Extended hub for a safety pen needle
a safety pen and hub technology, applied in the field of injection devices, can solve the problems of less sensible pressure on the patient's tissue, and achieve the effects of facilitating appropriate insertion depth, limiting the injection depth, and easy change of design
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
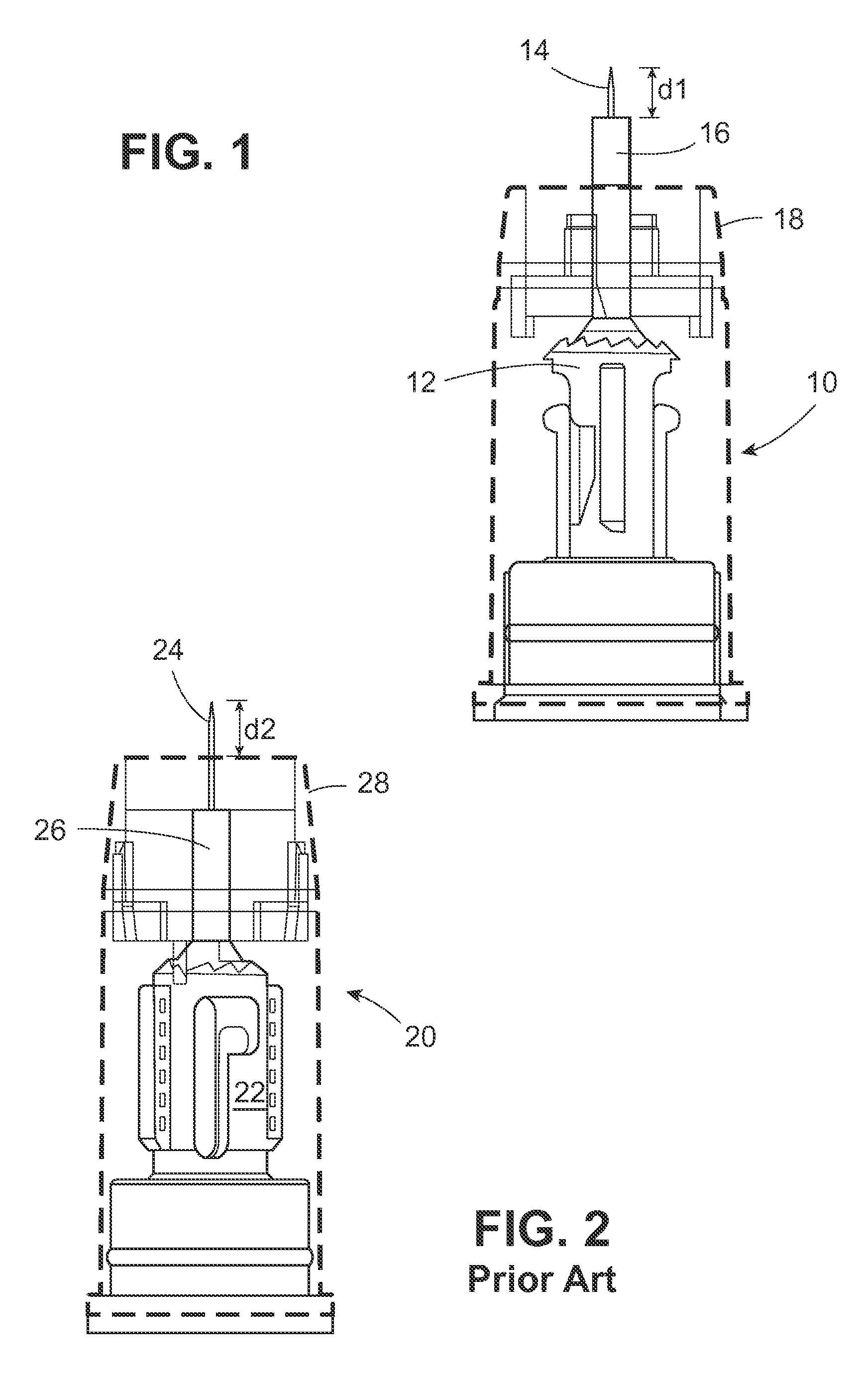
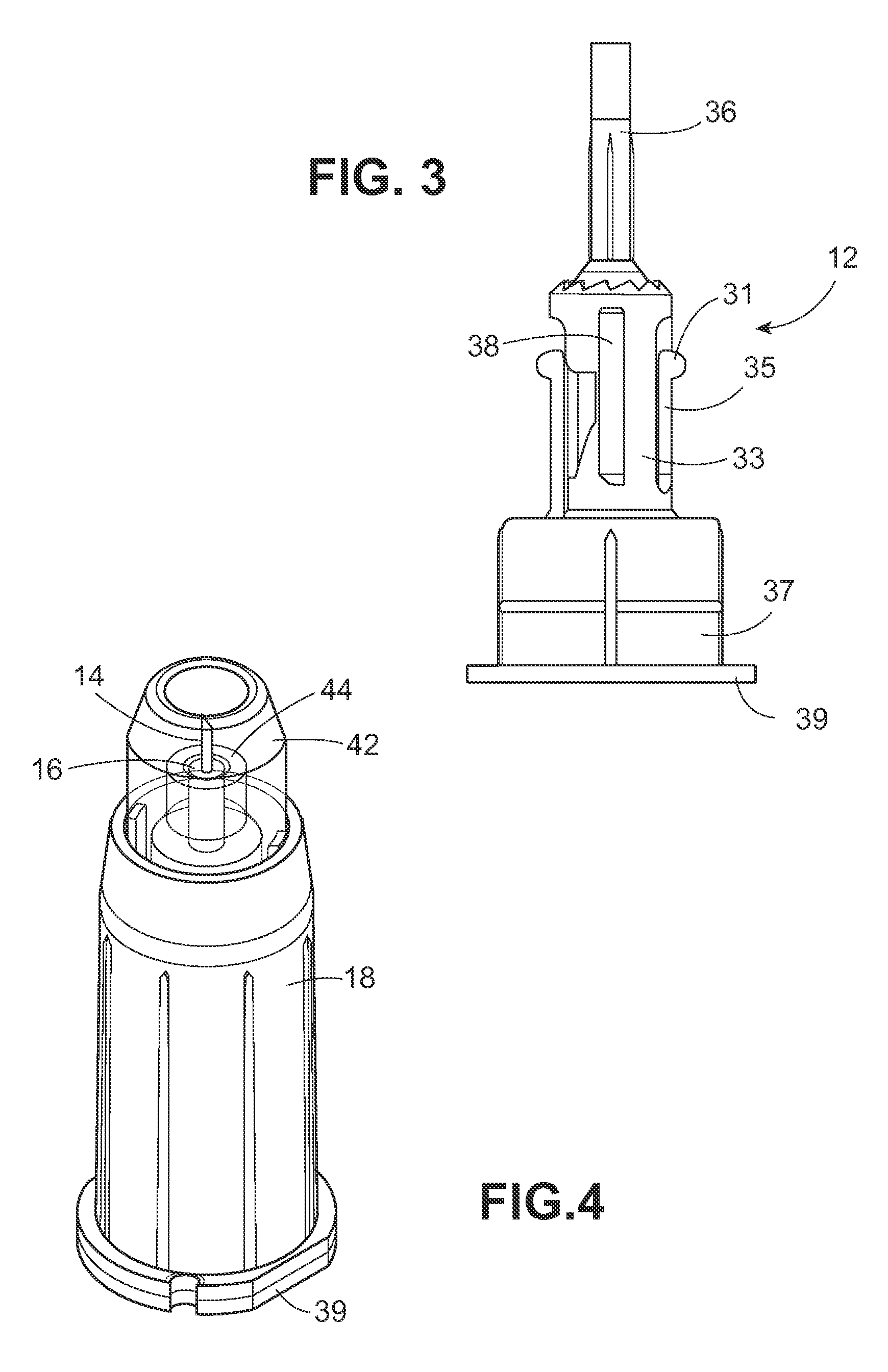
[0019]As used herein, the “distal” direction is in the direction of the injection site, and the “proximal direction” is the opposite direction. The “axial” direction is along the longitudinal axis of the injection device. The needle cannula is generally arranged axially in the device. “Radially” is a direction perpendicular to the axial direction. Thus, “radially inward” generally means closer to the needle. “Integral” means one-piece in the state normally encountered by the user—not intended to be taken apart easily. A “passive” shield is a shield on an injection device which is urged automatically into a position covering the needle cannula after an injection is administered without requiring manipulation by the user or health care professional.
