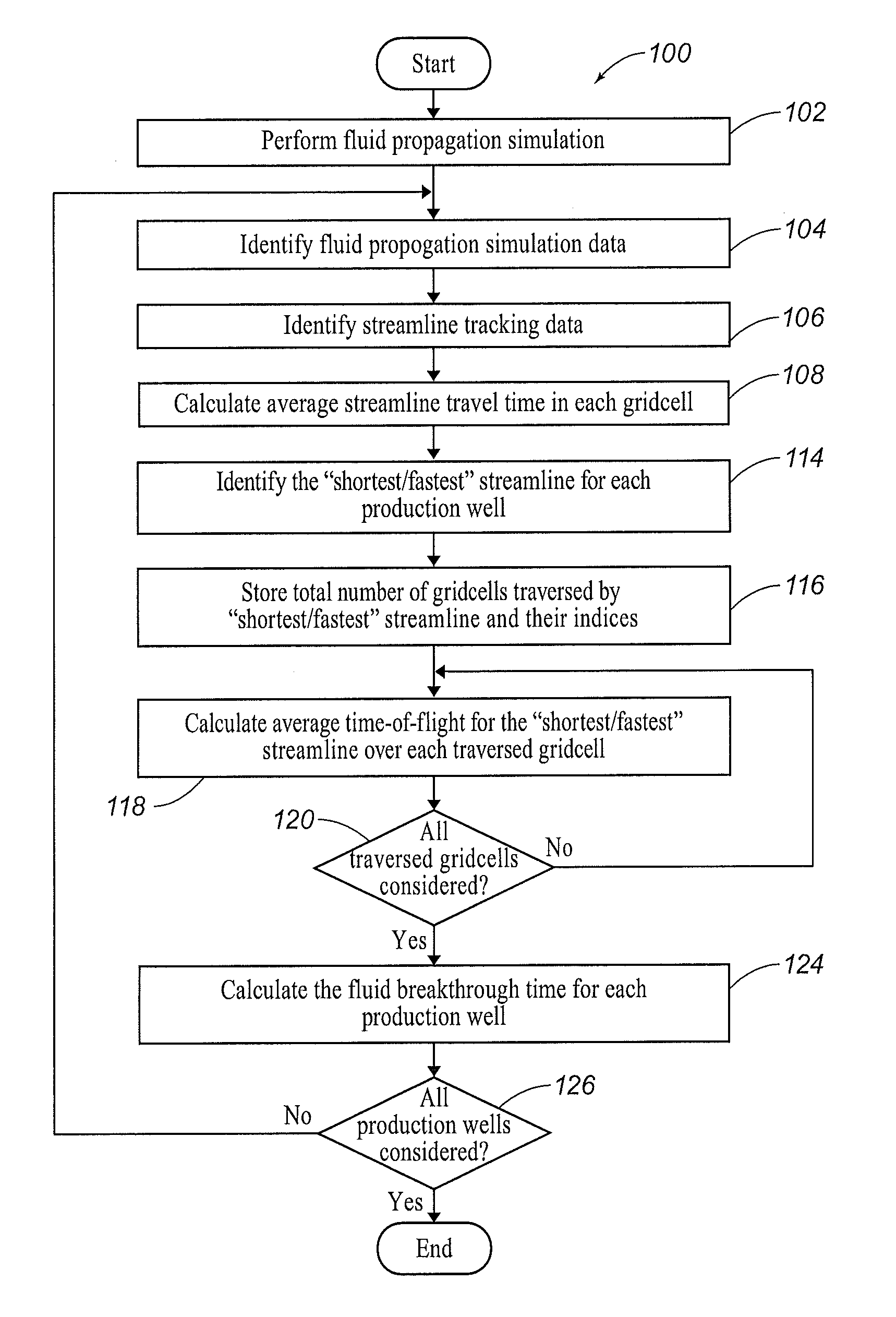
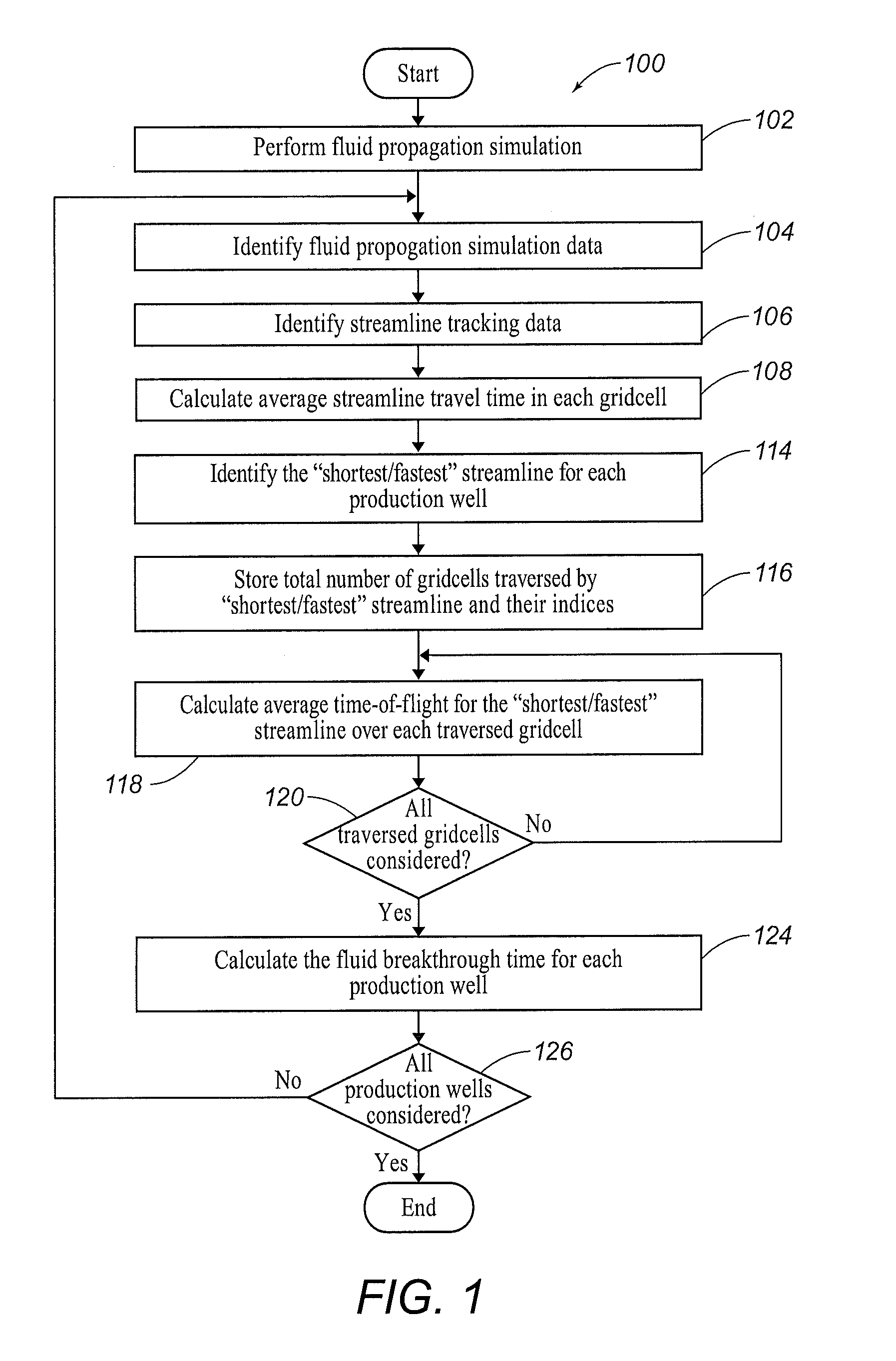
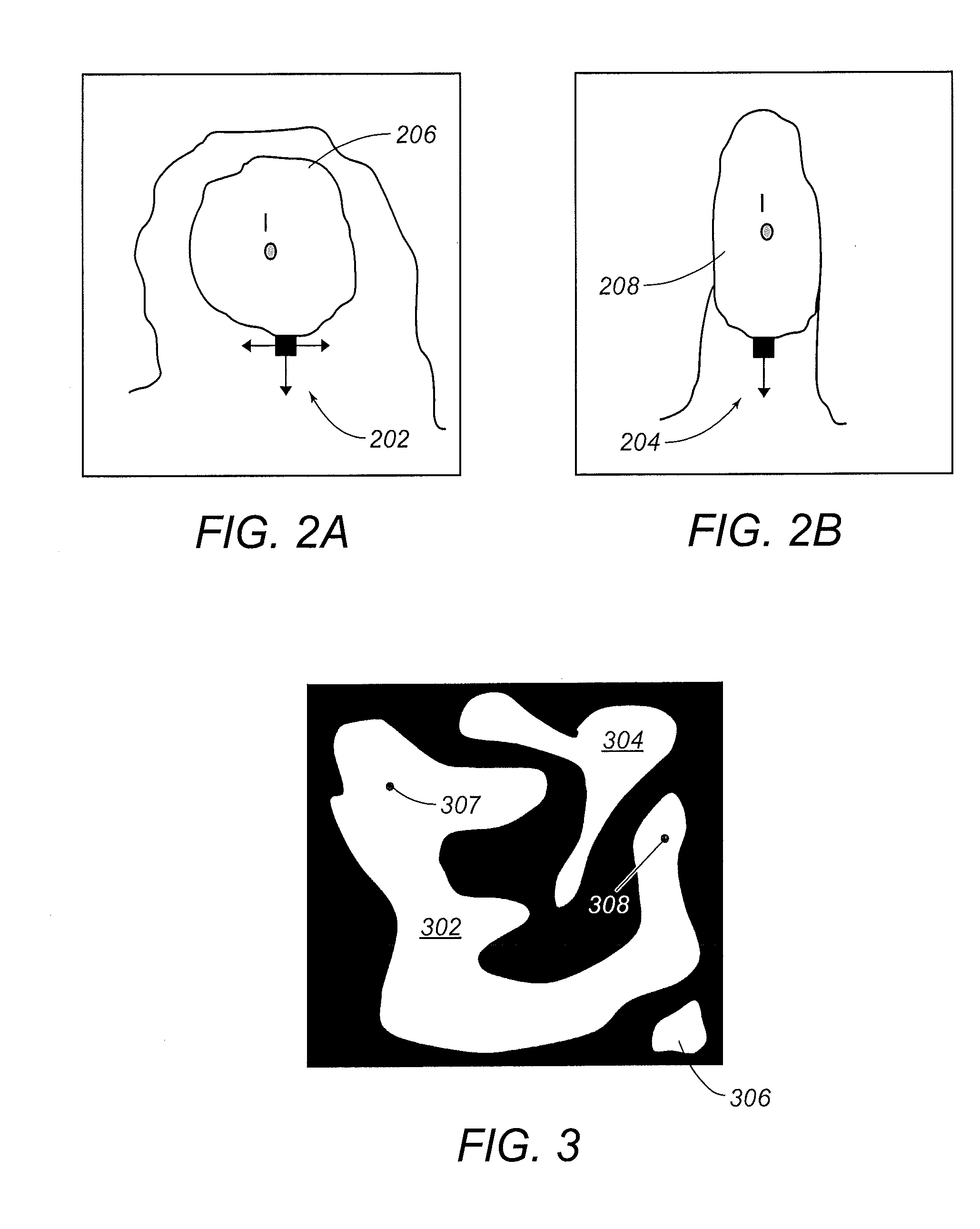
Systems and Methods for Estimating Fluid Breakthrough Times at Producing Well Locations
a technology of fluid breakthrough time and production well, which is applied in the field of estimating fluid breakthrough time at producing well locations, can solve the problems of inherently biased production data and noisy data
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0052]Referring now to the synthetic 2D permeability model in FIG. 4A, the observed (measured) water-cut curves for the configuration model in FIG. 4A are given in FIGS. 7A, 7B, 7C, and 7D for each of the four production wells (P1, P2, P3, and P4).
[0053]The date / time data points on the x-axis in FIGS. 7A-7D correspond with the physical dates associated with the water injection plan (water breakthrough data points) presented in Table 1 below:
TABLE 1Data pointPhysical Date (dd / mm / yyyy)117 / 9 / 200024 / 6 / 2001319 / 2 / 200246 / 10 / 2002524 / 7 / 200369 / 4 / 2004725 / 12 / 2004811 / 9 / 2005
[0054]The observed water breakthrough times deduced from FIG. 4A, are given in Table 2 below. Moreover, Table 2 lists the water invasion times calculated by the FPS algorithm the water breakthrough times (TB7) calculated using the proposed method in FIG. 1 and the uncertainty associated with result obtained by the proposed method in FIG. 1.
TABLE 2Invasion TBT by Observed TBTTimeproposedUncertaintyProducer(days)(iterations)meth...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com