Pitch period extracting apparatus of speech signal
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
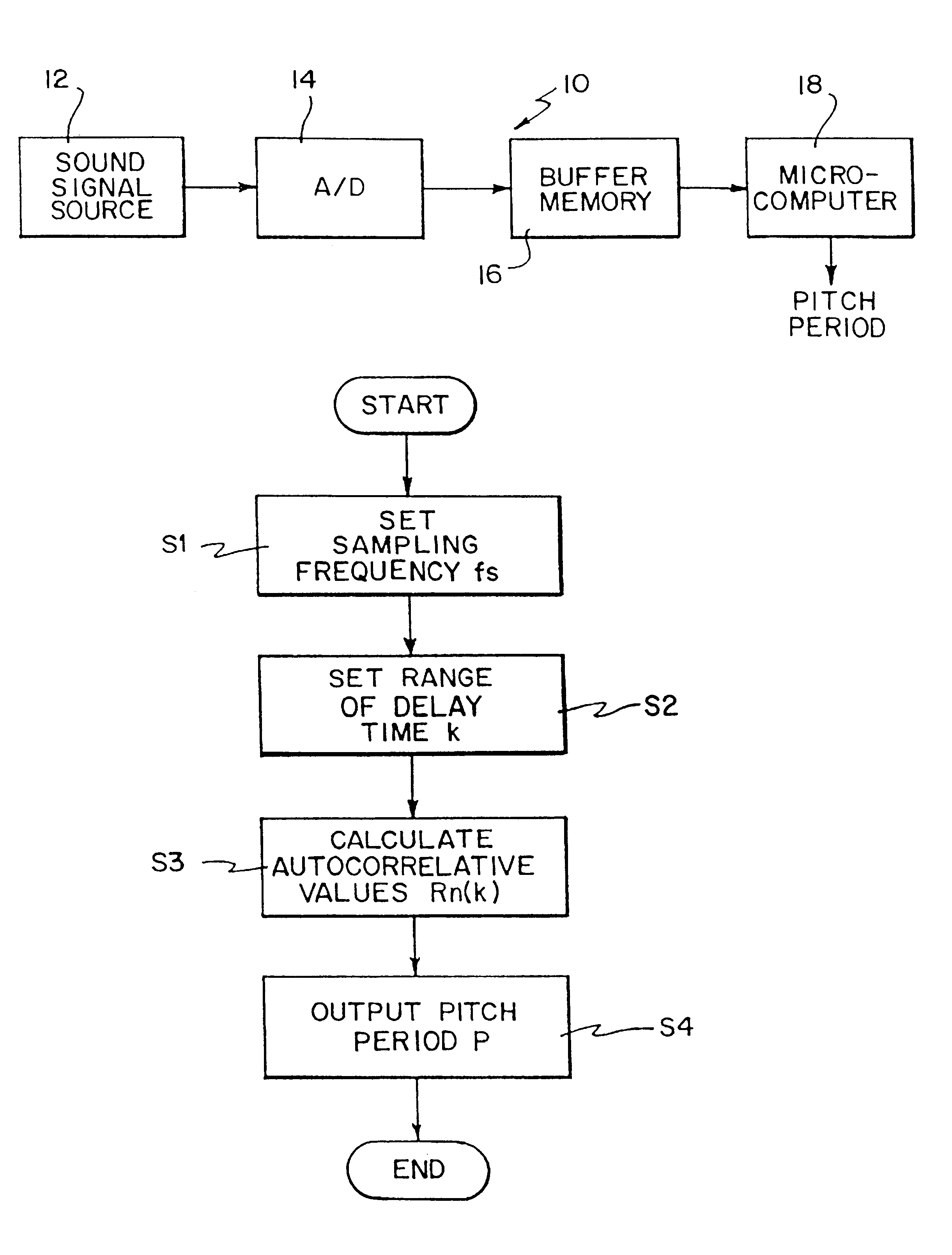
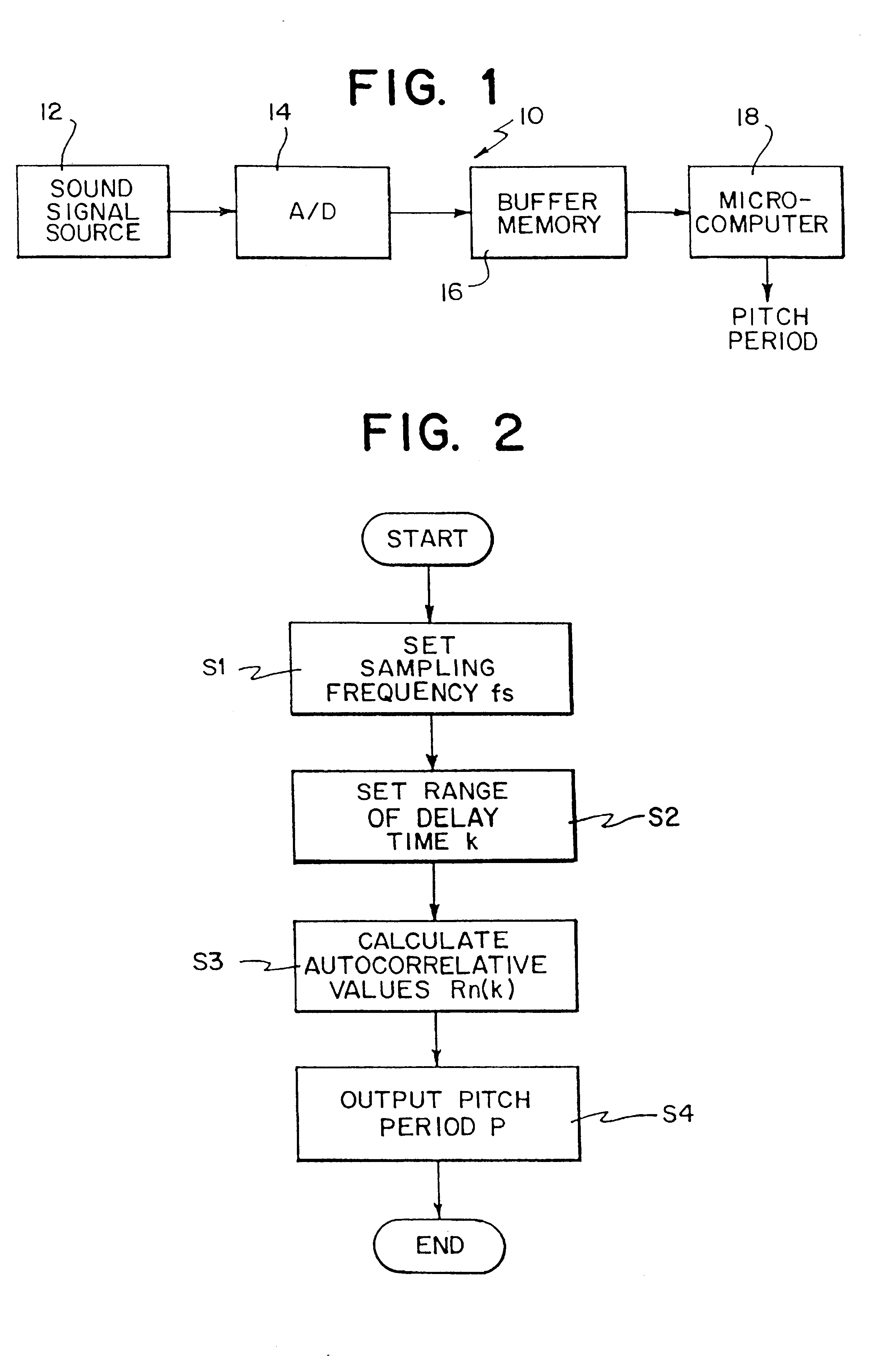
[0033]With referring to FIG. 2, in a first embodiment, the microcomputer 16 set the sampling frequency fs of the A / D converter 14, 8 kHz or 6 kHz, in a first step S1. According to the sampling frequency fs thus determined, the AID converter 14 converts the analog speech signal x(t) into speech signal data x(n). In a next step S2, the microcomputer 18 determines delay times k with referring to data of the sampling frequency fs in the first step S1. That is, in a case of the sampling frequency is 8 kHz, the microcomputer 18 sets the delay times k in the range of 20 samples≦k≦100 samples. In a case where the sampling frequency is 6 kHz, the microcomputer 18 sets the delay times k in the range of 15 samples≦k≦75 samples.
[0034]Then, in a step S3, the microcomputer 18 sequentially reads-out the speech signal data x(n) stored in the buffer memory 16, and calculates the autocorrelative values Rn(k) on the basis of the following equation (3) and according to the delay times k set in the step...
