Electric field driving device and electronic apparatus
A driving type, electric field technology, applied in instruments, nonlinear optics, optics, etc., can solve problems such as display quality deviation, liquid crystal alignment state disorder, and display quality degradation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
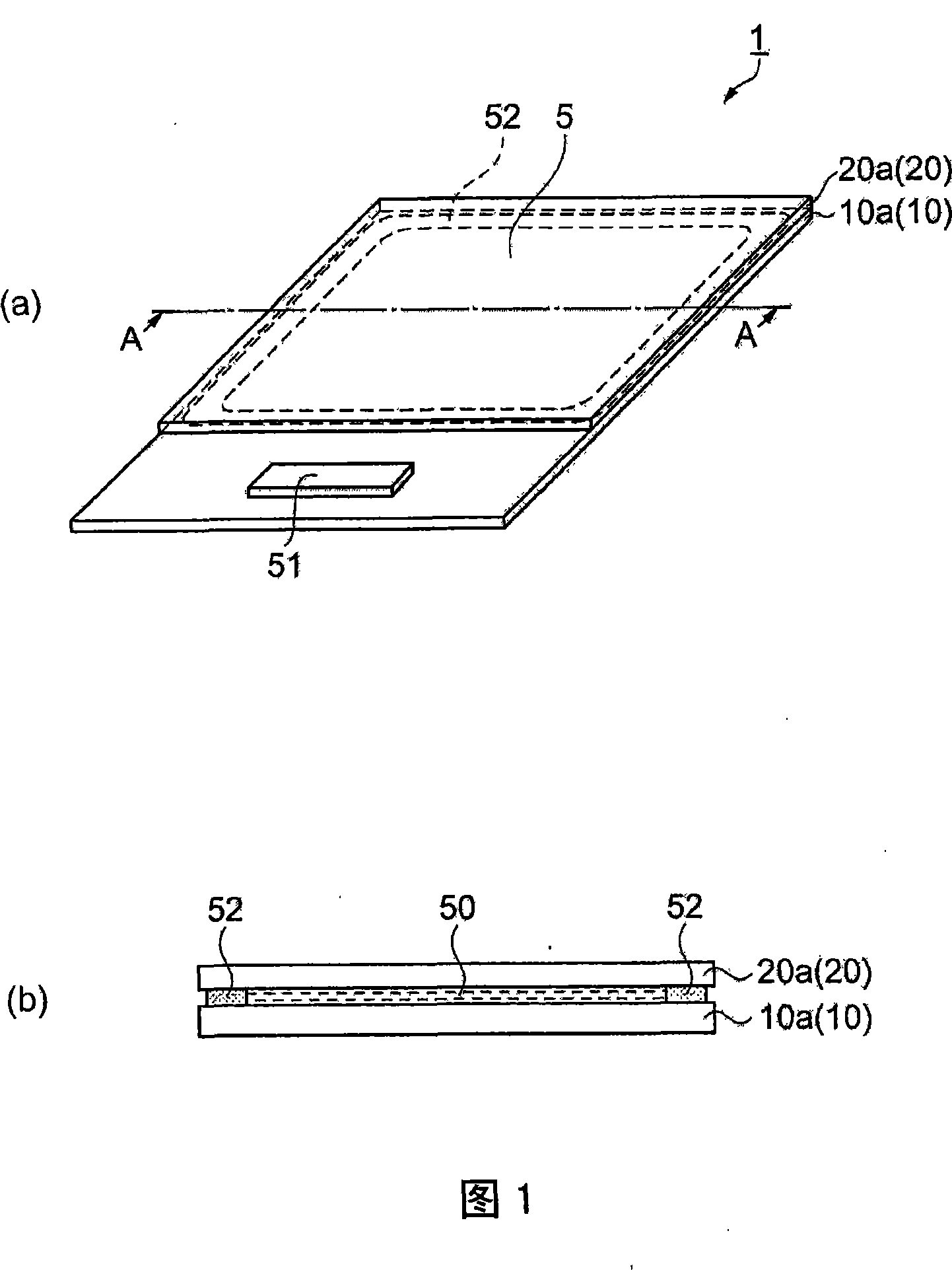
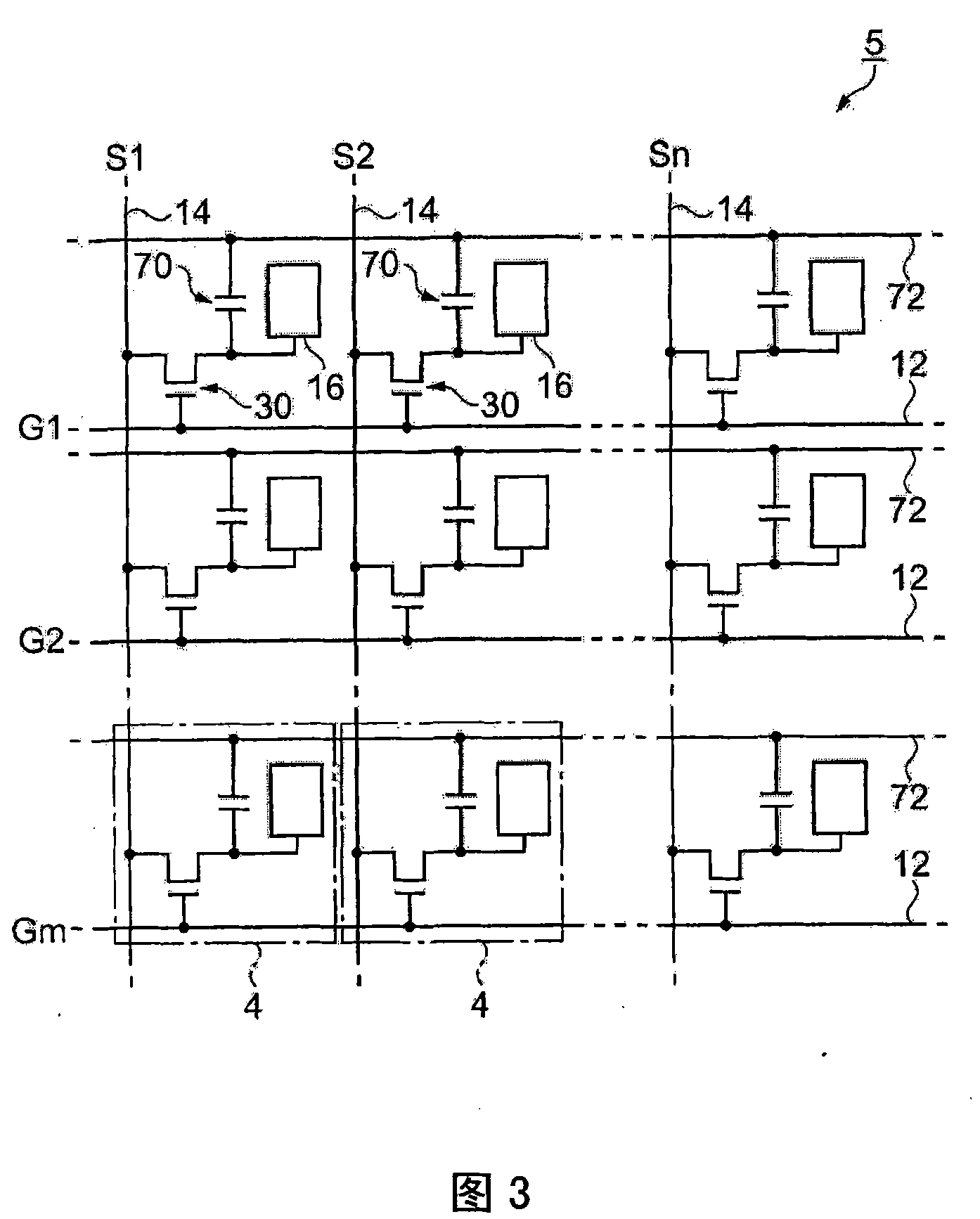
[0069] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of the liquid crystal device 1 as an electric field drive type device, (a) is a perspective view, and (b) is a cross-sectional view taken along line A-A in (a). The liquid crystal device 1 has an element substrate 10 a and a counter substrate 20 a that are laminated to face each other via a frame-shaped sealing material 52 . The element substrate 10 a includes a glass substrate 10 as one substrate, and the counter substrate 20 a includes a glass substrate 20 . A liquid crystal 50 is sealed in a space surrounded by the element substrate 10 a , the counter substrate 20 a , and the sealing material 52 . The element substrate 10a is larger than the opposing substrate 20a, and a part thereof is attached in a state protruding from the opposing substrate 20a. On this protruding portion, a drive IC 51 for driving the liquid crystal 50 is mounted. The liquid crystal 50 corresponds to "a substance driven by an electric field generated by a po...
no. 2 approach
[0092] Next, a second embodiment will be described. The liquid crystal device 1 of this embodiment is based on the first embodiment, except that the arrangement of the common electrodes 26 and the slits 27 and the configuration of the pixels 3 are changed, and other points are the same as those of the first embodiment. In each of the drawings used in the following description, the same reference numerals are attached to the same elements as those of the first embodiment, and description thereof will be omitted.
