Multi-rotor wind turbine supported by continuous central driveshaft
A technology for driving shafts and rotors, which is applied in the direction of engines, wind turbines, machines/engines, etc. It can solve the problems of complex support structures, at least effective power output is not important, and achieve cost reduction, small solidity, and high lift-to-drag rate Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
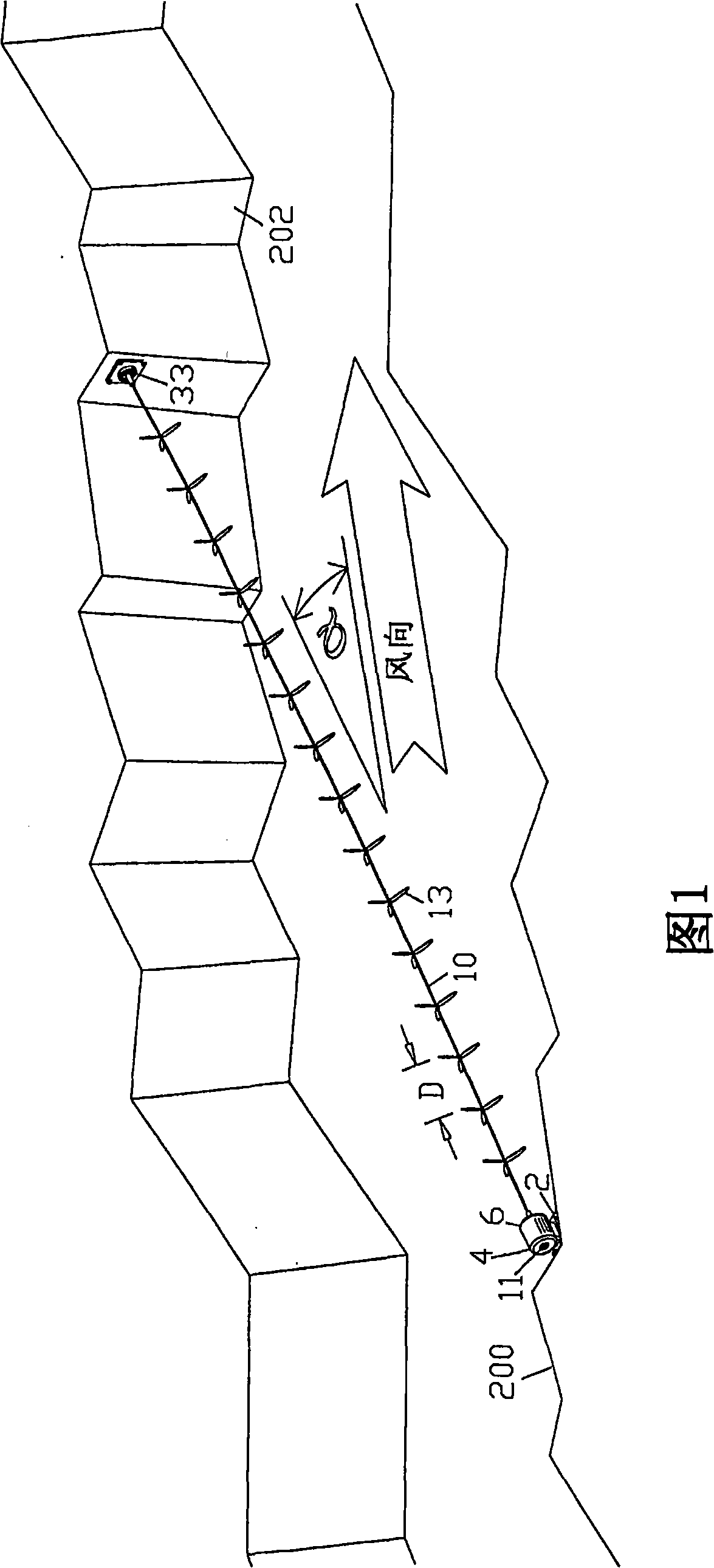
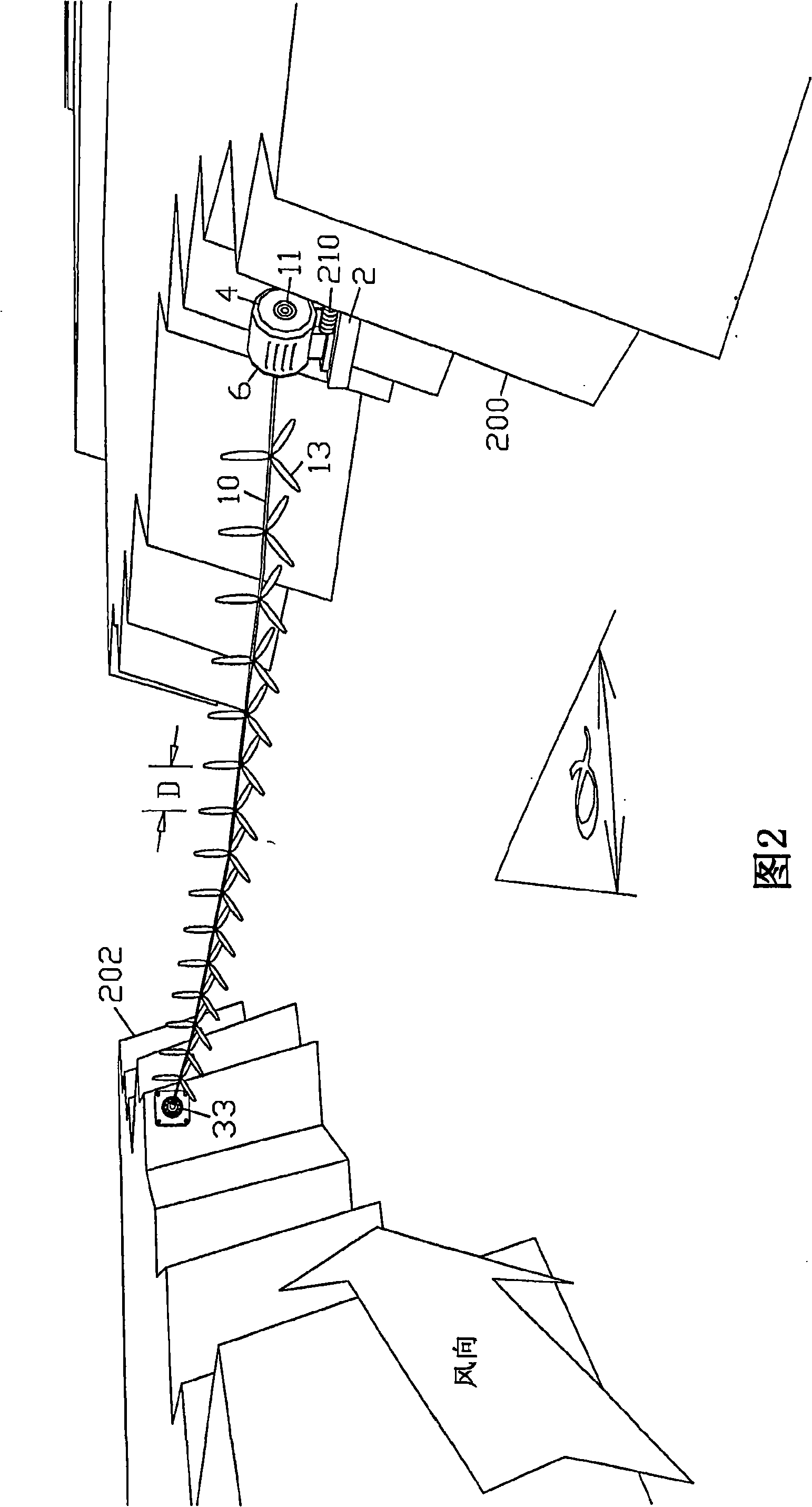
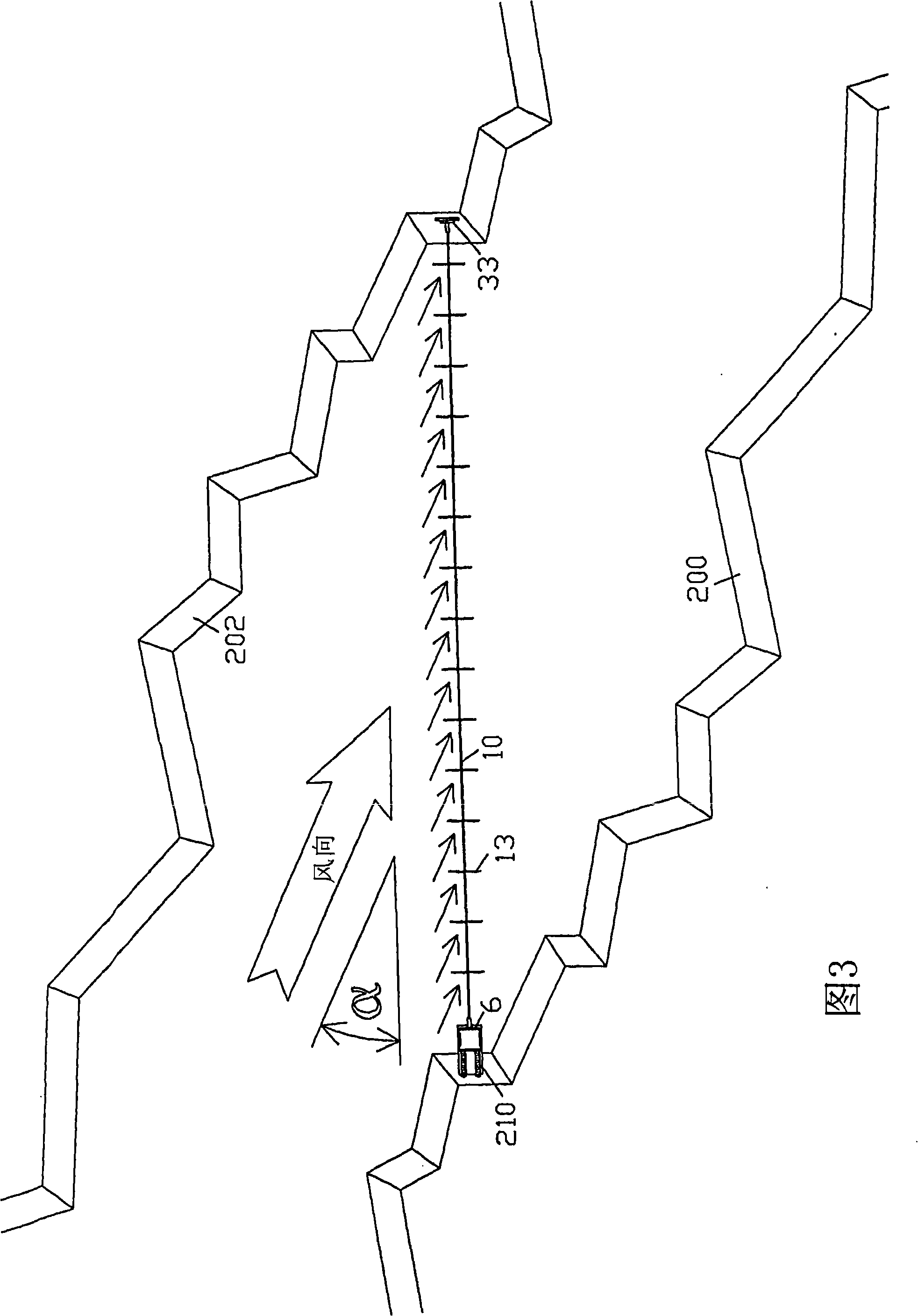
[0196] [0129] 1. The first embodiment - a catenary coaxial multi-rotor turbine across the canyon; Figures 1-5, 29, 30, 39, 40-43:
[0197] [0130] The canyon provides a unidirectional wind source (FIG. 39) and a mounting point on its raised walls 200 and 202. A single drive shaft 10 spans the canyon at an angle α (alpha) to the wind direction. A series of horizontal axial rotors 13 are coaxially mounted on the drive shaft at intervals, denoted by the rotor pitch D. The rotors combine to rotate around the drive shaft, all together as a single unit. In a similar embodiment in a prior patent issued to the present inventor, the spacing D between the rotors, combined with the orientation to the wind at an angle α (alpha), allows the clear wind to reach each rotor such that all rotors All can effectively use wind energy to provide power for the system. The rotor should ideally have modern, high speed, high efficiency, light weight blades with high efficiency propellers capable of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com