System and method for power-efficient charging and discharging of a capacitive load from a single source
a capacitive load and charging system technology, applied in the field of electronic circuits and systems, can solve the problems of limiting battery life, high cost, and low efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
Illustrative embodiments and exemplary applications will now be described with reference to the accompanying drawings to disclose the advantageous teachings of the present invention.
While the present invention is described herein with reference to illustrative embodiments for particular applications, it should be understood that the invention is not limited thereto. Those having ordinary skill in the art and access to the teachings provided herein will recognize additional modifications, applications, and embodiments within the scope thereof.
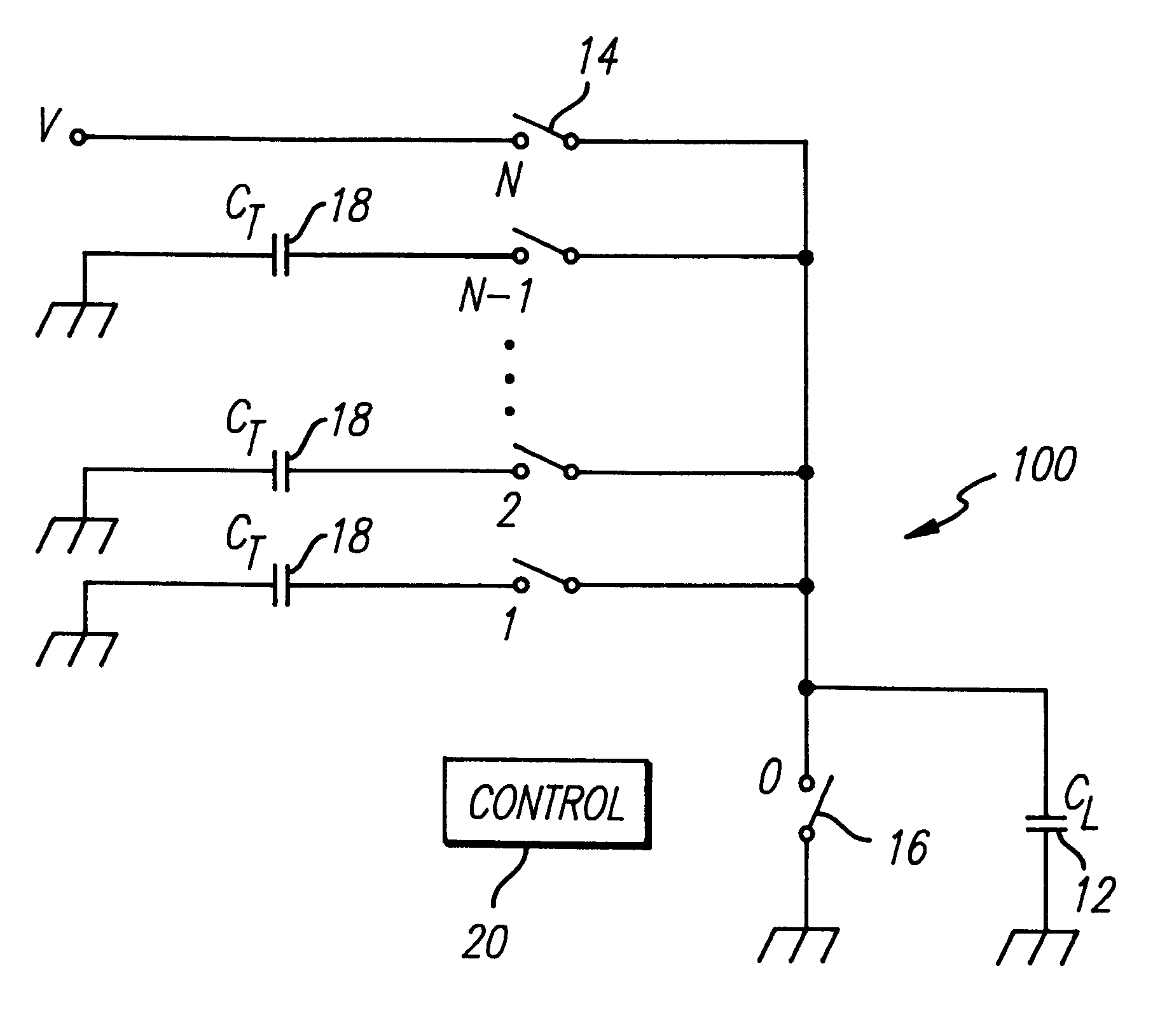
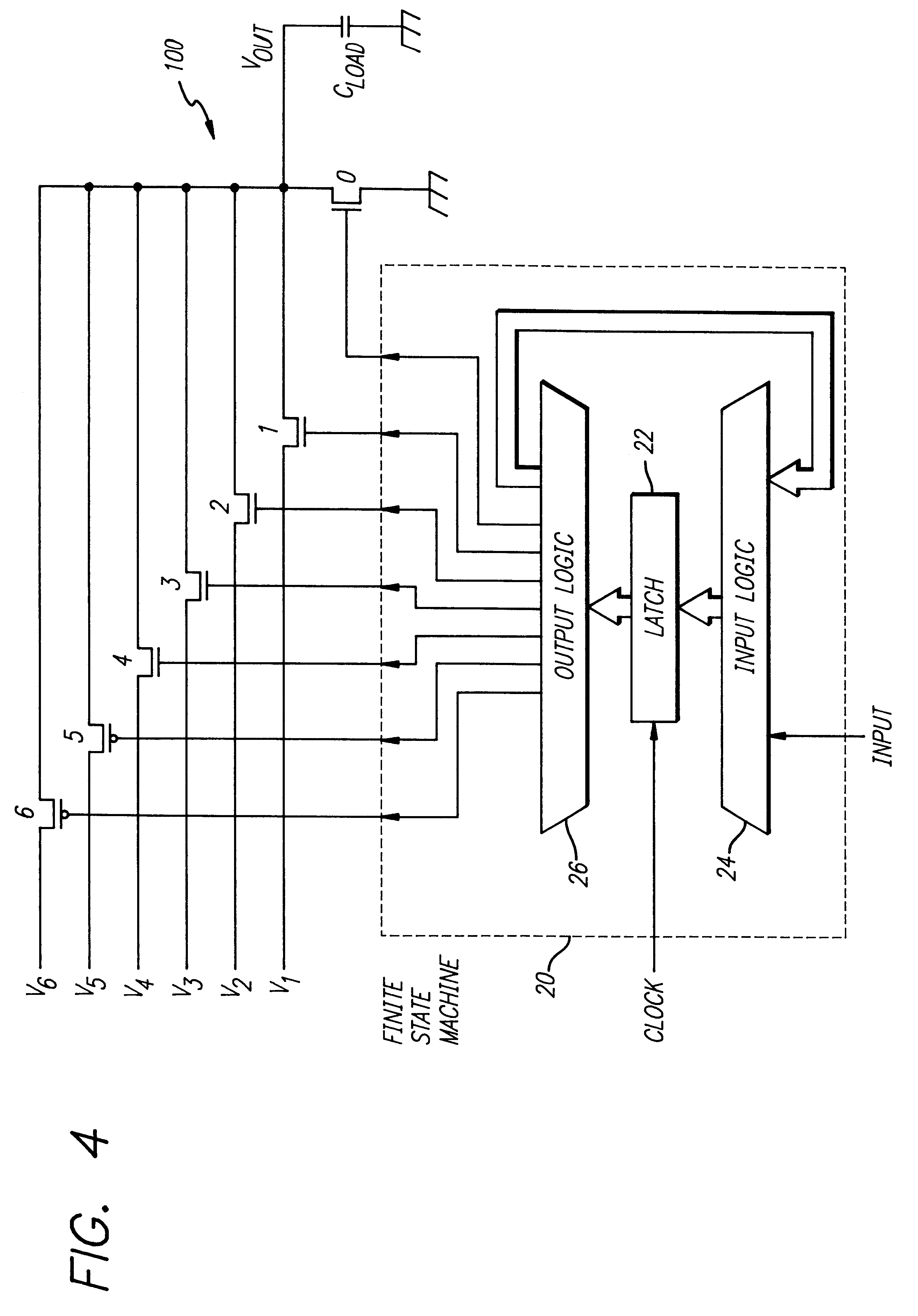
Most of the power dissipation in digital CMOS circuits is due to repeated charging and discharging of capacitive loads including those internal to the circuit and those associated with the output signals.
