Sock
a technology of socks and sock pads, applied in the field of socks, can solve the problems of not allowing the inside and outside of the foot to substantially simultaneously land on the ground, the load on the foot cannot be reduced sufficiently, and the socks cannot be sufficiently twisted in the everting direction, etc., to achieve the effect of sock splint, easy widening, and stable sock splin
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
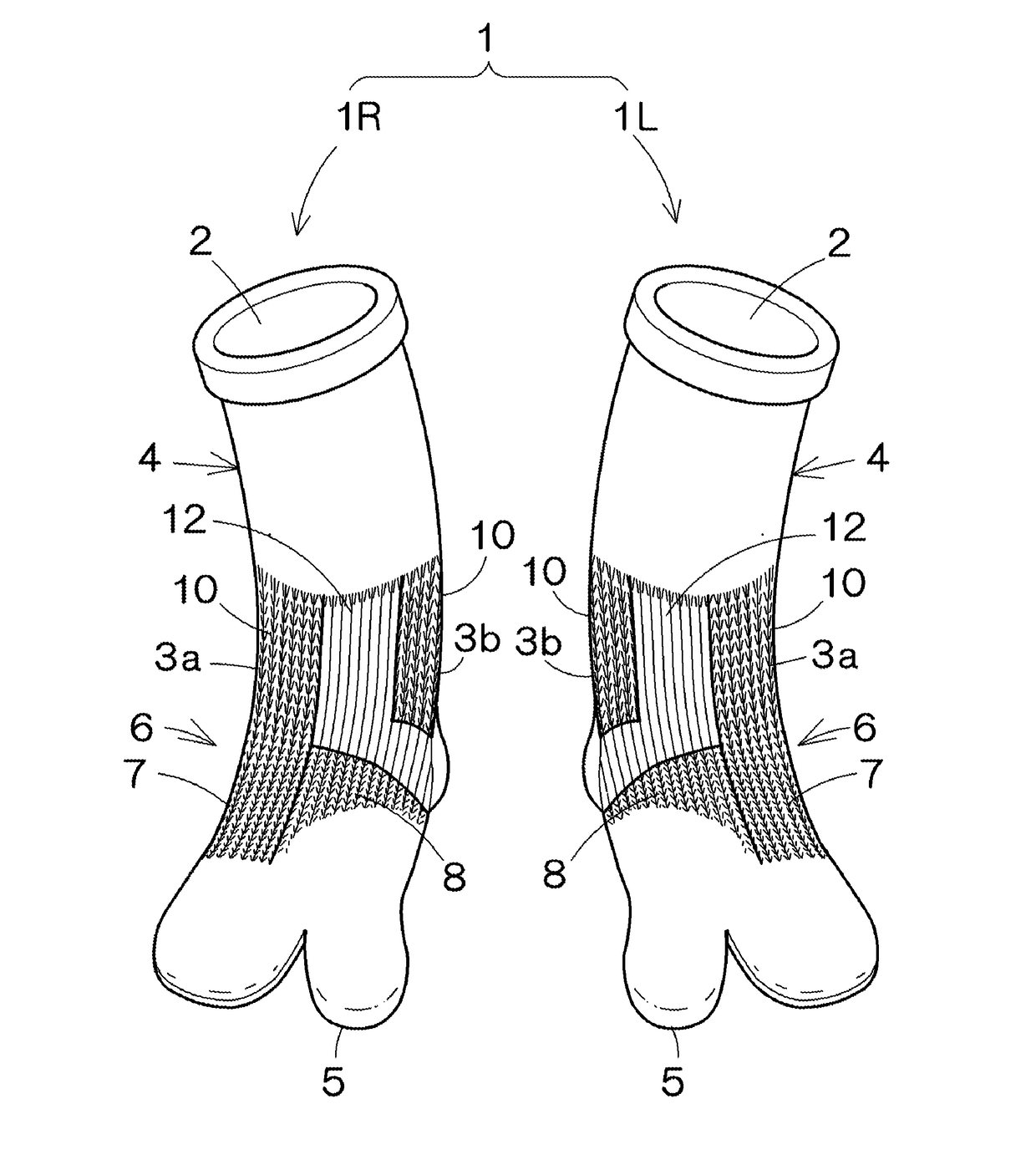
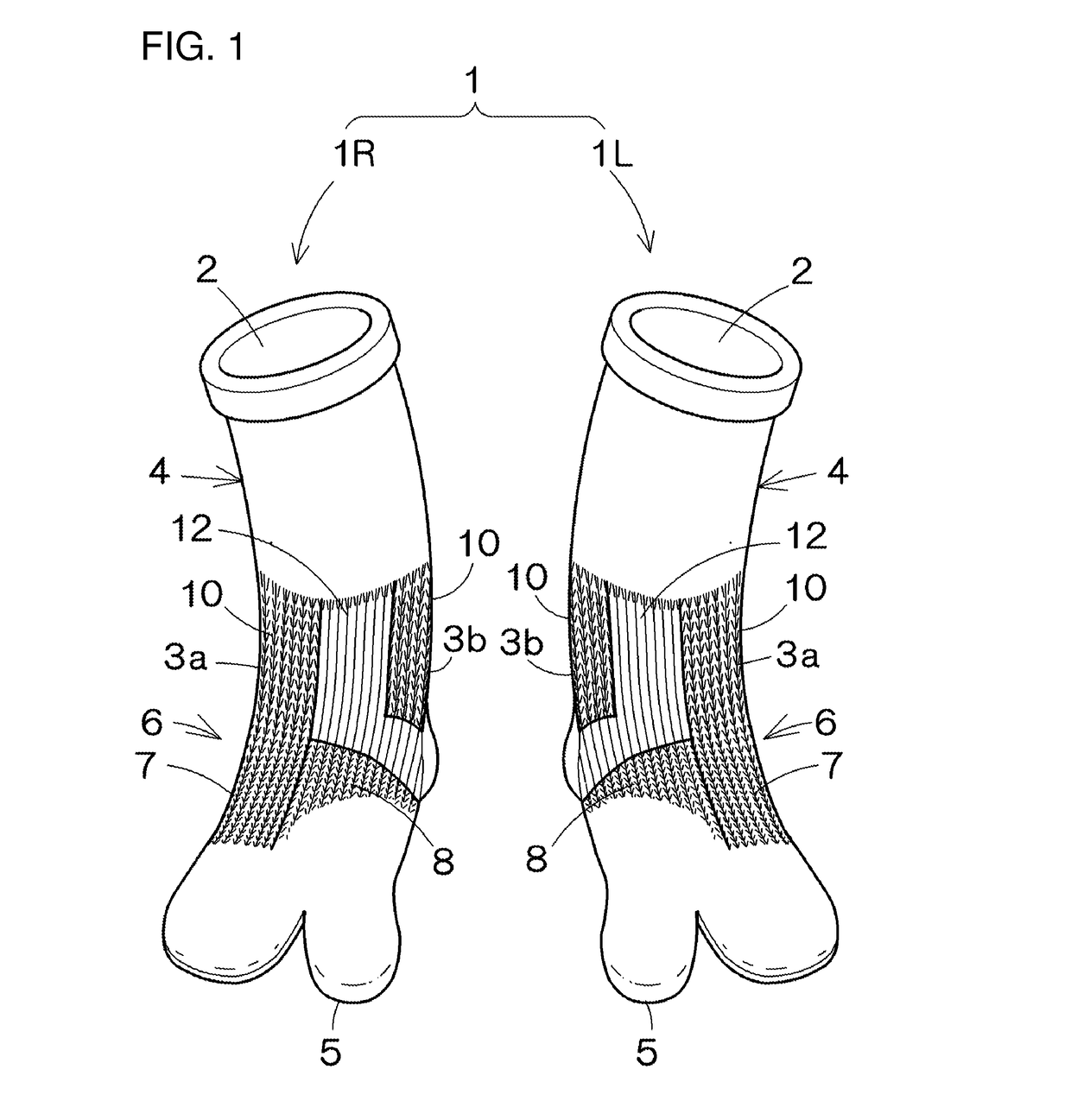
