Quick gray scale transform method for liquid crystal display
A liquid crystal display, fast technology, applied in static indicators, instruments, nonlinear optics, etc., can solve problems such as afterimage, image transition afterimage, image blur, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
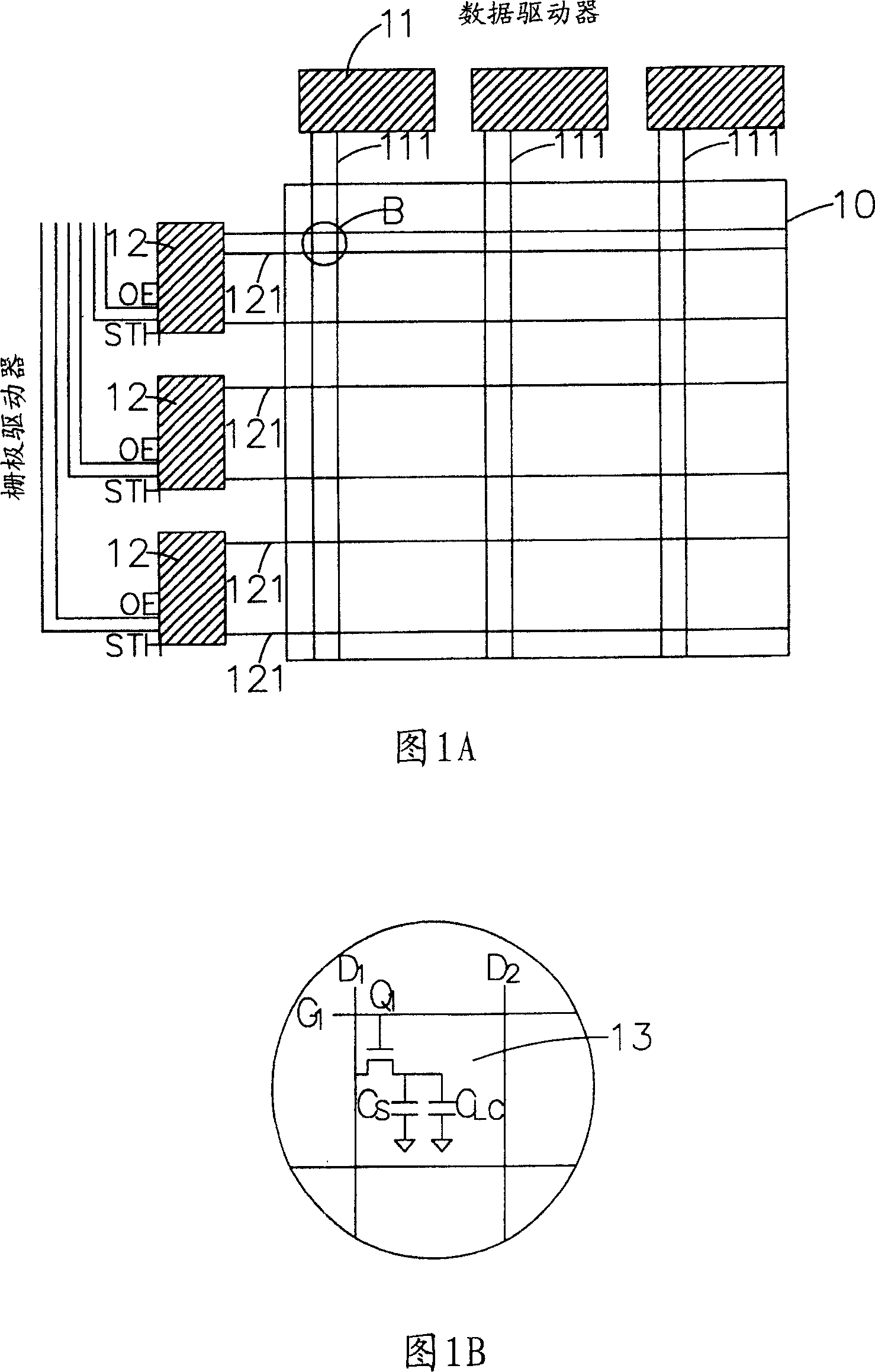
[0044] In order to clearly express the technical features of the present invention, an embodiment in which the gate lines of the liquid crystal display are divided into two areas and two scanning signals are synchronously transmitted is firstly described.