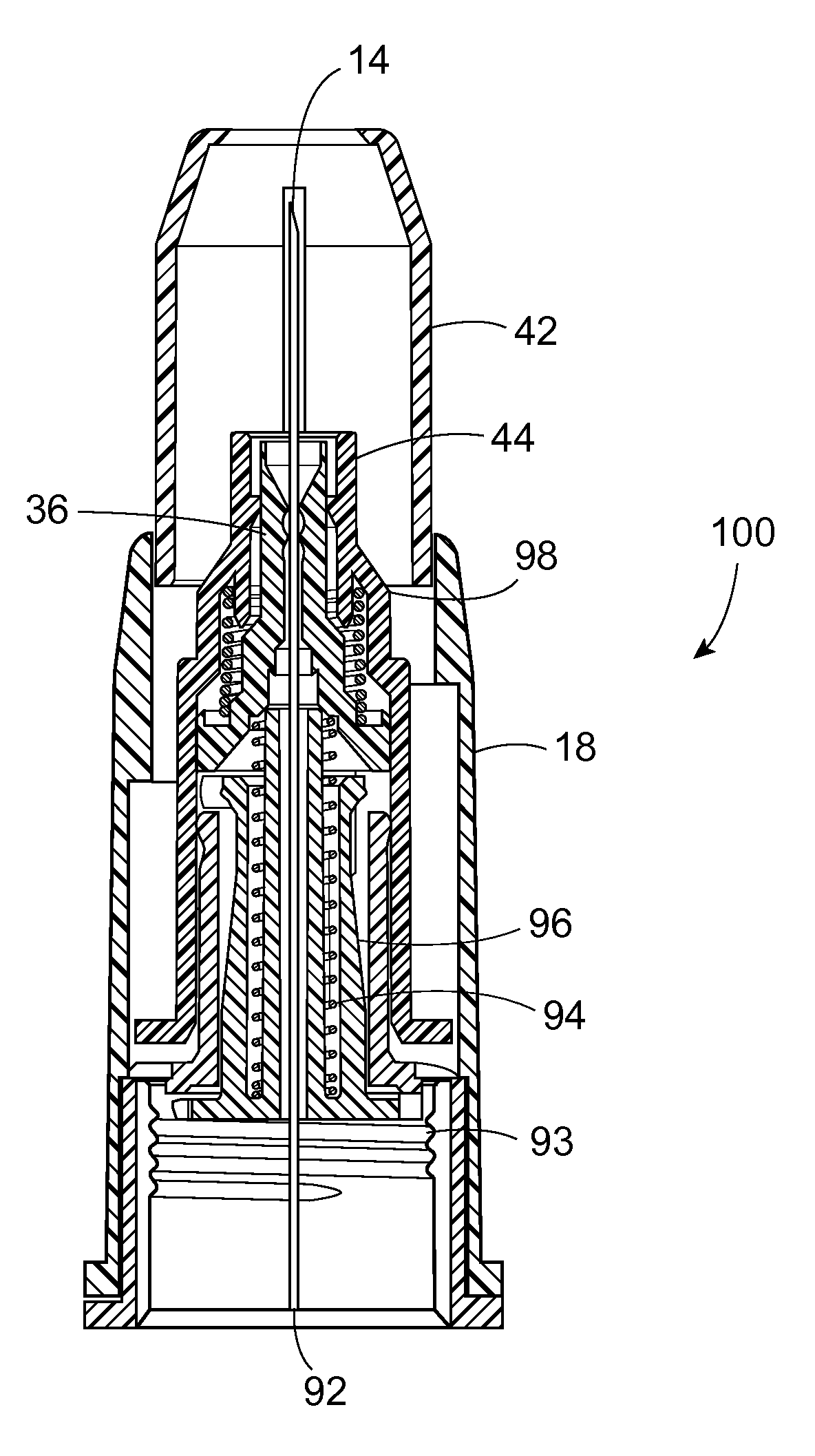
[0020]FIG. 1 shows a partial pen needle assembly 10 including the extended hub post 16 on hub 12 positioned distally of the outer sleeve 18 which is shown in outline. The inner and outer sleeves are removed from FIG. 1 to more clearly delin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com