Method and device for cooling a layer of bulk material on a conveyor grate
a technology of conveyor grate and bulk material, which is applied in the direction of handling discharged materials, lighting and heating apparatus, combustion process, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the drive power required, requiring correspondingly high drive and ventilation power, and affecting so as to improve the degree of emptying and improve the degree of design. , the effect of easy manufacturing and installation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
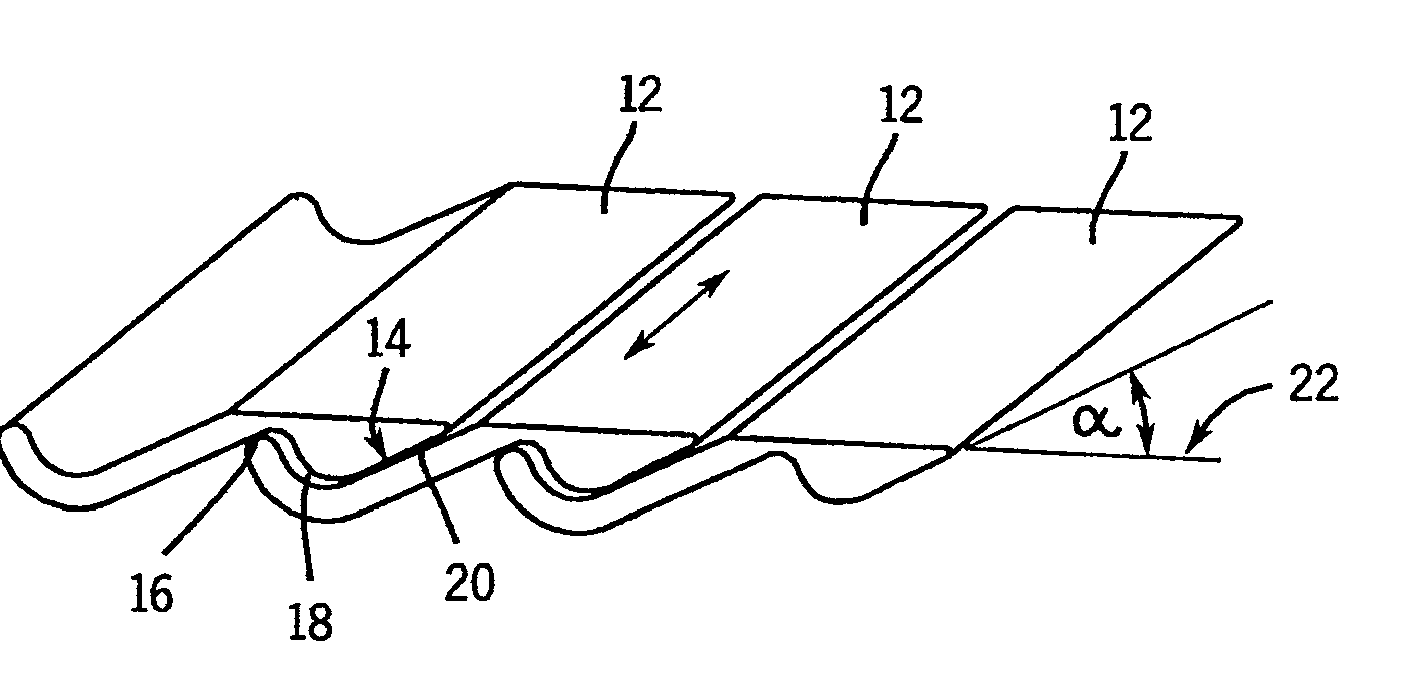
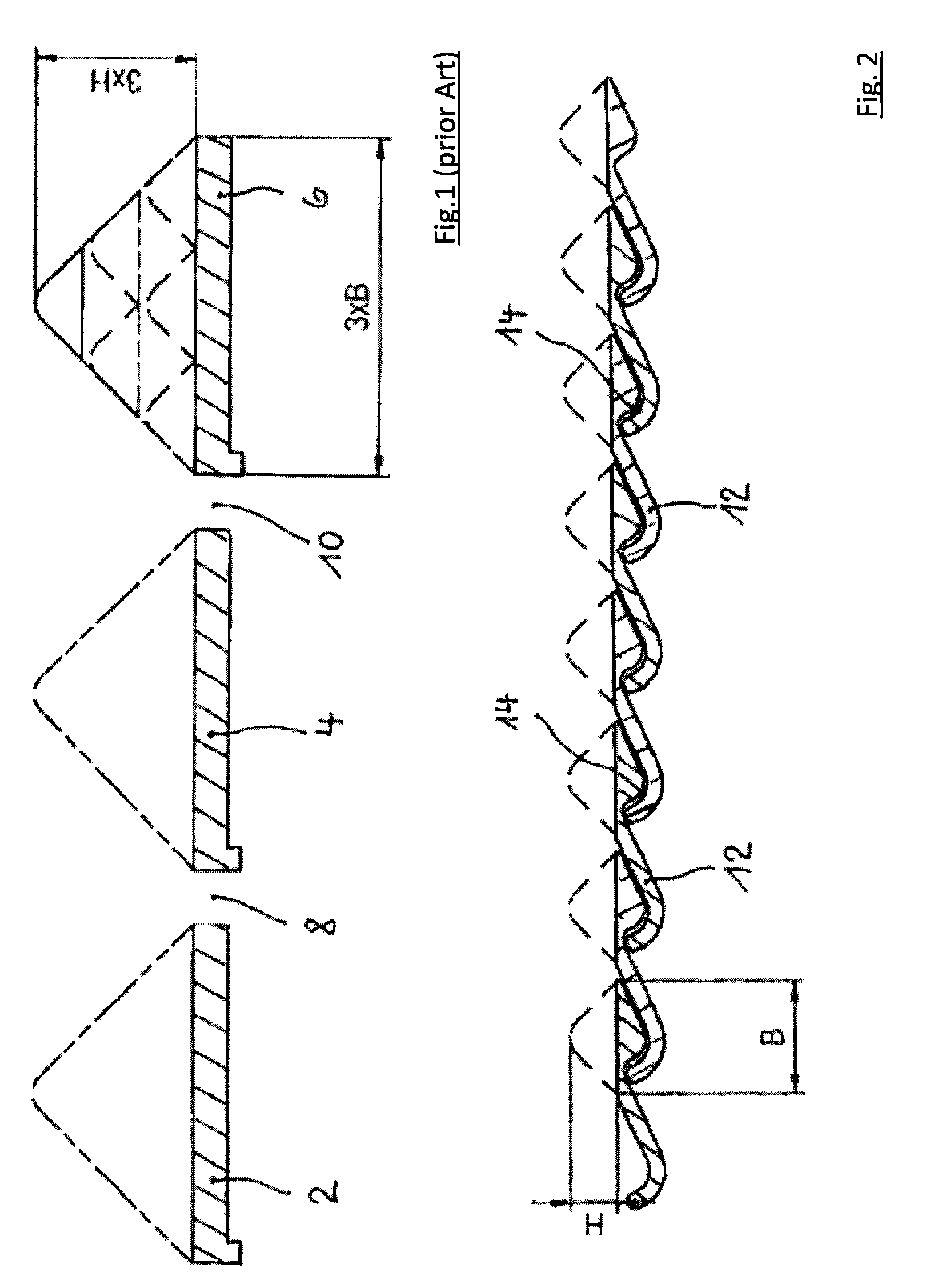
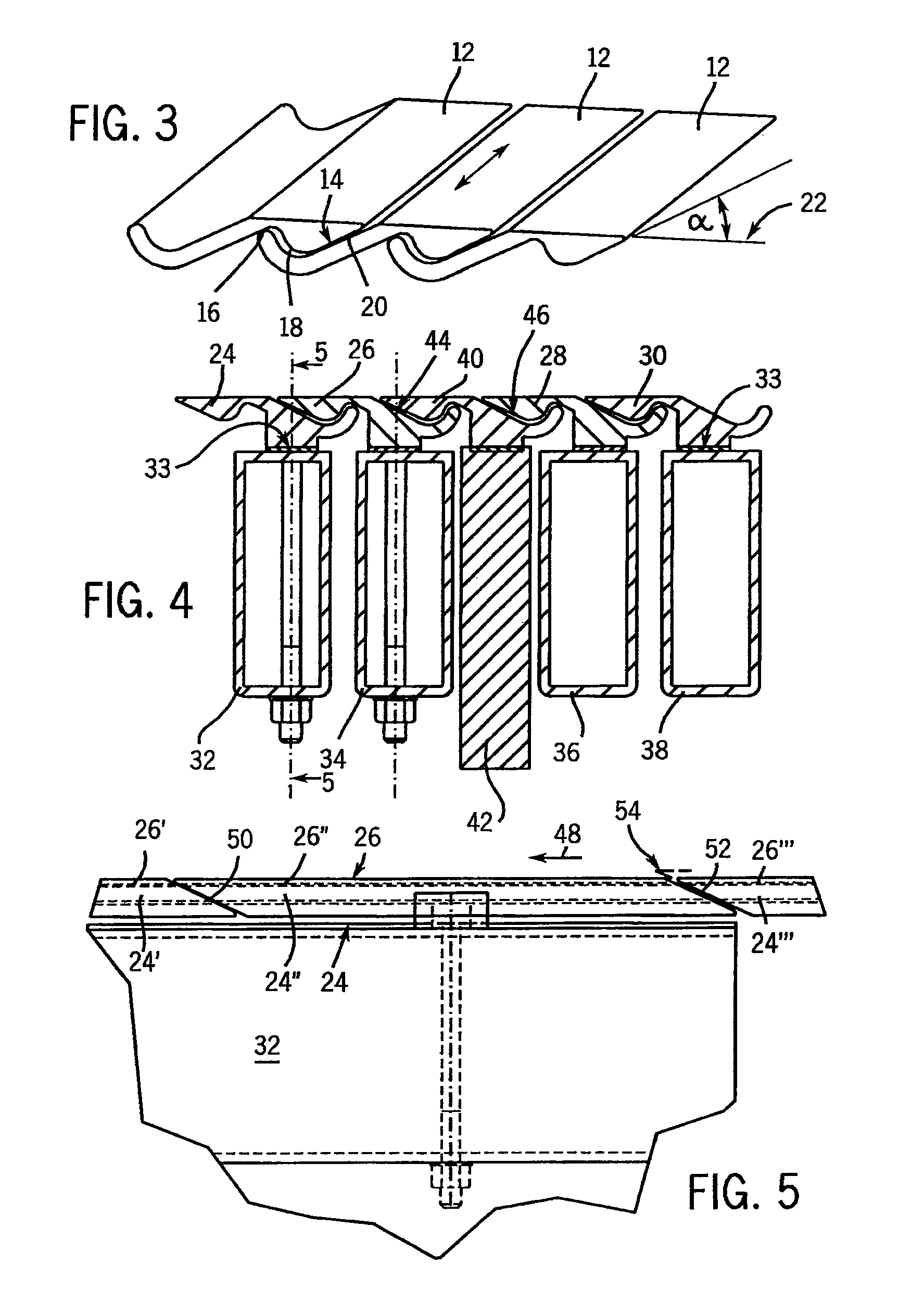
[0039]FIG. 1 schematically shows three adjacently positioned planks 2, 4, 6 of a conventional conveyor grate with moving gaps 8, 10 situated therebetween. The moving gaps 8, 10 have a relatively wide design to accommodate the labyrinth structures, not illustrated in the figure for improved clarity, which prevent bulk material from falling into a chamber located beneath the planks 2, 4, 6. As described above, the moving gaps 8, 10 become filled with bulk material. The area above the moving gaps 8, 10 does not take part in the ventilation. To achieve a specified desired ratio of the surface area of the planks taking part in the ventilation to the surface area of the moving gaps not taking part in the ventilation, the planks 2, 4, 6 must have a relatively wide design. As previously described, an open grate surface area of, for example, 2.5% of the total grate surface area is sought, whereby in the conventional grate illustrated in FIG. 1 the blow openings must be distributed on the pla...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com