Method of measuring efficacy of treatment for multiple sclerosis
a multiple sclerosis and efficacy technology, applied in the field of animal studies involving diagnosis and treatment of multiple sclerosis, can solve the problems of poor animal activity measurement, limited study size, and high cost due to human labor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
.
[0021]From the above term definitions, we may now provide a summary of embodiments.
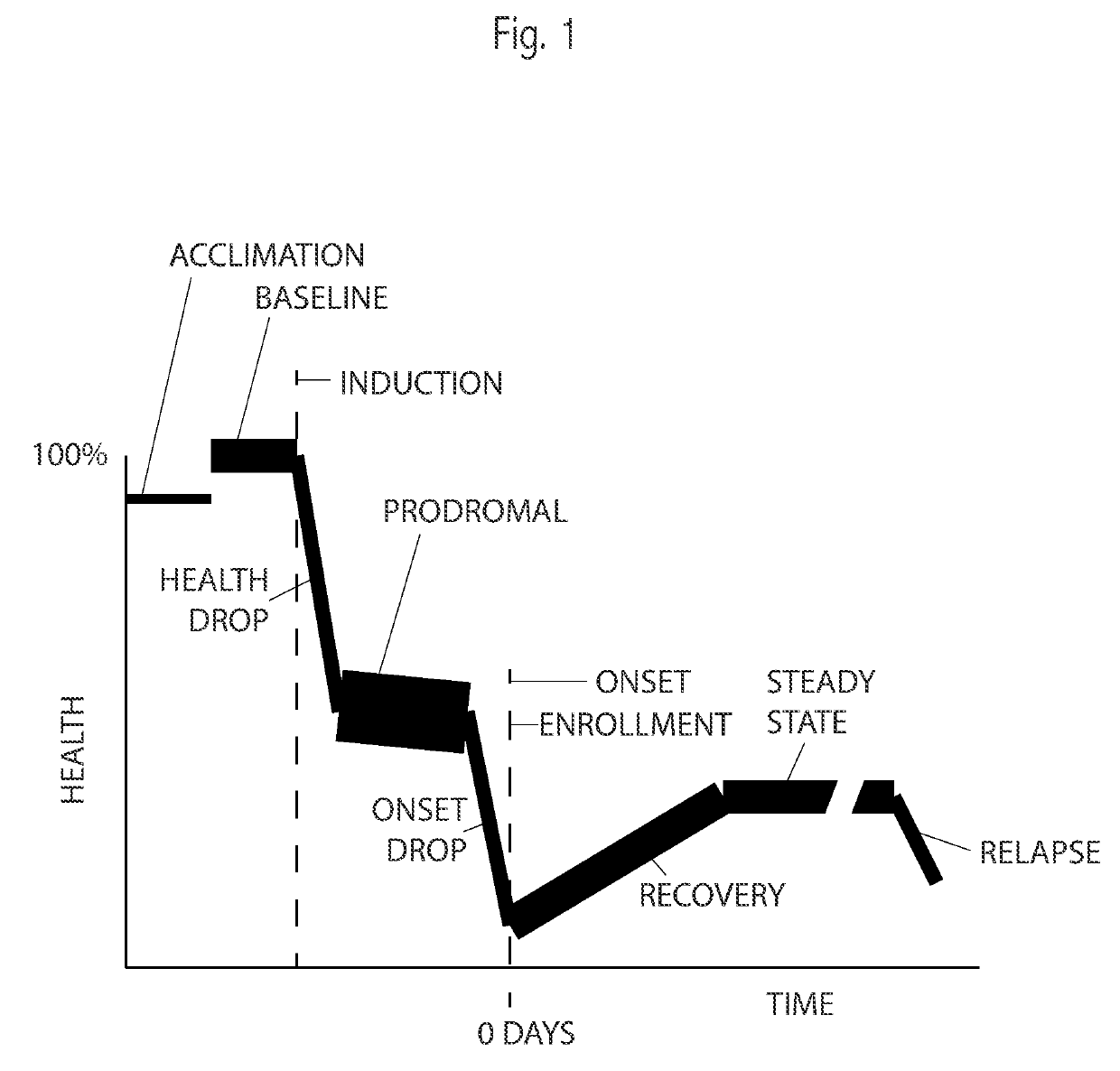
