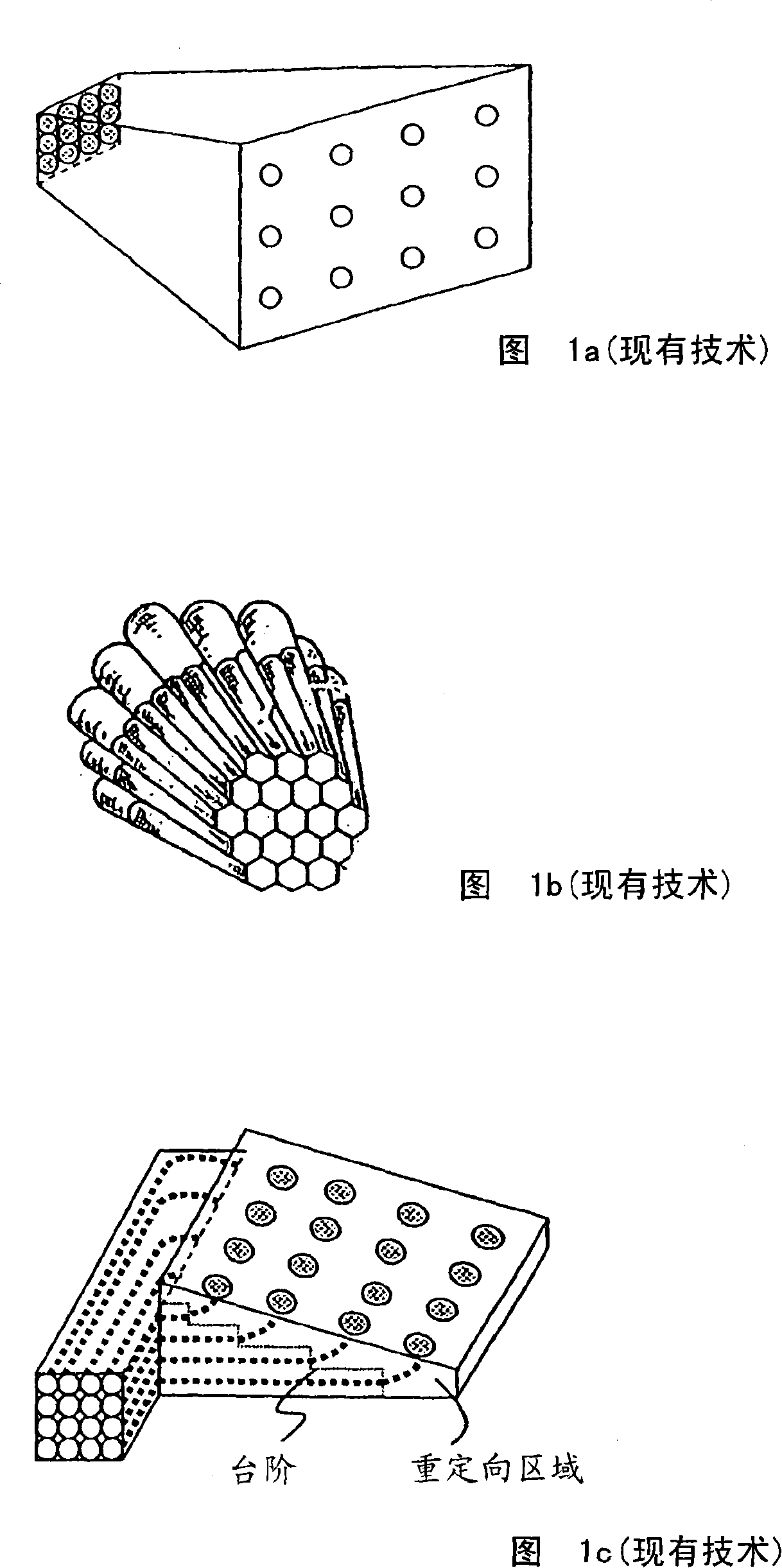
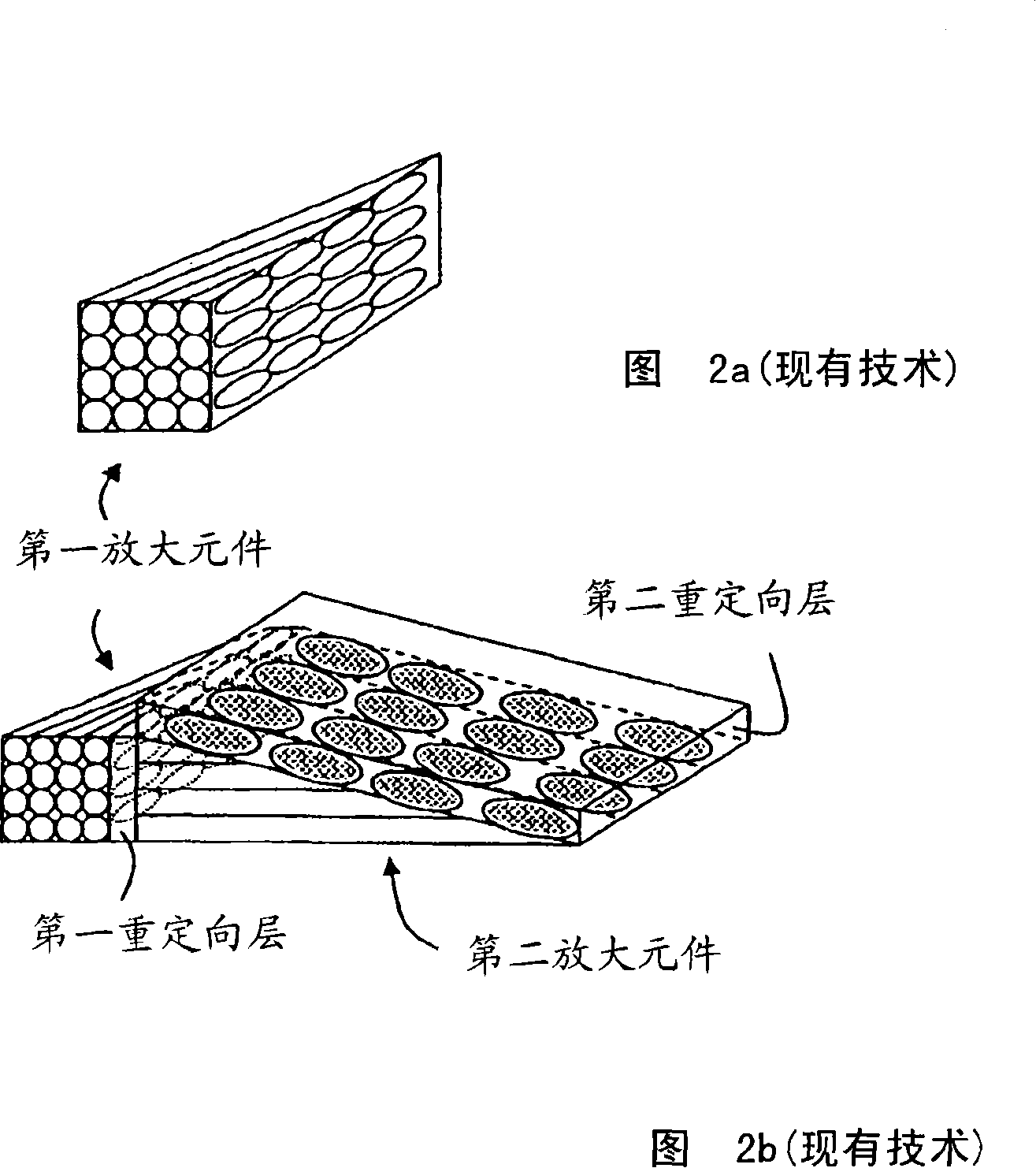
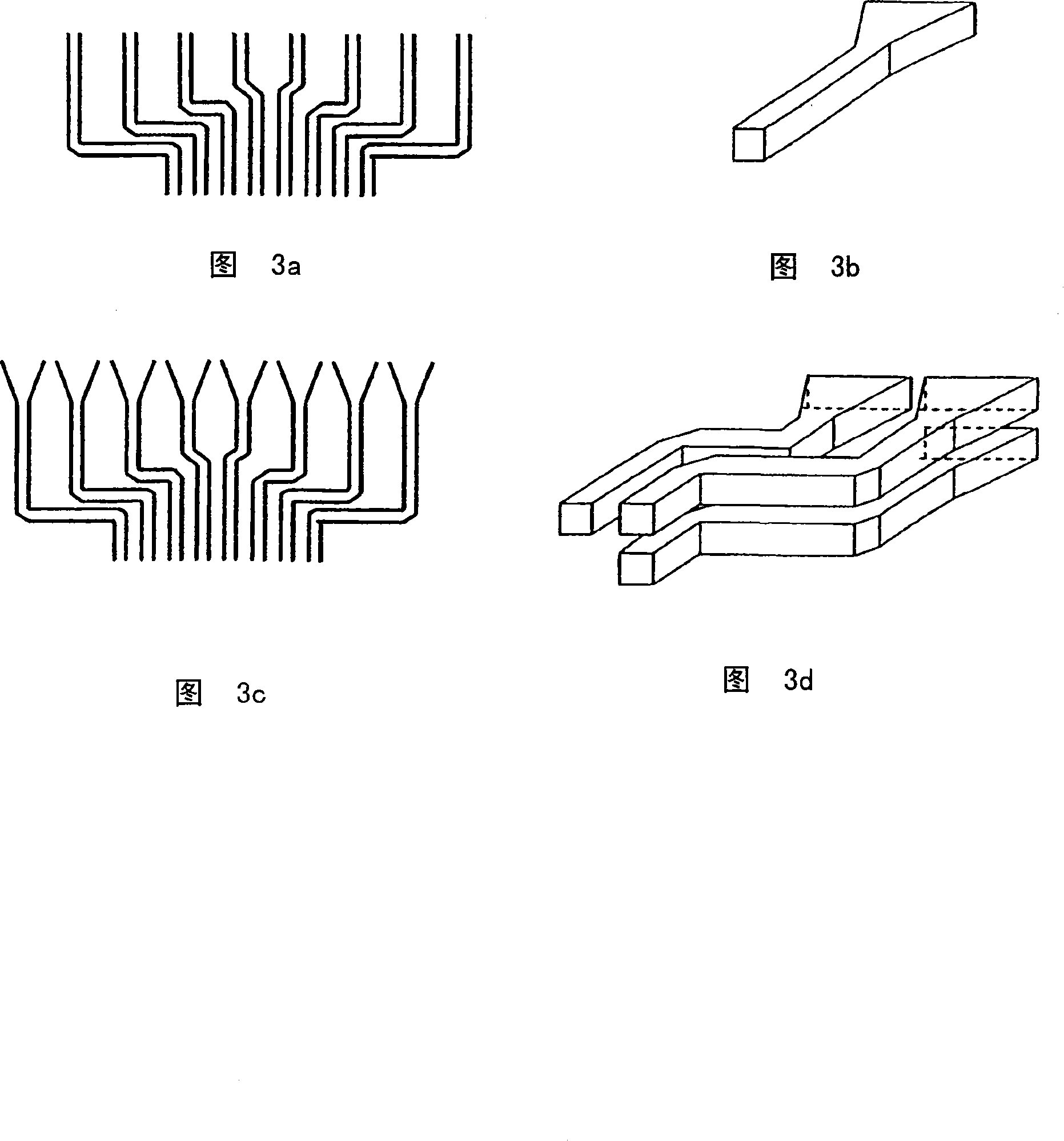
Device and method for optical resizing
A technology for adjusting device and size, applied in the field of optics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0294] Optical Loss Optimization
[0295]The transparency of the device is affected by several loss mechanisms: (i) propagation loss in the device; (ii) bending and tapering loss in the device; (iii) coupling loss between the optical elements of the device; and (iv) at the interface reflection loss.
[0296] For polymeric waveguides, the lowest reported propagation was obtained using polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) and deuterated polyfluoromethacrylate (d-PFMA) materials