit 3.
[0111]The data distribution management device 10 is provided with a transmission gateway SG, a distribution management table 1, a protocol management table 5, a transmission buffer 6, and a receiving buffer 7. The transmission gateway SG is provided with a communications section 17 that performs the input / output processing of data packets f...
second embodiment
[0168]A second embodiment of this invention is explained below. In the second embodiment, the tmpACK use control processing shown in FIG. 7 is applied to prepare and transmit tmpACK in the procedure of time-based delay ACK.
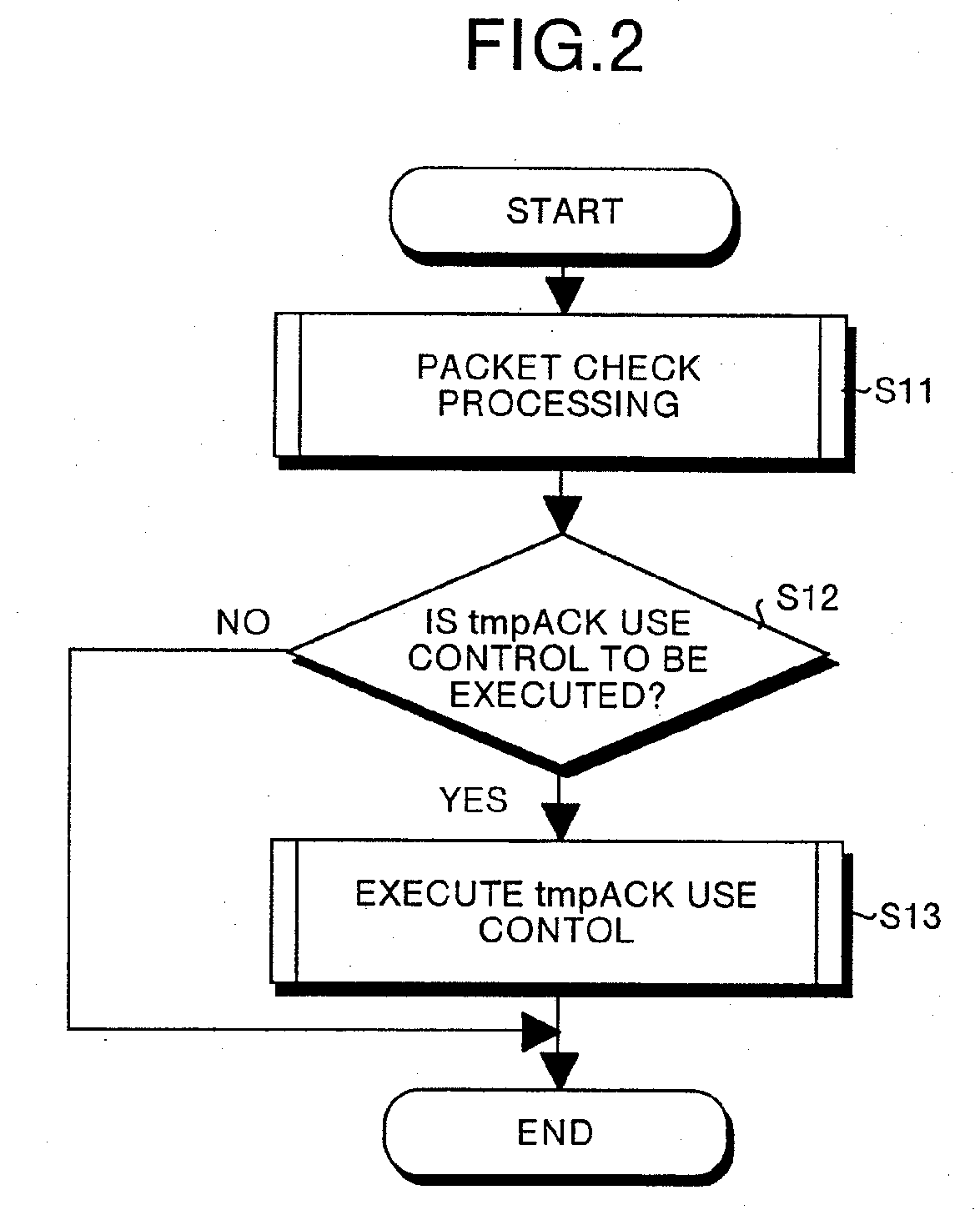
[0169]FIG. 15 is a flowchart showing the tmpACK use processing procedure of the data distribution management device of the second embodiment of this invention. In FIG. 15, the value of the FIN received flag as set by a series of processes shown in FIG. 2 is referred to decide whether the communication-end data packet has been received or otherwise (step S201). When it is decided that the FIN packet has been received (step S201, YES), then and there a return is made to step S13.
[0170]When on the other hand it is decided that the FIN packet has not been received (step S201, NO), a decision is then made whether there is a flag standing to show the lapse of delay time for temporary ACK (step S202). When the delay time for temporary ACK is found to have elapsed (step S...
third embodiment
[0179]A third embodiment of this invention is explained below. In the third embodiment, the tmpACK use control processing shown in FIG. 7 is applied to prepare and transmit tmpACK in the procedure of delay ACK based on the number of packets received.
[0180]FIG. 16 is a flowchart showing the tmpACK use processing procedure of the data distribution management device that is the third embodiment of this invention. In FIG. 16, by referring to the value of the FIN received flag as set by a series of processing in FIG. 2, it is decided whether the data packet after communication is ended has been received or otherwise (step S301). When it is decided that FIN packet has been received (step S301, YES), then and there a return is made to step S13.
[0181]On the other hand, when it is decided that the FIN packet has not been received (step S301, NO), it is decided whether data segments in numbers matching delays have been received (step S302). When data segments in numbers matching the delays ha...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com