Dynamic bin allocation for payment card transactions
a technology for payment card transactions and bin allocations, applied in payment protocols, instruments, credit schemes, etc., can solve problems such as uncertainty as to the exact amount of merchants, virtual payments incur interchange fee overhead, and banks do not expect to make a significant amount of money
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
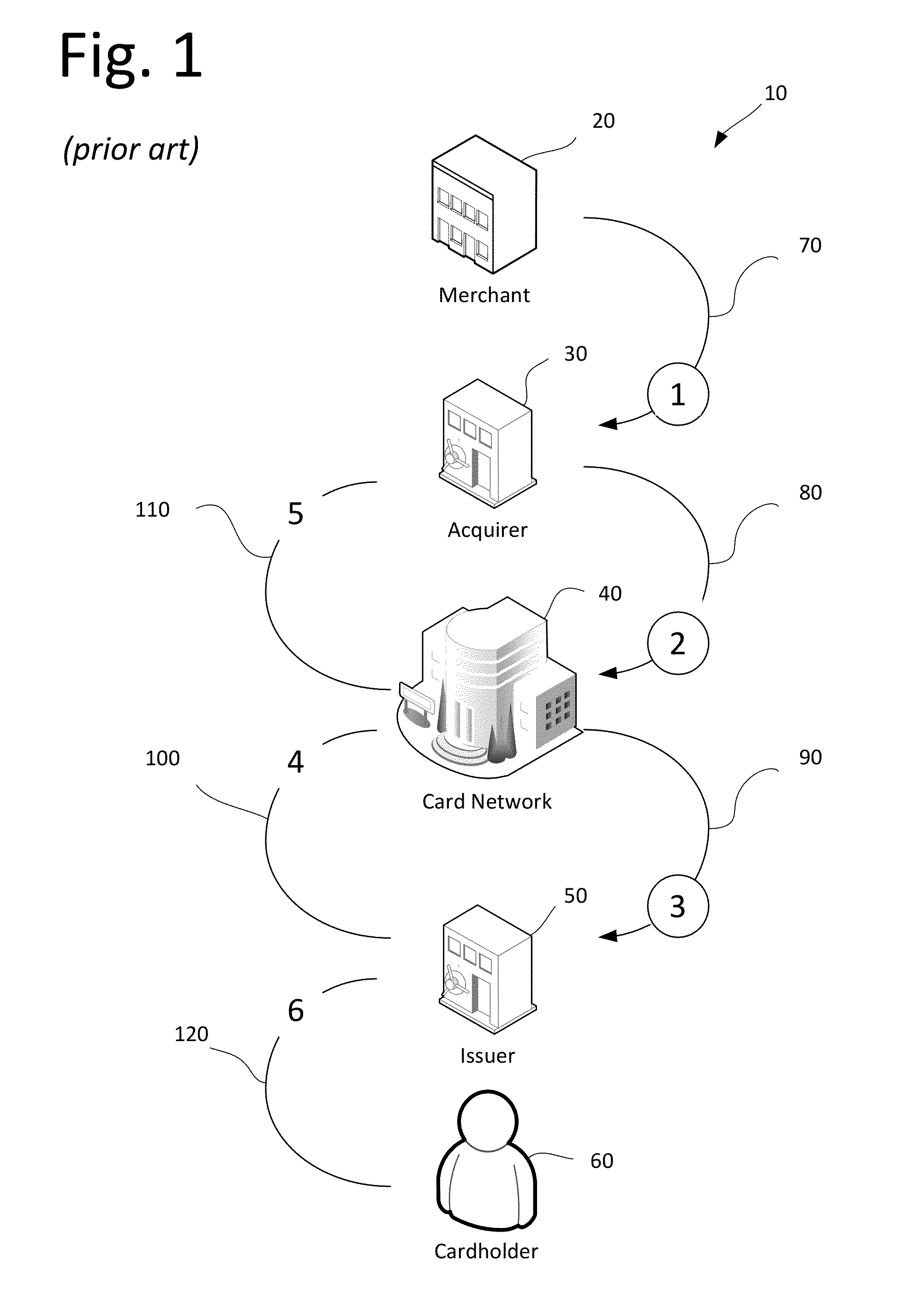
[0045]A typical payment card transaction is denoted as a whole in FIG. 1 by the reference numeral 10. Cardholder 60 purchases goods or services from merchant 20. Merchant 20 effectively “sells” the transaction 70 to an acquirer bank 30 and is reimbursed the amount of the sales ticket less a discount fee. Acquirer 30 then submits 90 the transaction to the issuing bank 50 for payment through an interchange and settlement system 80 provided by card network 40. Issuing bank 50 pays 110 acquirer 30 through the card settlement system 100. Finally, cardholder 60 repays 120 issuing bank 50 for the goods or services originally purchased from merchant 20.