second embodiment
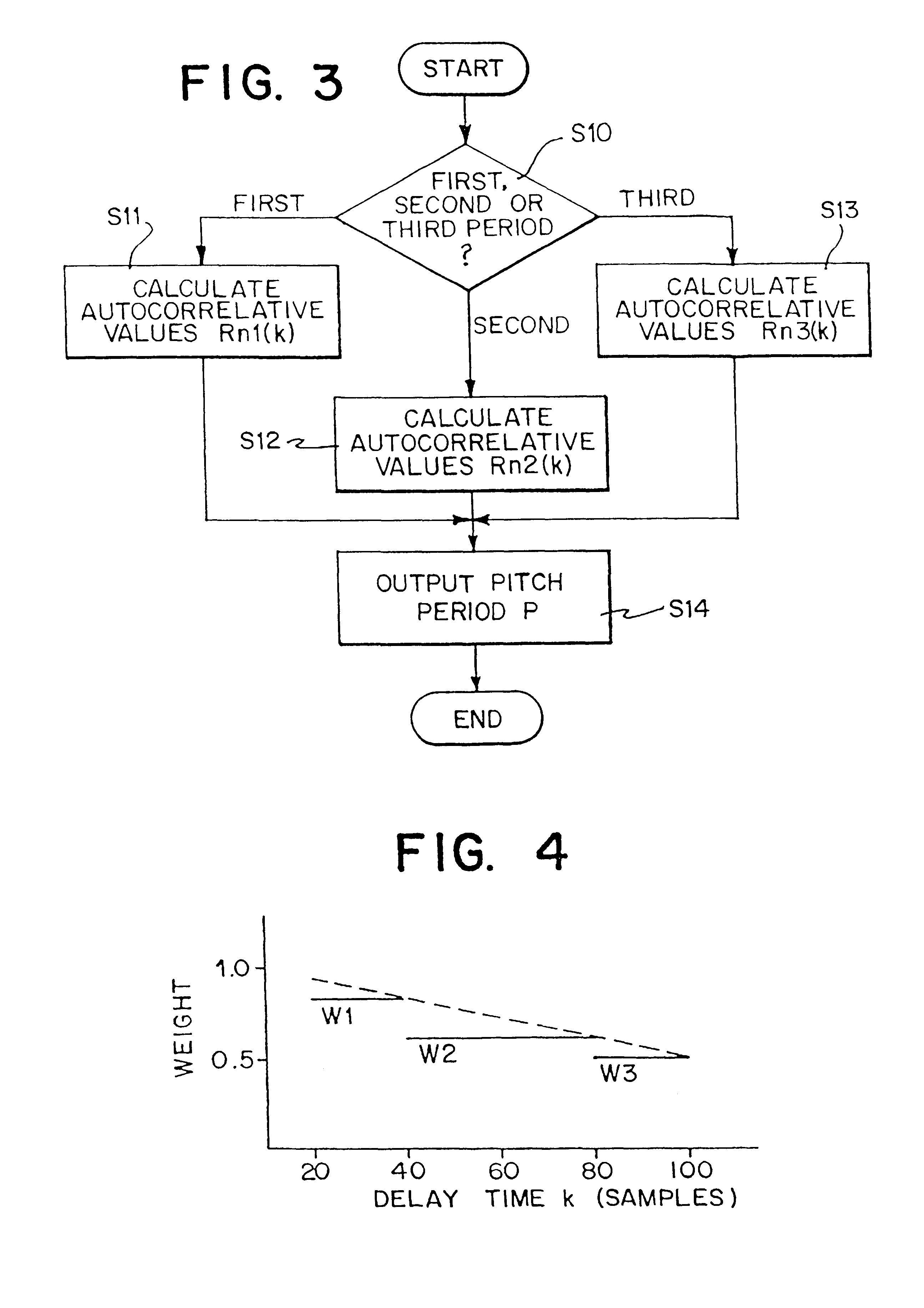
[0036]In the second embodiment, the microcomputer 18 sets a most suitable range of the delay times k according to the sampling frequency fs. In contrast, in FIG. 3 embodiment, the microcomputer 18 sets a plurality of periods within the range of the delay times k in calculating the autocorrelative values Rn(k),
[0037]More specifically, in this embodiment shown, the microcomputer 18 divides the range of the delay times k which is a pitch period searching time period in calculating the autocorrelative values Rn(k) into a plurality of periods. In such a case, respective starting values and end values of the respective periods are determined such that the end value of the period does not include double the starting value of that period. Then, autocorrelative values Rn1(k), Rn2(k) and Rn3(k) of the respective periods are calculated.
[0038]With referring to FIG. 3, in a first step 510, the microcomputer 18 determines the plurality of periods within the range of the delay times k according to...
third embodiment
[0047]FIG. 5 is a flowchart showing a third embodiment in which the FIG. 2 embodiment (a first embodiment) and FIG. 3 embodiment (a second embodiment) are simultaneously included. In a step 520 of FIG. 5, the microcomputer 18 sets a sampling frequency fs of the A / D converter 14, that is, 8 kHz or 6 kHz. The A / D converter 14 converts the analog speech signal into the speech signal data x(n) with the sampling frequency fs thus set. In a next step 521, the microcomputer 18 determines the respective periods within the range of the delay times k with referring to the data of the sampling frequency fs in the step 51. That is, when the sampling frequency fs is 8 kHz, a range of 20 samples≦k<40 samples, a range of 40 samples≦k<80 samples, and a range of 80 samples≦k≦100 samples are set as the first period, the second period, and the third period. In addition, if the sampling frequency fs is 6 kHz, a range of 15 samples≦k <30 samples, a range of 30 samples≦k<60 samples, and a range of 60 sam...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com