Variable valve mechanism
A valve mechanism and variable technology, applied in the direction of mechanical equipment, engine components, machines/engines, etc., can solve the problems of increasing contact load between gears, acceleration loss, etc., to improve responsiveness, suppress current consumption, and reduce drive torque Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
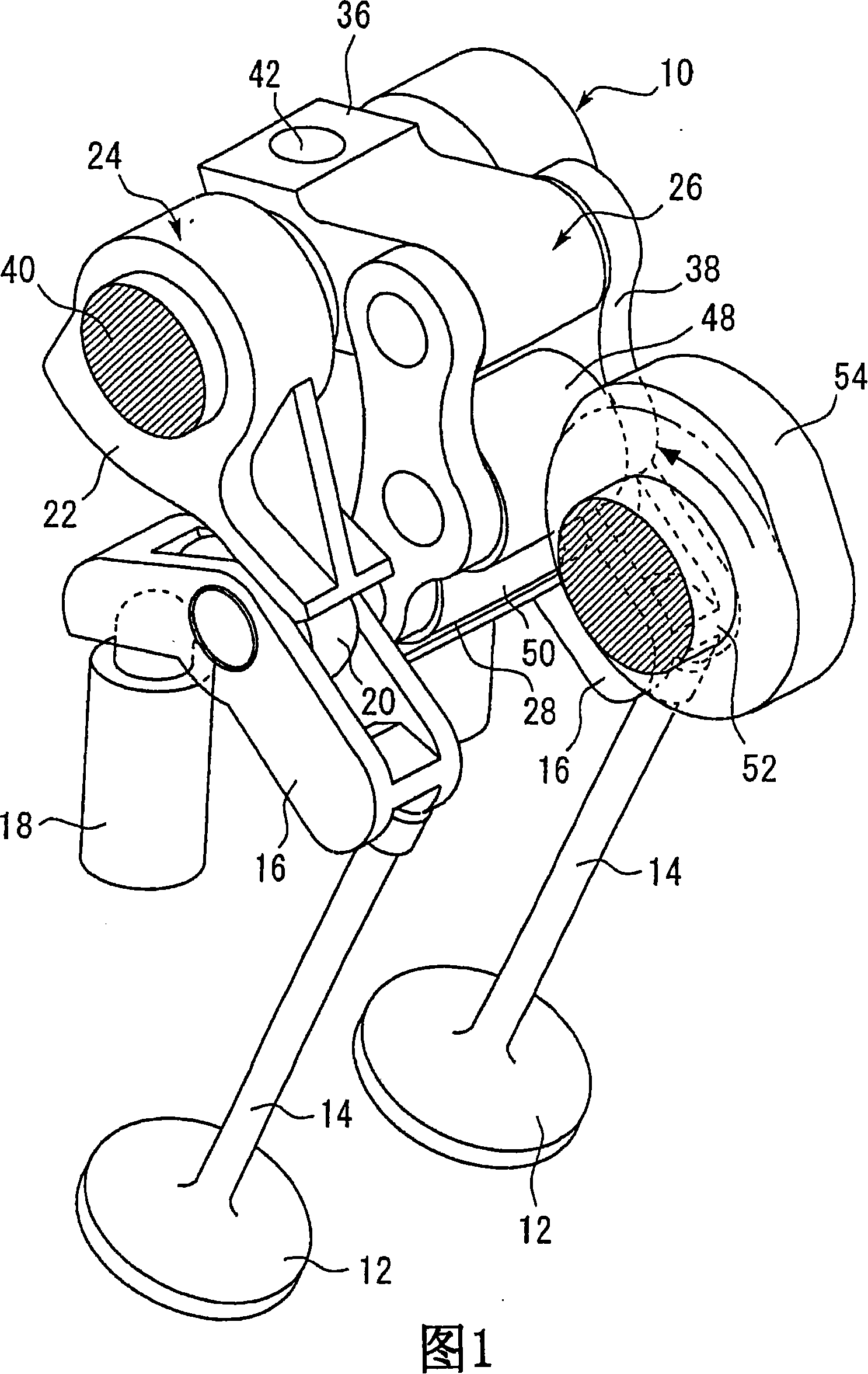
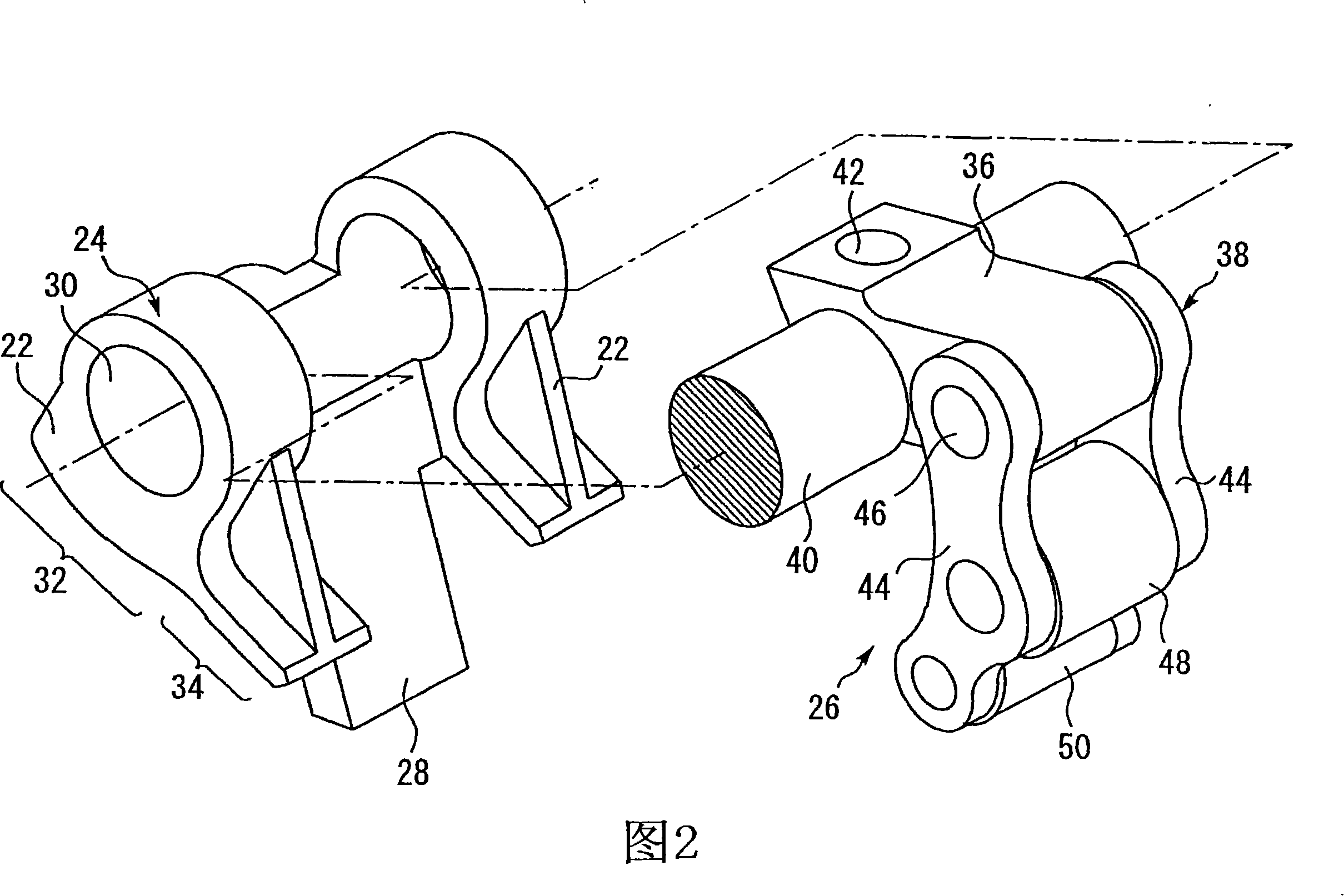
[0051] FIG. 1 is a perspective view of main parts of a variable valve train 10 according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. The variable valve mechanism shown in FIG. 1 is a mechanism for driving a valve body of an internal combustion engine. In this case, each cylinder of the internal combustion engine has two intake valves and two exhaust valves. Furthermore, the structure shown in FIG. 1 functions as a mechanism for driving two intake valves or two exhaust valves arranged on a single cylinder.
[0052] The structure shown in FIG. 1 has two valve bodies 12 functioning as intake valves or exhaust valves. Valve shafts 14 are respectively fastened to the valve body 12 . The end of the valve shaft 14 is connected to a pivot arranged at one end of the rocker arm 16 . The urging force of the valve spring 62 described below acts on the valve shaft 14 , and the rocker arm 16 is urged upward by the valve shaft 14 receiving this urging force. The other end of the rocker arm...