that do not contain C–H vibration-absorbing bonds. loss. In the visible region, values below 0.001 dB / cm have been reported for bulk materials [L. Hornak, "Polymers for lightwave and integrated optics," Marcel Dekker, Inc, 1992]; at λ = 0.68 μm wavelength Next, for multimode waveguides, 0.01dB / cm is reported [Yoshimura et al., "Low loss polymeric optical waveguides fabricated with Deuterated Polyfluoromethcrylate," J.Lightwave Tech, vol16, 1030-1037, 1998], and for singlemode waveguides, At wavelength λ = 1...
example 2
[0309] Field of view optimization
[0310] According to a preferred embodiment of the present invention, device 30 is designed and constructed to provide sized light at a predetermined field of view. One way to achieve a predetermined field of view for device 30 is to judiciously choose waveguide parameters for the optical elements from which device 30 outputs light (eg, element 34 ). According to a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the waveguide refractive index and numerical aperture (N.A.) are selected to satisfy the formula: N.A.=sinα=√(n 1 2 -n 2 2 ), where n 1 and n 2 are the refractive indices of the core and cladding, and α is half the diffraction angle. For a waveguide terminated in a linear taper, the effective numerical aperture is N.A / M, where M is the tapering magnification [Peli et al., supra]. In this way, an effective field of view can be selected by adjusting the taper shape, ie using a non-linear taper shape. In particular, different fiel...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com