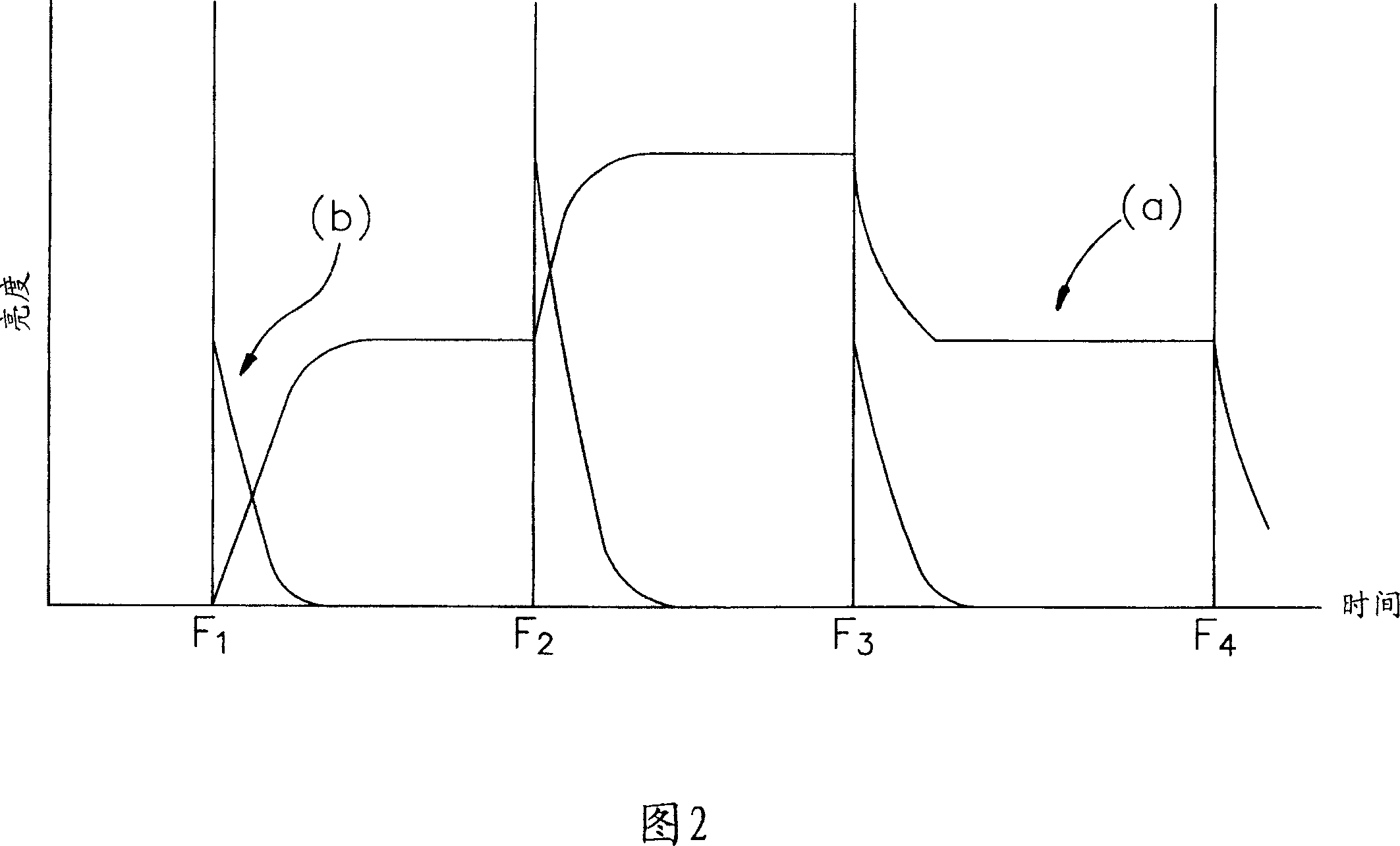
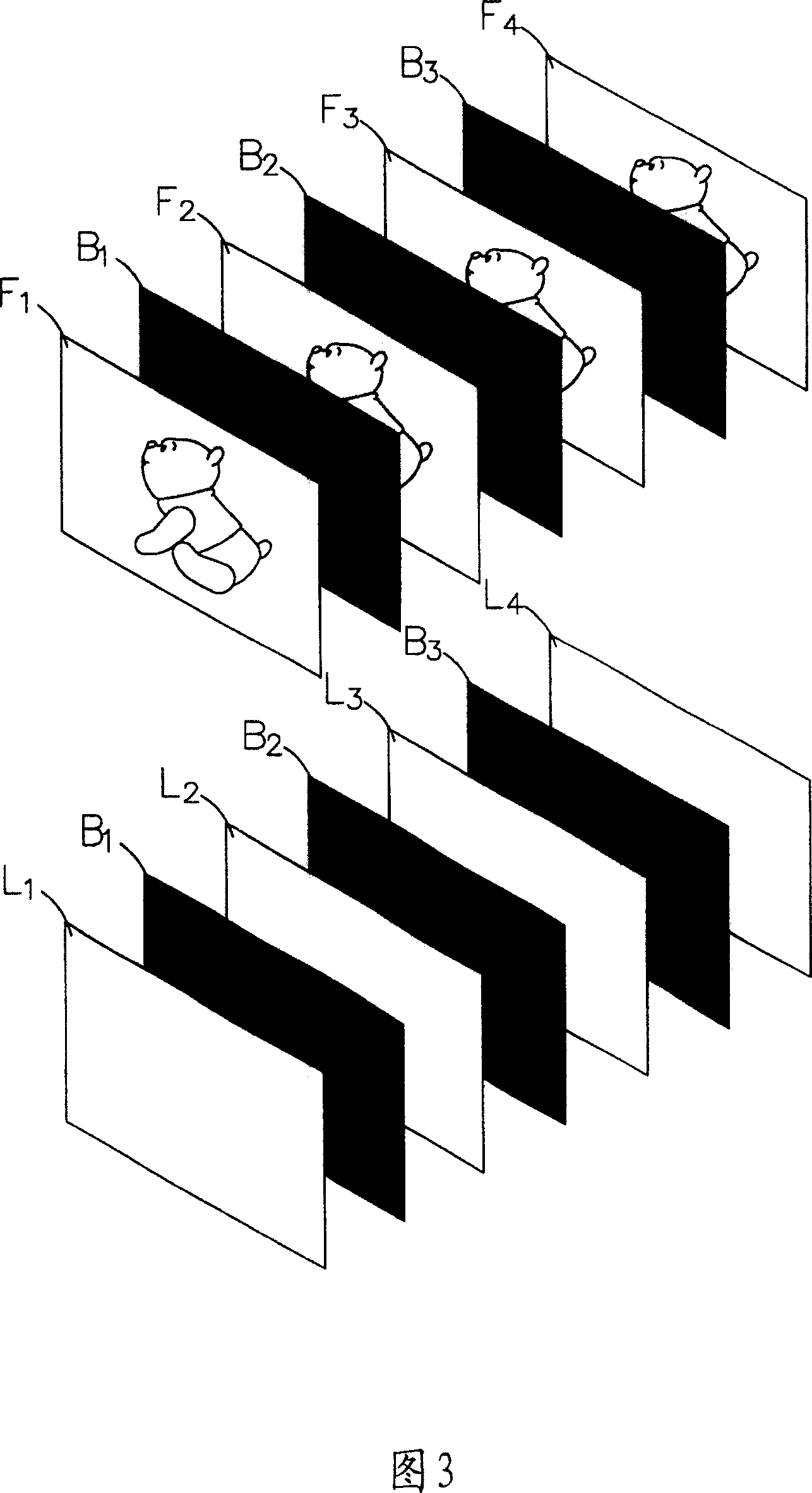
[0045] Please refer to Fig. 5, Fig. 6A and Fig. 6B, Fig. 5 shows the output driving voltage waveform and brightness change curve (a) (b) of a pixel at a gate line position on a display panel, and its horizontal axis represents time, unit is ms, the frame interval time is T, and it is divided into two sub-intervals t 1 , t 2 , and t 1 :t 2 =1:1, FIG. 6A shows that the set gate line on the display panel 40 is divided into two regions M 1 ,M 2 , assuming that the number of gate lines in the first area is m, the number of gate lines in the second area is also m, and the total number of gate lines is 2m, so the ratio of the number of gate lines in the two areas is 1:1.
Embodiment approach
[0046] Assuming that a continuous image data enters the frame interval (Frame N) from the previous frame interval (Frame N-1) and the brightness of the data is code 120, the brightness can select a data voltage from the look-up table (LUT) to drive the display panel 40, To make the display panel 40 reach brightness within a specific time, the implementation method of the fast grayscale conversion of the present invention is as follows:
