Self-adapted adjustment method for transmission rate of transport layer in wireless self-organized network
A wireless self-organizing and self-adaptive adjustment technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve problems such as increasing network load, increasing conflict and congestion, and having no relevant reports
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] The embodiments of the present invention are described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings: this embodiment is implemented on the premise of the technical solution of the present invention, and detailed implementation methods and specific operating procedures are provided, but the protection scope of the present invention is not limited to the following the described embodiment.
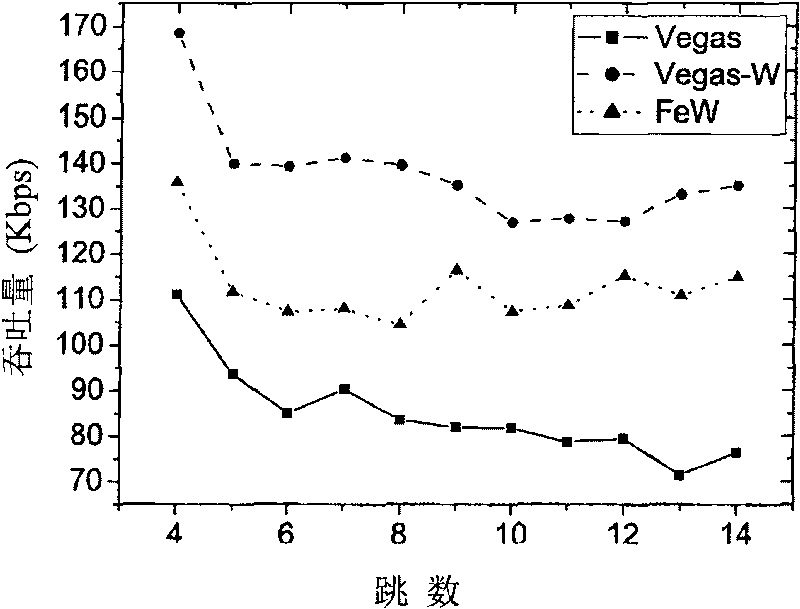
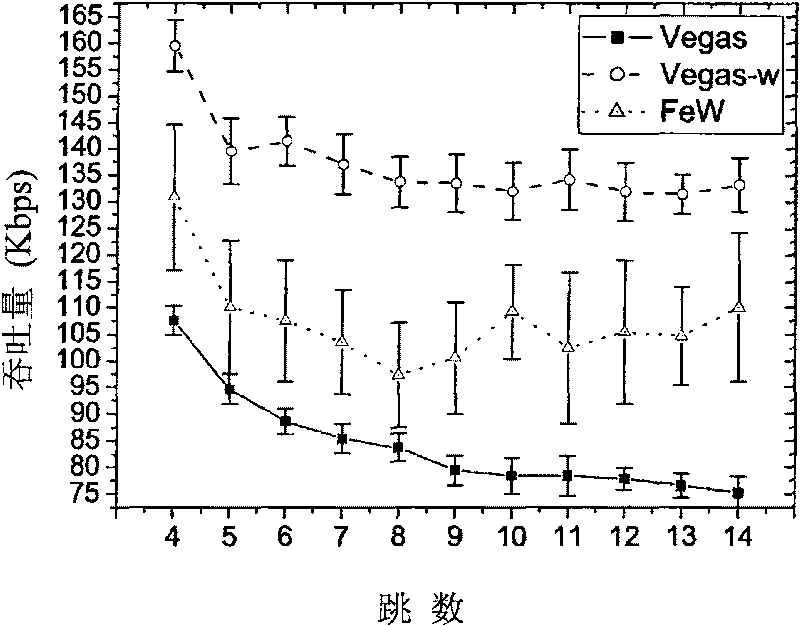
[0025] The simulation environment parameters of this embodiment are set as follows: 802.11 is used as the MAC layer protocol, the channel bandwidth is 2Mbps, the transmission distance is 250m, the interference distance is 500m, the distance between adjacent nodes is 200m, and the packet length is 1024 bytes. The parameters are set as follows: window increase 1 / W threshold α=1; window decrease 1 / W threshold β=3; window decrease threshold γ=1; window decrease ratio p=1 / 8; threshold N s =10; preset threshold N CA =100; The default confirmation number NS CA =100; timeout ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com