Embodiment approach 2
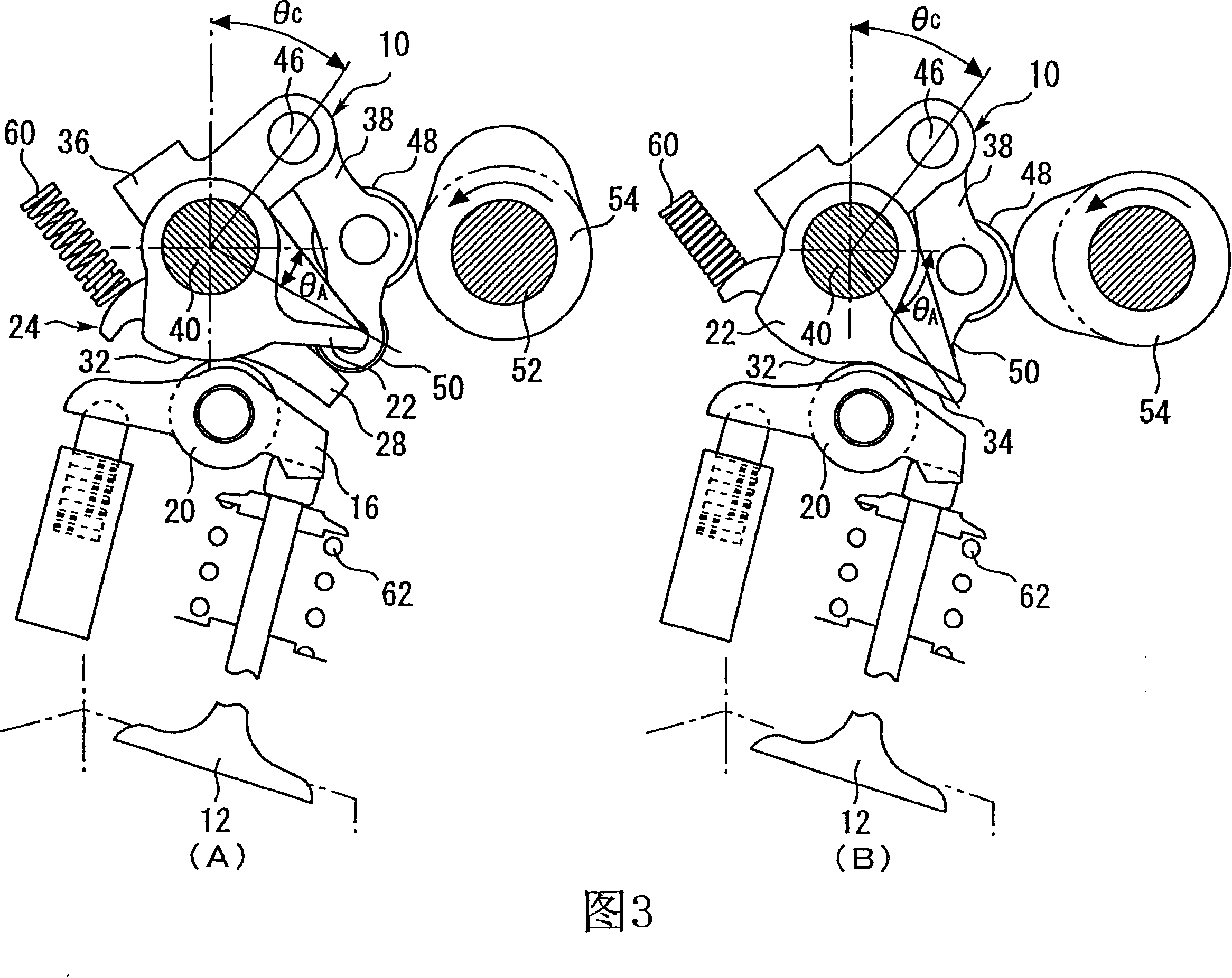
[0102] Next, Embodiment 2 of the present invention will be described. FIG. 9 is a schematic diagram for explaining the variable valve train 10 according to the second embodiment. The basic structure of the variable valve mechanism 10 of the second embodiment is the same as that of the first embodiment.
[0103] As in the first embodiment, assist springs 64 for reducing the driving torque of the control shaft 40 are provided on the cylinders No. 1 to No. 4 . In Embodiment 2, the urging force of each auxiliary spring 64 is set to a different value in consideration of the deformation of the control shaft 40 .
[0104] As described in Embodiment 1, the urging forces of the lost motion spring 60 and the valve spring 62 act on the control shaft 40 in the same rotational direction. Since one lost motion spring 60 and two valve springs 62 are provided for one cylinder, the loads generated by these springs act on the control shaft 40 common to each cylinder.
[0105] Therefore, when...
Embodiment approach 3
[0121] Next, Embodiment 3 of the present invention will be described. The basic structure and operation of the variable valve mechanism 10 according to the third embodiment are the same as those of the first embodiment described with reference to FIGS. 1 to 4 .
[0122] FIG. 11 is a diagram for explaining a variable valve mechanism 10 according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention. Specifically, FIG. 11(A) is a plan view showing the variable valve mechanism 10, and FIG. 11(B) is a side view showing the mechanism as viewed along the arrow B shown in FIG. 11(A). In addition, FIG. 11(C) is a sectional view obtained by cutting the main part of the variable valve mechanism along the C-C section shown in FIG. 11(B).
[0123] The structure shown in FIG. 11 includes a cylinder head 80 of an internal combustion engine. The cylinder head 80 rotatably holds the control shaft 40 via a control shaft bearing (not shown). Although illustration is omitted in FIG. 11 , the structure of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com