Hewlett packard development co (us)
A technology of electromagnetic mode and quantum state, which is applied in quantum computers, nanotechnology for information processing, instruments, etc., and can solve the problems of wasting photons and auxiliary photons
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
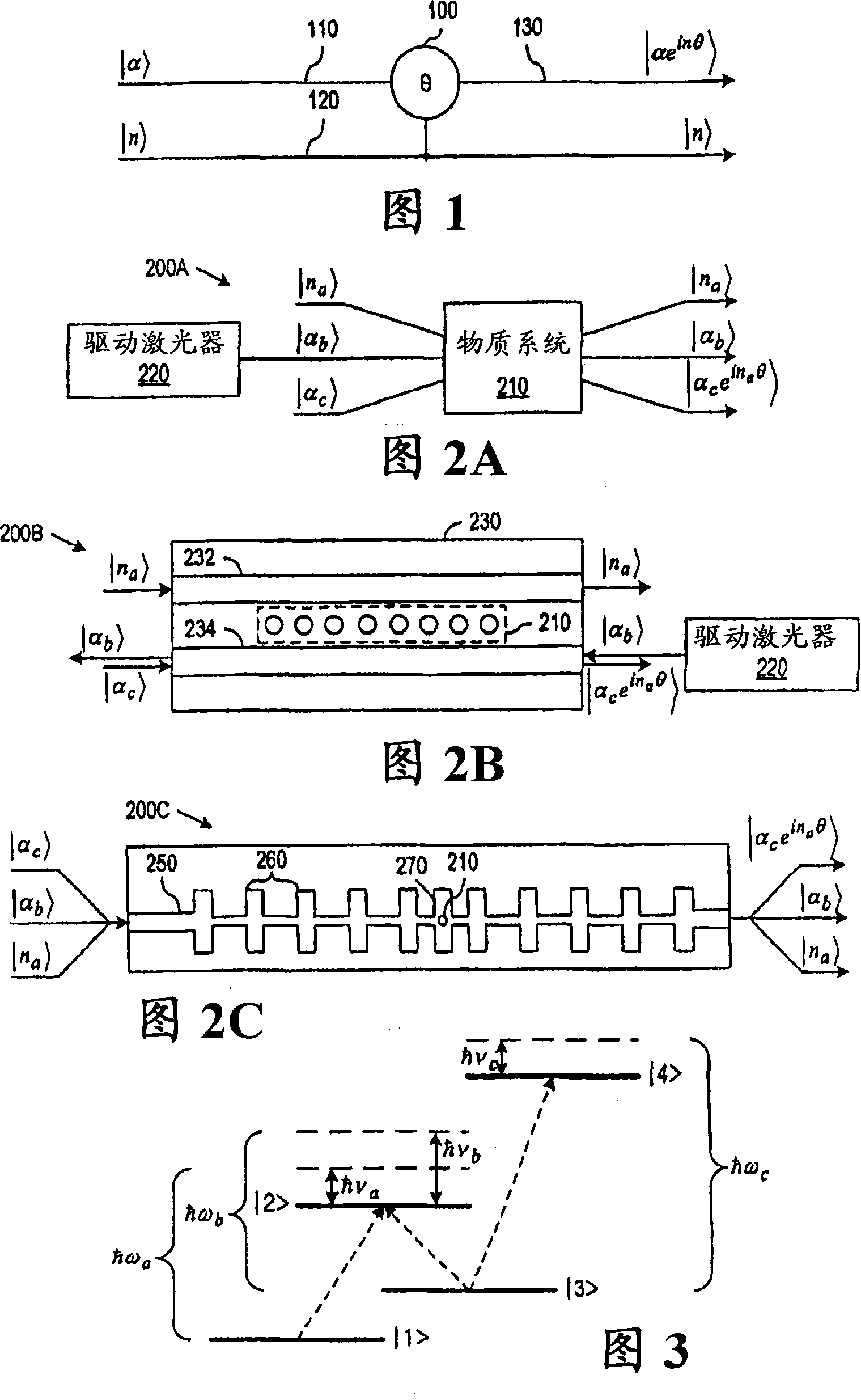
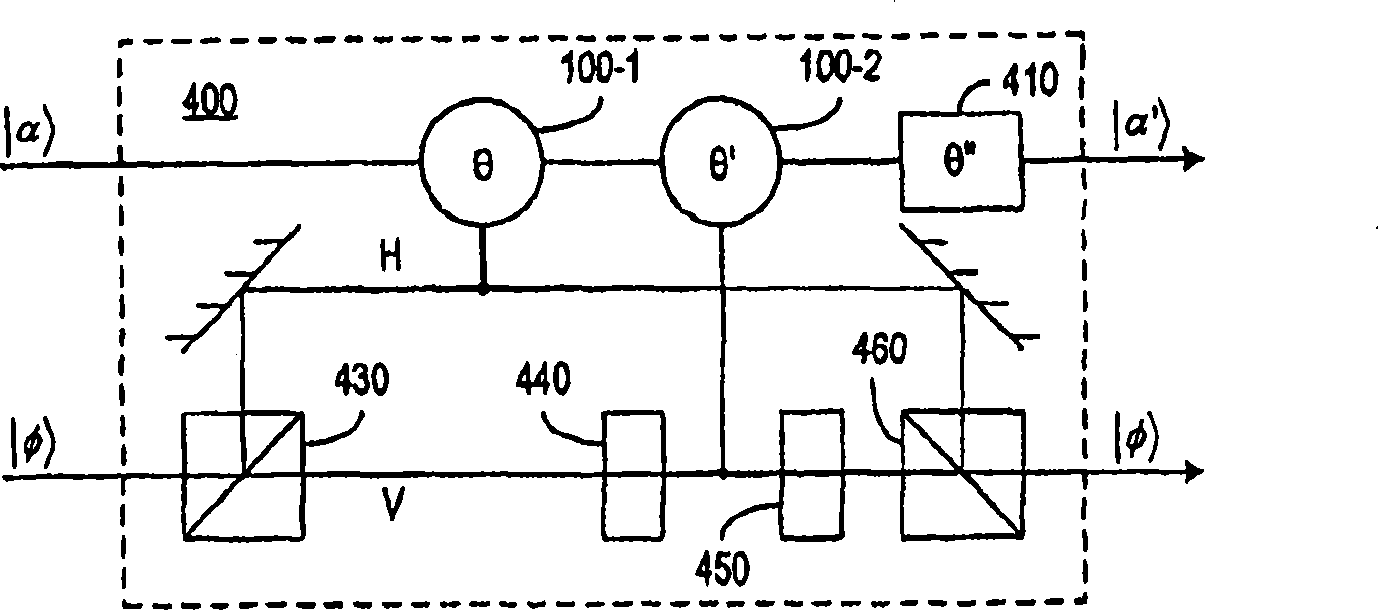
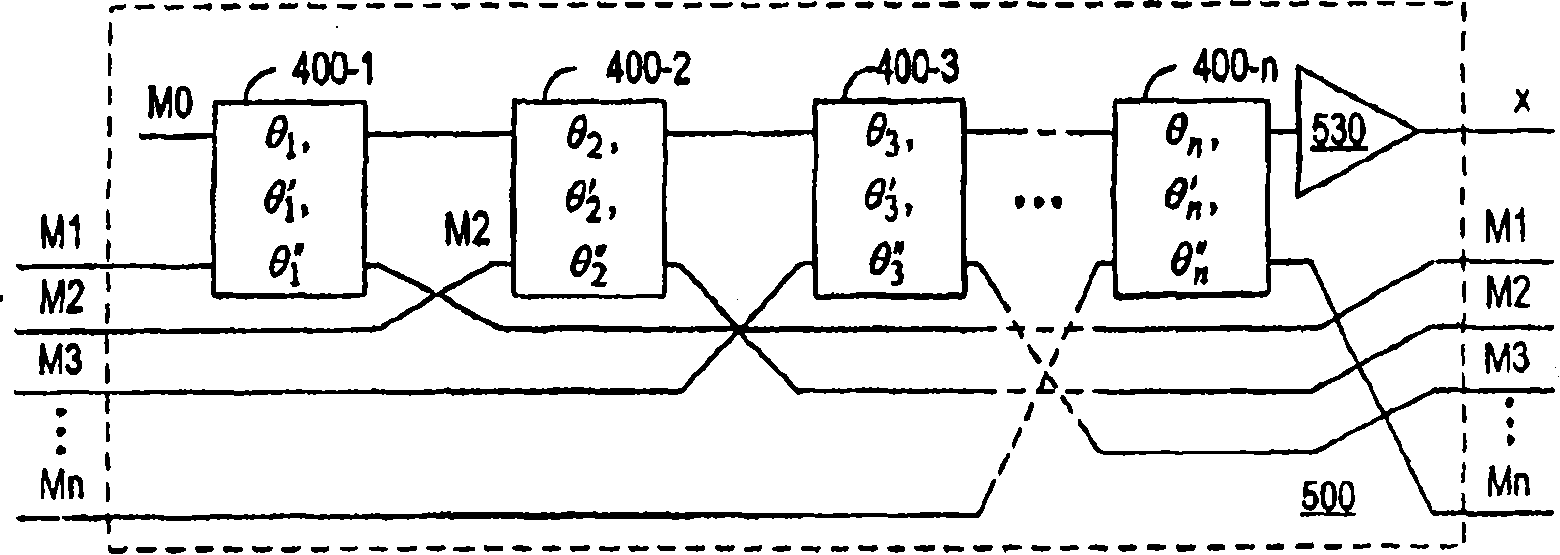
[0021] According to one aspect of the present invention, nonlinear optical elements can efficiently perform quantum information processing tasks such as controlled phase shifting, non-destructive state detection, non-destructive Bell state analysis, heralded state preparation, quantum non-destructive Destructive coding and basic quantum gate operations. Direct exploitation of optical nonlinearities can amplify small phase shifts and exploit feed-forward systems in a near-deterministic manner with high operating efficiency.
[0022] Preferred embodiments of the present invention exploit nonlinear effects such as Electromagnetic Induced Transparency (EIT) to produce measurable phase shifts and can be achieved using waveguides and interaction sites such as EIT atoms, which can utilize nanoscale structures to manufacture. For example, R.G.Beausoleil, W.J.Munro and T.P.Spiller's "Coherent Particle Number Conversion in Quantum Information "Applications of CoherentPopulation Transf...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com