Ultra-High Strength Stainless Alloy Strip, a Method of Making Same, and a Method of Using Same for Making a Golf Club Head
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0012]A preferred embodiment of the invention includes an elongated strip article having the following composition in weight percent:
C0.03max.Mn1.0max.Si0.75max.P0.040max.S0.020max.Cr10.9-11.1Ni10.9-11.1Mo0.9-1.1Ti1.5-1.6Al0.25max.Nb0.7-0.8Cu1max.B0.010max.N0.030max.
The balance is iron and the usual impurities.
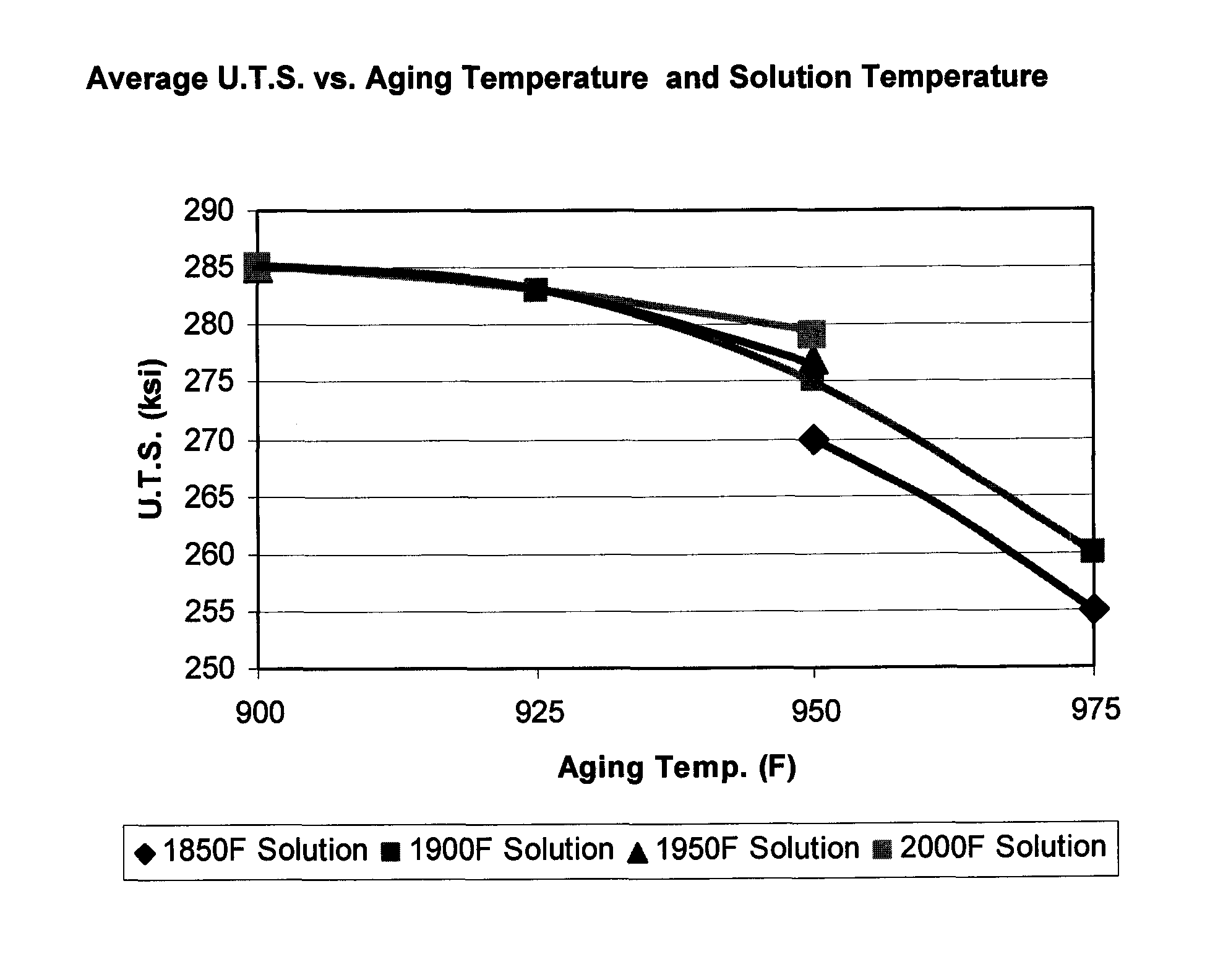
[0013]The alloy composition is preferably melted using vacuum induction melting (VIM). The steel is cast into one or more ingot molds. For additional cleanness, the alloy is vacuum arc remelted (VAR) after the VIM step. After solidification, the alloy is formed into strip by intermediate pressing of the ingot to form a billet and then hot rolling the billet to form elongated strip. Alternatively, the strip material can be formed by hot rolling the ingot from a starting temperature of about 1900° F. to 2250° F. The strip can be provided in the overaged condition by heating at about 1100° F. to 1350° F. for about 2 to 8 hours and then cooling in air. Alternatively, and for bette...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com