Multiple coil flux pad
a flux pad and coil technology, applied in the direction of electric vehicle charging technology, inductance, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the magnetic field leakage present in the system, no power transfer possibility, and mismatch between charging and pickup pads
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
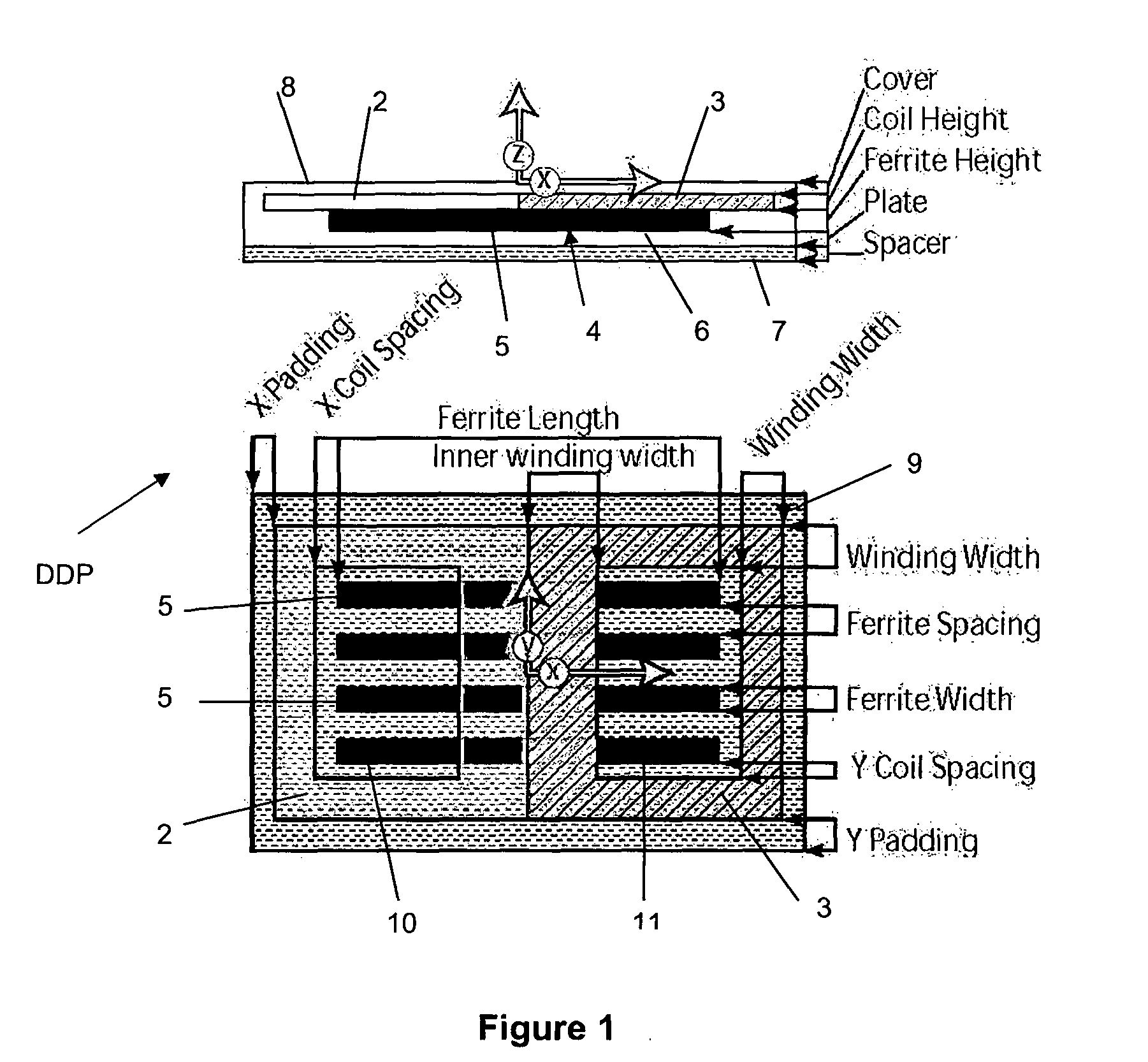
[0116]FIGS. 1 to 3 are prior art arrangements taken from the aforementioned International Patent Publication No. WO 2011 / 16737.
