Unwanted E-Mail Filtering System Including Voting Feedback
a technology of unwanted e-mail and filtering system, applied in the field of data processing system, can solve the problem that a large amount of unwanted e-mail is generally still able to pass through such systems, and achieve the effect of fast respons
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
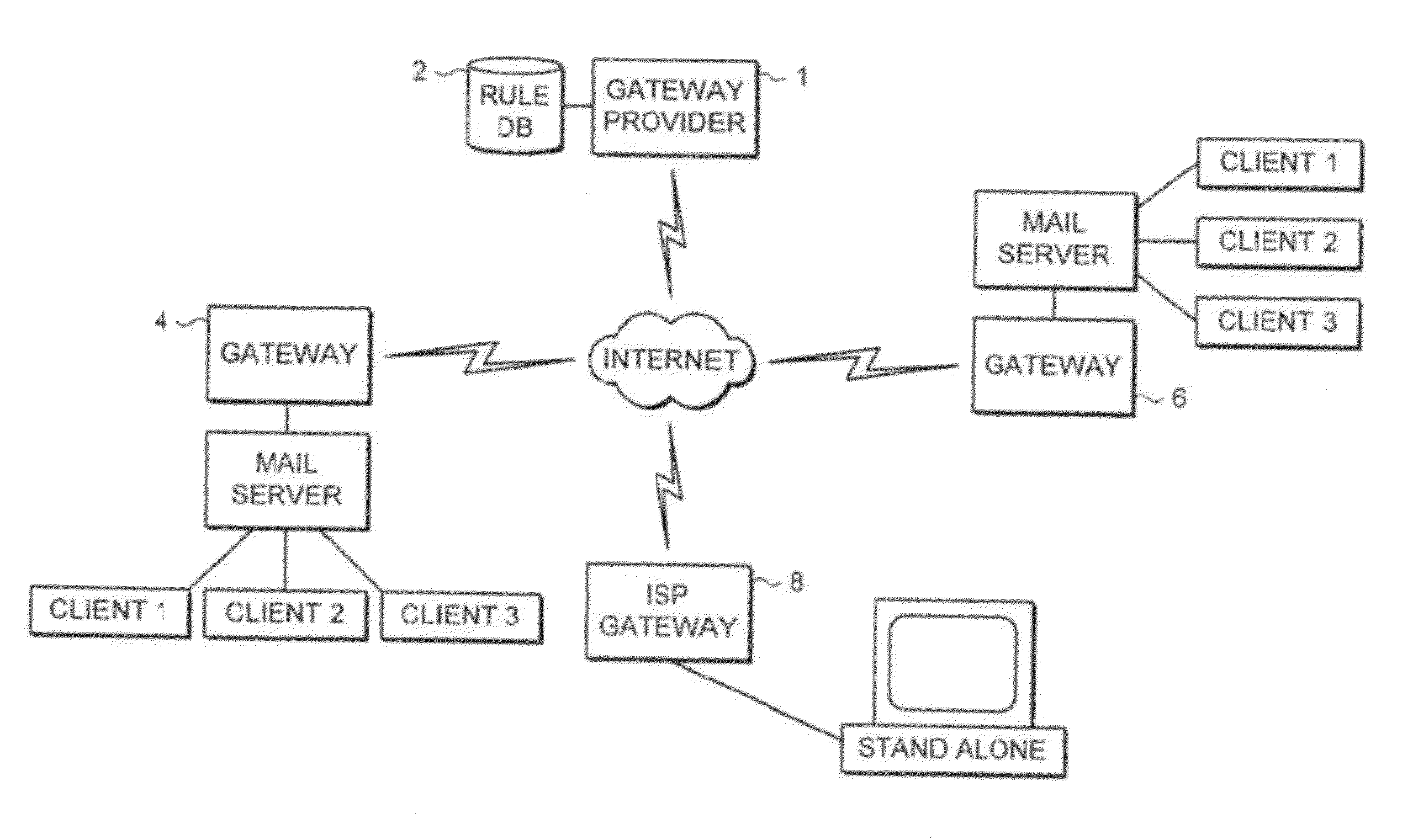
[0033]FIG. 1 illustrates a plurality of e-mail users in the form of client computers connected via respective mail servers and gateways through the internet. A central provider 1 of the downloadable filter data uses an attached rule database 2 to generate filter data files that may be downloaded by individual connected gateway computers 4, 6, 8. These gateway computers apply the downloaded filter data specified tests to received e-mail messages prior to passing these along to their associated mail servers. The individual gateways 4, 6, 8 may also apply locally defined filtering rules specific to that particular organisation or user.
