Method of manufacturing wind turbine blade
A technology for wind turbines and blades, which is applied in the field of manufacturing the blade roots of wind turbine blades, and can solve the problems of expensive blades, weakened structures, and consuming a lot of time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
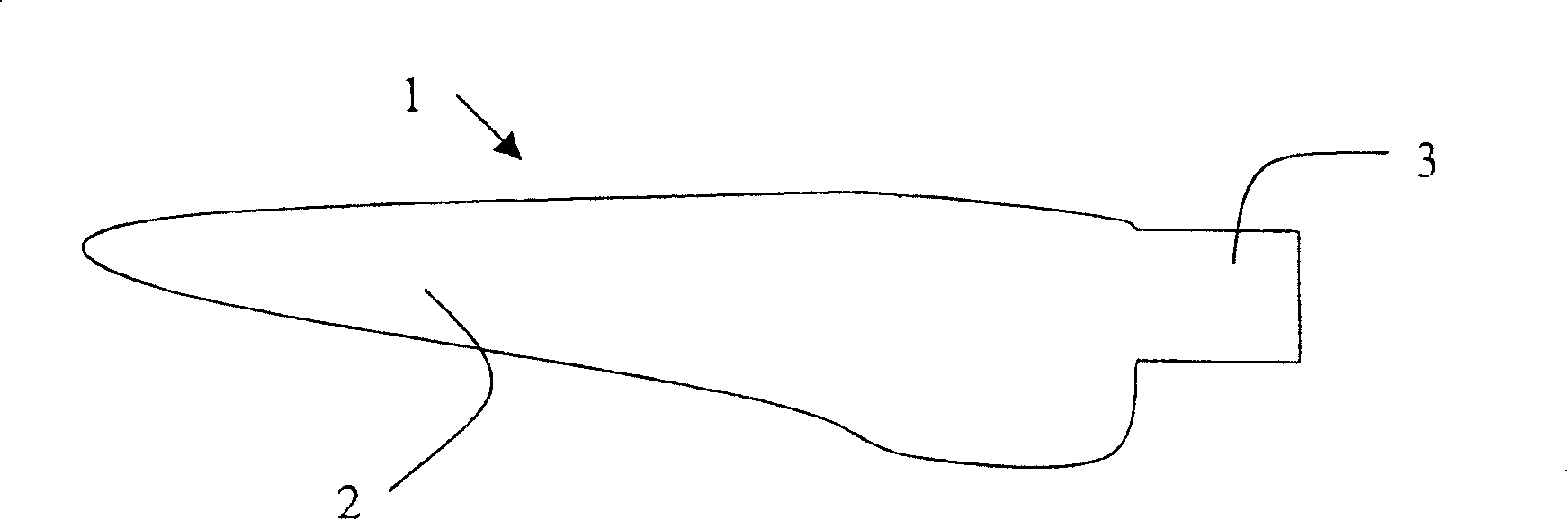
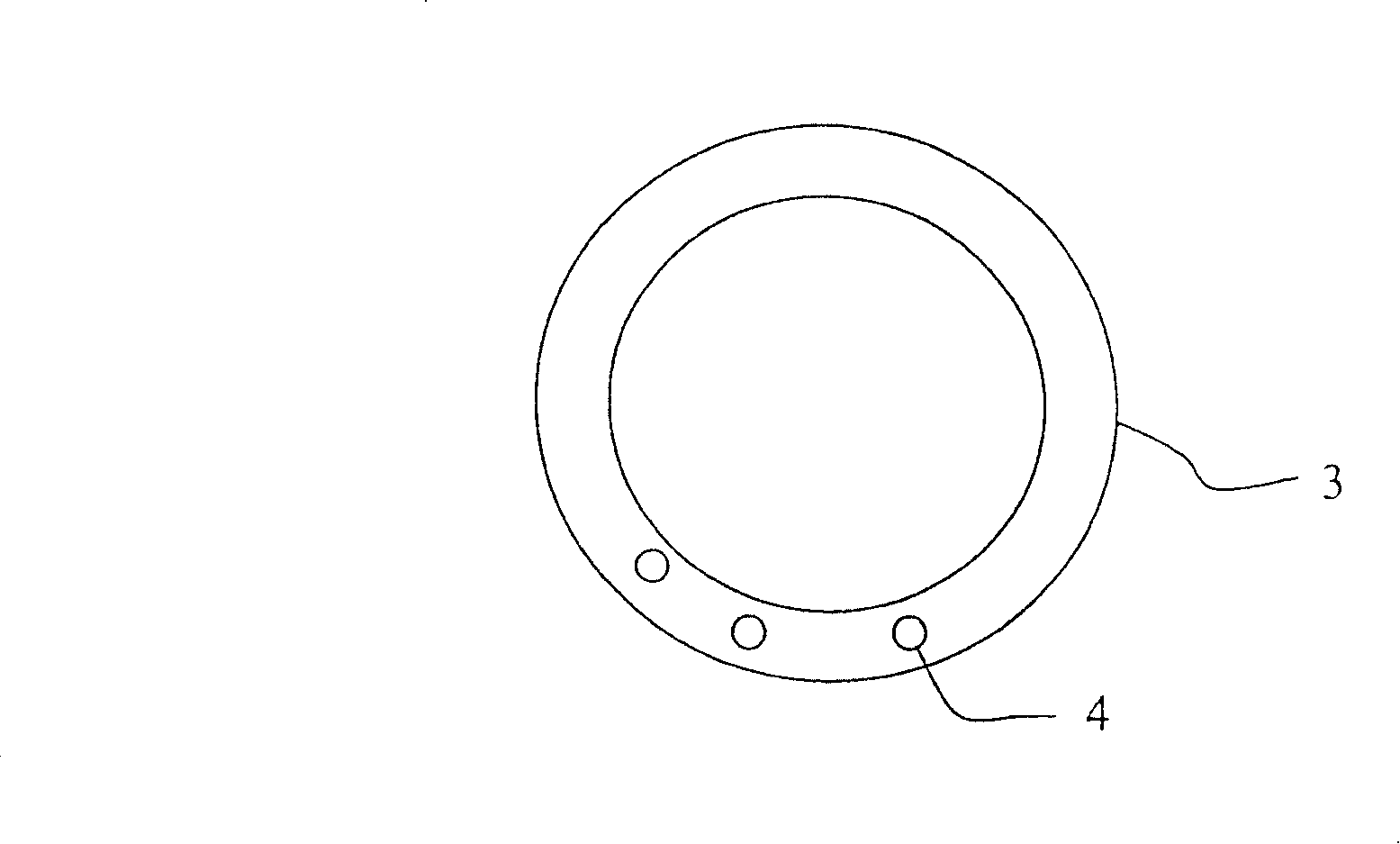
[0029] in figure 1 The wind turbine blade 1 can be seen in the plan view. The blade 1 includes an aerodynamically designed part 1 having a shape most suitable for wind energy development and a blade root 3 for connecting to a hub (not shown) of a wind turbine. Because the wind turbine blade is subjected to a large force caused by wind, rotating mass, etc., the blade root 3 is a highly strained area of the wind turbine blade. As an example, the size of a common wind turbine blade 1 for a 1.5MW wind turbine is about 35m, and the mass of each blade is about 6000kg. Most modern wind turbine blades include a central hollow high-strength beam and an aerodynamic covering with limited strength, and generally the beam and covering are made of composite materials such as fiber reinforced plastics. Other blade designs include I-beams, or do not include beams because the cover is reinforced to achieve self-support.
