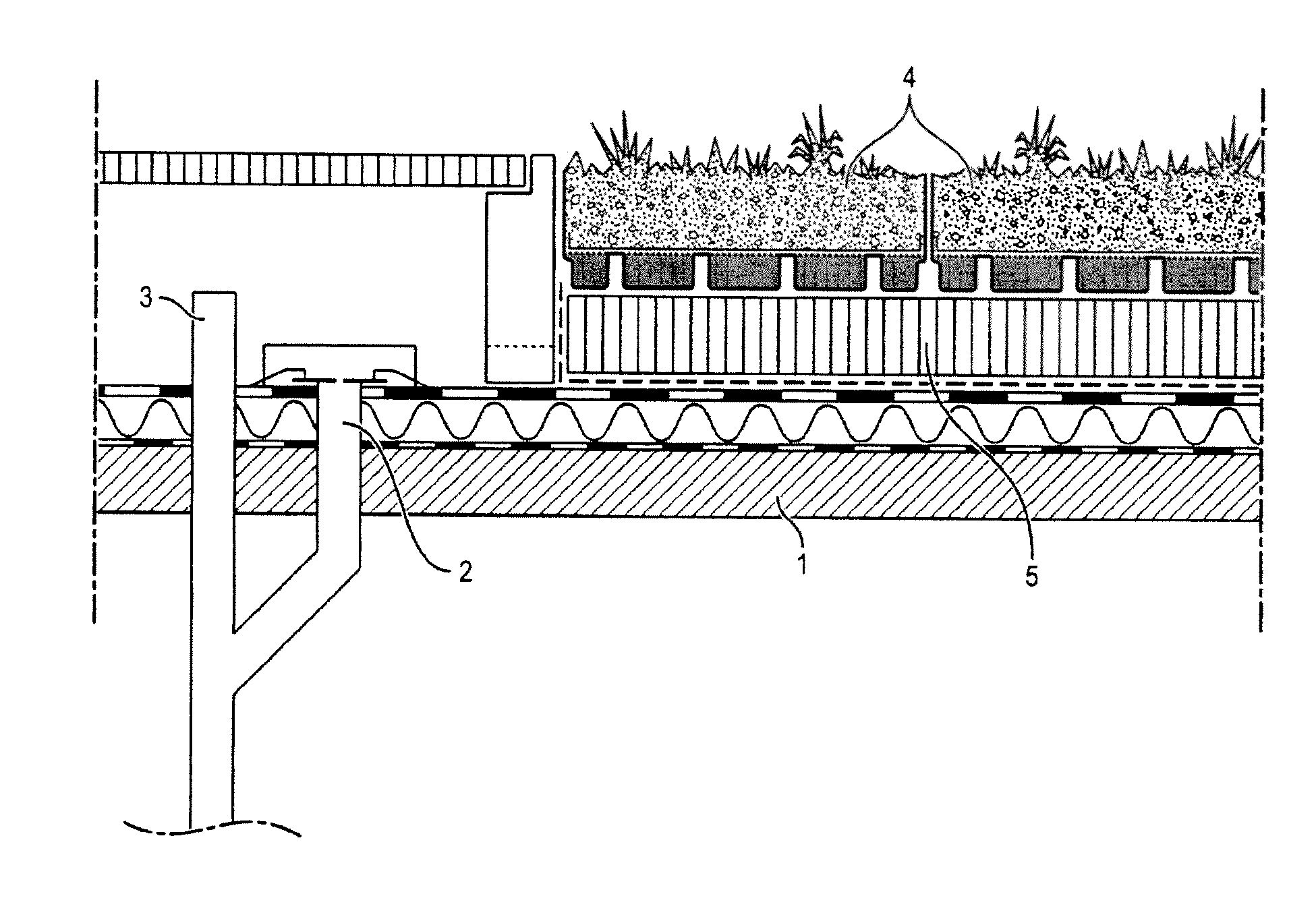
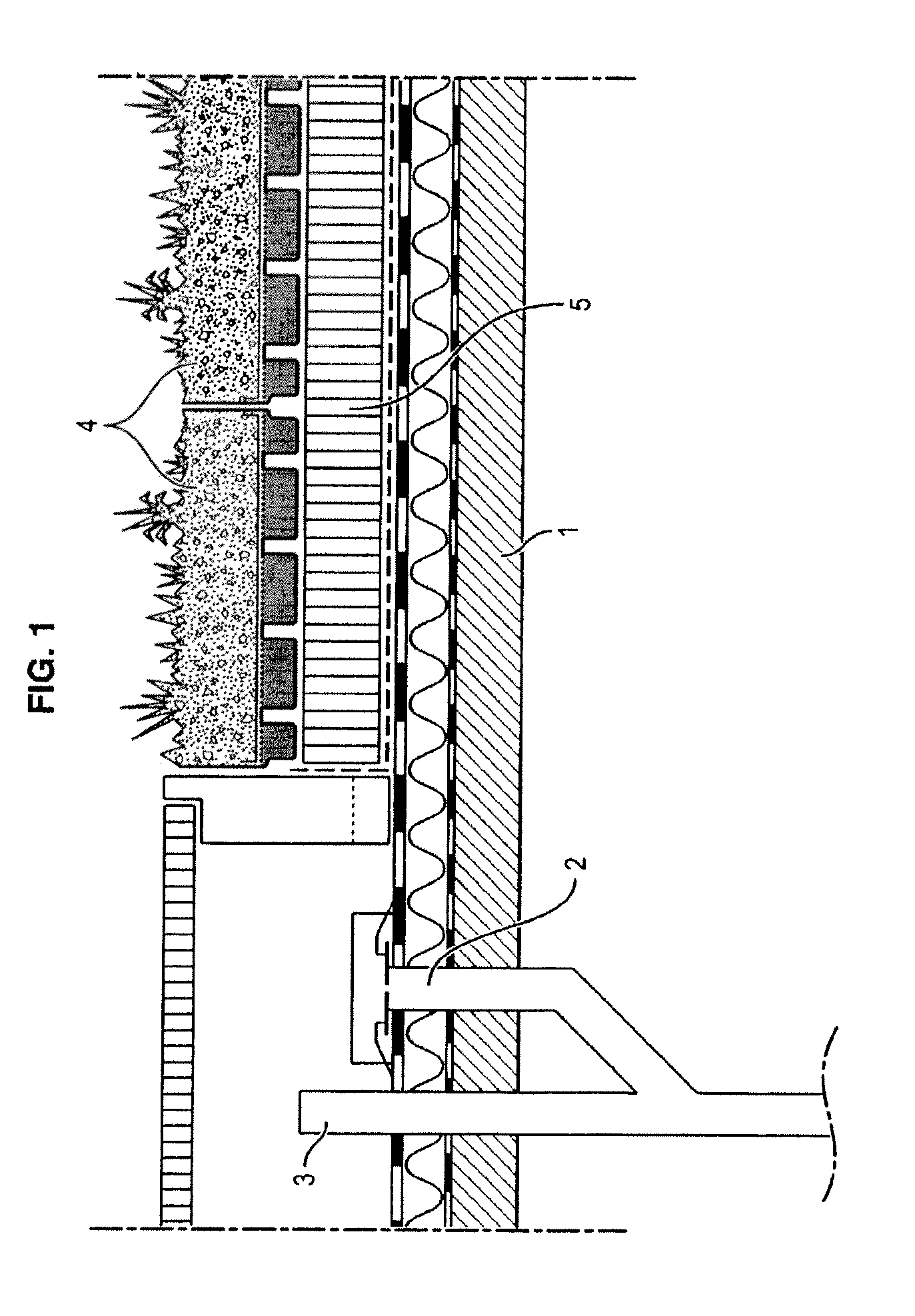
Container for temporarily holding water on the roof of a building with a controlled leakage rate
a technology for storing containers and roofs, applied in drinking water installation, roof improvement, gas/liquid distribution and storage, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the risk of flooding, and increasing the cost of collection, so as to reduce the leakage rate and control the effect of the leakage ra
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
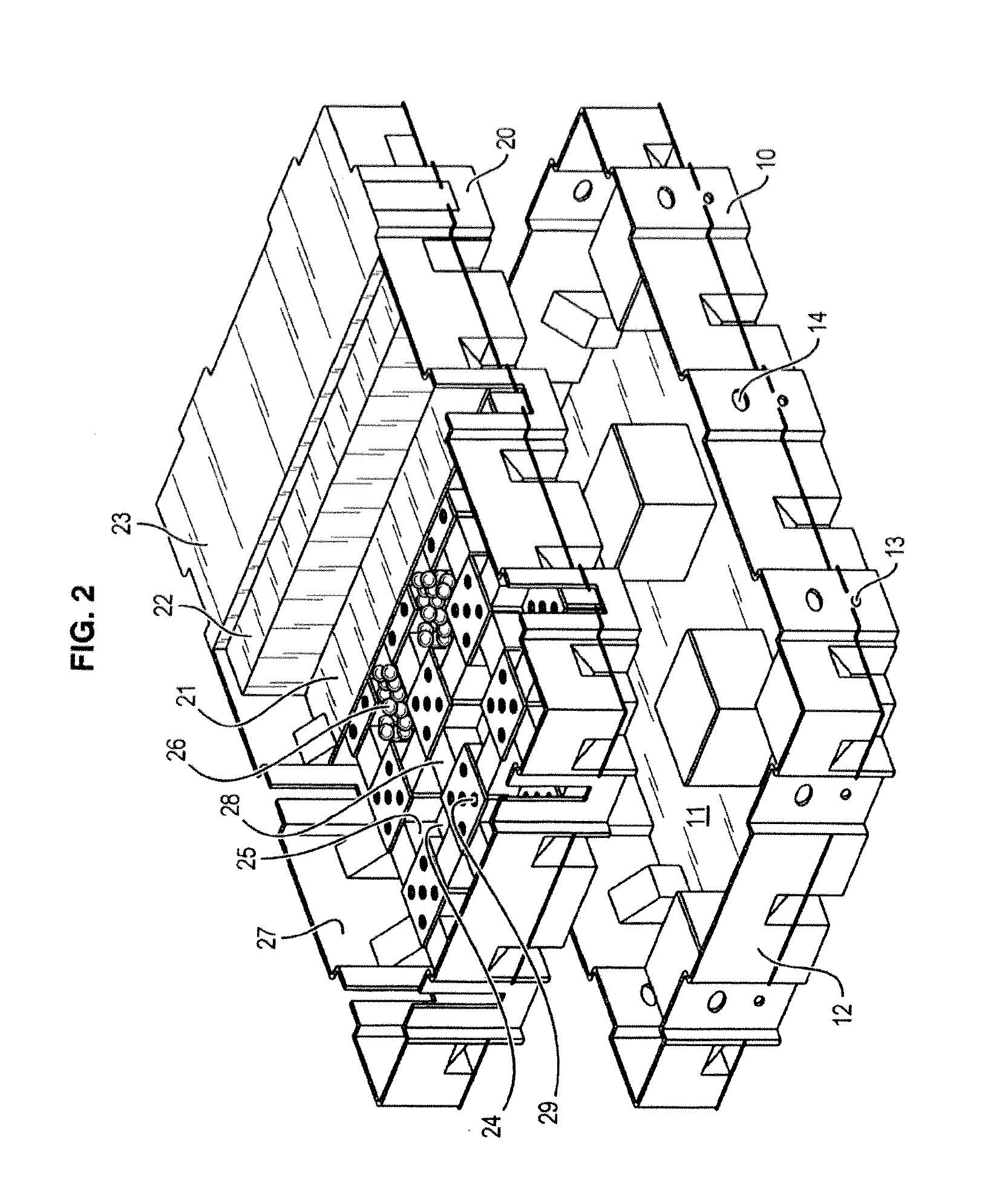
first embodiment
shown in FIGS. 3a and 3b, the obturator 32 is rotated in front of the orifice 14. The obturator is for example in the form of a portion of a disc 32 in which a slot 31 with progressive opening is formed. This progressive opening ensures a constant leakage rate when the temporary