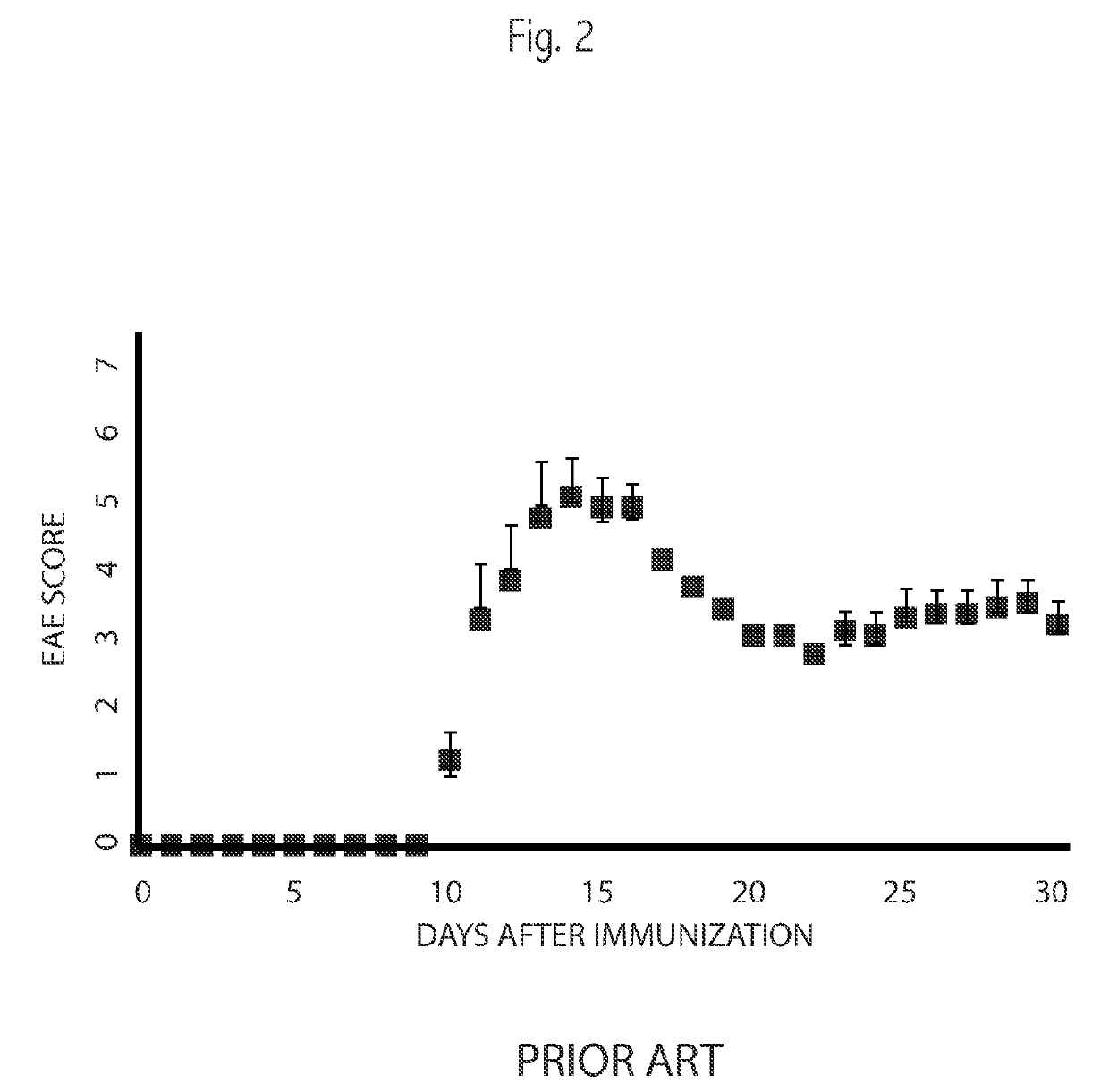
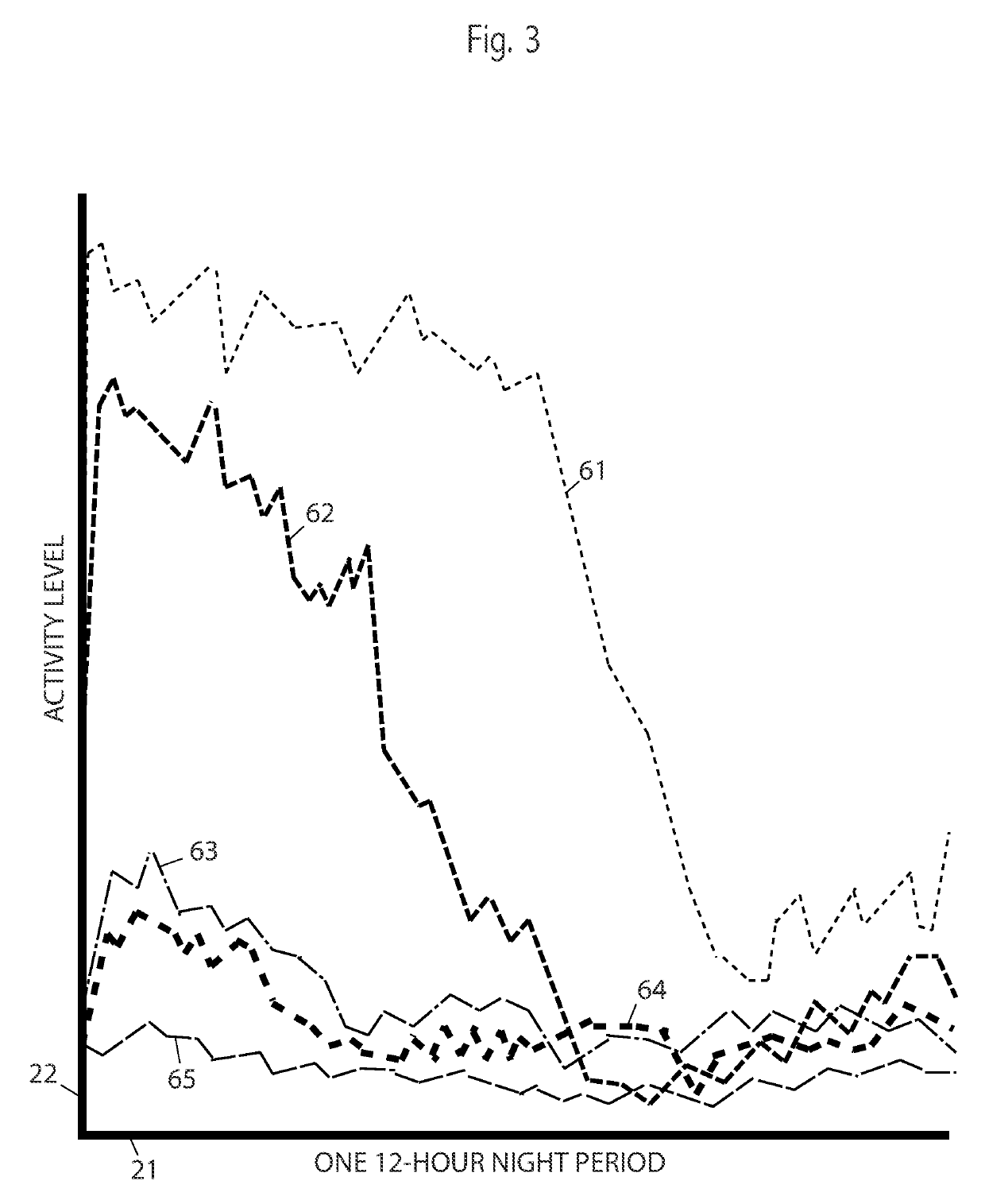
[0022]Following a Baseline period and Induction, an animal's activity is measured automatically multiple times per night. The course of activity during the night follows certain patterns. By analyzing these patterns various predictions may be made and efficacy of treatment measured. Activity may initially be high, followed by a rapid drop, followed by a lower level of activity. Embodiments measure the time and amplitude of the activity-drop during the night. Some embodiments consider the relative activity between the high-activity level and the low-activity level. Some embodiments adjust or compensate a measurement with a minimum activity level during the night or with an animal's activity as measured previously during its Baseline, prior to Induction.
[0023]Based on these measurements, computations and physical elements, in one embodiment, MS may be detected early in the study, prior to Onset. In ano...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com