Method and system for media audience measurement and spatial extrapolation based on site, display, crowd, and viewership characterization
a technology of spatial extrapolation and media audience, applied in television systems, selective content distribution, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to take audience surveys using traditional methods, high cost, and high potential bias of on-site interviews, and achieve more reliable estimates of crowd dynamics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
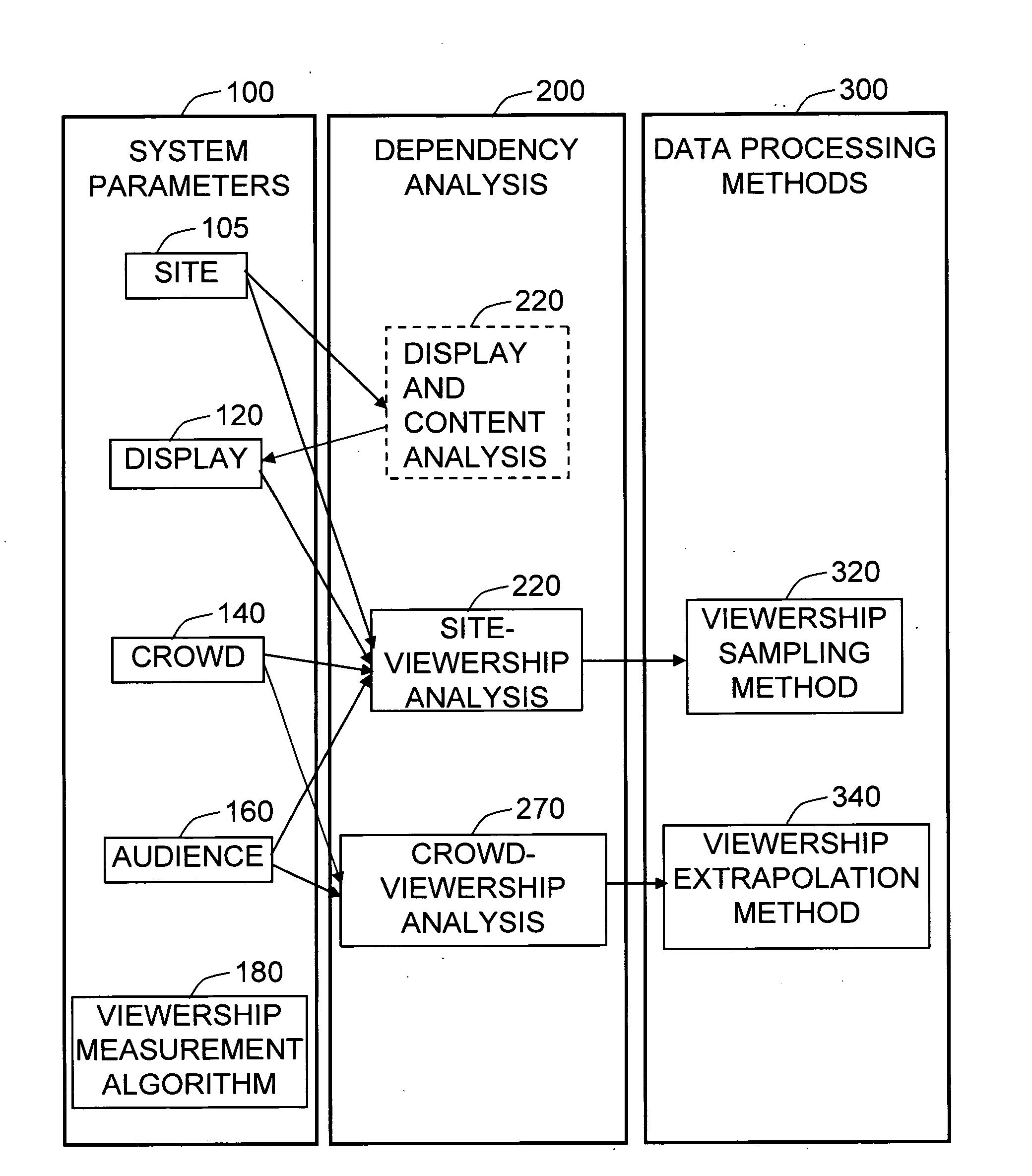
