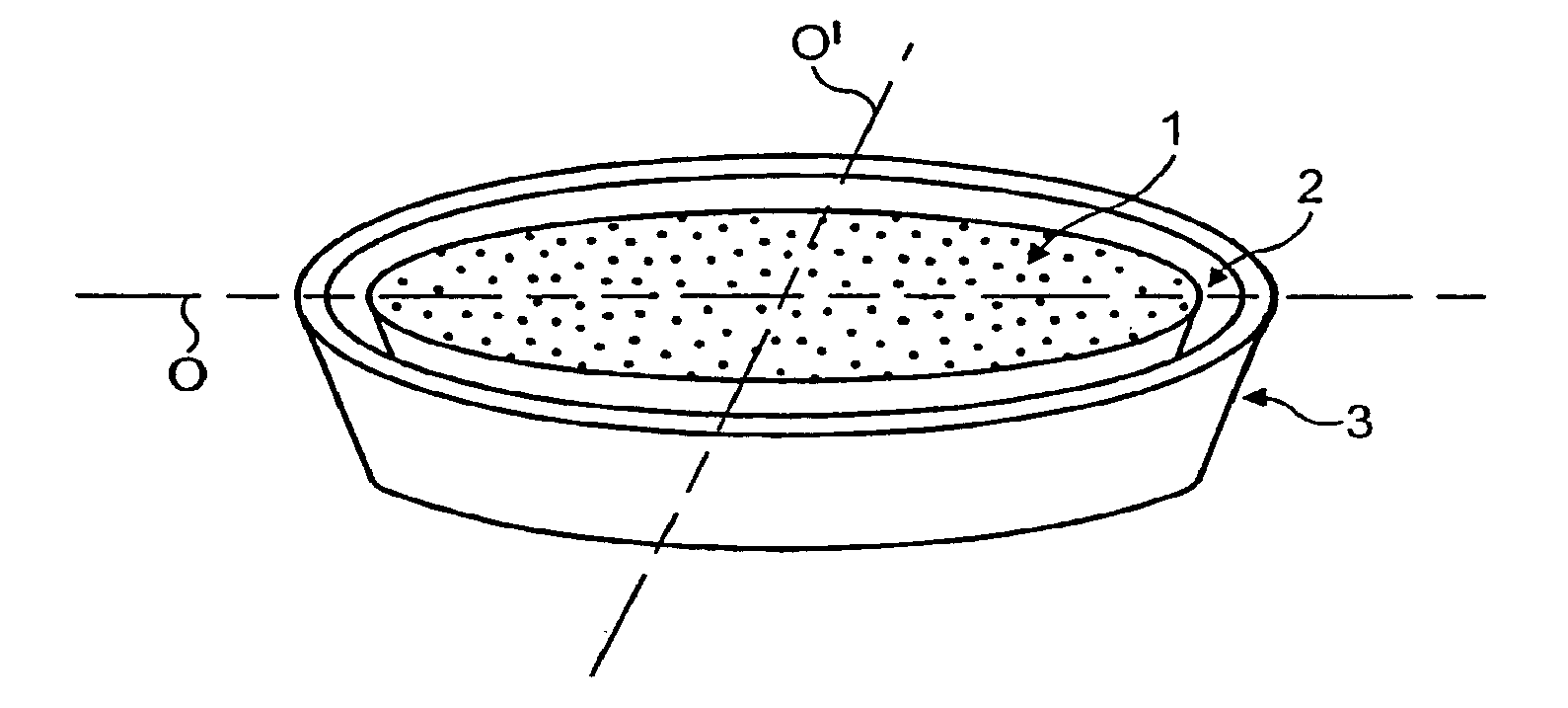
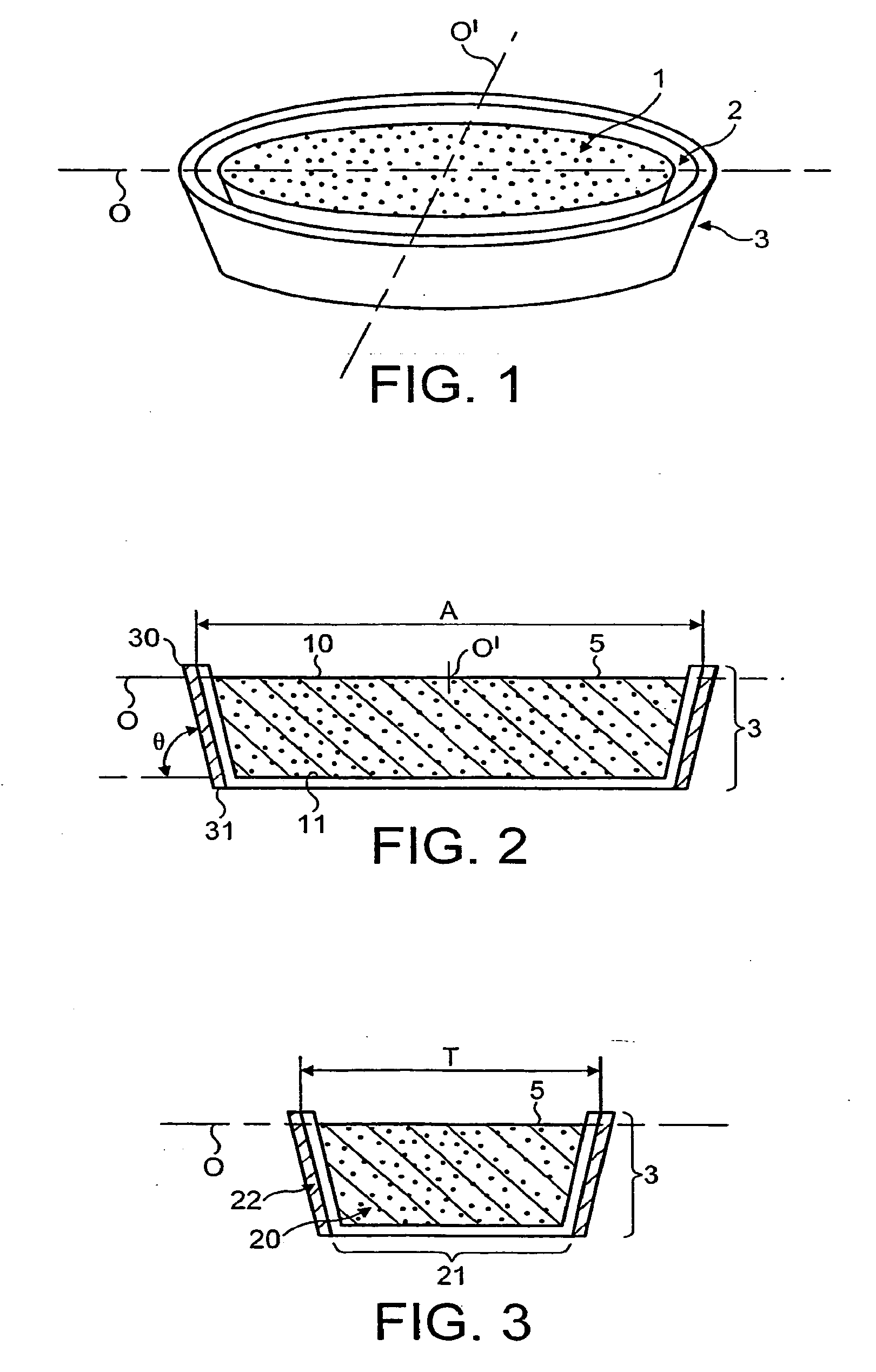
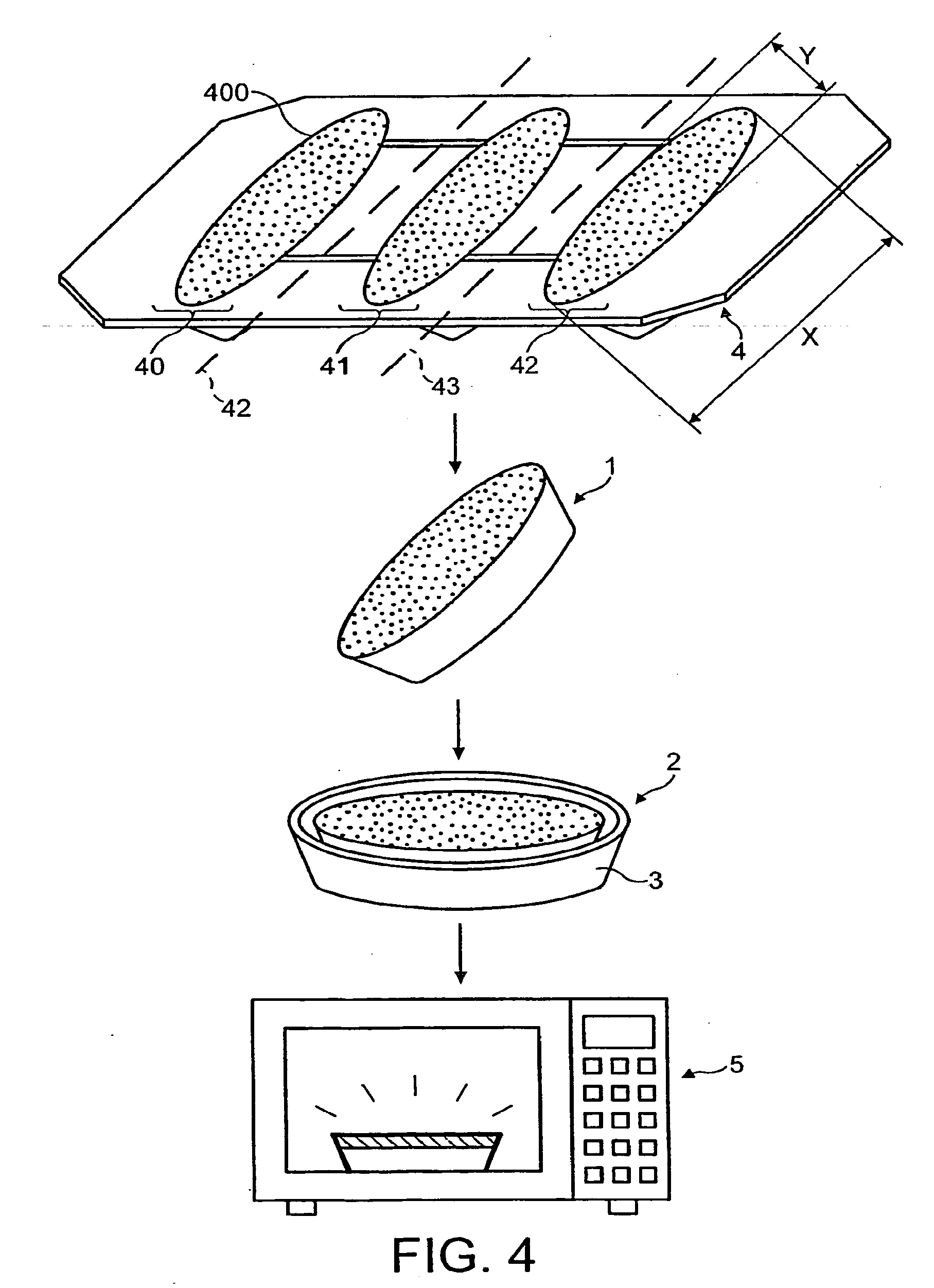
Uniform microwave heating of food in a container
a microwave oven and container technology, applied in the field of microwave oven uniform heating, can solve the problems of difficult microwave heating of frozen food, serious burnt spots on meals, and overcooking of some portions, so as to improve microwave reheating of food and uniform heating of frozen food. , the effect of improving the heating
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Comparative
Heating of Lasagna in Oval Plate without Metallic Side Band