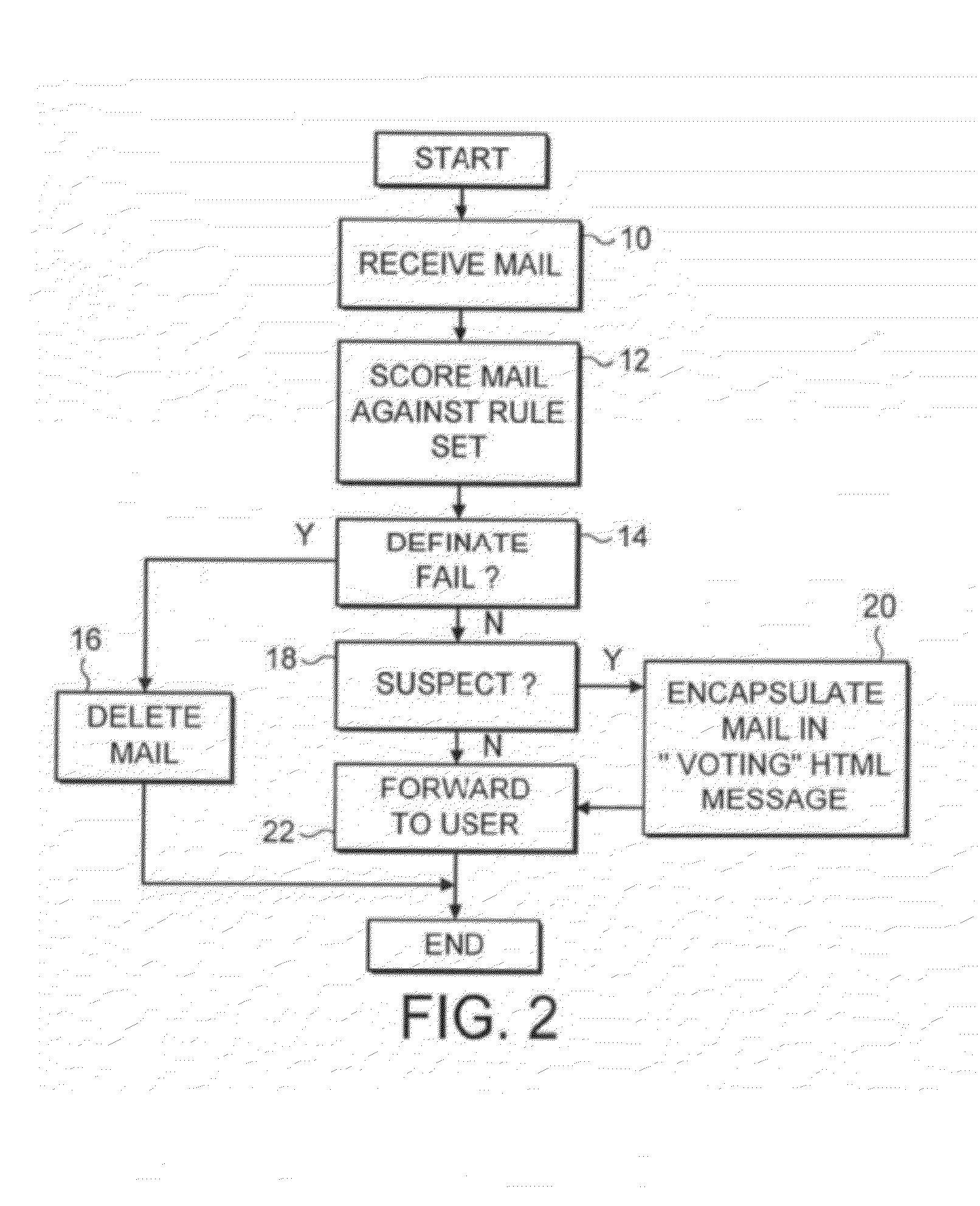
[0034]The rules specified in the rule database 2 may be of an algorithmic form rather than a less flexible direct regular expression form. A predetermined list of words identified as common within unwanted e-mail messages may be established. Words such as “buy”, “free”, “credit” and others have a relatively higher likelihood of occurrence within unwanted ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com