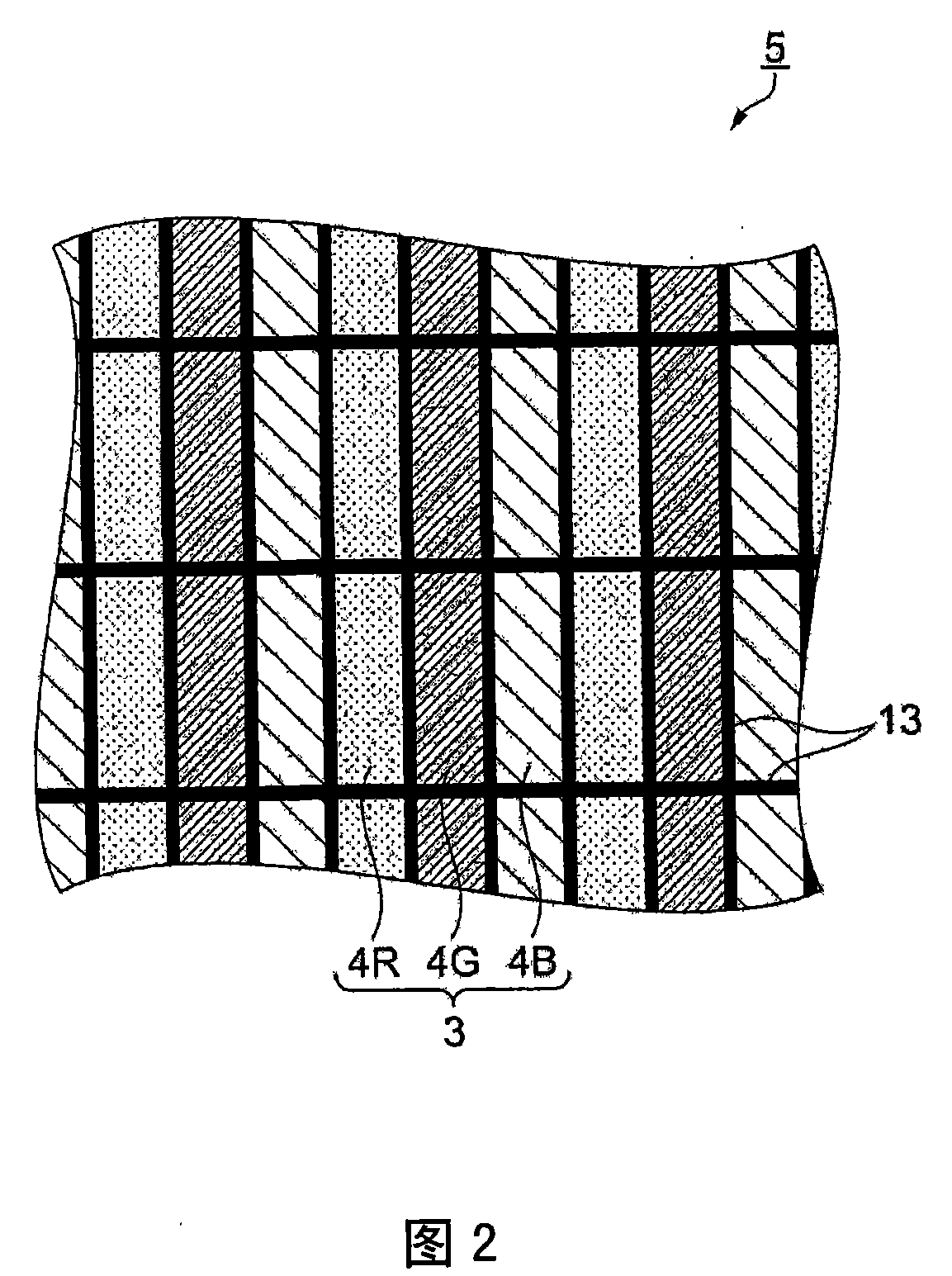
[0093] Figure 8 It is a plan view extracting and showing a portion corresponding to two adjacent pixels 3 in the pixel region 5 of the liquid crystal device 1 of the present embodiment. The pixels 3 of the present embodiment are composed of four colors arranged along the longitudinal direction of the slit 27. 4 sub-pixels. Specifically, the pixel 3 is composed of sub-pixels 4R, 4G, 4B, and 4C that contribute to the display of red, green, blue, and cyan. Therefore,...
no. 3 approach
[0100] Next, a third embodiment will be described. This embodiment is also based on the first embodiment, and the arrangement of the common electrode 26 and the slit 27 and the configuration of the pixel 3 are changed, and other aspects are the same as the first embodiment.
[0101] Figure 9 It is a plan view extracting and showing a part of the pixel region 5 of the liquid crystal device 1 of the present embodiment. The pixel 3 in this figure is composed of two-color sub-pixels 4 arranged along the longitudinal direction of the slit 27 . Specifically, the pixel 3 is composed of sub-pixels 4R and 4G that contribute to red and green display.
[0102] In the present embodiment, a set of two pixels 3 arranged along the longitudinal direction of the slit 27 is called "pixel block 2". The layout of the pixel region 5 including the pattern of the common electrode 26 and the slit 27 is composed of the pixel block 2 as the minimum unit of repetition.
[0103] Nine strip-shaped po...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com