Networking method of TD-SCDMA system multi-frequency point community
A TD-SCDMA, multi-frequency point technology, applied in network planning, power management, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as power resource fragmentation, poor service support capability, and uncontrolled interference of dedicated channels, so as to achieve performance potential, Effect of improving power usage efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
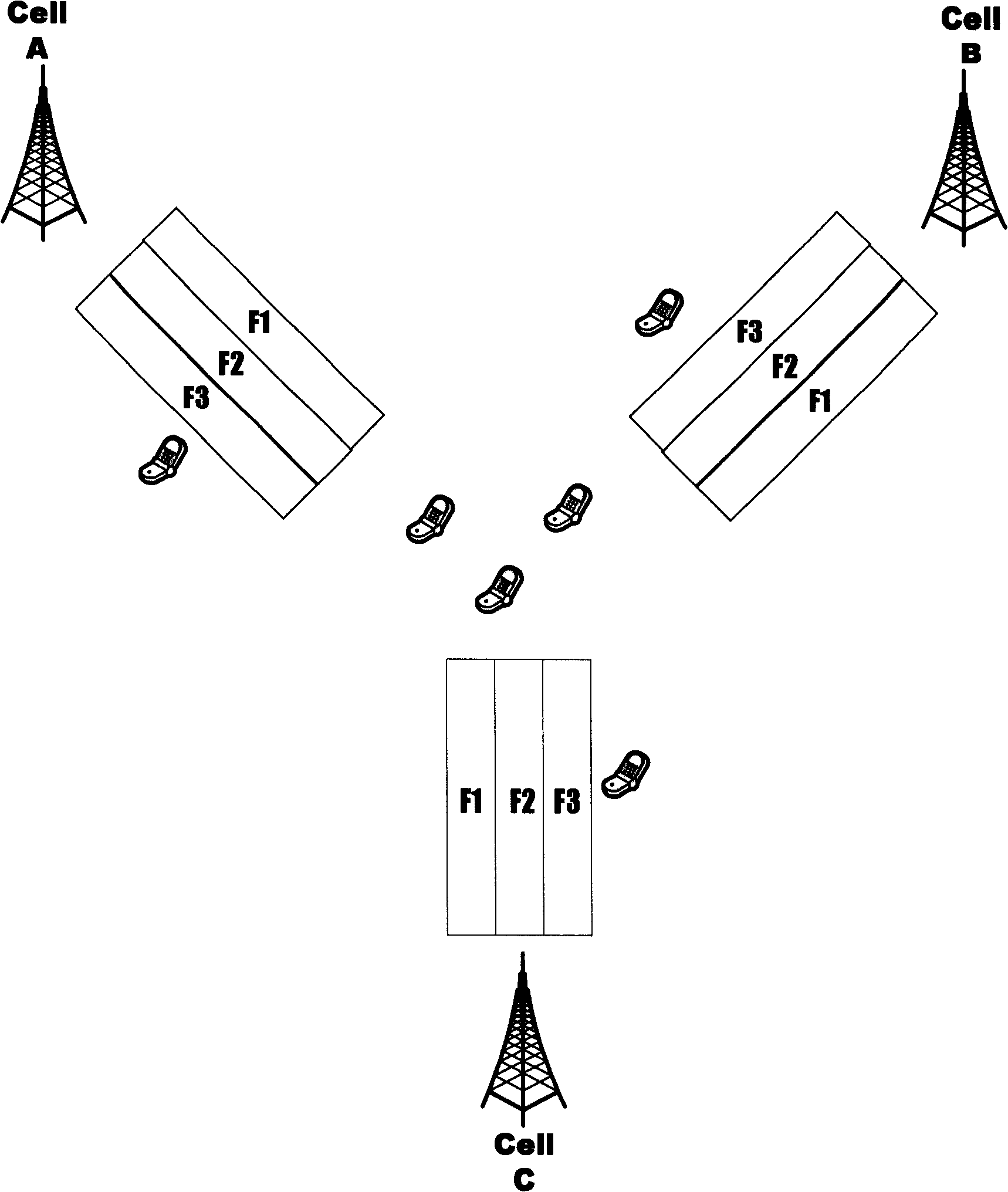
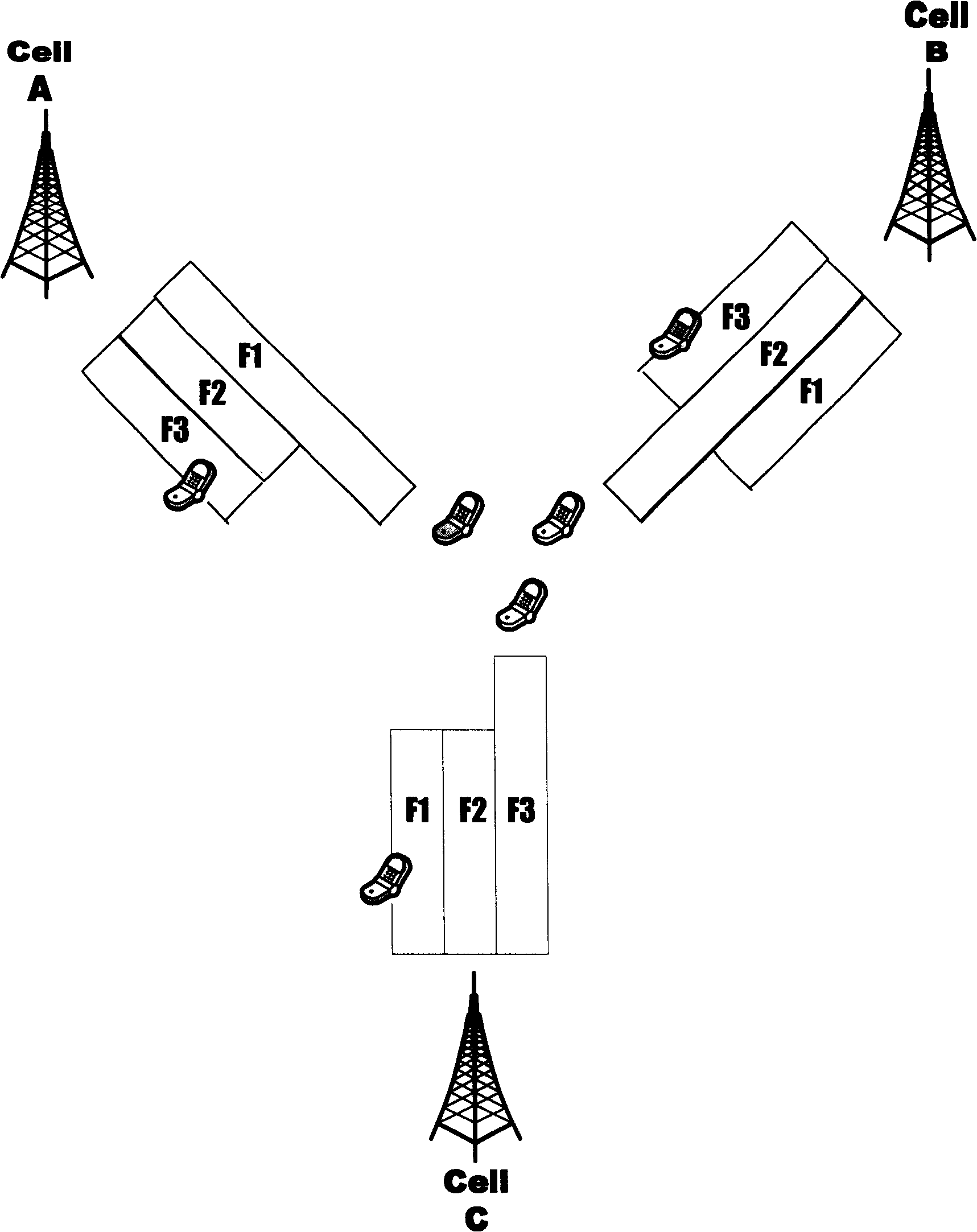
