Method of manufacturing an optical fibre, preform and optical fibre
a manufacturing method and technology of optical fibre, applied in the direction of glass making apparatus, instruments, material analysis, etc., can solve the problems of undesirable oh groups in the external surface of the support tube, group problems in regard to optical properties, and said oh groups produce adverse effects in the light conducting part of the optical fibre, and achieve the effect of negative effect on the deposition efficiency of dopants
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
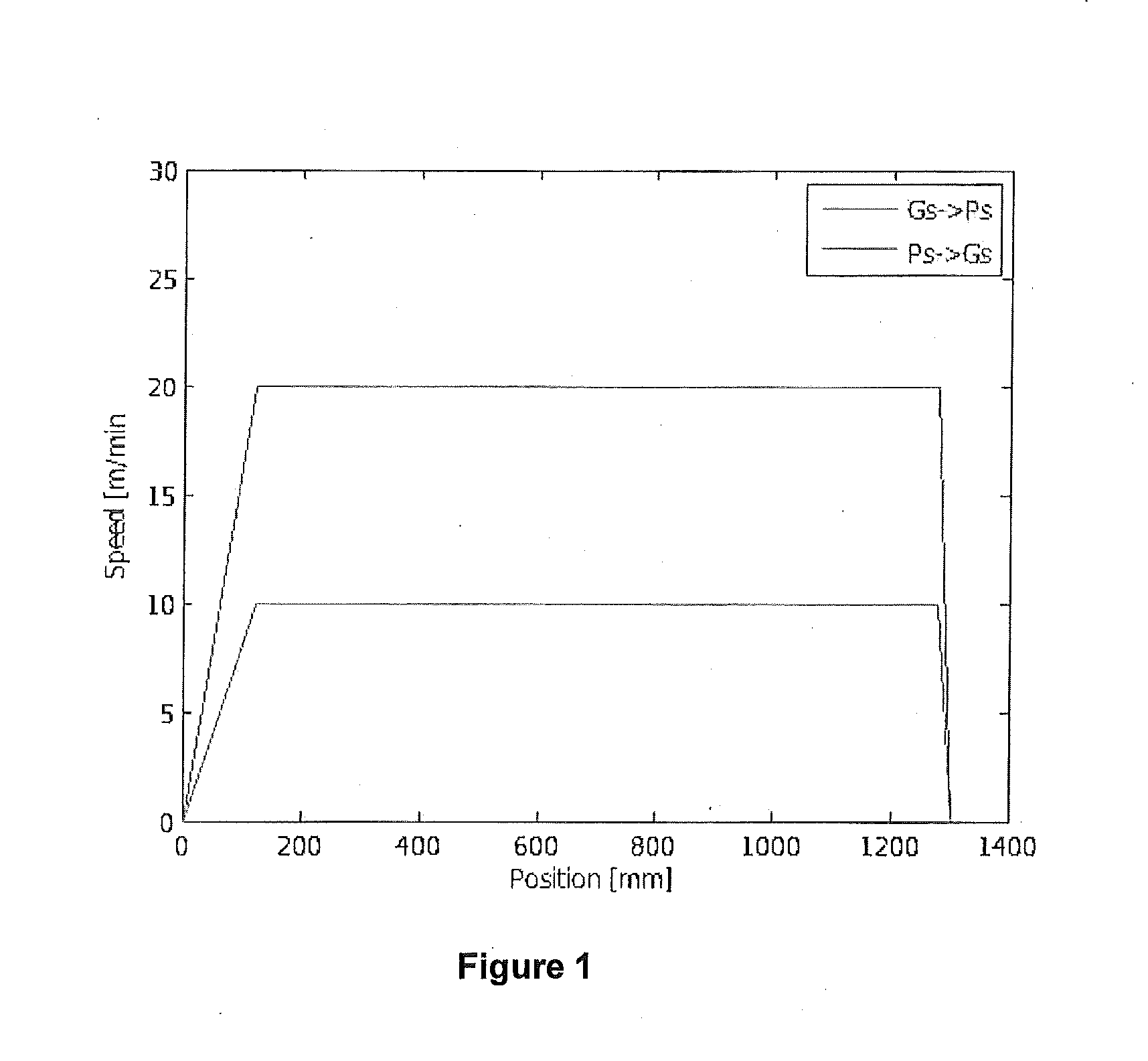
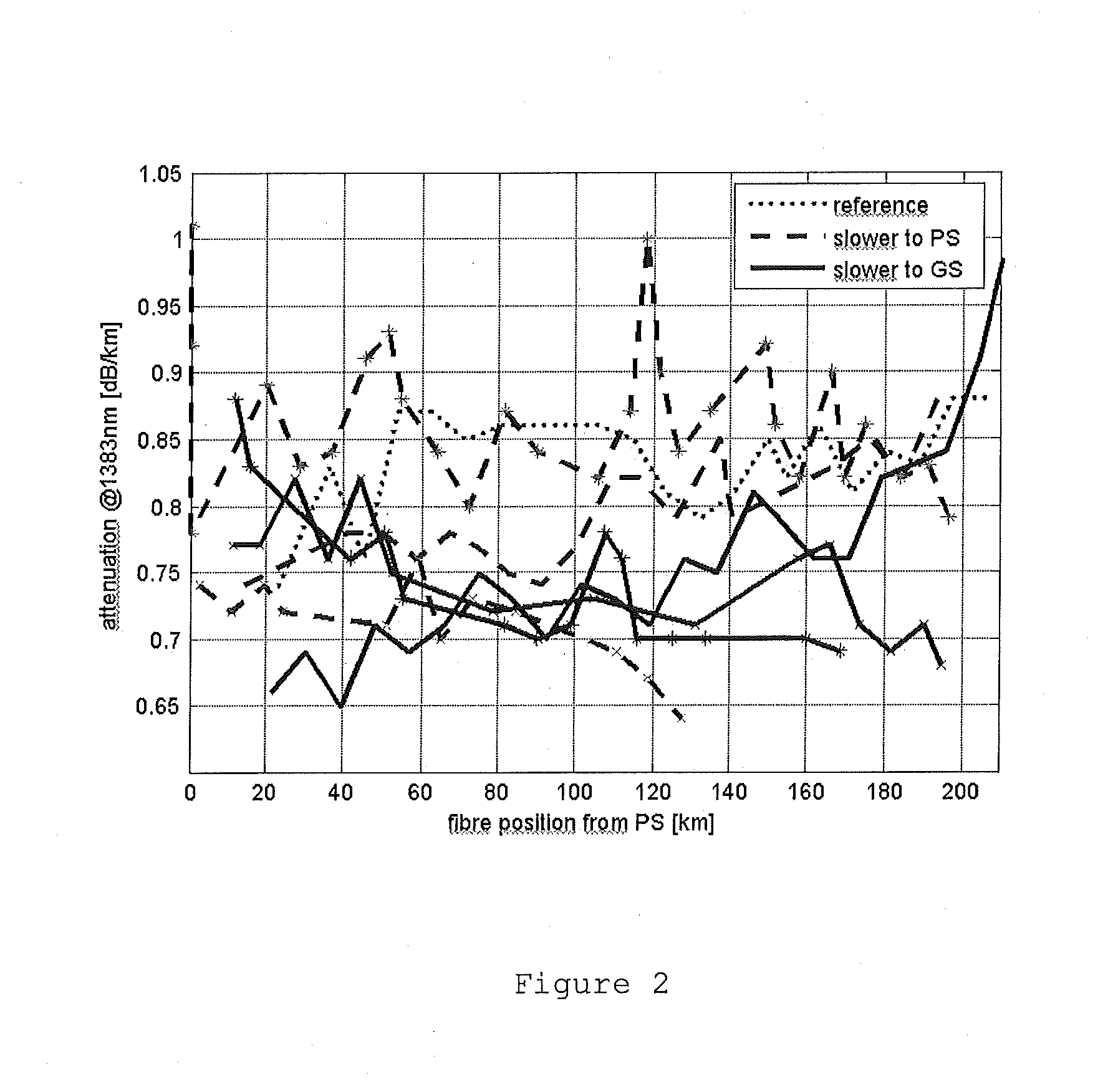
[0049]Using the PCVD technique a preform was produced. As shown in FIG. 1, the velocity profile of the reaction zone over the length of the supply side-to-discharge side is higher than the velocity of the reaction zone over the length of the discharge side-to-supply side. The substrate tube was surrounded by an oven and the reaction zone traveled over the length of substrate tube during the deposition process. The power of the reaction zone, i.e. microwave power, was 7000 Watt. The pressure inside the hollow substrate tube was approximately 14 mbar. The temperature of the oven was set between 1070 and 960 degrees Celsius. The composition of the gaseous components flowing in the hollow substrate tube was about ⅔ parts oxygen, 4 / 6 parts SiCl4 and between 0 and ⅙ parts GeCl4. The deposition process took about 620 minutes. In fact, according to the embodiment disclosed in FIG. 1, the velocity of the reaction zone from gas-side to pump-side was set at a constant value of 20 m / min, wherea...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| velocity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| velocity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| transmission wavelengths | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com