[0047] in the first subinterval t 1 Inside, the gate driver 41 synchronously turns on the two gate lines on the display panel 40, and in the first area M 1 The first gate line G 1 Give the data voltage code120 of the frame interval N, in the second area M 2 The first gate line G m+1 Give the previous frame interval N-1 a voltage code 0 to display a black screen, and then sequentially and synchronously turn on the next gate line of each area, and give the same voltage value as the previous gate line, that is, the gate of the same area The l...
no. 2 example
[0054] The second embodiment is further described by dividing the gate line into three areas and synchronously controlling three scanning signals. Please refer to FIG. 7 , FIG. 8A and FIG. 8B . The output driving voltage waveform and brightness change curve (a)(b) of a pixel at a position, the horizontal axis represents time, the unit is ms, and the frame interval time is T, which is divided into two sub-intervals t 1 , t 2 , t 3 , t 1 :t 2 :t 3 =1:1:1, as shown in FIG. 8A, set the gate lines on the display panel 50 to be divided into three regions M 1 ,M 2 ,M 3 , assuming that the number of gate lines in the first zone is m, the number of gate lines in the second zone is m, the number of gate lines in the third zone is also m, and the total number of gate lines is 3m, the gate lines in the two zones The number ratio is 1:1:1.
[0055] As shown in Figure 7, assuming that a continuous image data enters the frame interval (Frame N) from the previous frame interval (Frame...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com