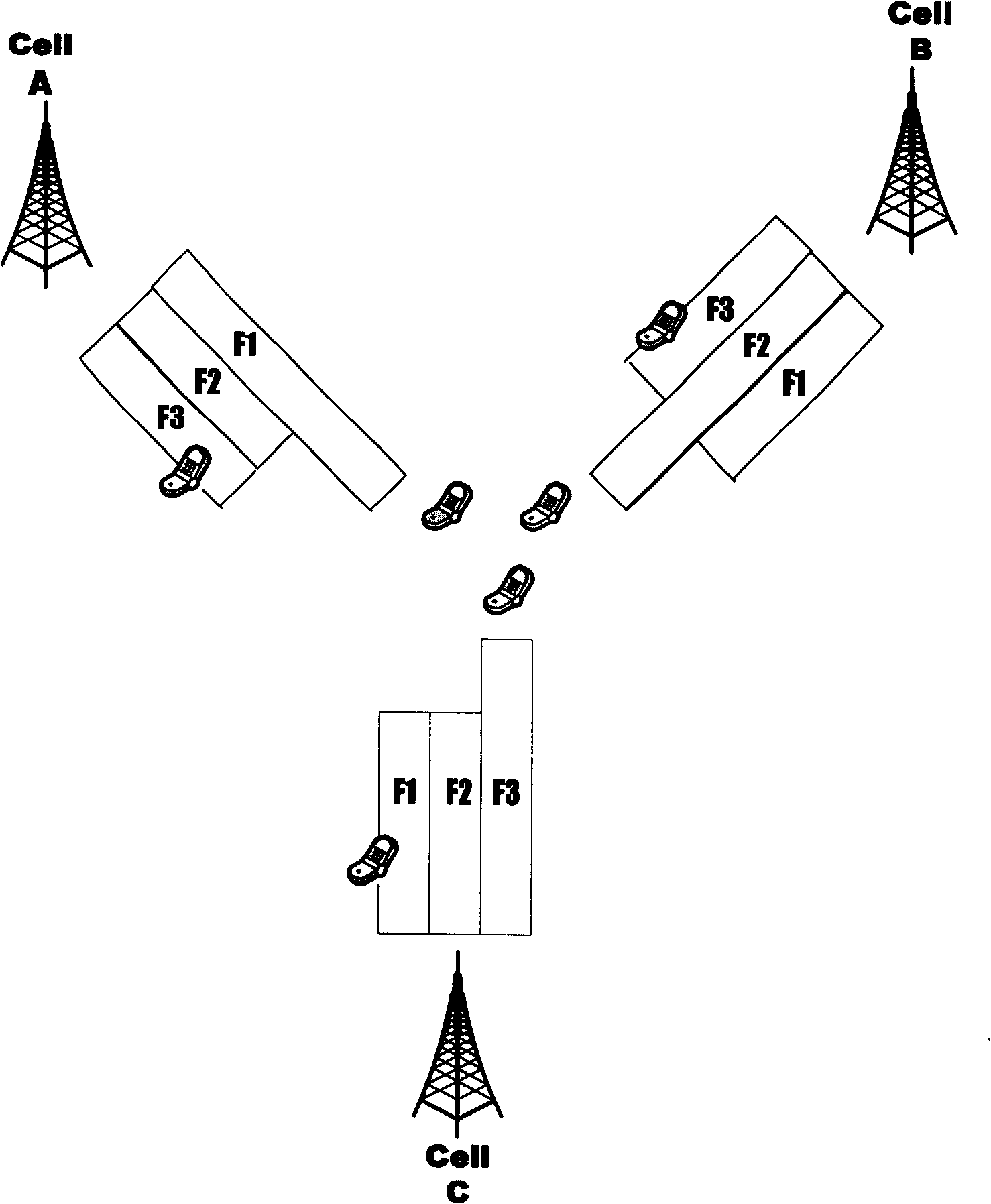
[0013] The method of the present invention will be described in further detail below by introducing a specific embodiment in conjunction with the accompanying drawings. Such as figure 2 Shown: the multi-frequency point cell networking method of the present invention is illustrated by taking N=3 as an example. The system implementing this method includes a network and a terminal. The network includes 3 multi-frequency cells CELL A, CELL B, and CELL C. The service channel of each cell is set up at the main frequency point and / or the secondary frequency point, and the total is F1, For F2 and F3, the adjacent multi-frequency cells select different carriers as the main frequency points, as shown in the figure: the main frequency points of CELL A, CELL B, and CELL C respectively select F1, F2 and F3, and at the same time make any multi-frequency The downlink transmit power of the primary frequency of the frequency cell is always not less than the downlink transmit power of any sec...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com