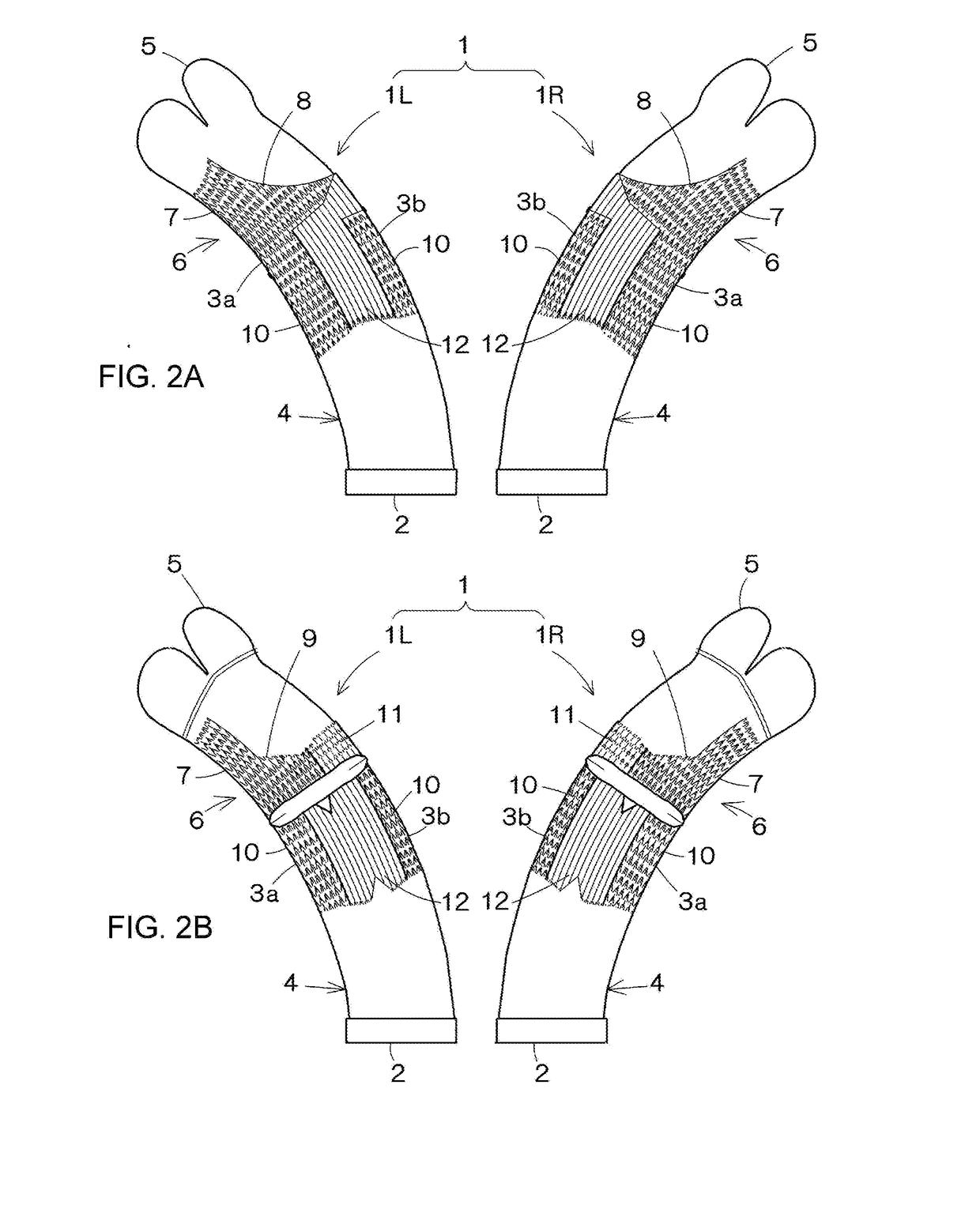
[0019]A first embodiment of a sock according to the present invention will be hereinafter described with reference to the drawings. Here, FIG. 1 is a front perspective view of socks according to an embodiment of the present invention, FIG. 2A is a front view of the socks, and FIG. 2B is a back view of the socks.
[0020]As shown in FIG. 1, socks 1, namely a right sock 1R and a left sock 1L have a left-right symmetrical shape. Each sock 1 is formed with an annular body portion 4 that constitutes an area from an opening 2 into which the foot is inserted to substantially a malleolus part 3, and the foot portion 6 that is formed integrally with the body portion 4 and constitutes an area from an end of the malleolus part 3 to a toe tip part 5. The sock 1 is provided with low-elasticity portions that are less elastic than the other parts. Here, the malleolus part 3 refers to a portion around the malleolus, and is a concept that also includes a part slightly above the malleolus and a part sli...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com