HIERARCHICAL STORAGE FOR LSM-BASED NoSQL STORES
a storage and node technology, applied in the field of data storage management, computers and computer applications, can solve the problems of comparatively slow read access and not necessarily having an optimized technique for point queries, and achieve the effect of increasing access latency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
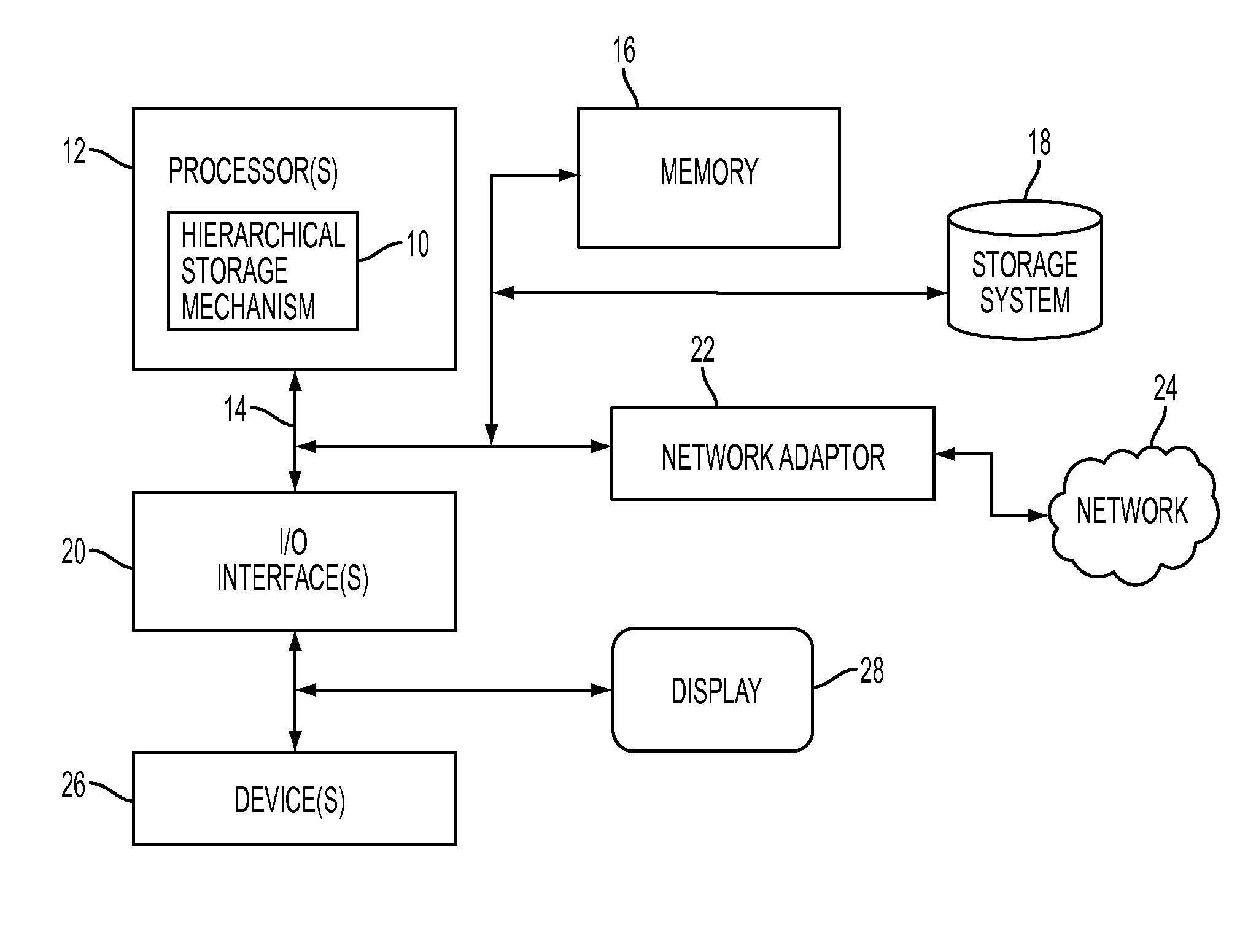
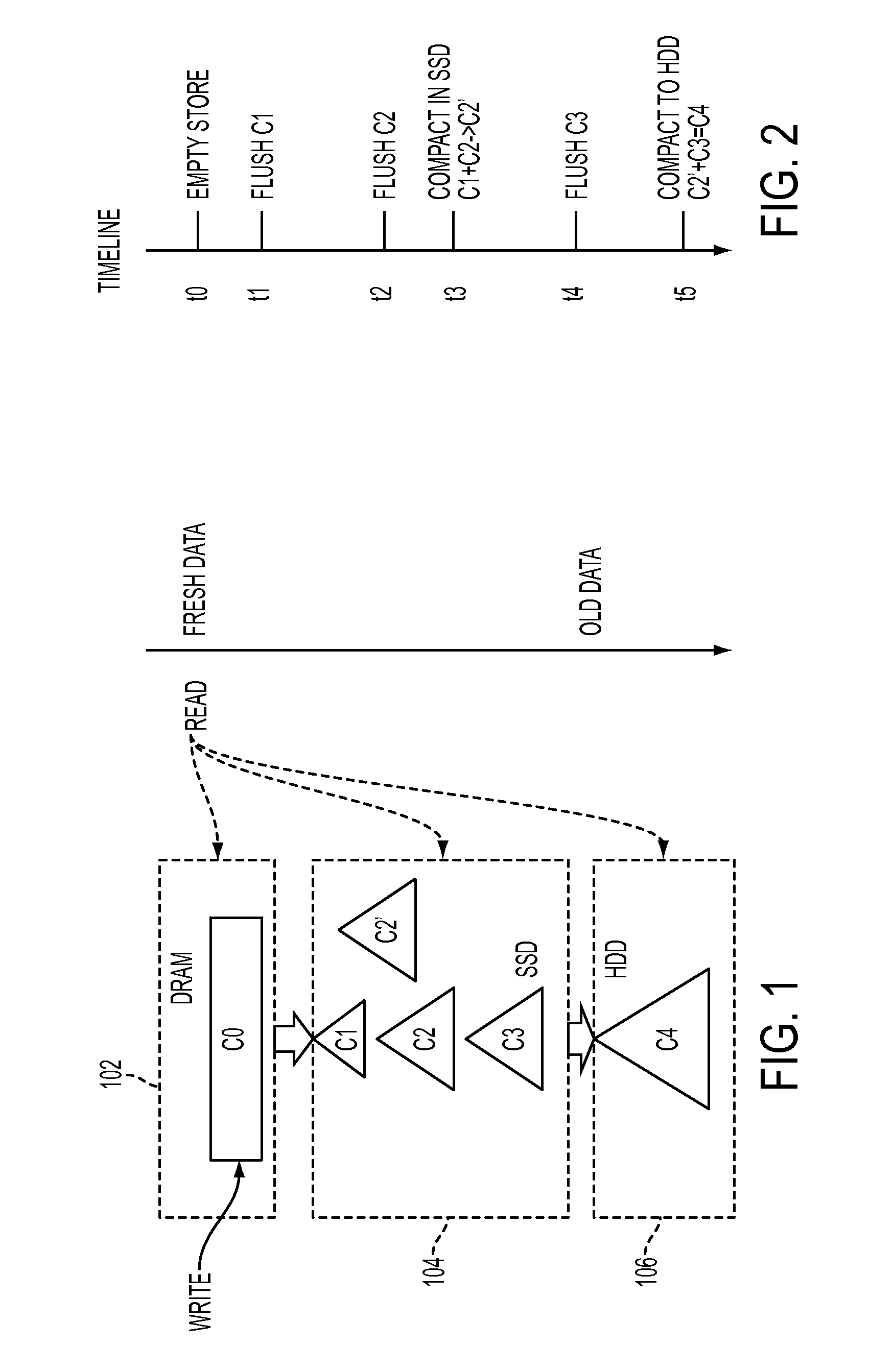
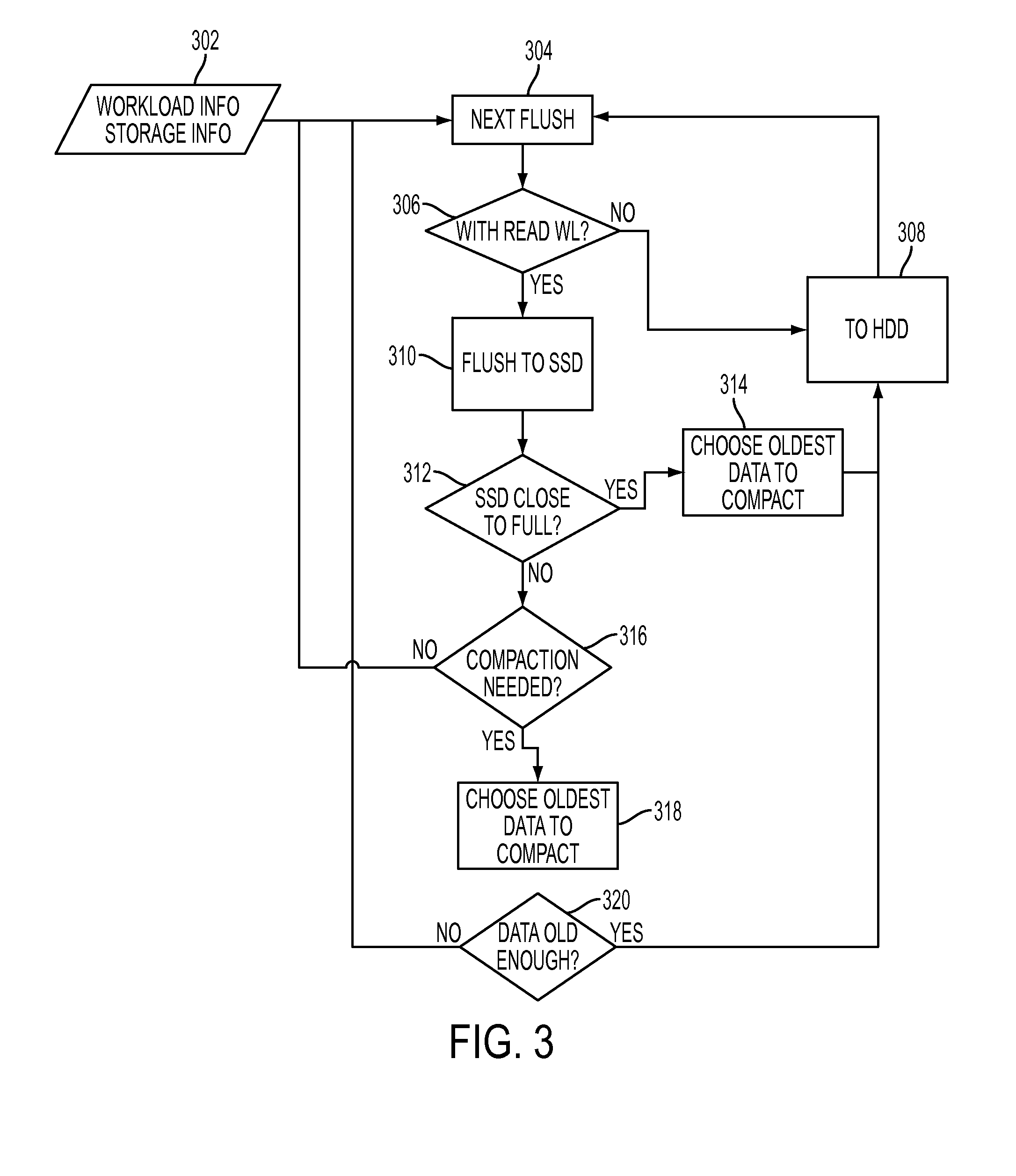
[0012]A multi-tier flush and compaction methodology providing, e.g., a hierarchy of storage devices, for LSM stores are presented. The term “flush” refers to data movement from a higher to lower tier of storage. The term “compaction” refers to sorting and merging data of different versions to fewer or to a single version, in the same layer. The LSM-tree is a data structure composed of multiple data components, e.g., some data component stored in memory and some other data component stored on disk. The component on disk may comprise multiple versions of data that are periodically compacted. Storage devices in the hierarchy may comprise both volatile and non-volatile memory. In one embodiment of the present disclosure, hierarchical or tiered storage comprise a layer of storage with comparatively fast access (e.g. solid state drive (SSD)) and another (e.g., next) layer being a traditional disk (e.g. HDD) of comparatively slower access. In one embodiment, compaction occurs within the hi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com