Low-Torque Valve and Assemblies Including Said Valve
a low-torque, valve technology, applied in the direction of diaphragm valves, engine diaphragms, operating means/releasing devices of valves, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, limited battery life, and high cost of mains electricity installation of motor-driven valves, so as to prolong the operation life of devices and reduce power and torque.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0050]Embodiments of the disclosure may be further understood with reference to the figures.
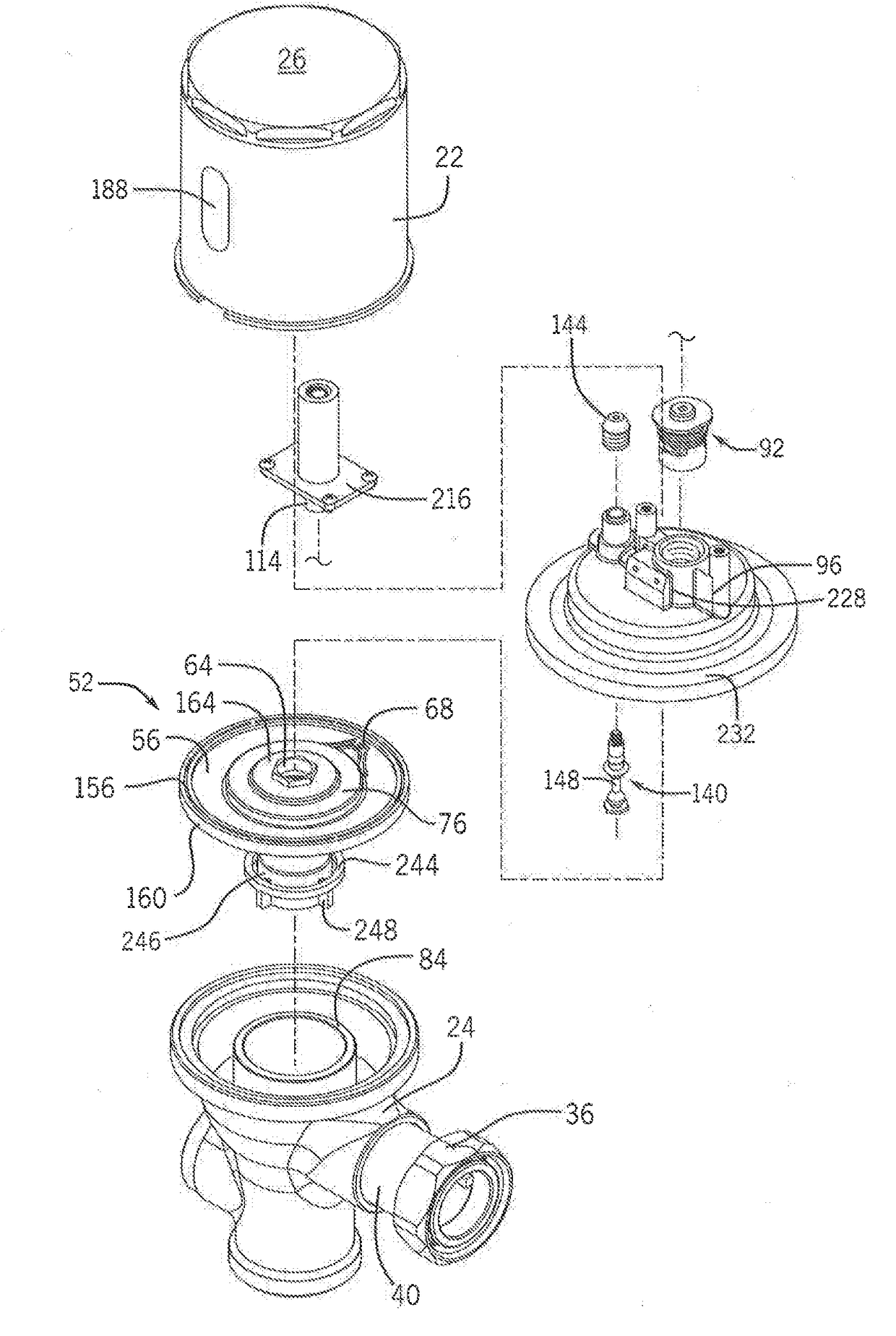
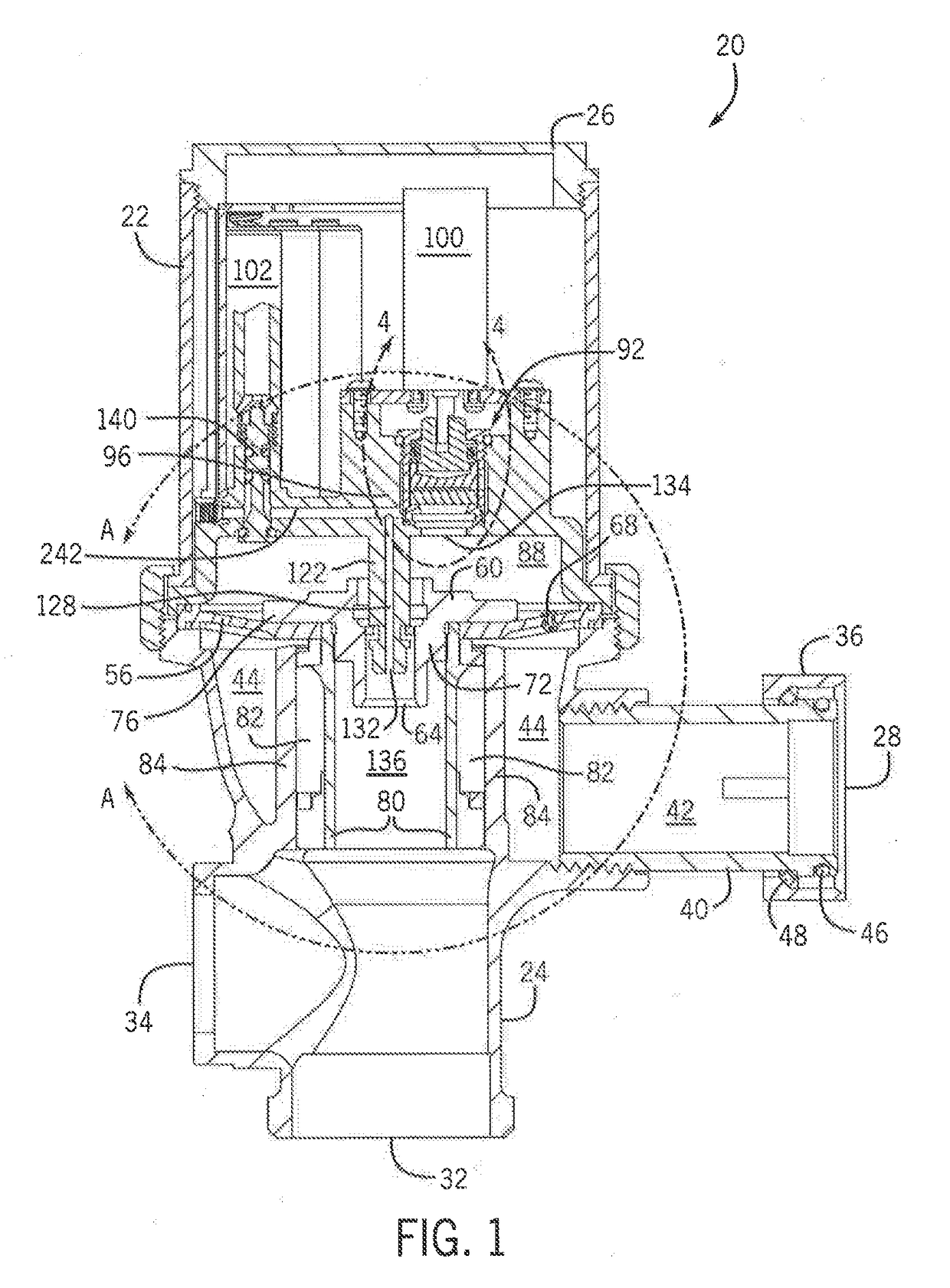
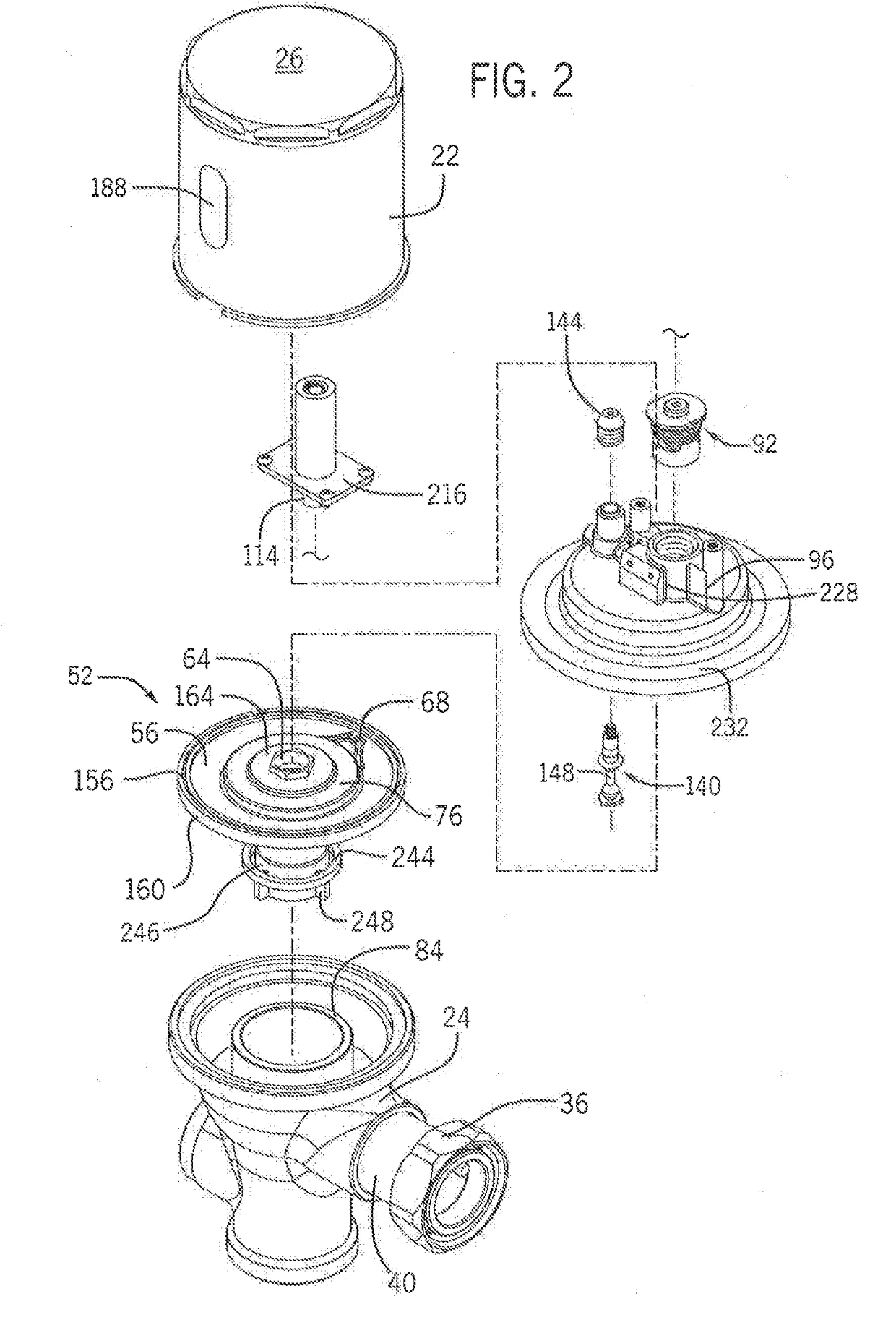
[0051]FIGS. 1 and 2 illustrate one exemplary embodiment of a flush valve assembly 20. Although a flush valve assembly is shown, it is to be appreciated that the disclosure is not limited to flush valves, flushing mechanisms, or the like.
[0052]The flush valve assembly 20 has a housing that includes an upper housing body 22 and a lower housing body 24 that may be connected such that the upper housing body 22 and lower housing body 24 enclose the flush valve assembly 20. In a non-limiting example, the upper housing body 22 may be threaded into connection with the lower housing body 24. The lower housing body 24 may have an inlet 28, an outlet 32, and a cap over an opening 34 that would traditionally accommodate a mechanical flush lever. The inlet 28 to the lower housing body 24 may connect the lower housing body 24 to a fluid source and provide fluid communication therebetween. The inlet 28 may ...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap