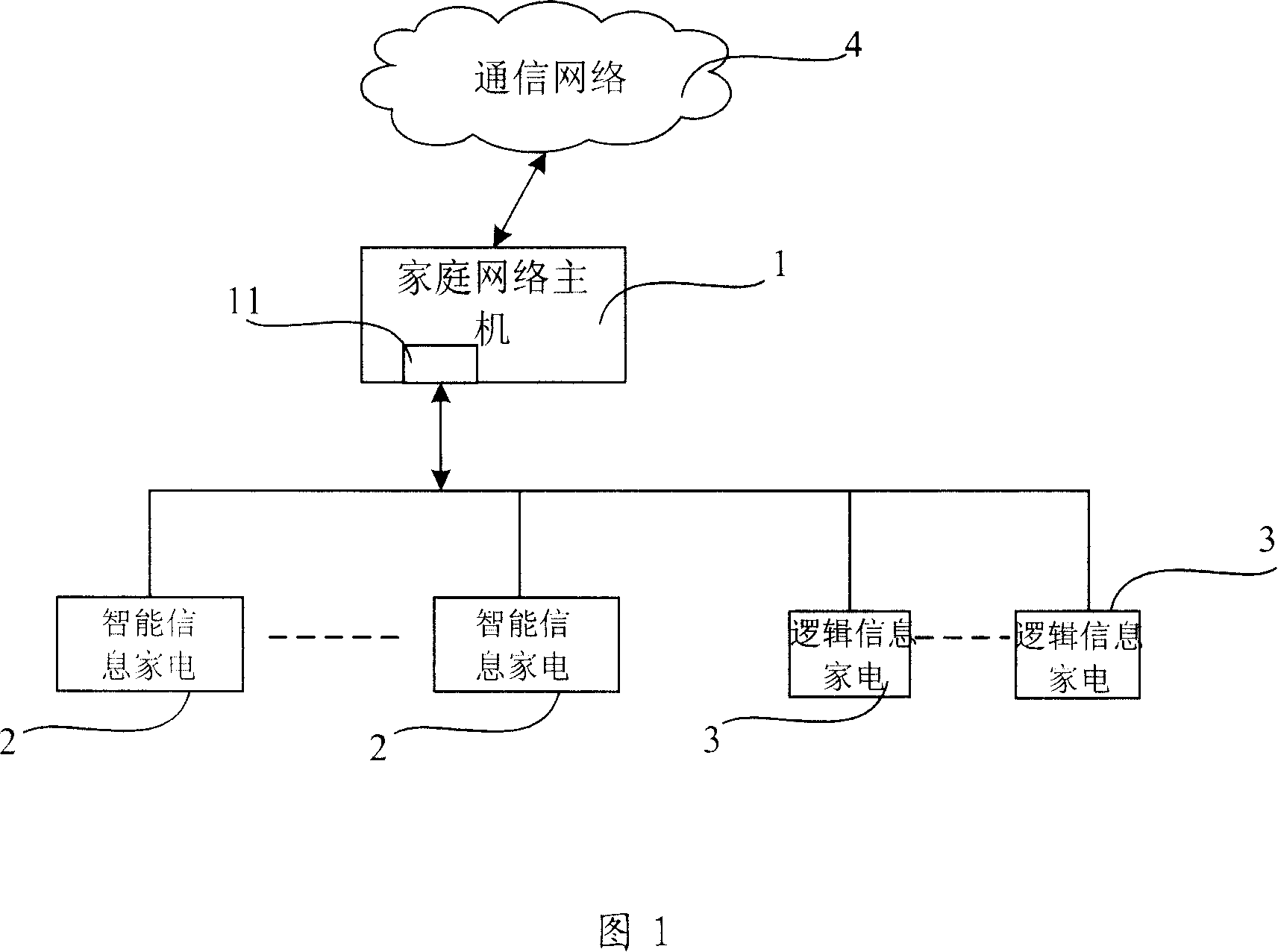
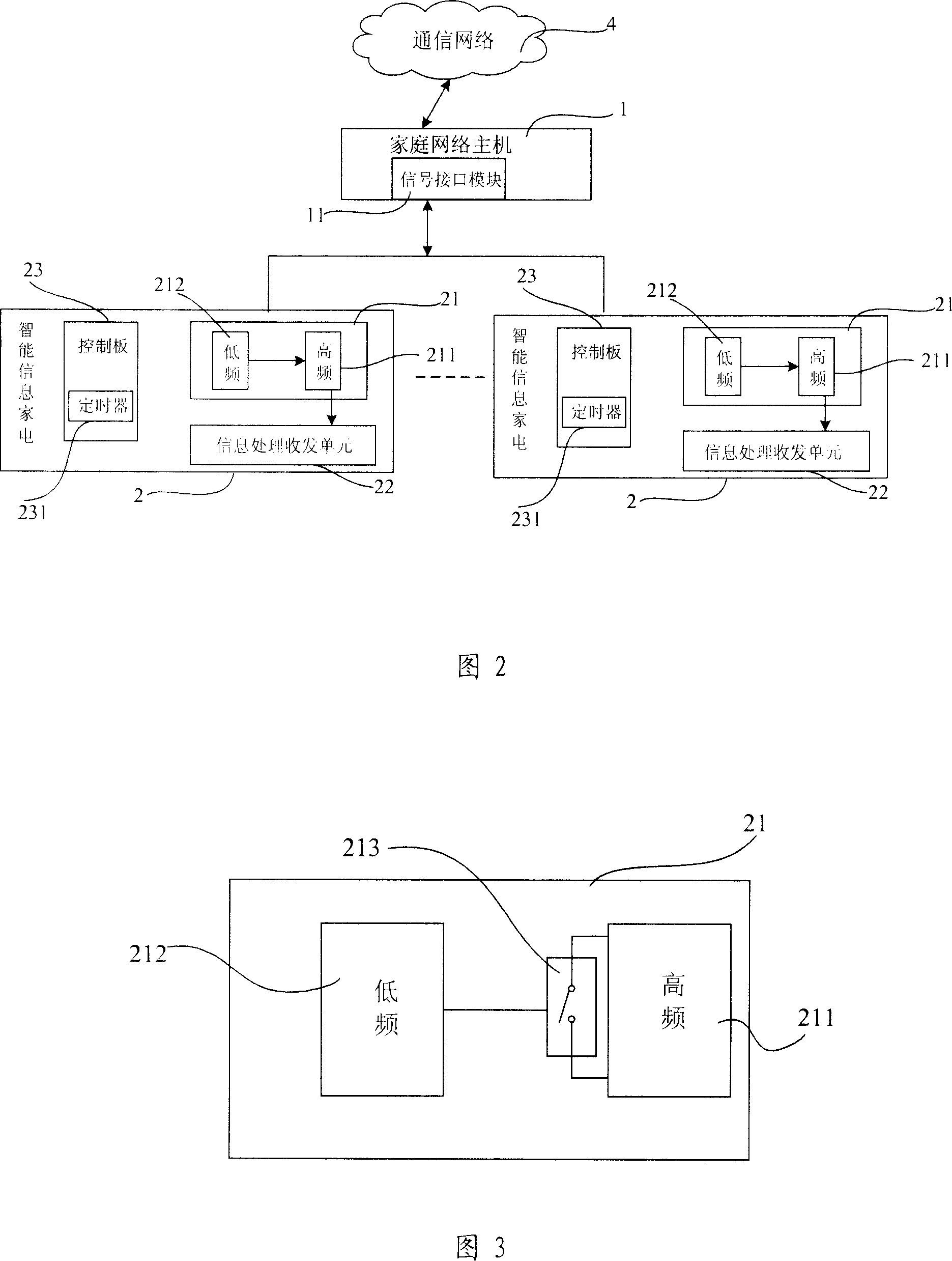
Energy-saving information household appliance network and energy-saving control method
A technology for information home appliances and energy-saving control, applied in home automation networks, energy-saving ICT, data exchange networks, etc., can solve problems such as wasting electric energy and damage to important components, reduce energy consumption, reduce the probability of damage, and have good practical application value effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
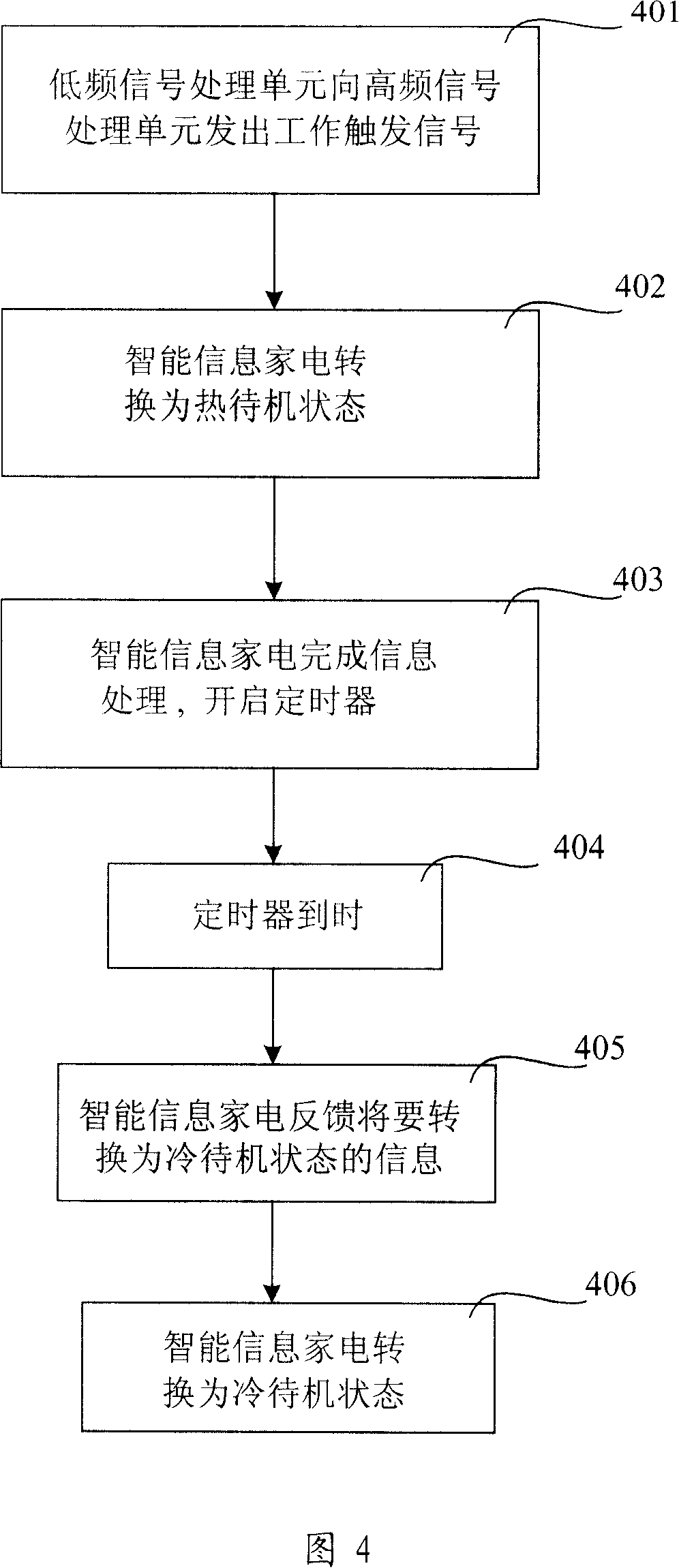
[0036] As shown in Figure 4, this embodiment at least includes the following steps:
[0037] Step 401. During the normal operation of the energy-saving information appliance network of the present invention, when a certain smart information home is in a cold standby state, the low-frequency signal processing unit of the smart information home receives the low-frequency signal from the signal interface module installed in the home network host. After the trigger signal, send a work trigger signal to the high-frequency signal processing unit in the smart information home;
[0038] Step 402, the high-frequency signal processing unit triggers the smart information appliance through the information processing transceiver unit in the smart information appliance, so that the smart information appliance switches from a cold standby state to a hot standby state. At this time, the smart information home appliance can receive operation instructions from the home network host;
[0039] S...
no. 2 example
[0046] Fig. 5 shows another preferred embodiment of the energy-saving control method of the present invention, which executes the following steps:
[0047] Step 501, when the energy-saving information home appliance network is working normally, when the low-frequency signal processing unit of a certain smart information home receives a low-frequency trigger signal from the signal interface module installed in the home network host;
[0048] Step 502, judging whether the smart information appliance is currently powered off, if yes, then end; if not, then execute step 503;
[0049] Step 503, judging whether the smart information appliance is currently in a hot standby state, if yes, execute step 506; if not, continue to execute step 504;
[0050] Step 504, the low-frequency signal processing unit sends a work trigger signal to the high-frequency signal processing unit in the smart information home;
[0051] Step 505: After the high-frequency signal processing unit is triggered,...
no. 3 example
[0064] Figure 6 shows another preferred embodiment of the energy-saving control method of the present invention. The difference between this embodiment and the embodiment shown in Figure 5 is that step 501 is the first power-on signal, and this embodiment performs the following steps:
[0065] Step 601, the smart information appliance receives the first power-on signal;
[0066] Step 602, the smart information appliance enters the hot standby state;
[0067] Step 603, the smart information appliance starts a timer, and waits for an operation instruction;
[0068] Step 604, the smart information appliance judges whether it has received an operation instruction for information processing, if yes, execute step 605; if not, execute step 612;
[0069] Step 605, judging whether a shutdown signal is received, if yes, then 610; if not, then execute step 606;
[0070] Step 606, the smart information appliance clears the timer;
[0071] Step 607: The smart information appliance compl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com