volume of water decreases or increases by rotating the disc 32 and therefore modifying the position of the slot in front of the orifice.
In a variant, it is possible to provide, in place a slot formed in a disc portion, a blade the thickness of which varies progressively in order to ensure a constant leakage rate when the blade closes off the opening.
With reference to FIG. 3a, the orifice 14 is formed through the wall of the container close to the bottom 11 of the container. The progressive-opening slot 31 is formed in a disc 32 mounted so as to rotate about the rotation spindle 33 perpendicular to the wall. The disc is connected to the float 30 via the arm 34 pivoting about the spindle 33, so as to pivot aga...
second embodiment
shown in FIGS. 4a-4b and FIGS. 5a-5b, the obturator 37, 38 is rotated about a spindle 33 through the orifice 14.
The obturator for example takes the form of a horn 37, 38 associated with an arm 34 pivoting about the spindle 33 under the action of a float 30 to which it is connected. The horn, the diameter of which increases progressively, thus adjusts the opening of the orifice according to the volume of water remaining to be drained in the container. The orifice can be formed in the bottom of the container (FIGS. 4a-4b) or through a wall of the container (FIGS. 5a-5b), which creates a residual volume of water 42.
In the variant shown in FIGS. 6a-6b, the means of discharging water with a constant leakage rate comprise an obturator 43 directly driven by a float 30 in translation through the orifice 14.
The obturator is for example formed by a cone 43, at the head of which a float 30 is provided. The orifice 14 is here formed in the bottom of the container, while the cross-section of the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com