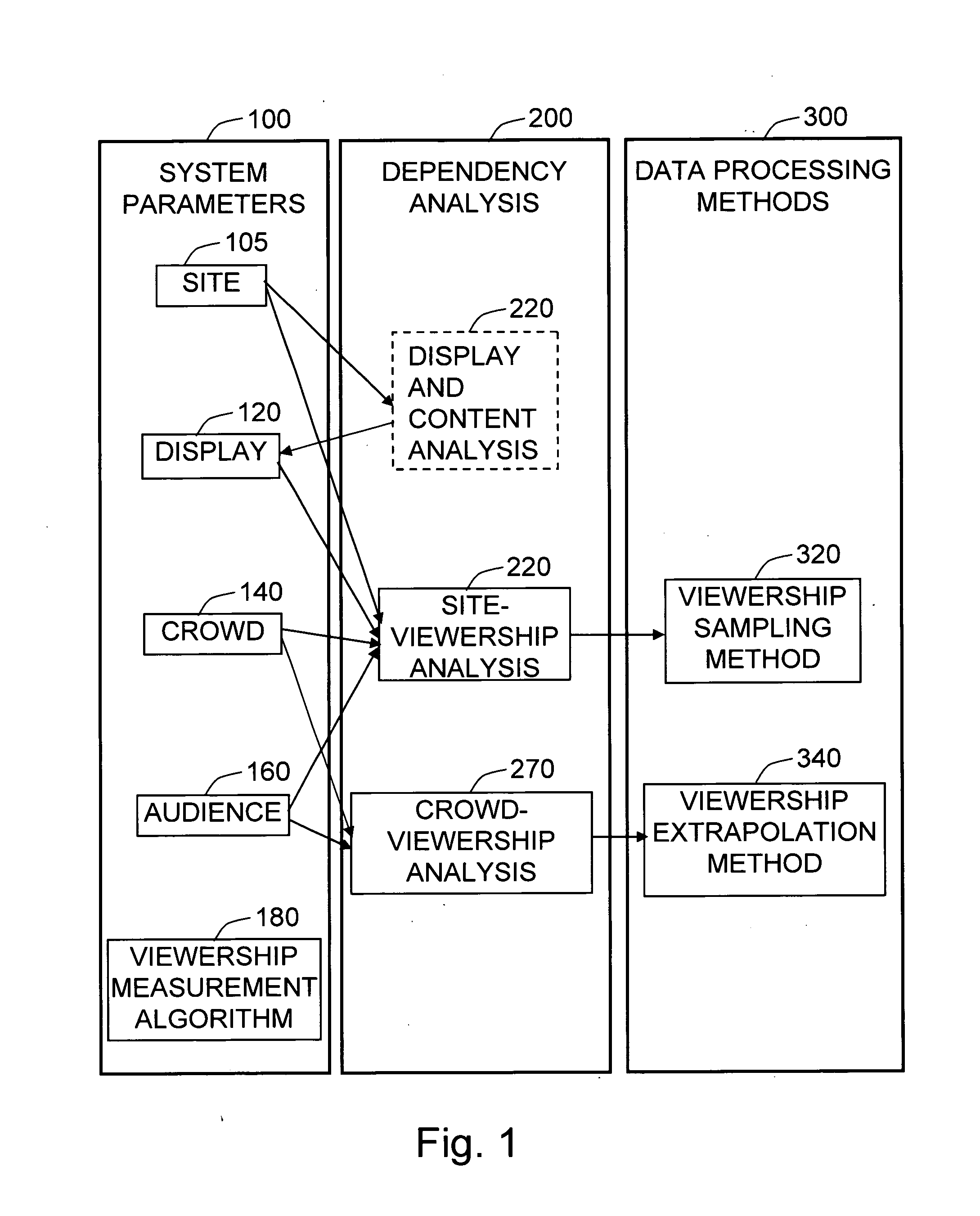
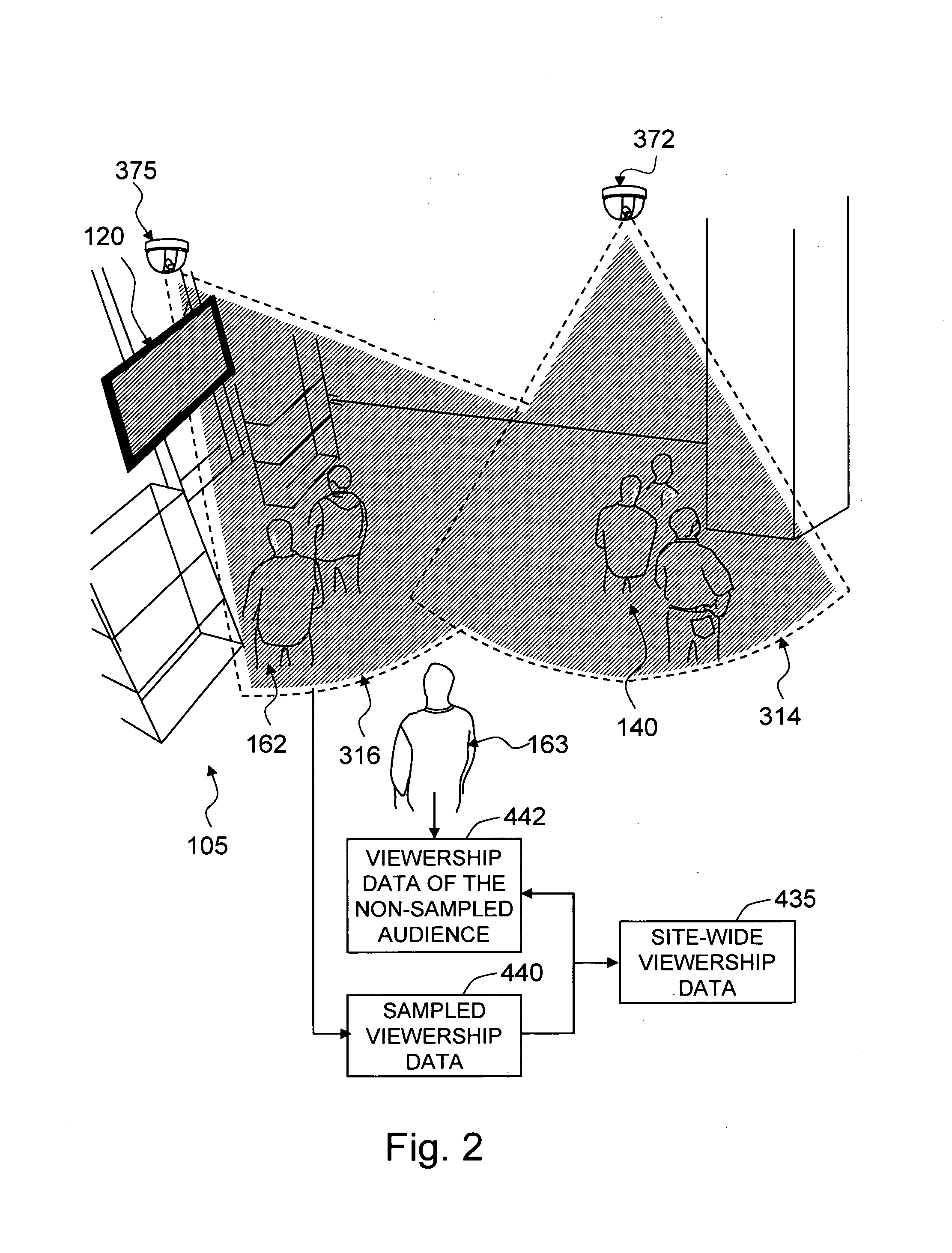
[0085]A preferred embodiment of the closure of the present invention is illustrated in FIG. 1. It shows four major system parameters 100 of the media audience measurement system, and their dependencies (marked by arrows) identified by the dependency analysis 200, in the process of designing the media audience measurement system. From the dependency analysis 200, data processing methods 300 are derived. The site 105 parameter influences the position and size of the display 120 in a way that the display 120 should be well visible in the targeted area on the site. The site parameters, such as the arrangement of the pathways and obstacles, also affect the crowd 140 behavior. The display 120 specifications are determined based on the site 105 characteristics; the display and content analysis 220 procedure is not a scope of the present invention. Based on the analysis about the influence of the site 105, the display 120, and the crowd parameters on the behavior of the audience 160, the si...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com