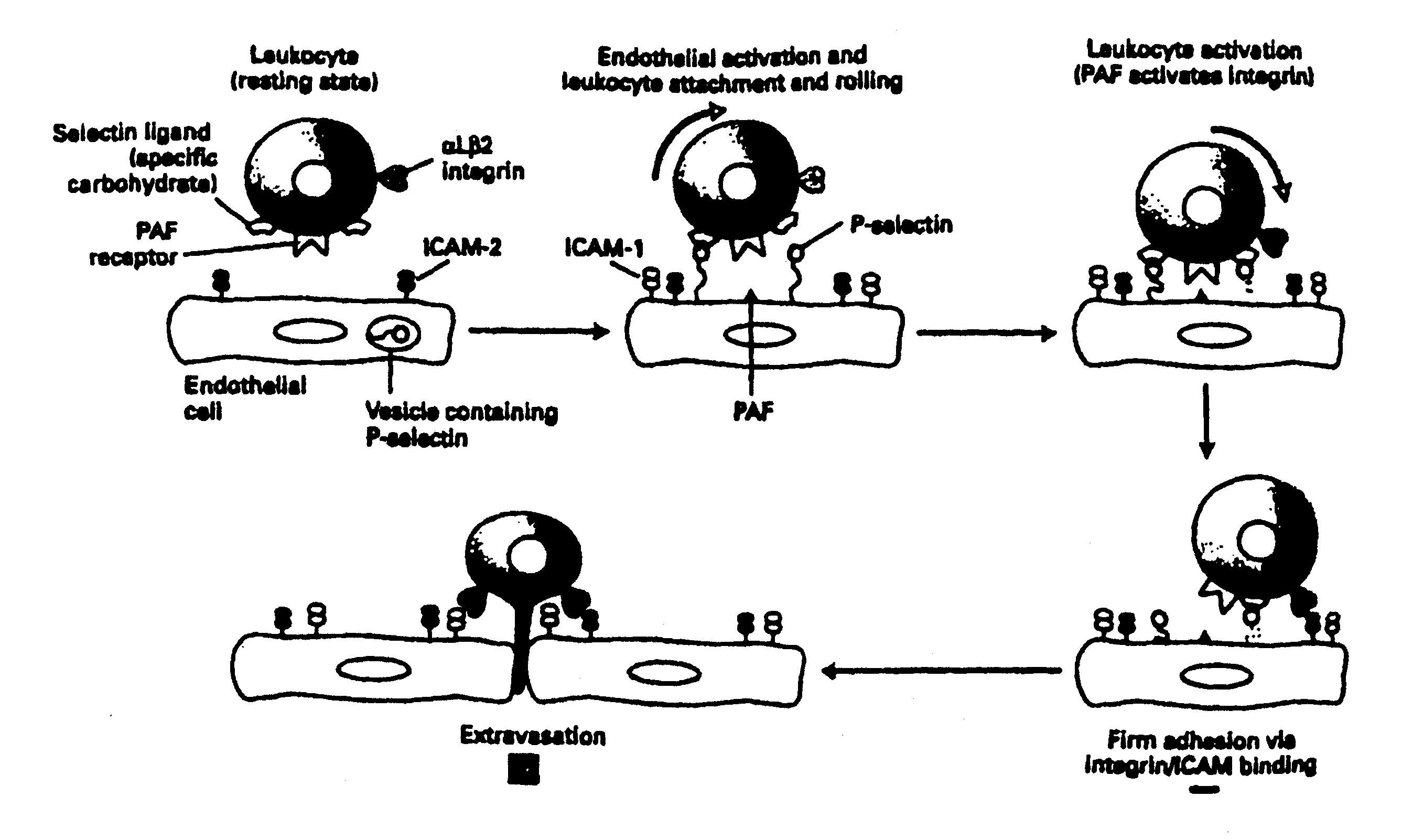
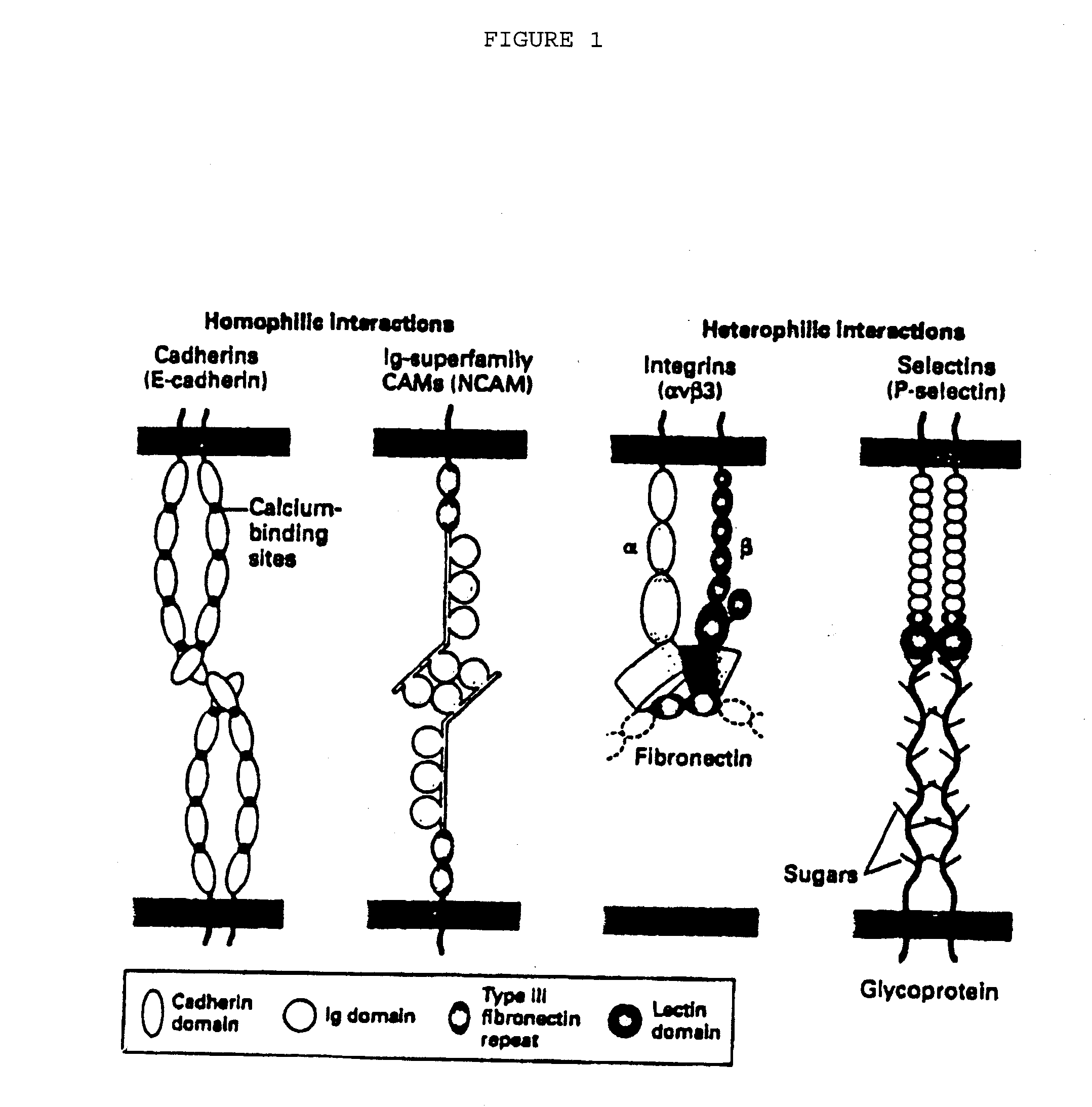
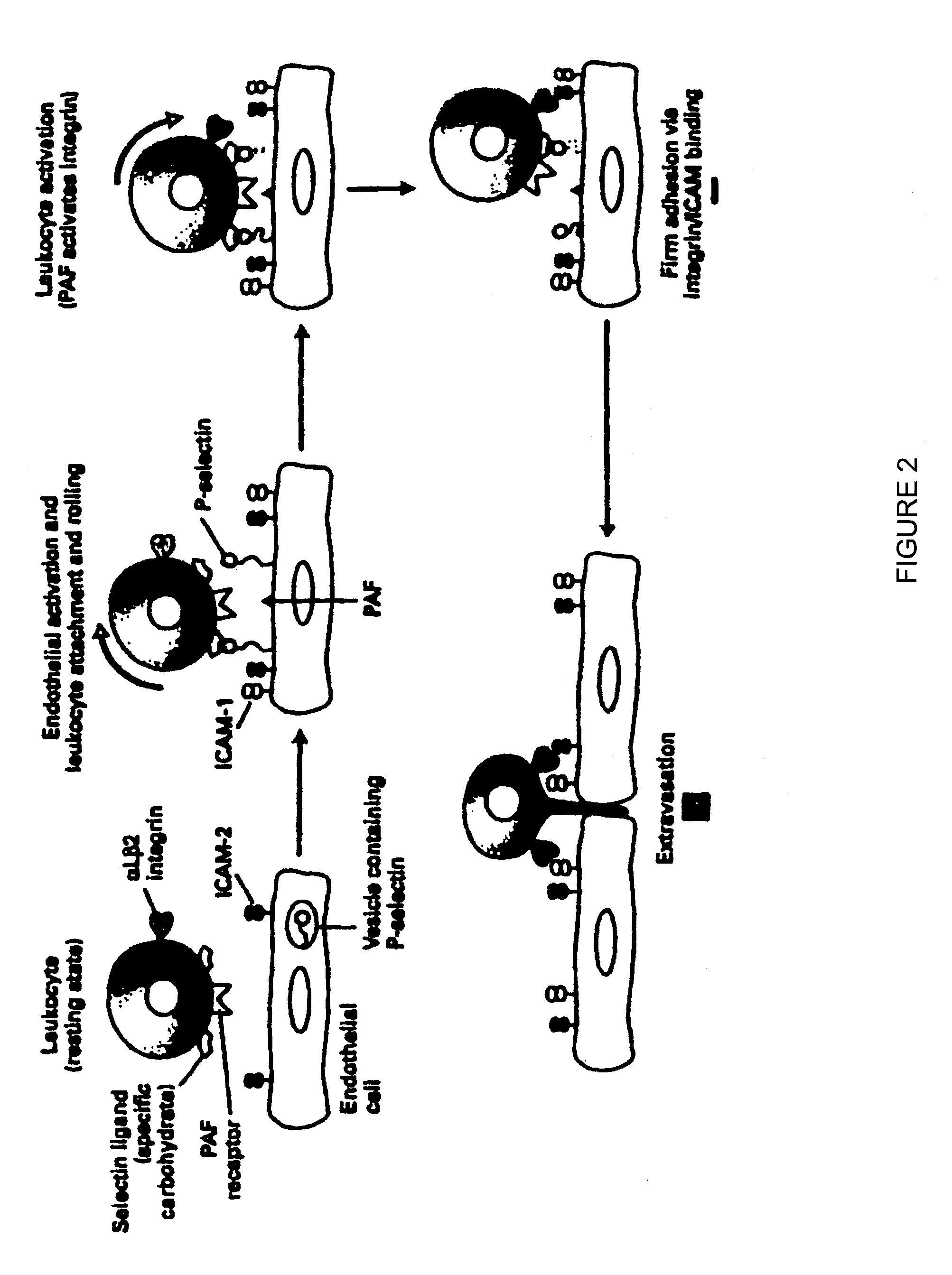
Methods of reducing extravasation of inflammatory cells
a technology of inflammatory cells and extravasation, which is applied in the direction of biocide, drug composition, peptide/protein ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of damage to normal tissue, further impair tissue function, and unadjusted inflammatory process, so as to achieve the effect of altering the extravasation of cells associated with the extravasation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0076]Toxicity Studies. Female Long Evans rats from Charles River Laboratories, weighing approximately 210 grams were housed in the Acorda Animal Care Facility for 5 days prior to injection to ensure health and weight stability. Rats were anesthetized with isoflurane and injected i.v. via tail veins with chondroitinase ABC I (Seikagaku; Cat number 100332, lot number E02201). Animals were injected with either 0, 0.2, 0.775 or 7.775 mg / kg with solutions containing 0, 0.2, 0.775 and 7.775 mg / ml, respectively in Hank's balanced salt solution.
[0077]Additionally, toxicity studies were conducted for Intrathecal (IT) catheter administration. Intrathecal catheters were placed in 16 normal, un-injured female rats at about the T13 / L1 vertebral junction for delivery of chondroitinase. Catheters were fed rostrally to rest at the T9 / T10 level to simulate previous chondroitinase studies. Twenty-four hours after intrathecal catheter placement animals were dosed with 0, 0.06, 0.6 or 6.0 Units of Aco...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| apparent molecular mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com