[0077]A frozen lasagna product of 387 grams is placed in an oval plate (“plat a sabot”) having a long axis of 17.8 cm, a short axis of 10.4 cm, height of 3.1 cm, and no metallic shielding on the side wall. The food product is heated in Welbilt microwave oven (850 Watts) for 6 minutes. The temperature measurement showed a cold spot below 18° C. and edges boiled over.
[0078]FIG. 8 shows the corresponding thermograph at the end of the heating stage.
example 2
Heating of Lasagna in Oval Plate with Half Upper Metallic Side Band
[0079]The same food product is heated in a plate of identical dimension with a metallic shielding tape adhesively attached to the upper half of the upward sides of the plate. The lower half of the sides is left uncovered. The product weighed 389 grams and was heated in the same oven as Example 1 for 6 minutes. The product showed a cold spot below 39° C. and edge slightly boiled over.
[0080]FIG. 9 shows the corresponding thermograph at the end of the heating stage.
example 3
Heating of Lasagna in Oval Plate with a Full Metallic Side Band
[0081]The same food product is heated in a plate of identical dimension with a metallic shielding tape adhesively attached onto the full sides of the plate. The bottom of the plate is left uncovered. The product weighed 386 grams and was heated in same oven and for 6 minutes. It had no cold spot with a temperature of the surface higher than 65° C. and no burnt edge and corner.
[0082]FIG. 10 shows the corresponding thermograph at the end of the heating stage.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com