Bcma chimeric antigen receptors
a technology of chimeric antigen receptors and bcma, which is applied in the direction of viruses, vectors, fusion polypeptides, etc., can solve the problems of humanized anti-bcma cars unsuitable for t cell therapy, and achieve the effect of treating, preventing, or ameliorating b cell related conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Construction of Anti-BCMA Cars
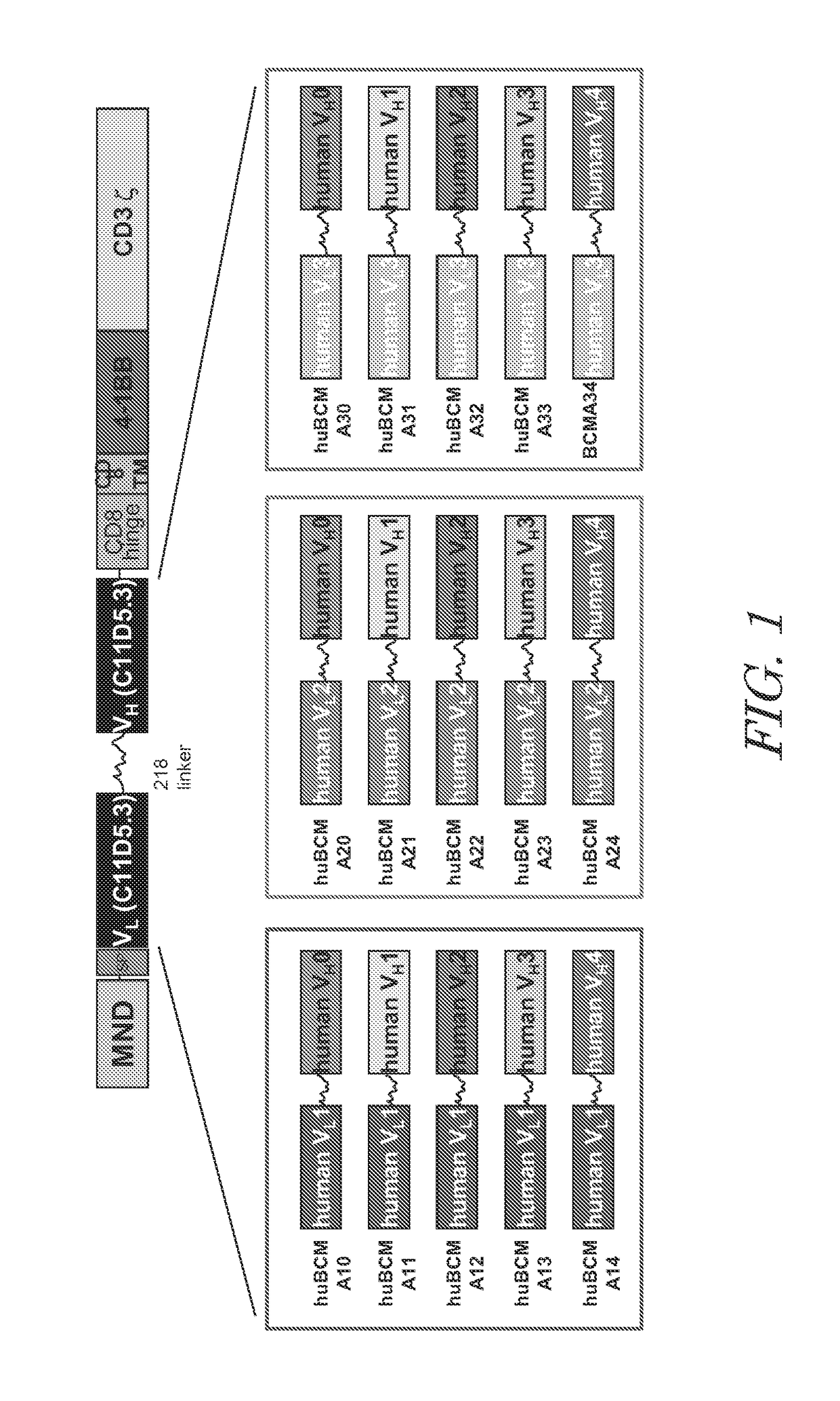
[0401]CARs containing humanized anti-BCMA scFv antibodies were designed to contain an MND promoter operably linked to anti-BCMA scFv, a hinge and transmembrane domain from CD8α and a CD137 co-stimulatory domains followed by the intracellular signaling domain of the CD3ζ chain. FIG. 1. The anti-BCMA CARs comprise a CD8α signal peptide (SP) sequence for the surface expression on immune effector cells. The polynucleotide sequences of the anti-BCMA CARs are set forth in SEQ ID NOs: 30 to 44, 70, and 72; polypeptide sequences of the anti-BCMA CARs are set forth in SEQ ID NOs: 15 to 29, 71, and 73; and the vector maps is shown in FIG. 1. Tables 3 to 5 show the Identity, Genbank Reference, Source Name and Citation for the various nucleotide segments of various exemplary anti-BCMA CAR lentiviral vectors.