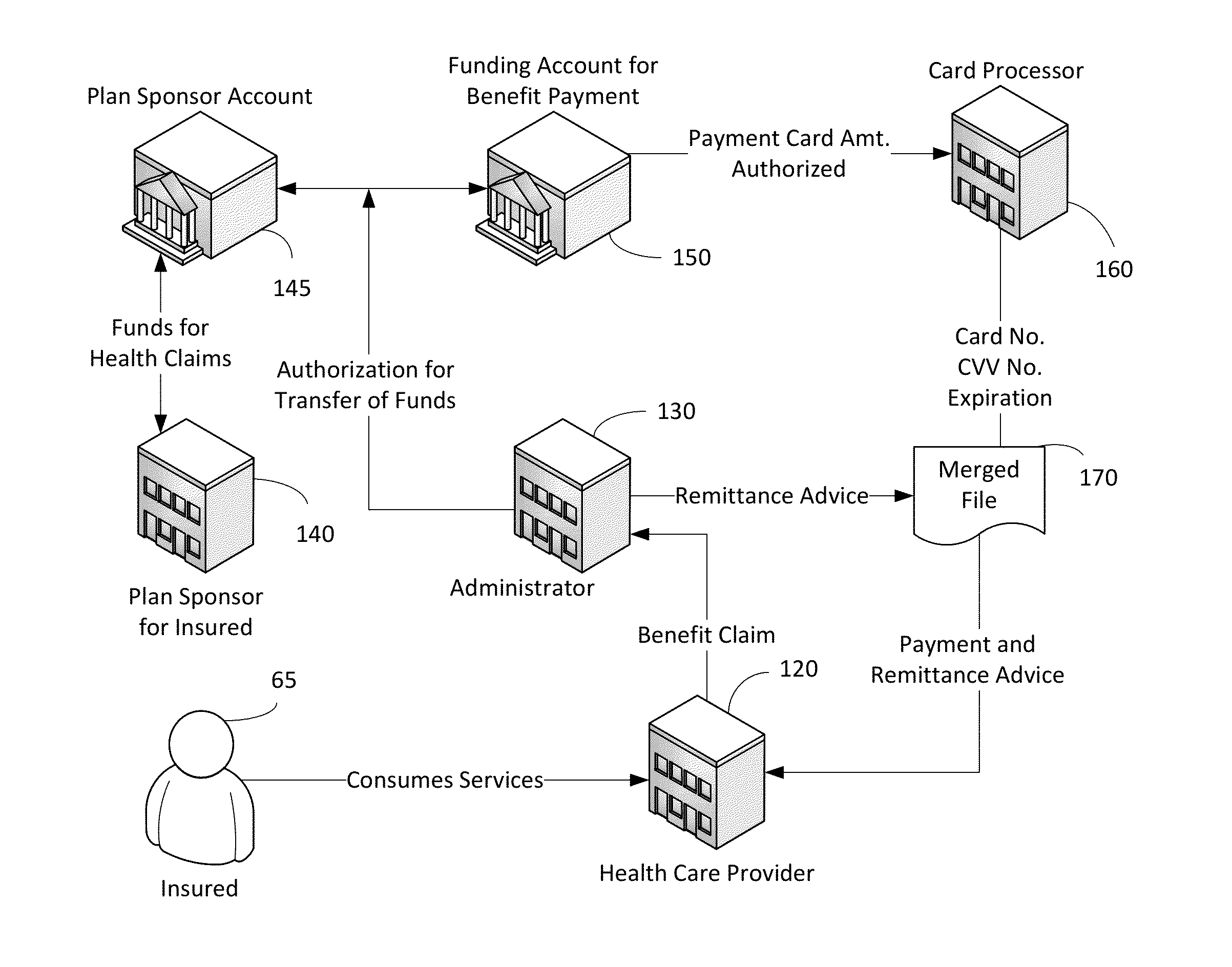
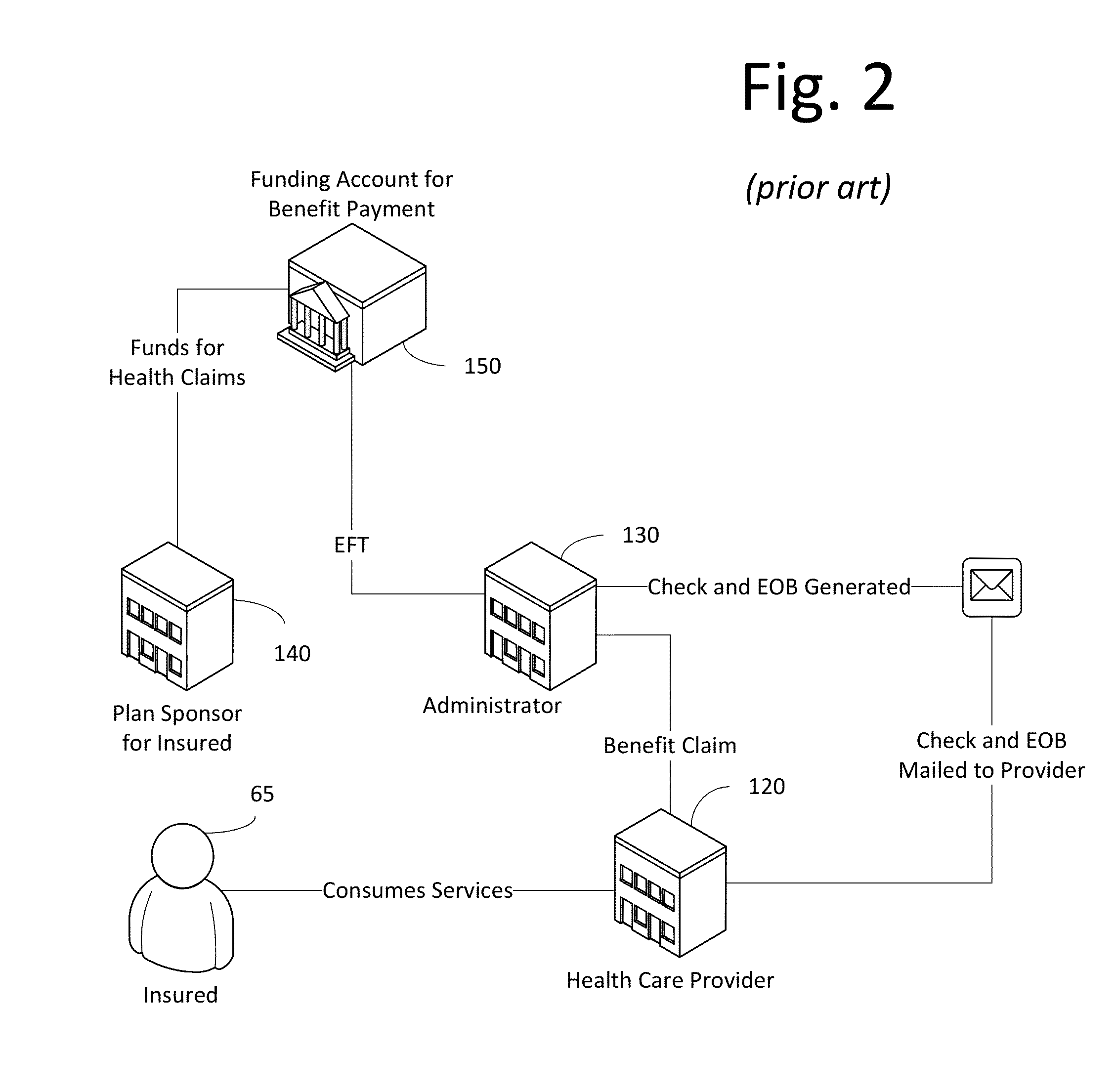
[0046]In FIG. 2, insured 65 consumes services of health care provider 120. Provider 120 submits a benefit claim to a third party administrator 130 against an insurance policy held by insured 65. Plan sponsor of the insured 140 funds account 150 which is used by administrator 130 to generate a check and an explanation of benefits (EOB). The ch...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com