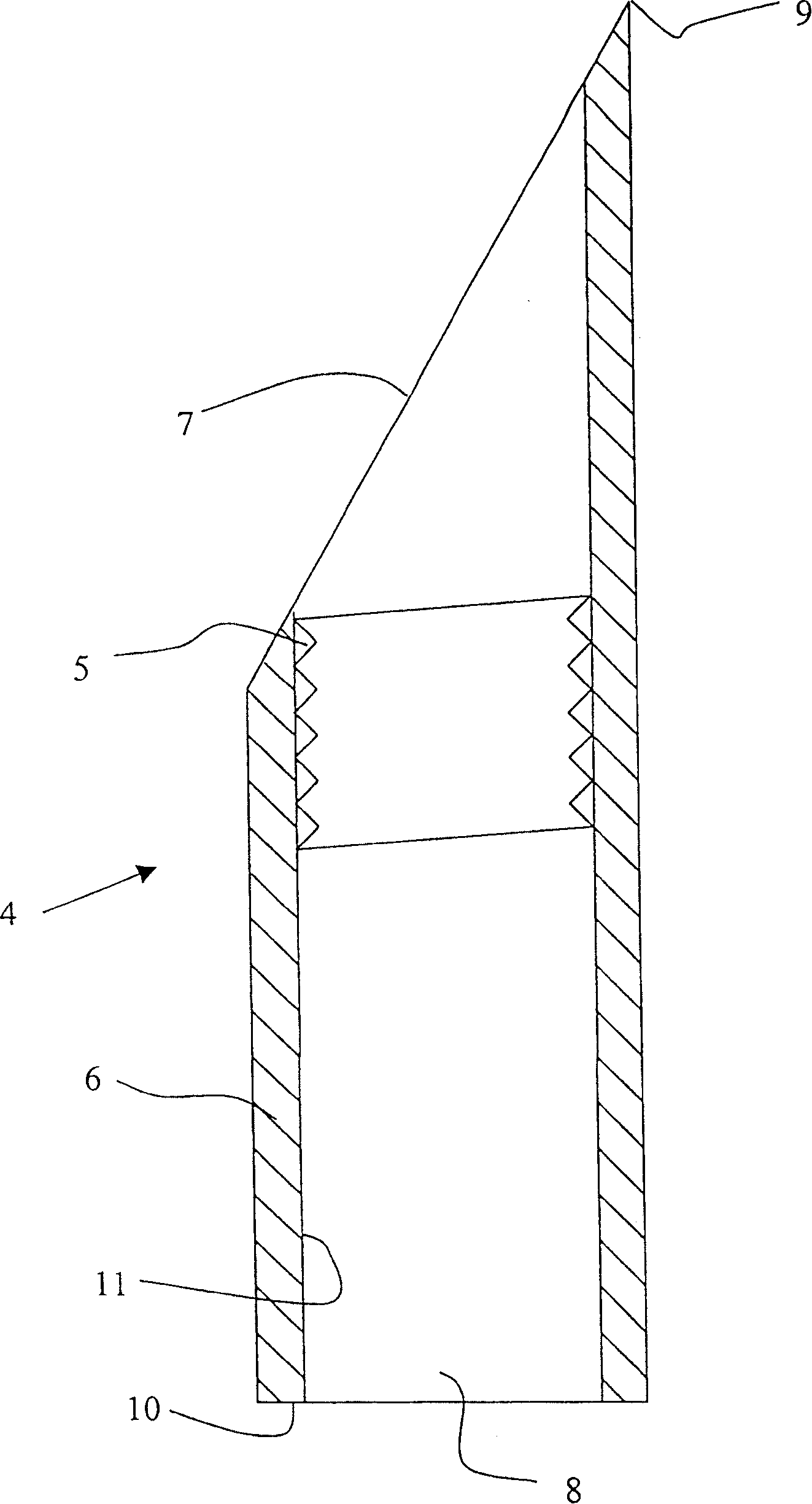
[0030] figure 2 You can see the leaf root 3 more closely in figure 2 I...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com