TABLE 3NucleotidesIdentityGenBank ReferenceSource NameCitation 1-185pUC19 plasmidAccession #L09137.2pUC19New Englandbackbonent 1-185Biolabs 185-222LinkerNot ap...
example 2
High Throughput Screen of Humanized Anti-BCMA Car
[0402]A microculture assay was developed to rapidly screen anti-BCMA CARs. The microculture assay can compare 15-20 CAR modified T cells (CART cells). Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were cultured in 24-well plates in media containing IL-2 (CellGenix) and antibodies specific for CD3 and CD28 (Miltenyi Biotec) to initiate outgrowth of T cells. The expanded T cells were >99% CD3 positive T cells after 7 days of culture.
[0403]T cells expanded from PBMC were modified by lentiviruses to express the anti-BCMA CARs. Transient lentiviral supernatants were added to the PBMC culture at 1:1 ratio (volume:volume) one day after culture initiation. Cultures were split as needed with fresh media containing IL-2 after becoming optically confluent using an inverted light microscope. After twelve days of culture, CAR T cells were harvested and evaluated for CAR expression and function.
[0404]Expression of CARs on the T cell surface was assayed...
example 3
Antigen Specific Reactivity of Car T Cells
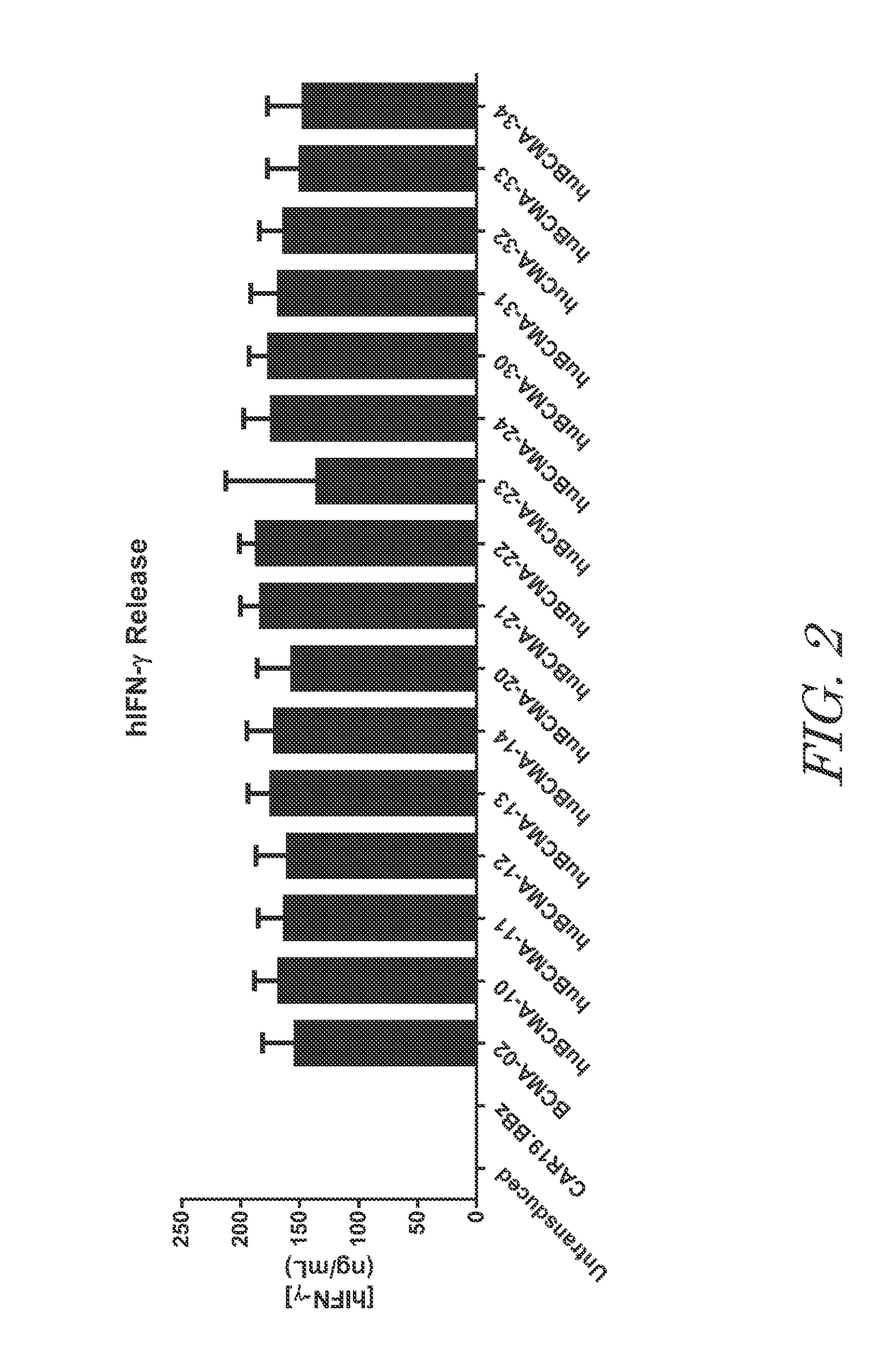
[0405]Antigen-specific reactivity was examined after co-culture with BCMA-positive cell lines. Anti-BCMA CAR T cells were co-cultured with BCMA-engineered K562 (K562-BCMA) cells for 24 hours. Reactivity of the anti-BCMA CAR T cells to K562-BCMA was assayed by IFN-gamma (IFNγ) release into the supernatant by ELISA. All humanized anti-BCMA CART cells tested released similar amounts of IFNγ and the amounts were comparable the parental mouse anti-BCMA CAR. FIG. 2. In contrast, IFNγ was not detected in cultures containing either untransduced or CD19-specific CAR T cells confirming that BCMA-specificity of the CAR T cells was required for reactivity to K562-BCMA cells.