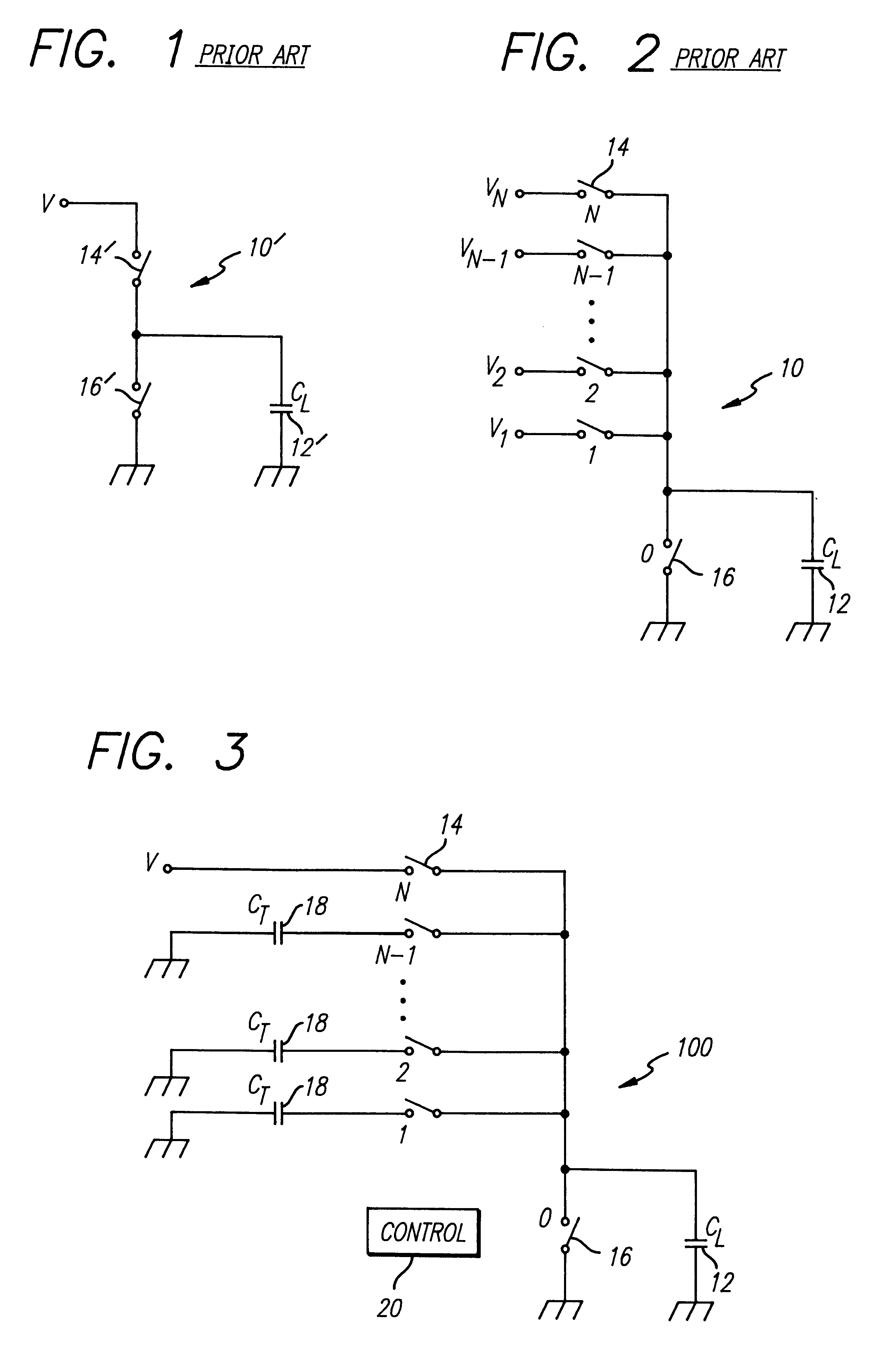
FIG. 1 is a simplified representation of a conventional driver for a capacitive load. The load C.sub.L represents the capacitance of a load and the interlead capacitance of the lines connecting the driver 10' to the load 12'. The load 12' is cha...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com