[0117]Referring to FIG. 1, a prior art magnetic flux pad construction is shown. For convenience, this general construction is referred to herein as a DDP pad, and is generally referenced DDP in the relevant drawing figures.
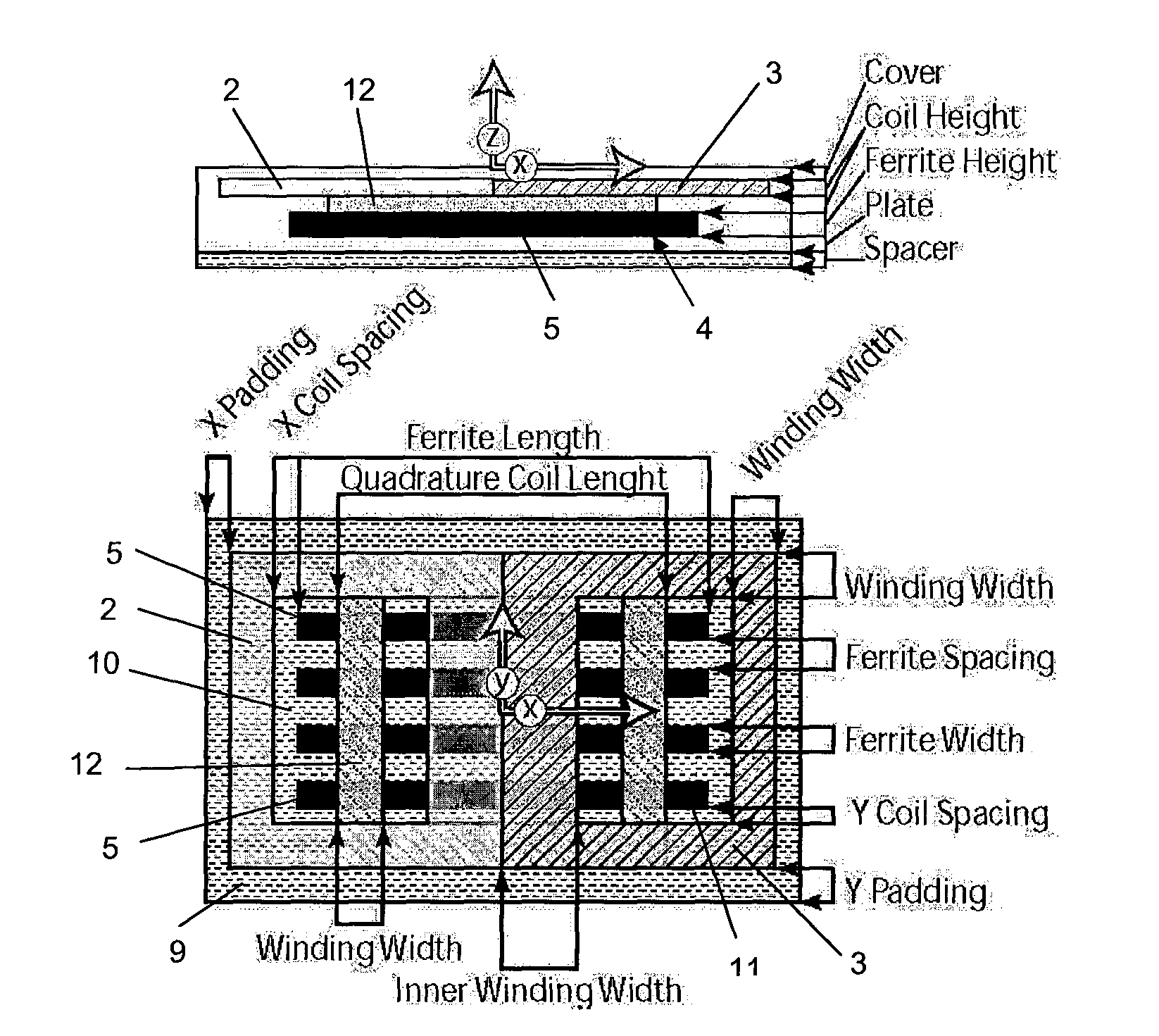
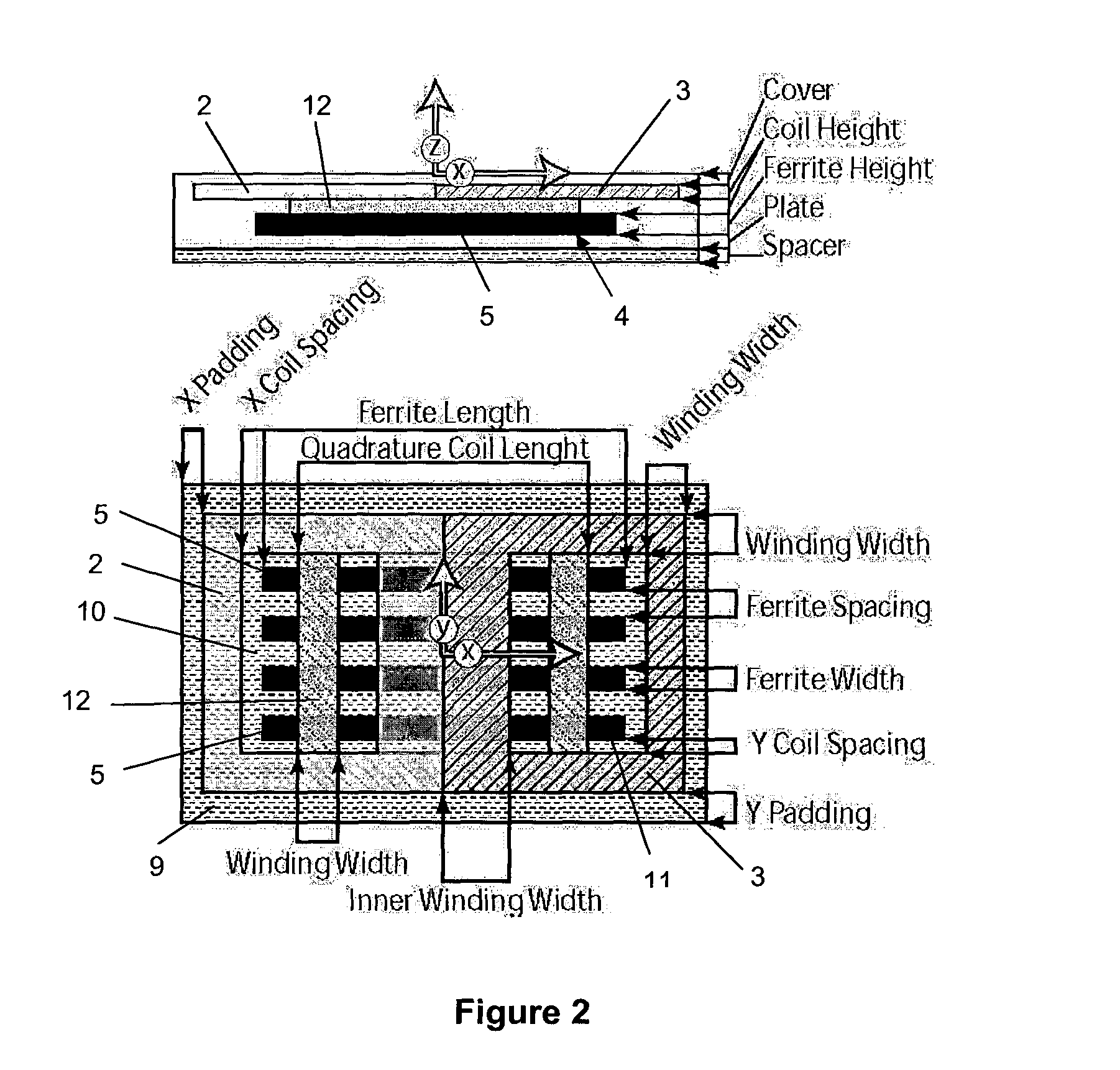
[0118]The DDP pad shown in FIG. 1 generally comprises two substantially coplanar coils referenced 2 and 3 which are magnetically associated with, and sit on top of, a core 4. As can be seen, the core 4 may consist of a plurality of individual lengths of permeable material such as ferrite strips or bars 5 which are arranged parallel to each other but spaced apart. The pad construction may include a spacer 6 on which the core is located, and a plate 7 below the spacer. A cover 8 may be provided on the other surface of the flat coils 2 and 3. Padding 9 may be provided about the periphery of the pad. As can be seen, the coils 2 and 3 each defi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com