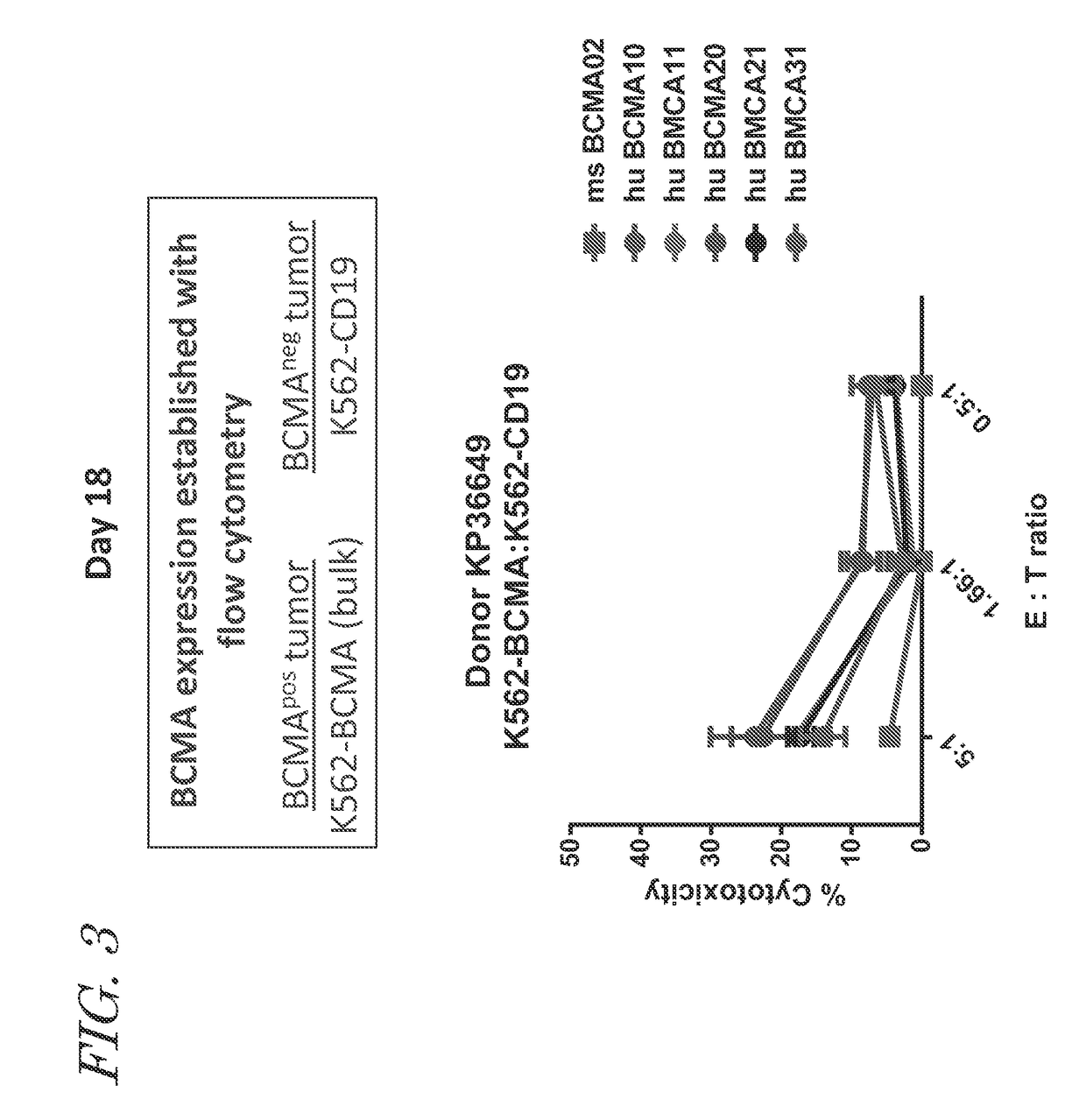
[0406]In another set of experiments, tumor cytolytic activity of T cells expressing one of five humanized anti-BCMA CARs was examined. anti-BCMA CAR T cells were co-cultured with K562-BCMA cells for four hours. The five humanized anti-BCMA CAR T cells exhibited similar cytolytic acti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com