File aggregation in a switched file system
a file system and file system technology, applied in the field of network file management, can solve problems such as the limitation of communication of certain client devices
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0038]Definitions. As used in this description and related claims, the following terms shall have the meanings indicated, unless the context otherwise requires:
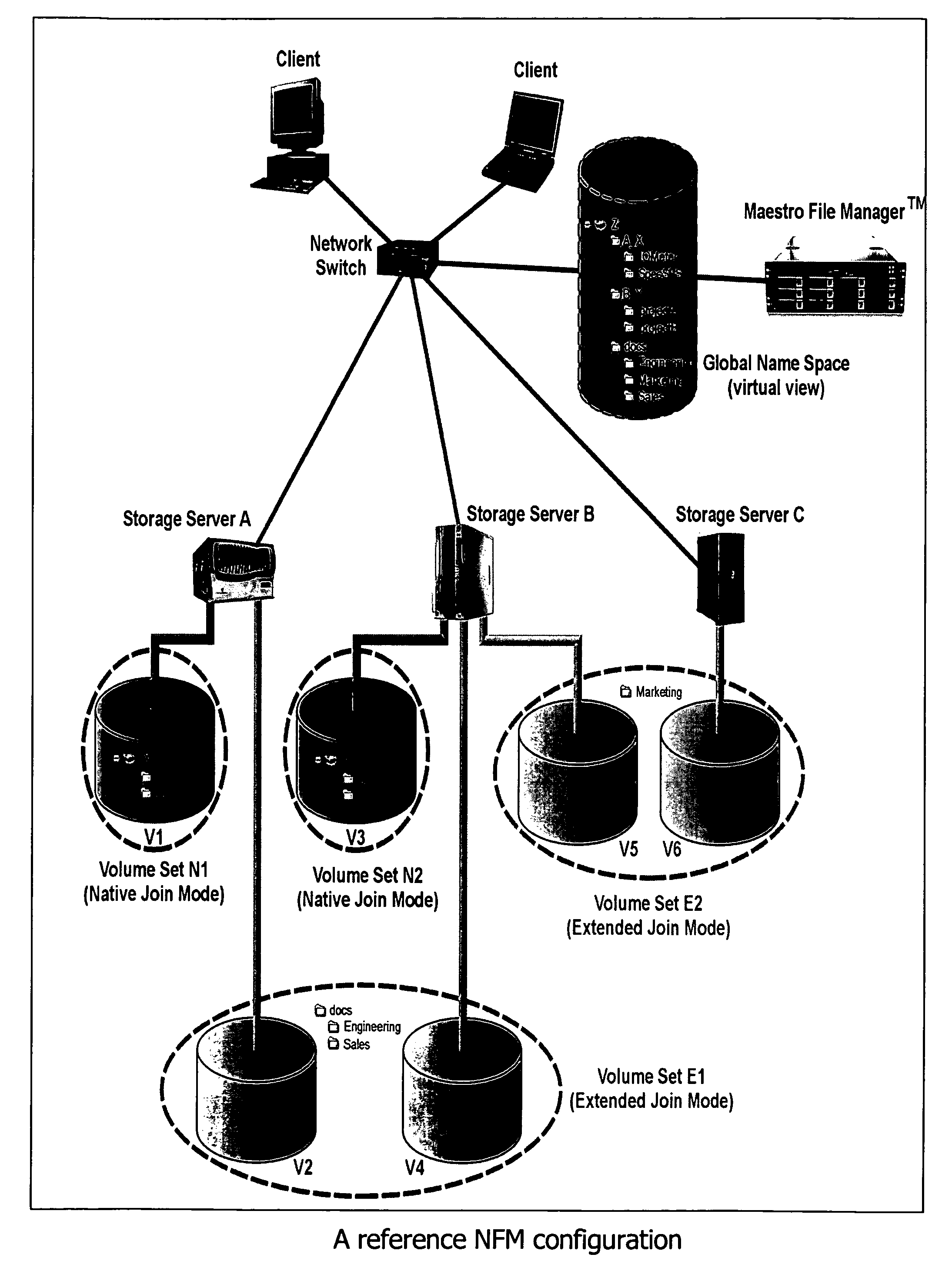
