Determining Distances Between Wireless Devices
a wireless device and distance measurement technology, applied in data switching networks, frequency-division multiplexes, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of old problems in determining the location of wireless devices
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
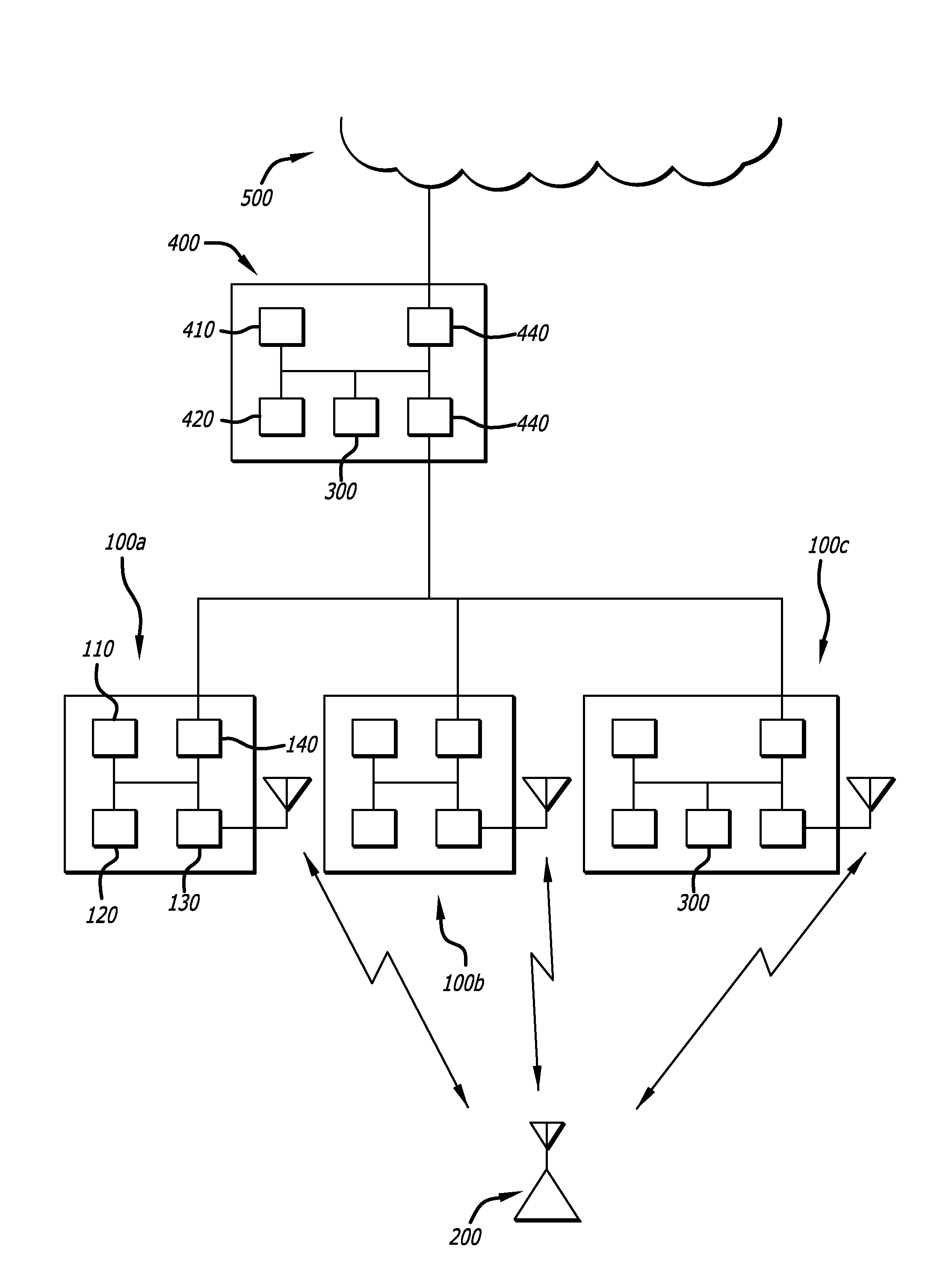
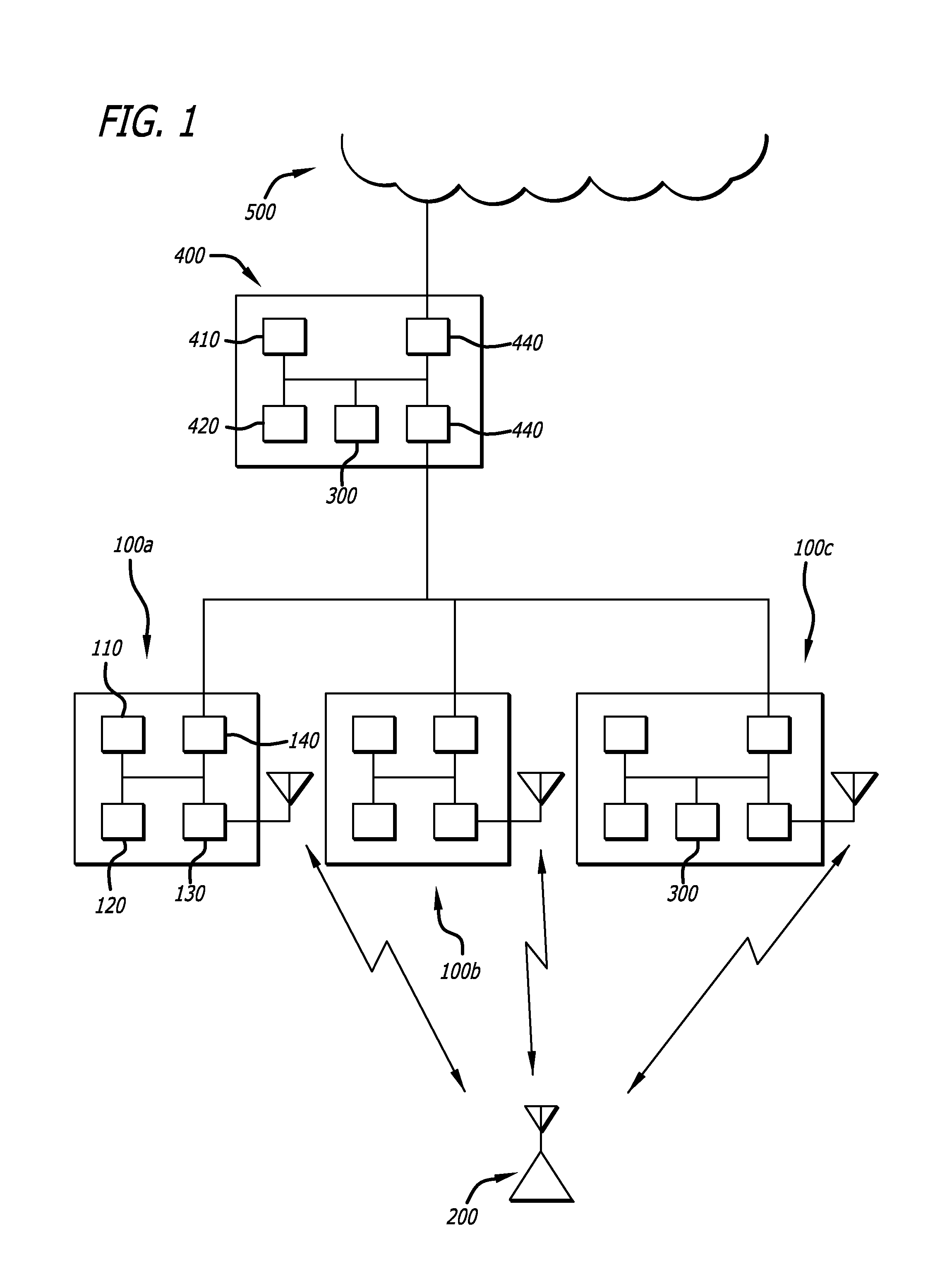
[0010]Embodiments of the invention relate to methods of estimating the location of a wireless device operating in the range of a wireless digital network.
[0011]According to the present invention, a locating device (LD) attached to a network transmits frames to a device to be located (DTL) and receives an Acknowledgement (ACK) response when the frame has been received by the DTL without error. The LD varies transmission parameters of the frames transmitted to the DTL, looking for a change in the failure rate of the ACKs received from the DTL. Transmission parameters varied by the LD include transmit power, attenuation and transmit data rate. The LD searches this transmission parameter space looking for the critical level where the DTL goes from not being able to receive the frame to being able to successfully receive and acknowledge the frame. Since the signal level at the DTL to successfully decode a frame with a given set of parameters is known, and the transmit path and therefore ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com