Yarns, high wear resistance fabrics and objects made therefrom
a technology of wear resistance and fabric, applied in the field of yarns, high wear resistance fabrics and objects made therefrom, can solve the problems of reducing the mechanical properties of fabrics containing cellulosic fibers, and it is difficult to obtain both in a fabric, so as to achieve good comfort or wear, good abrasion and tear resistance, good balance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples 1 to 6
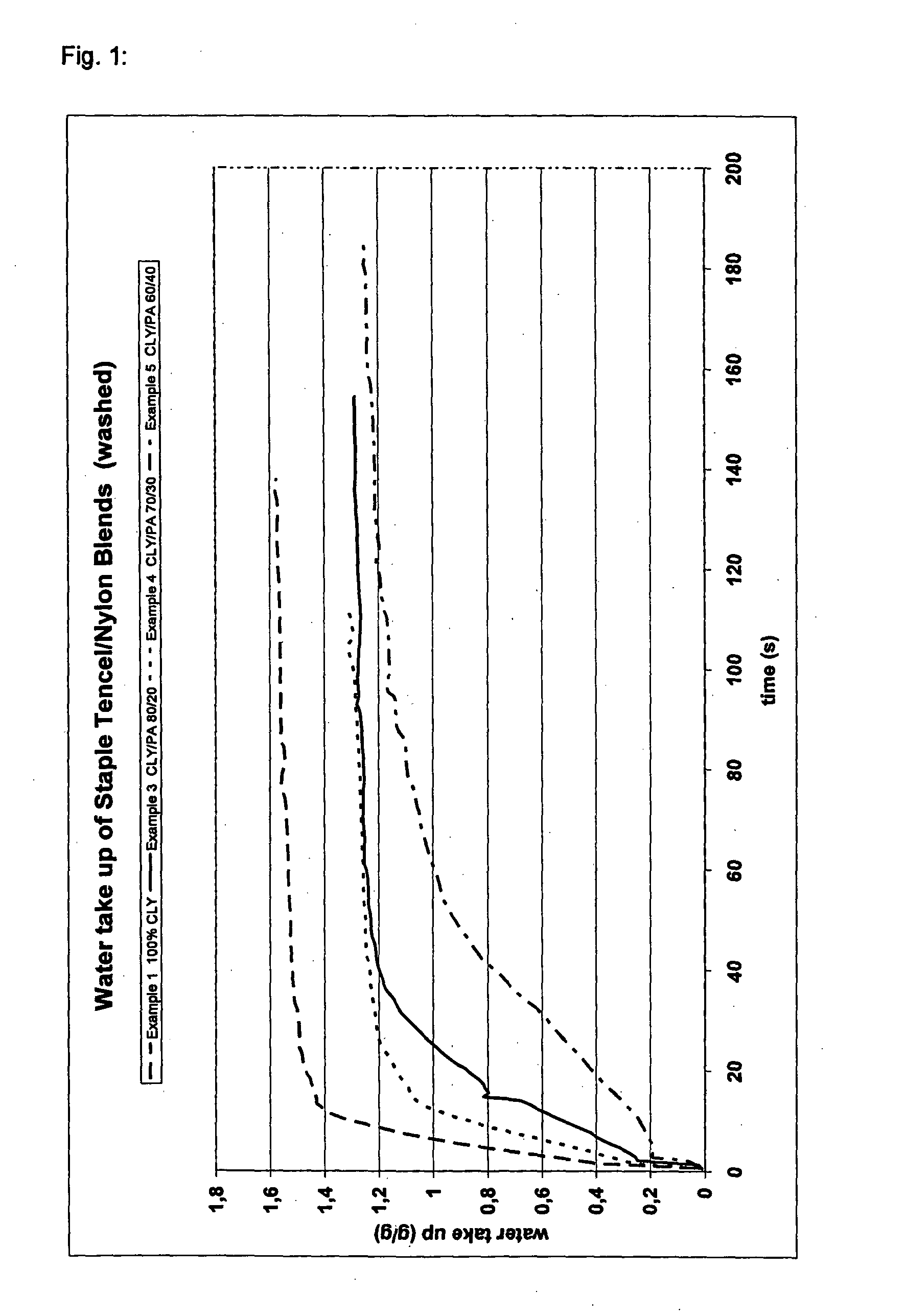
[0047]Commercially available PA-6.6 staple fibers with a titer of 2.0 dtex and 38 mm cut length were mixed in the ratios described in table 1 with commercially available TENCEL® staple fibers with a titer of 1.4 dtex and 38 mm cut length and spun to a yarn of Nm 1 / 26 (Ne 1 / 15).
[0048]The yarns were further processed by weaving a 2×1 twill with a weight of 249 g / m2 and 32 ends and 24 picks. The woven fabrics were then singed, desized, scoured, dried, heat set at 205° C., printed to meet the IR reflectance specifications from military and finished with an FC water repellent. These methods are well known to anyone skilled in the art.
[0049]The tear strength in the warp as well as in the weft direction was measured and the Martindale test was applied to each so-finished fabric.
TABLE 1RatioTenacityTearTearTencel / PAyarnstrengthstrengthMartindaleExample6.6 [w / w][cN / tex]warp [N]weft [N][rubs]1100 / 0 25.4183020.000290 / 1024.0253265.000380 / 2023.32642>100.000470 / 3022.02840>100.000560 / 4020.92842>10...
example 7 to 9
[0052]2×1 twills were made out of a Ne 1 / 15 yarn containing a mixture Tencel / PA-6.6 70% / 30% (w / w) of fibers according to example 1. Weight and finish varied according to Table 2, but the process steps were the same as in Examples 1 to 6.
[0053]In example 8a conventional Proban® treatment was applied afterwards. In example 9a different fabric construction was made, but by using the same yarns as in example 7.
TABLE 2FabricTearTearConstructionweightstrengthstrengthMartindaleExample[ends / picks][g / m2]warp [N]weft [N][rubs]Remark739 / 222053527>100.000—839 / 222052721>100.000Proban FRfinish930 / 201793631>100.000Lighterweight
[0054]It can be seen that all three fabrics according to the invention fulfill the U.K. Military specification of 28 cN (warp), 20 cN (weft) and 45.000 Martindale rubs. The fabric of example 8 also passed the flame retardant test of EN 532.
example 10
[0055]A 2×1 ripstop twill with 30 ends / 22 picks and 180 g / m2 was made from the 70 / 30 yarn of example 4 but with a 350f / 136 nylon filament ripstop thread as every ninth pick. Table 3 shows the comparison with the U.K. military specification for ripstop fabric.
TABLE 3Tear strengthTear strengthMartindaleAir permeabilityExamplewarp [N]weft [N][rubs][l / m2 s]Specification256030.0002001039>50 unable>100.000415to tear
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| cut length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tenacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com