Assessing Neural State from Action Potentials
a neural state and action potential technology, applied in the field of neural potential assessment, can solve the problems of difficult diagnosis of neuropathic disease and monitoring progress, difficult treatment of neuropathic pain, and poor response to standard pain treatmen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
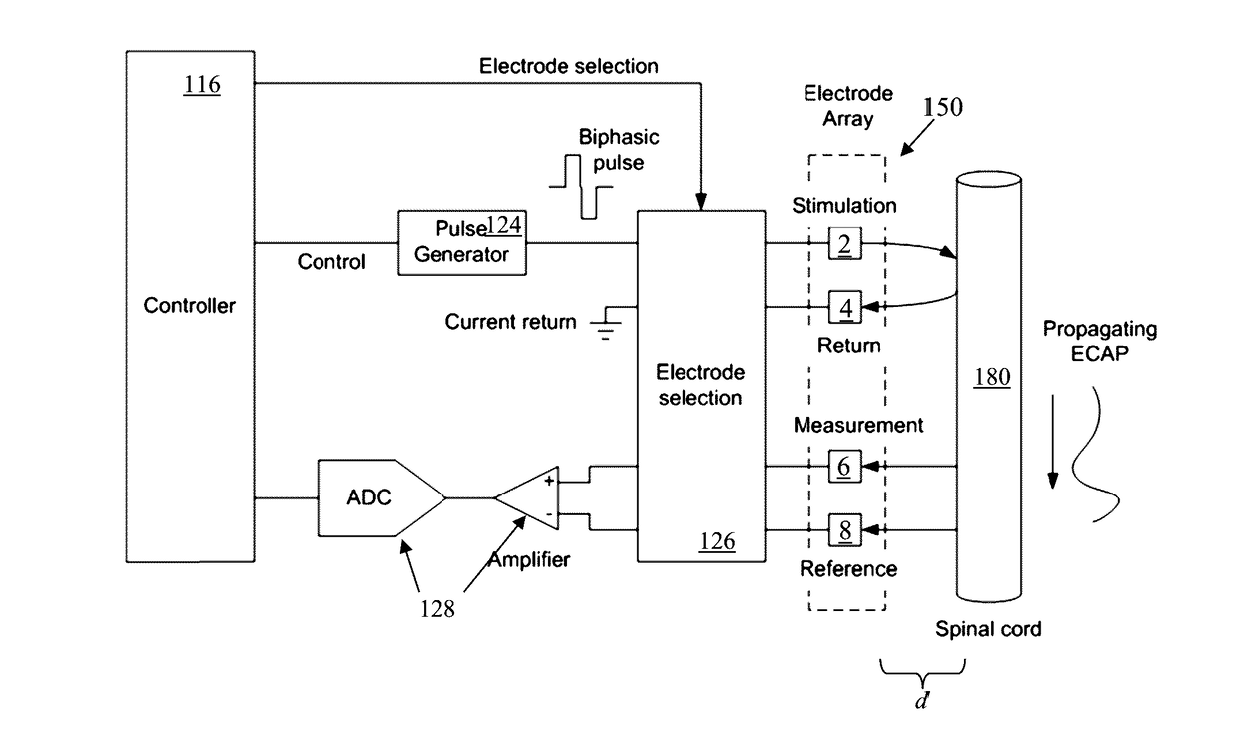
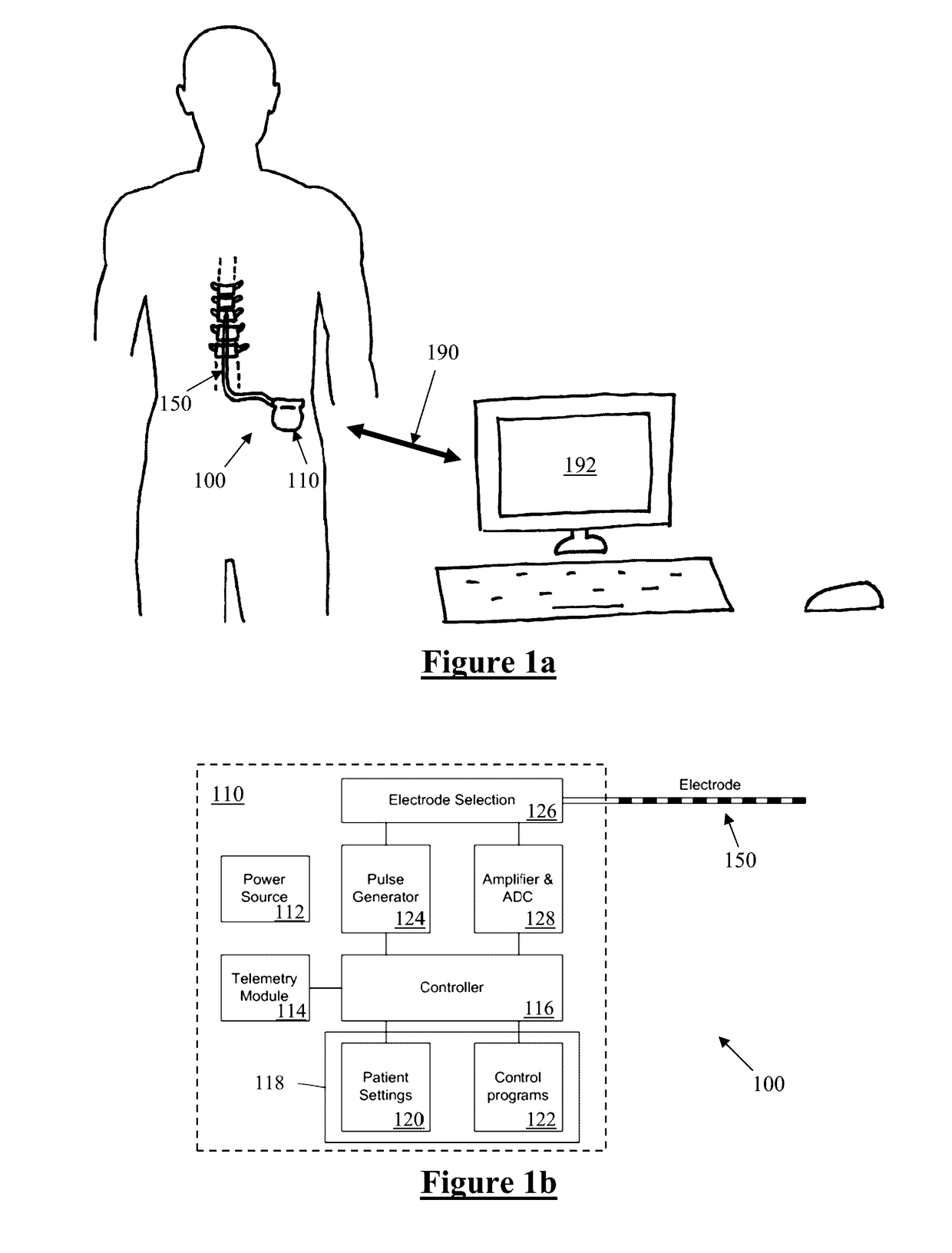
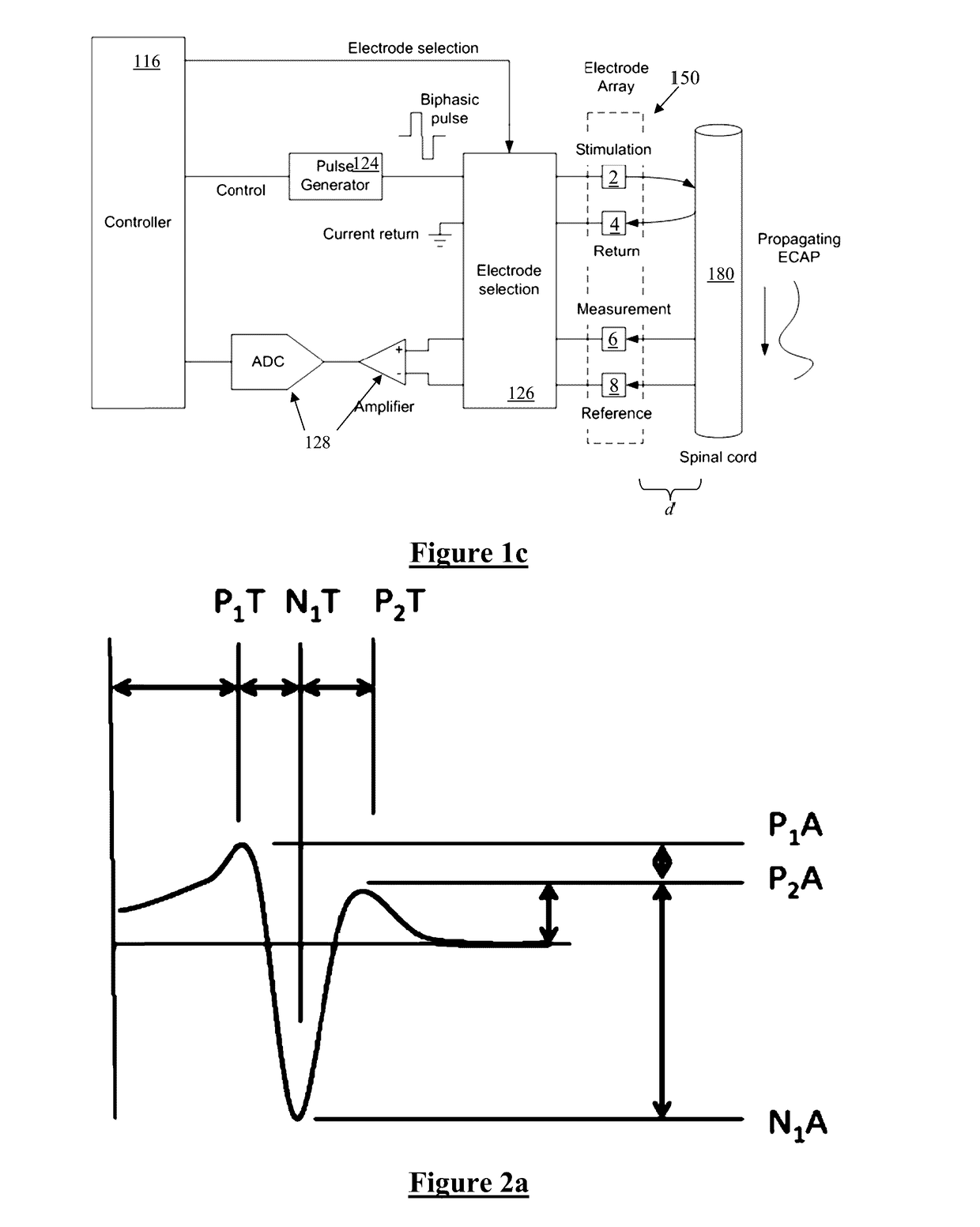
[0060]Comparison of ECAP measurements from the dorsal column of a number of different human subjects was undertaken in order to identify systematic differences which relate to either genetic or pathological differences between subjects. Measurements of dorsal column evoked compound action potentials show distinct differences between the ECAP shapes measured at different electrodes along the array.
[0061]FIG. 3 shows a “normal” ECAP, being a triphasic P1, N1, P2 response, as obtained from “patient 25”. The use of epidural ground inverts the N1 at a time when the response passes the ground electrode. As the recorded response of FIG. 3 exhibits no significant abnormalities as compared to the predicted response of FIG. 2, Patient 25 can be diagnosed as having no measurable neuropathic disease.
[0062]In contrast, FIG. 4 shows data from patient 34, measured in both the orthodromic and antidromic directions at respective electrodes either side of the stimulus electrode, each spaced apart fro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com