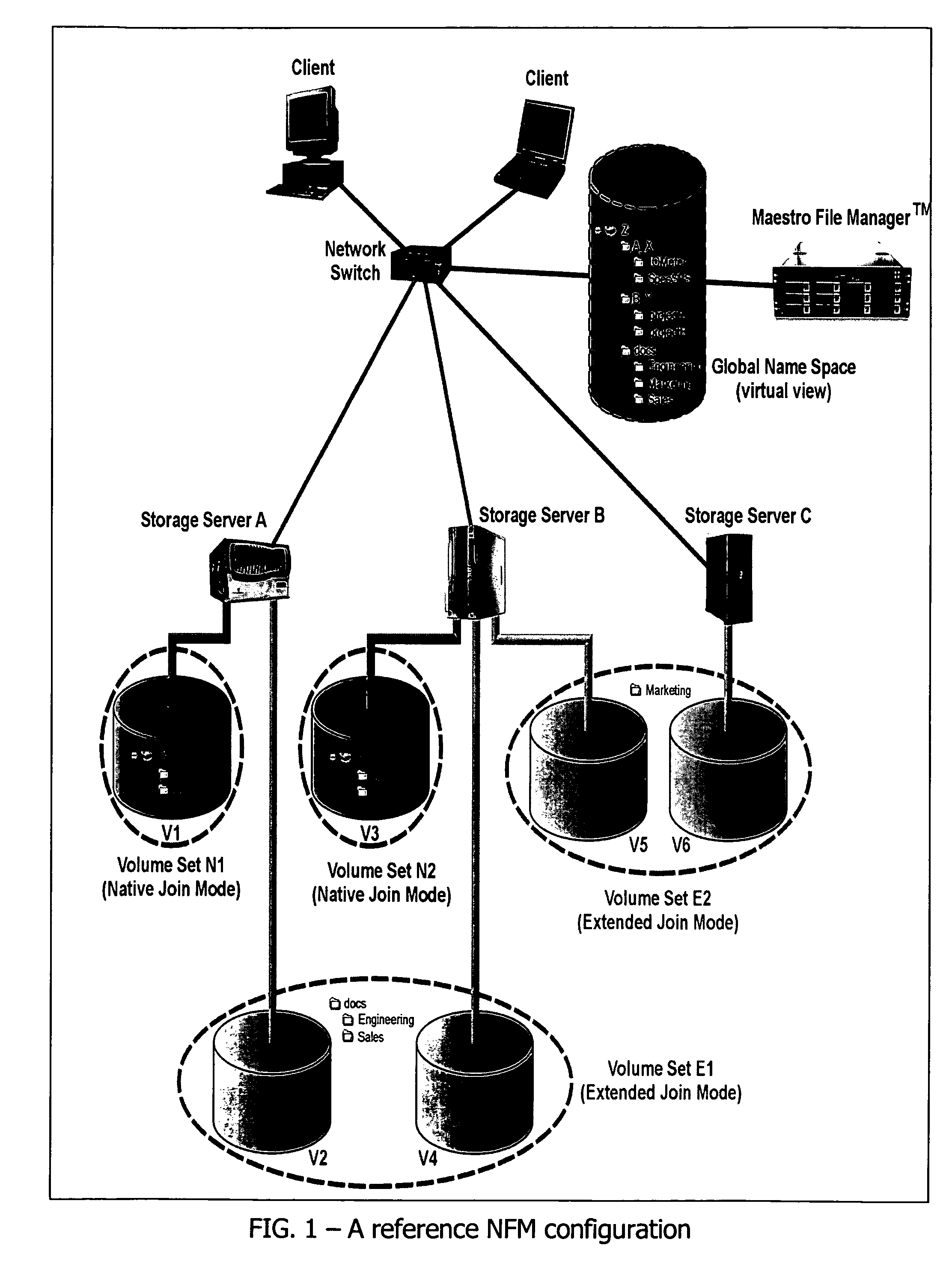
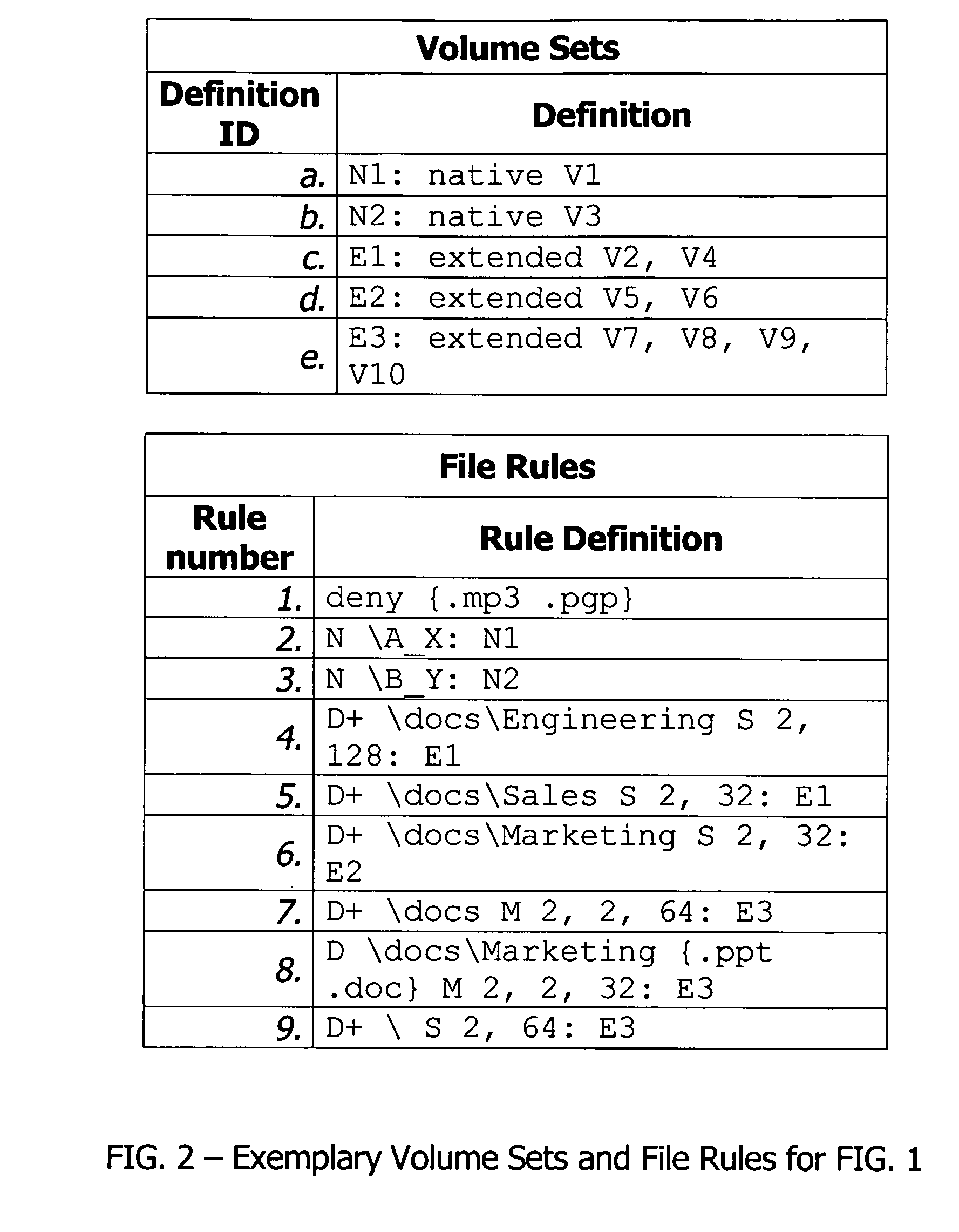
[0039]Aggregator. An “aggregator” is a file switch that performs the function of directory, data or namespace aggregation of a client data file over a file array.
[0040]Data Stream. A “data stream” is a segment of a stripe-mirror instance of a user file. If a data file has no spillover, the first data stream is the stripe-mirror instance of the data file. But if a data file has spillovers, the stripe-mirror instance consists of multiple data streams, each data stream having metadata containing a pointer pointing to the next data stream. The metadata file for a user file contains an array of pointers pointing to a descriptor of each stripe-mirror instance; and the descriptor of each stripe-mirror instance in turn contains a pointer pointing to the first element of an array of data streams.
[0041]File Array. A “file array” consis...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com